To check hemoglobin at home, you need a MiniGem 540 hemoglobinometer device (price 47 thousand rubles) or a similar one. For testing, a drop of blood is taken from a finger, mixed with a reagent, and placed inside the device. Light is passed through the solution and the unabsorbed flux is recorded. The method is accurate and suitable for patients requiring long-term monitoring. The second method is a universal biochemical analyzer, for example, Easy-Touch, costing 6,000 rubles.
It additionally determines cholesterol and glucose, but each analysis requires special strips (1,700 rubles for 25 pieces for hemoglobin). A drop of blood is applied to the strip and after 6 seconds the result appears on the display. This device is needed to monitor the treatment of anemia (low hemoglobin) or erythrocytosis (high level). Based on the symptoms of the color of the skin of the face, sclera of the eyes, mucous membranes, hands, one can only suspect a deviation from the norm - when it decreases there is pallor, when it increases there is redness, this is a reason to consult a doctor, but not for self-medication.
How to test hemoglobin at home
You can check hemoglobin at home using a hemoglobinometer (for example, MiniGem 540) or test strips for a biochemical analyzer (Easy-Touch). In the first case, the device is designed only for monitoring hemoglobin; a drop of blood is placed in it and mixed with the reagent; after 20 minutes you can get the result.
A simpler and more universal method is to use test strips and the Easy-Touch home biochemical analyzer. It measures several indicators (glucose, cholesterol, hemoglobin), but the disadvantage is the need to purchase test strips for each type of test.
Device for measuring hemoglobin at home
MiniGem 540
A device for measuring only one hemoglobin indicator at home is called a hemoglobinometer. The most popular MiniGem 540 model determines the level of red blood cell protein by the optical density of the solution, that is, the degree of transparency. To do this, there is a light source inside and a sensor that captures the unabsorbed part. This device has high measurement accuracy; it is used in mini-laboratories in ambulances and field medical stations.
To work with it, you do not need a medical education, since the measurement technique is extremely simple. Designed to carry out 100,000 measurements, the warranty period is at least 4 years, subject to continuous operation 4 hours a day. The cost of MiniGem is 540 – 47,000 rubles. It makes sense to purchase it only if constant monitoring of hemoglobin is necessary for patients with congenital diseases or those requiring very long-term treatment.
Universal device
EasyTouch blood analyzer
Using the Easy-Touch device, hemoglobin determination at home can be combined with monitoring cholesterol and glucose levels. Such a biochemical analyzer also has advantages in the price of the device itself (6,000 rubles), but a set of test strips of 25 pieces must be purchased separately (1,700 rubles).
Measurements take place very quickly, no addition of solutions is required, the kit includes a pen for painless finger pricking. This option can be considered optimal for patients with the most common forms of decreased or increased hemoglobin in the blood.
Patients usually need to be tested no more than twice a week, so one package lasts for 2 months, which is how long an opened package can be stored. In most cases, this time is enough to normalize the indicator at home. The device can also store the results of the last 50 hemoglobin measurements.
The role and exclusivity of the CGMS method
Any adjustment to therapy can only be based on reliable data, and the CGMS method is becoming an integral part of the management of patients with impaired carbohydrate metabolism. It should be noted that the possibilities of using the method are not limited only to patients with diabetes. With its help, you can diagnose hypoglycemic conditions in people who do not suffer from diabetes, as well as analyze changes in glycemia in obese patients and detect carbohydrate metabolism disorders at the earliest stages.
In patients with diabetes mellitus, the technique is used to diagnose the following conditions:
- postprandial hyperglycemia, which allows us to evaluate the effectiveness of glucose-lowering therapy and the rate of absorption of various carbohydrates;
- nocturnal hypoglycemia;
- blood sugar response to physical activity;
- hidden asymptomatic hypoglycemia, etc.
The collected and analyzed information makes it possible to individually adjust therapy, the frequency and time of taking glucose-lowering drugs, the schedule and degree of physical activity and, of course, nutrition, its qualitative and quantitative characteristics.
Repeated monitoring of glycemia after correction of therapy allows you to objectively assess the effectiveness of changes (Fig. 7).
