Pathology of lipid metabolism has become a common problem among the population that has crossed the threshold of adulthood. One of the manifestations of impaired fat metabolism is an increased level of serum cholesterol. Most often, there is an imbalance of high-density lipoproteins HDL and low-density lipoproteins LDL, which is fraught with the risk of developing atherosclerosis.
When identifying a problem of this kind, the level of plasma cholesterol should always be kept under control. But patients do not always have the opportunity to visit a laboratory to take a blood test for cholesterol. Therefore, people with hypercholesterolemia often ask the question: “How can you check your cholesterol at home?”
Indications for cholesterol testing:
- Atherosclerosis and related diseases of the cardiovascular system
- Liver and kidney diseases
- Pancreatic diseases
- Obesity
- Endocrine pathology (myxedema, diabetes mellitus)
- If close relatives have high cholesterol or have diseases associated with atherosclerosis
- If you are over 39 years old and care about your health
Reasons for the increase
Why does cholesterol increase? In most cases, high blood cholesterol levels are caused by poor lifestyle choices and unhealthy habits. The main reasons are as follows:
- Abuse of fatty foods, insufficient inclusion of fresh vegetables and fruits in the diet.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Constant stress.
- Bad habits: alcohol, smoking.
- Obesity.
In addition, the following categories of people are at risk:
- having a hereditary predisposition;
- men;
- aged people;
- women during menopause.
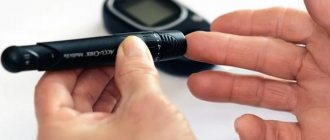
Measuring cholesterol at home
- On-site laboratory: Some laboratories offer a home visit service. Cholesterol analysis in this case is carried out in the same way as in the laboratory.
- Portable device: Cholesterol can be measured using a special device (such as Accutrend) and a set of test strips for it. This method is most suitable for a person who already has high cholesterol, or if there is a high risk of increasing it. Also, the device helps track the effectiveness of treatment if a person is taking cholesterol-lowering medications.
Often, such a device is capable of measuring glucose levels in addition to cholesterol content, that is, it can also be used as a glucometer.
Meters for quick testing
Now, thanks to the achievements of modern medical science, it is not necessary to visit a laboratory to determine the concentration of blood cholesterol. Today, scientists have developed devices that can be used to measure cholesterol at home.
In terms of their technical characteristics, portable devices for home use have some differences. Some allow you to quickly measure only cholesterol, others make it possible to control the content of glucose, serum lactate, urates, and ketone bodies. Despite some distinctive nuances, the algorithm for working with these devices is no different:
- the measurement of the desired indicator is carried out on an empty stomach, preferably in the morning;
- to turn on the device, you need to press the “Start” button;
- Next, you need to insert the sensitive strip into the hole provided for this purpose on the body of the device;
- A special scarifier is used to puncture the fingertip, and the resulting drop of blood is applied to the reagent;
- After the programmed time has elapsed, a digital response appears on the device display.
Having a portable device to measure your cholesterol and other blood levels at home has many benefits. Its compact size makes it suitable not only for home use - you can take the device with you to work to take measurements if necessary.
The starter kit contains strips soaked in the reagent, which can then be purchased at any pharmacy chain. To get results you don’t have to wait long; usually the treasured numbers appear on the device’s display within 2 minutes after the start of the measurement. And finally, buying a device for determining cholesterol concentration at home is more profitable than regularly visiting biochemical laboratories, because most of them provide paid services.
Sample menu for lowering cholesterol
Breakfast: boiled brown rice with olive oil, barley coffee, oatmeal cookies.
Second breakfast: berries or any fruit.
Lunch: Vegetable soup without meat, vegetables with boiled fish, whole grain wheat bread, any fresh juice (vegetable or fruit).
Afternoon snack: carrot salad with olive oil.
Dinner: lean boiled beef with mashed potatoes, low-fat cottage cheese, green tea, lean cookies.
At night: yogurt.
Nutrition for high cholesterol
First of all, you need to exclude from the menu foods that increase bad cholesterol. These include the following:
- meat;
- fatty dairy products;
- seafood, fish;
- confectionery;
- fried foods;
- everything is fat;
- chicken egg yolks.
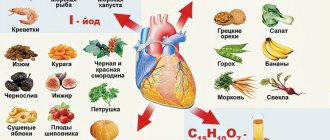
It is important to remember that low levels of good cholesterol lead to the development of atherosclerosis and blockage of blood vessels. Good cholesterol helps cleanse blood vessels from atherosclerotic plaques. Therefore, it is imperative to include foods containing it in your food. A proper diet will help reduce bad cholesterol and cleanse the blood. Products that normalize its level are as follows:
- olive oil reduces bad cholesterol (LDL) by 18%;
- Avocado reduces total HDL by 8% and increases beneficial HDL by 15%;
- blueberries, cranberries, raspberries, strawberries, lingonberries, pomegranate, red grapes, chokeberries promote the production of HDL and increase it by 5%;
- salmon and sardine fish oil is rich in healthy fatty acids, this is an excellent way to normalize cholesterol levels;
- cereals;
- whole grain cereals;
- legumes;
- soy;
- flax seeds;
- White cabbage;
- garlic;
- dill, lettuce, spinach, parsley, onion reduce bad cholesterol;
- apricots, sea buckthorn, dried apricots, carrots, prunes;
- red wines;
- wholemeal bread, bran bread, oatmeal cookies.
Why do you need to check your cholesterol levels?
Home › Articles › Why do you need to check your cholesterol levels?
Date of publication: 02/27/2018
Cholesterol – what is it?
Cholesterol
- one of the most important substances for any living creature belonging to the animal kingdom. This fatty monohydric alcohol (that is, it is a substance that belongs to lipids) is one of the natural intermediate products of metabolic processes.
The name “cholesterol” comes from the Greek words “chole” (bile) and “stereo” (hard, hard), since it was first discovered in gallstones, i.e. in solid form. It circulates in the blood and is used as a building block for all cells of the body (cholesterol can be found in large quantities in the muscles, brain and liver), and is also involved in the production of many sex hormones.
Cholesterol is a vital substance because... it plays a very important role in cell metabolism. It is an essential component of all cell membranes and is involved in the production of all steroid hormones, including testosterone, estrogen and cortisol. It is also essential for the brain and supplies body tissues with antioxidants.
The main part of cholesterol is produced in the human body - this is about 80% of the total volume, the rest (20%) comes from food (milk, meat, eggs). The main synthesis of cholesterol occurs in the liver (4/5 of the total number of lipid molecules is formed here).
A smaller amount is synthesized in other cells (in the kidneys, intestines, sweat glands - up to 1/5 lipids are formed in them). Cholesterol enters the blood from the intestines or liver.
In total, the adult body synthesizes about 1 g of cholesterol during the day. After its use (processing into bile, arrangement of new membranes, synthesis of vitamins and hormones), the excess is excreted. This is about 100 mg per day or 1/10 of the synthesized amount. Thus, the intake and consumption of lipids balance each other.
Problems begin when a person eats too much fatty foods or when metabolism and cholesterol production in the liver are impaired.
Then free low-density lipoproteins (“bad” cholesterol) begin to accumulate in the blood and vessels. At the same time, the risk of developing serious cardiovascular diseases increases sharply.
"Good" and "bad" cholesterol
For the most part, cholesterol is transported in the blood not in its pure form, but in complex compounds, which come in two types: low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and high-density lipoproteins (HDL).
HDL is called the “good” lipoprotein because it removes cholesterol from artery walls, while LDL (called “bad”) carries cholesterol from the liver to the arteries, where it is deposited on the walls as a fatty substance in the form of plaques, causing vascular atherosclerosis
.
LDL carries 75% of cholesterol in the blood throughout the body. However, this cholesterol sometimes undergoes a process of oxidation (and becomes an unstable molecule), which allows it to penetrate the walls of the arteries, thereby creating a danger. The body produces antibodies in response to oxidized LDL. These antibodies are produced in such large quantities that they cause inflammation, which leads to further damage to the artery walls.
HDL, on the contrary, brings benefits to the body. As mentioned above, they remove cholesterol from the artery walls and return it to the liver. Additionally, they have been shown to prevent LDL oxidation and also keep arteries open and clear.
Atherosclerosis and hyperlipidemia.
Atherosclerosis
(
from the Greek athere - gruel and sclerosis - compaction) is a systemic disease that affects elastic arteries (aorta, iliac vessels) and muscular (coronary, carotid, intracerebral, arteries of the upper and lower extremities) type, characterized by deposition and accumulation in the vessel wall LDL (“bad” cholesterol) with subsequent reactive proliferation of connective tissue and the formation of atherosclerotic plaques.