Fig. 7: CGMS data after correction of therapy and regimen: target glycemic values achieved
How to do a hemoglobin test using a machine
The hemoglobin test using a hemoglobinometer apparatus is carried out according to the following scheme:
- Wash and dry your hands.
- Fill the test tube with 5 ml of reagent (usually hydrochloric acid is included in the kit).
- Wipe the ring finger with alcohol and pierce the side of the terminal phalanx with a sterile lancet.
- Place a drop of blood into the solution and mix thoroughly (shake the tube until a homogeneous mixture is obtained).
- Maintain exactly the required time, it is indicated in the instructions (for MiniGem 540 it takes 20 minutes to interact).
- Pour the mixture into an optical cuvette (a container that is inserted into the device).
- Place the cuvette in the hemoglobinometer cell.
After this, the device begins measurement, it is accompanied by a sound signal, then an indicator appears on the screen.
Watch a video on how to do a hemoglobin level test at home:
When using a universal biochemical analyzer with test strips you need:
- Wash and dry your hands.
- Insert the chip into the device (it is found in each package of test strips).
- Remove the hemoglobin test strip and insert it into the cell.
- Check that the device is turned on (happens automatically).
- Assemble the finger piercing pen.
- Wipe the end phalanx with alcohol and puncture.
- Bring the drop to the test strip field and distribute it evenly.
- After 6 seconds, the result will be visible on the screen.
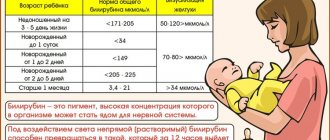
Indicators are normal
Normal hemoglobin level:
- newborns – 145-225 g/l;
- children under 12 years old – 110-160 g/l;
- men – 130-165 g/l;
- women outside pregnancy – 120-150 g/l;
- pregnant women – 110-140 g/l.
This range may differ slightly (by 2-3 units) depending on the measurement method, so there is usually an individual scale in the instructions. This is what you need to focus on when taking measurements.
How accurate is the test?
Checking hemoglobin using a hemoglobinometer has an error of no more than 2%, which is quite comparable to laboratory diagnostics. It is important to consider that the device must be verified at least once a year, that is, it must be taken to a service center for testing. Only in this case can you be sure that the indicators correspond to the true ones.
For universal biochemical analyzers, the research accuracy is within 92-95%. Therefore, they are not suitable for making a diagnosis, but are quite applicable for monitoring the level of hemoglobin in the blood. For patients with already prescribed treatment, such devices help assess its effectiveness, which is the main purpose of the analysis.
There is no need to rely on home appliances to identify the cause of a decrease or increase in indicators. They will only show the current level of hemoglobin in the blood, and approaches to therapy will completely depend on the disease that led to such a change. Patients with deviations from the norm need to undergo a full examination: a biochemical blood test with indicators of iron metabolism, ultrasound, sometimes tomography, bone marrow puncture.
Continuous long-term glycemic monitoring
But medicine is constantly evolving. of daily glycemic monitoring has appeared and is actively used . The essence of the method is the constant automatic measurement of blood sugar levels in intracellular (interstitial) fluid for several days. For such monitoring, a specialized software and hardware complex CGMS (Continuous Glucose Monitoring System) is used - a highly sensitive method of monitoring blood glucose levels .
The system includes three modules:
- highly sensitive platinum sensor;
- transmitter and monitor;
- a device for exporting data from the transmitter to a computer.
The sensor (Fig. 1) is an individual disposable device that records the level of sugar in the interstitial fluid; it is installed subcutaneously using a special device , with virtually no pain (Fig. 2).
a transmitter is attached to the sensor - a small device used to transmit a signal from the sensor to the monitor using Bluetooth technology. The monitor is hung on the patient’s belt and remains there throughout the entire study period (Fig. 3). The convenience of wireless signal transmission is obvious: there is no risk that the wiring will be damaged during body movements and the examination will be interrupted, and therefore the patient feels more free.