It is now generally accepted that atherosclerosis is a disease associated with the influence of various external and internal factors, among which hereditary, environmental and nutritional factors are of primary importance. In different forms of atherosclerosis, the role of individual factors varies. Thus, in people with family hereditary forms of early atherosclerosis, genetic factors come to the fore, while the massive spread of atherosclerosis is associated mainly with environmental factors and nutritional characteristics. There is often a combination of various factors, some of which are added during the development of the disease.
Risk factors for atherosclerosis.
Age over 40 for men and over 50 for women
· Male gender. Men develop atherosclerosis more often and 10 years earlier than women due to the fact that they smoke more often and are more exposed to stress factors.
· Heredity aggravated by atherosclerosis (myocardial infarction, stroke in the family in men under 50 years of age and in women under 60 years of age).
· Pathologically high levels of triglycerides, cholesterol, atherogenic lipoproteins in the blood - hyperlipidemia
- Arterial hypertension.
- Smoking.
- Impaired glucose tolerance, diabetes mellitus.
- Excess body weight.
- Physical inactivity.
- Chronic kidney disease
- Personality and behavior characteristics - the so-called stress type.
- Gout.
Hyperlipidemia (lipid metabolism disorders)
Most authors recognize hyperlipidemia as a leading risk factor for atherosclerosis. Interestingly, the causes of hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis coincide, indicating a strong relationship between both pathological conditions.
Causes of hyperlipidemia
- Elderly age
- Gender (male)
- hereditary predisposition,
- obesity,
- high fat diet
- lack of physical activity
- moderate or significant alcohol abuse,
- smoking
- diabetes,
- decreased thyroid function.
- Long-term use of certain medications (hormonal contraceptives, glucocorticosteroids
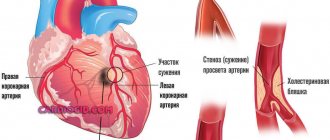
The mechanism of development of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerotic plaques.
The mechanism of development of atherosclerosis is quite complex; it is based on a violation of lipid metabolism.
- At the initial stage, amid complete external well-being, structural cellular changes begin on the inner wall of the arteries, causing a response of the connective tissue - proliferation;
- Floating with the bloodstream, LDL (“bad” cholesterol) is captured by the cells of the swollen inner lining of the artery and deposited on it;
- An atheromatous (atherosclerotic) plaque
is formed , the basis of which is LDL (“bad” cholesterol).
The development of the atherosclerotic process along the length of the vessel is called non-stenotic atherosclerosis
- As harmful cholesterol components accumulate, plaques begin to rise above the surface of the intima, move into the lumen of the vessel and thus narrow it.
This is already stenosing atherosclerosis
,
threatening to subsequently block the vessel ,
since the lumen of the artery continues to decrease over time, until it is completely closed.
Interestingly, a narrowing of up to 70% can go unnoticed, and the process is asymptomatic. Only occlusion (complete closure) of the vessel
, leading to acute ischemia (as a variant of the consequences of stenosing atherosclerosis), can become a “bolt from the blue”;
- In later stages, fibrous plaques can ulcerate and calcify, which further aggravates the situation by creating favorable conditions for the formation of blood clots.
Unstable plaques can rupture and cause a blood clot to form inside the artery. These blood clots can eventually block the artery and cause a heart attack.
This mechanism is characteristic not only of the arteries of the heart. Atherosclerotic plaques can form in almost all arteries of the human vascular system (in the aorta, arteries of the brain, neck, lower and upper extremities, arteries of internal organs, etc.).
Formation of atherosclerotic plaque and development of thrombosis.
Vascular atherosclerosis is a terrible disease
, significantly worsening the patient’s quality of life. Having many causes and a mild course, the disease in the first stages of its development has hidden symptoms and often goes unnoticed by the patient, who, afraid to see a doctor, prefers to ignore the symptoms instead of learning how to get rid of atherosclerosis. And when the problem becomes obvious, time is lost, and atherosclerosis affects most of the body’s vessels.
It should be noted that in terms of atherosclerosis, there is no particular reason for reassurance at a young age
,
it simply should not be confused with arteriosclerosis (arteriocalcinosis), when connective tissue grows with age and calcium salts are deposited, and as a result, all layers of the arterial wall become denser, and the vessel loses its functional abilities.
Symptoms of vascular atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is often the result of persistently high levels of cholesterol in the blood. Manifestations of atherosclerosis can be:
- angina (chest pain during exercise)
- myocardial infarction
- heart rhythm disturbances
- sharp pain in the chest or back (aortic aneurysm)
- dizziness, staggering when walking, sudden numbness or loss of sensation in one or another part of the body
- acute cerebrovascular accident (stroke)
- intermittent claudication (Charcot syndrome - pain in the legs when walking)
- sharp abdominal pain (ischemia of internal organs due to atherosclerosis of the arteries of internal organs)
- uncontrolled arterial hypertension (due to atherosclerosis of the renal arteries).
- pinkish-yellow deposits under the skin (xanthomas), especially around the eyelids or on the tendons of the lower leg (associated with familial hypercholesterolemia)
If you have any of the listed conditions, be sure to consult a doctor.
Competent consultation with a specialist can be obtained at Clinic-NM in Orekhovo-Zuevo, st. Dzerzhinsky, 41
Cholesterol control
By controlling cholesterol levels, we improve our overall health, increase our body's stamina, and generally improve our quality of life.
After 40 years, it is recommended to take a lipid profile once a year - a blood test that determines the level of total cholesterol in a person’s blood. The ratio of “bad” cholesterol to “good” cholesterol is present in the blood plasma.
You can take tests at Clinic-NM, Dzerzhinskogo, 41
Lipidogram or lipid spectrum
includes
- total cholesterol
- LDL
- HDL
- Triglycerides
Extended lipid spectrum
required for people who have had a cardiovascular event (myocardial infarction or stroke), or have a family history of cardiovascular disease (heart attack in the family in men <55 years old and women <60 years old)
- Triglycerides
- Total cholesterol (cholesterol)
- Cholesterol-HDL (High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol)
- Cholesterol-LDL (Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol)
- Cholesterol - VLDL (Very Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol)
- Apolipoprotein A1
- Apolipoprotein B
- Lipoprotein (a)
A blood test is taken from a vein. Before the procedure, you must not eat for about 12 hours, so examinations are usually scheduled for the morning. A week before the test, it is recommended to stop taking medications that change the composition of the blood. You need to eat normally, without changing anything, so that the analysis results are reliable.
The research results must be reviewed by a specialist. Consultation with a specialist can be obtained from us at Clinic-NM, st. Dzerzhinsky, 41.
It is the doctor who can determine whether LDL is increased or HDL is decreased. The doctor may prescribe a special diet for the patient to normalize fatty alcohol levels. If there are significant, threatening readings of LDL or HDL, the specialist will prescribe a treatment that will help establish the optimal balance of “bad” and “good” cholesterol in the body.
It is malnutrition that, first of all, gives impetus to disturbances in metabolic processes, damage to the walls of blood vessels, their thickening and the formation of atherosclerotic plaques on them.
Norms of total cholesterol, LDL and HDL
*-high cardiovascular risk
- Long-term smoking history, cholesterol>8 mmol/l, blood pressure>180|110 mmHg
- Atherosclerotic plaque<50%
- Uncomplicated diabetes mellitus
- Moderate chronic kidney disease
- 10-year risk SCORE 5-10%
**- very high cardiovascular risk
- Presence of coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, atherosclerosis of peripheral arteries
- Atherosclerotic plaque >50% of any location
- Complicated diabetes mellitus or if there are additional risk factors (smoking, arterial hypertension, increased total cholesterol)
- Severe chronic kidney disease
- 10-year SCORE risk >10%
Cardiovascular risk score (SCORE)
Risk of death from cardiovascular disease within 10 years
Very high risk ≥ 10%
High risk ≥5% and <10%
Average risk ≥1% and <5%
Low risk < 1%
How to lower cholesterol levels?
Take the example of athletes and fitness enthusiasts and you can rest assured about your cholesterol level. The above risk factors can be minimized, and in some cases completely eliminated, by leading an active lifestyle.
Exercise and healthy eating associated with competition preparation help cope with daily stress. Stress, anger and irritability lead to heart disease. The fewer there are, the lower the risk of cardiovascular problems.
You can maintain body tone by working in the countryside in the fresh air, you can practice dancing, Nordic walking, swimming - all types of muscle activity improve your mood and well-being, having a beneficial effect on the condition of the vascular bed.