Fig.1: Sensor
Rice. 2: Sensor installation device
Fig.3: iPro transmitter
Rice. 4: System of devices for transferring data to a computer
The duration of the study is 3-5 days. The monitor automatically measures blood sugar every 10 seconds and records the average value (from the collected readings) once every 5 minutes. During the study, it is necessary to calibrate the monitor several times using finger blood sugar. This requires parallel self-monitoring of sugar on a glucometer . The monitor allows you to enter information about events in the patient’s life (eating or taking medications, physical activity, etc.). This helps improve the quality of interpretation of the collected data. After completion of the study, all obtained digital information is imported into a computer (Fig. 4) and analyzed by the attending physician. The monitoring results are presented in the form of graphs (Fig. 5) and summary tables (Fig. 6) with calculated average values of sugar indicators, limits of deviations from them, the ratio of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia as a percentage for various periods of time.
Automated glycemic monitoring provides the attending physician with the necessary amount of factual information about the nature of changes in sugar levels during the day and allows one to identify trends in deviations. Based on these data, the doctor prescribes the correct treatment tactics or makes timely adjustments to therapy.
Fig. 5: An example of a graphical representation of the data obtained during the study
Figure 6: Example of a summary table of continuous glycemic monitoring data
How to test hemoglobin in blood in the laboratory
To check hemoglobin in the blood, you need to donate blood from a vein or finger to the laboratory for a general (general clinical) blood test. It is performed in a shortened or expanded version (with a leukocyte formula); both are suitable for studying the content of red blood cells and hemoglobin protein.
There is a peculiarity of the study if the presence of abnormal forms of hemoglobin is suspected (hemoglobinopathies, thalassemia, drug poisoning, hemolytic anemia). In such cases, the doctor prescribes a special test - electrophoresis of hemoglobin fractions. It is based on the separation of normal and abnormal proteins using electrical current.
Hemoglobin electrophoresis in alkaline gel allows you to determine the percentage of the main hemoglobin isoforms and screen for hemoglobinopathies. Normally, in the blood of an adult, at least 96.5% of hemoglobin is represented by the HbA isoform, which consists of two pairs of polypeptide chains (globins): 2α and 2β, each of which is associated with heme. Hemoglobinopathies are associated with the presence of an abnormal variant of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin electrophoresis can screen for conditions associated with structural abnormalities of hemoglobin. However, the method does not allow establishing the type and nature of hemoglobinopathy.
English synonyms
Serum Hemoglobin Electrophoresis.
Research method
Electrophoresis and densitometry.
Units
Mg/dL (milligram per deciliter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before the test.
General information about the study
Hemoglobin electrophoresis in alkaline gel allows you to determine the percentage of the main hemoglobin isoforms and screen for hemoglobinopathies. Normally, in the blood of an adult, at least 96.5% of hemoglobin is represented by the HbA isoform, which consists of two pairs of polypeptide chains (globins) - 2α and 2β - each of which is associated with heme. HbA ensures adequate gas exchange and tissue oxygenation. Fraction HbA2 is a minor form of hemoglobin, has the formula 2α2δ. It is also possible for an adult to have trace amounts of fetal hemoglobin HbF (2α2γ), which is the predominant fraction during the prenatal period. During the first 6 months of life, HbF is replaced by HbA.
Disorders of hemoglobin structure are usually divided into two groups: hemoglobinopathies and thalassemias, although thalassemias are a form of hemoglobinopathies. Thalassemias are disorders of the synthesis of α-, β-, or both hemoglobin chains. There may also be disturbances in the synthesis of δ- and γ-chains. Most variants of α- and β-thalassemia are accompanied by changes in the levels of HbF and HbA2, so the determination of these isoforms can be used to screen for these conditions.
Other hemoglobinopathies are associated with the presence of an abnormal variant of hemoglobin. The most common and clinically significant abnormal hemoglobin variants are: S, D, E, C. The HbS and HbD variants are pathological forms of hemoglobin that exhibit identical migration in an alkaline gel and are the result of point mutations in the gene encoding β-globin. Options E and C with this method migrate as part of the HbA2 fraction; in their presence, the HbA2 fraction reaches more than 25%. The HbS variant, which leads to sickle cell anemia, is of greatest clinical significance.
Alkaline gel electrophoresis of hemoglobin allows screening for conditions associated with structural abnormalities of hemoglobin. However, the method does not allow establishing the type and nature of hemoglobinopathy.