The android type of obesity, when excess fat is distributed around the waist and abdomen, is a serious risk factor for diabetes, hypertension, coronary artery disease, and atherosclerosis. Check your measurements: maximum waist circumference – 94 cm (for men) and 84 cm (for women). Body weight control plays an important role in the fight against excess cholesterol.
The dangerous connection between smoking and total cholesterol levels has long been studied and documented in many scientific works. Smoking very noticeably disrupts the balance of bad and good cholesterol (HDL) in favor of bad cholesterol (LDL). Cholesterol levels are highly dependent on the number of cigarettes smoked per day and the intensity of smoking.
Do not forget about the danger of disrupting normal cholesterol levels. Bad cholesterol, together with free radicals from tobacco smoke, enhance the atherosclerotic process. Smoking doubles the risk of diseases of the heart, brain, etc. Neglecting this can lead to serious, life-threatening diseases. When you quit smoking, as a rule, the level of good cholesterol increases and bad cholesterol decreases. Consequently, the risk of disease or progression of vascular atherosclerosis is not only reduced, but the protection of blood vessels from atherosclerosis is increased, which means the risk of developing severe diseases of the heart, brain, etc. is also reduced.
To avoid the development of dyslipidemia, the following rules must be followed:
- Normalize weight
- To live an active lifestyle,
- Avoid stress
- Regularly undergo medical examinations,
- Eat properly,
- Fight smoking and alcoholism,
- Timely and correct treatment of diseases leading to dyslipidemia.
Diet therapy
indicated for manifestations of dyslipidemia and consists in limiting the intake of animal fats into the body
. Patients should eat foods rich in vitamins and dietary fiber. In this case, the calorie content of the daily diet should correspond to the patient’s physical activity. Fatty and fried meats should be replaced with boiled sea fish, chicken, turkey, and butter with vegetable oil. A lot of fats, especially hidden ones, are found in sausages and industrial cheeses. The majority of the diet should consist of vegetables, fruits, berries, cereals, low-fat lactic acid products, beans, and greens.
DO increase fiber-rich foods in your diet
Oats and cereals are a safe way to correct LDL. If for breakfast you replace the usual sandwich with oatmeal and grain products made from wheat, rye, buckwheat, the fiber they contain normalizes cholesterol and increases intestinal motility.
Legumes reduce cholesterol thanks to their soluble fiber. They, like soy, contain protein that replaces red meat, which is dangerous if LDL is high.
You MUST take foods rich in phytosterols
| Cholesterol-lowering agents | Phytosterol level per 100g of product |
| Rice bran | 400 mg |
| Sprouted wheat | 400 mg |
| Sesame | 400 mg |
| Pistachios | 300 mg |
| Sunflower seeds | 300 mg |
| pumpkin seed | 265 mg |
| Flax seeds | 200 mg |
| Almonds | 200 mg |
| Cedar nuts | 200 mg |
| Cold pressed olive oil | 150 mg |
In 1 tbsp. l. olive oil 22 mg of phytosterols - a sufficient amount to normalize cholesterol. If you use this type of vegetable oil instead of saturated fats, bad cholesterol levels are reduced by 18%
Cholesterol Lowering Supplements
Vitamin E
. It is a very strong antioxidant. It is also believed to prevent the breakdown of LDL cholesterol and thus prevent the formation of fatty plaques. Studies have shown that people who take vitamin E have a reduced risk of heart disease.
Omega-3 fatty acids
. Contained mainly in fish oil. They have been shown to protect against inflammation, prevent blood clots, and lower triglyceride levels. All this helps reduce the risk of atherosclerosis. Omega-3 can be taken as a supplement or obtained from natural foods such as flaxseed, canola, and primrose oil.
Green tea
. Green tea contains compounds that prevent the occurrence of atherosclerosis. These phytochemicals (or polyphenols) improve lipid metabolism and lower cholesterol levels. In addition, they are also antioxidants.
Garlic
. Garlic has been shown to have blood thinning properties, which in turn prevents the formation of clots in the arteries. It has also been proven to lower cholesterol levels. Garlic owes its medicinal properties to sulfur compounds, in particular alliin, which are part of it. It is recommended to consume raw chopped garlic.
Soy protein
. The effect of soy isoflavones is similar to the effect of estrogens: they reduce the risk of atherosclerosis. Genistein also plays an important role in preventing the oxidation of LDL cholesterol as it has antioxidant properties. In addition, soy helps lower cholesterol levels by increasing the secretion of bile acids.