Electrophoresis is a sensitive method that can be used to exclude hemoglobinopathies or determine the tactics of further examination to establish an accurate diagnosis of the disease. The method is characterized by a high intra-staging (SD
The research method is based on electrophoresis of hemoglobin obtained by lysis of washed red blood cells of the subject. After hemoglobin is divided into fractions, the migration zones are stained. The hemoglobin content in the fractions is measured using digital densitometry.
When is the study scheduled?
- Screening for hemoglobinopathies;
- presence of a family history of hemoglobinopathies, family planning;
- microcytic anemia not associated with iron deficiency;
- hemolytic anemia of unknown etiology;
- detection of altered red blood cells (sickle deformation) during microscopic examination of blood.
What do the results mean?
Reference values
| Component | Age | Reference values, % |
| Hemoglobin HbA | 5,9 — 77,2 | |
| 1 - 3 months | 7,9 — 92,4 | |
| 3 - 6 months | 54,7 — 97,1 | |
| 6 - 9 months | 80,0 — 98,0 | |
| 9 - 13 months | 86,2 — 98,0 | |
| 13 - 24 months | 88,8 — 98,0 | |
| > 2 years | ≥ 96,50 | |
| Hemoglobin HbA2 | 0,0 — 2,1 | |
| 1 - 3 months | 0,0 — 2,6 | |
| 3 - 6 months | 1,3 — 3,1 | |
| 6 – 24 months | 2,0 — 3,3 | |
| > 2 years | ≤ 3,5 | |
| Hemoglobin HbF | 22,8 — 92,0 | |
| 1 - 3 months | 7,6 — 89,8 | |
| 3 - 6 months | 1,6 — 42,2 | |
| 6 - 9 months | 0,0 — 16,7 | |
| 9 - 13 months | 0,0 — 10,5 | |
| 13 - 18 months | 0,0 — 7,9 | |
| 18 - 24 months | 0,0 — 6,3 | |
| > 2 years | ||
| Abnormal hemoglobin variants | Not detected | |
| Conclusion | The level of HbA, HbA2, HbF corresponds to age norms, pathological forms of hemoglobin have not been identified |
Is preparation necessary before measuring hemoglobin?
With any method of measuring hemoglobin in the blood you need:
- stop taking iron supplements 5-7 days in advance (required when making a diagnosis, and when monitoring treatment, the doctor may recommend not interrupting the course);
- a day before, give up alcohol and overeating, as the transparency of the blood serum changes, it is important to avoid stressful and heavy physical activity;
- take a break from eating - from 4 to 12 hours, it is best to choose the same time of day for repeated studies;
- Eliminate smoking and active movements within half an hour.
You can check your hemoglobin level at home only using a device - a hemoglobinometer or a universal analyzer. They are suitable for monitoring treatment, but to select a treatment method, one indicator is not enough, since you need to find and eliminate the cause of the decrease or increase, that is, you should consult a doctor.
Why is blood sugar monitoring needed?
How important is self-control for a diabetic? Blood sugar is a very variable indicator. It reacts to any changes in the environment and internal environment, even imperceptible to the patient himself, by participating in the body’s adaptation mechanisms. Any changes in this indicator are very important - an increase (hyperglycemia) or a decrease below normal (hypoglycemia).
The state of hyperglycemia can be provoked by the following factors:
- eating carbohydrate foods;
- emotional stress;
- long-term hard physical work;
- increased body temperature and blood pressure;
- exacerbation of a chronic disease or acute pathology - conditions accompanied by the production of counter-insular hormones...
…and vice versa:
- moderate physical work;
- fasting or not eating carbohydrate foods.
More details about the service
Dysfunction of the endocrine glands (hypothyroidism, hypocortisolism) leads to a decrease in blood sugar ( hypoglycemia ). If in a healthy person in such situations the normalization of glucose concentration occurs due to changes in internal regulatory mechanisms, then a patient with diabetes mellitus requires correction independently or with the participation of medical personnel. Otherwise, the absence or untimeliness of these measures can lead to tragic consequences.
It is important to know that long-term hyperglycemia associated with malnutrition, insufficient physical activity or an inadequate dose of hypoglycemic drugs leads to chronic irreversible damage to target organs, accelerating pathological processes and leading to the development of complications (angiopathy, nephropathy, retinopathy, gastropathy, etc. .). Frequent large fluctuations from hypo- to hyperglycemia are also dangerous.