Folic Acid, Vitamin B12 and Vitamin B6
. It has been found that low levels of vitamins B12 and B6 lead to increased levels of homocystine, which negatively affects heart function. This significantly increases the risk of developing atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease.
Lipid-lowering diet
The almost indigestible name of the diet is actually easily and clearly deciphered - hypo
means
less, under-
, and the word
lipids
(fat) is known to everyone who wants to lose weight. Reducing the amount of fat, as well as unnecessary cholesterol coming from outside, are the main goals of a lipid-lowering diet. By and large, this diet is not a diet; the nutritional method developed by doctors was intended at the very beginning for overweight heart patients and people who had undergone operations on the heart and blood vessels.
Subsequently, a lipid-lowering diet was approved and recommended for all categories of healthy people, with the exception of children, adolescents, pregnant and lactating women and insulin-dependent patients. The diet helps cleanse the body of “bad” cholesterol and promote stable weight loss. Of course, in order to consolidate the results, physical activity is necessary in reasonable quantities.
The essence of the lipid-lowering diet:
The essence of a lipid-lowering diet is to reduce calorie intake due to the almost complete rejection of fat-containing animal products. The advantages of the diet are that a strict menu simply does not exist; the lipid-lowering diet is structured in such a way that a person assembles the products recommended for consumption at his own discretion. You should eat 5-6 times a day, in small portions, avoid frying foods, especially in batter and deep-fried, drink liquid before meals or an hour after. Dinner no later than 19 o'clock; if you go to bed very late, then a glass of low-fat kefir or any fruit can be safely eaten after dinner.
List of prohibited foods on a lipid-lowering diet:
- All types of animal fats - margarine, spread, pork fat, as well as coconut and palm oil;
- Semi-finished products, canned food, fast food products;
- Lard, fatty meats, smoked products, sausages, rich meat broths;
- Red poultry meat;
- Meat and poultry by-products;
- Crayfish, shellfish, caviar, shrimp, sturgeon;
- Pasta, pasta and dumplings;
- Confectionery;
- Bananas, grapes;
- Bread and baked goods made from wheat flour;
- Sweet carbonated and alcoholic drinks (liqueurs, beer, liqueurs, champagne);
List of products recommended for consumption 2 times a week on a lipid-lowering diet:
- Lean veal and beef, white poultry, steamed or boiled, broth in “second” water;
- River fish;
- Dairy products;
- Potatoes, baked or boiled;
- Eggs and mushrooms;
- Nuts;
- Instant coffee, a glass of dry wine.
List of products recommended for consumption in unlimited quantities on a lipid-lowering diet:
- Vegetable oil - olive, sunflower, flaxseed;
- All types of vegetables containing little starch: carrots, beets, zucchini, eggplants, white cabbage, cauliflower and broccoli, radishes, cucumbers, tomatoes, beans, corn, peas, etc. fresh, boiled, baked or steamed;
- Seasonal berries and fruits with skin: currants, raspberries, plums, cherries, apricots, peaches, apples, pears, etc.;
- Leafy vegetables (lettuce, spinach, sorrel, basil) and herbs (dill, cilantro, parsley, onion);
- Sea fish, seaweed, squid;
- Whole wheat bread;
- Cereals and dishes made from them;
- Mineral and melt water, fruit drink, compote, tea.
Here is an approximate set of dishes that can lower cholesterol without drugs:
Breakfast:
- Cereal porridge with olive oil, rolled oats or dark rice;
- Omelet (without yolks);
- Green tea with honey or milk;
- Coarse flour bread, dry biscuits.
Snack:
Berries or apple, rosehip tea, crackers.
Dinner:
- Soup made from potatoes, carrots, green peas, onions, beans;
- Steamed or baked fish with some vegetable salad;
- Carrot, pomegranate or cranberry juice;
- Bread with bran.
Afternoon snack:
carrot salad with vegetable oil, 2 fruits.
Dinner:
- Beef (lean) with mashed potatoes;
- Low fat cottage cheese;
- Tea, honey;
- Cracker.
For the night
: a glass of kefir.
Self-medication with folk remedies is not such a harmless activity, because everyone’s health status and body reactions are different, so herbal medicine and diet are best used under the supervision of specialists.
Competent consultation with a specialist can be obtained at Clinic-NM, Orekhovo-Zuevo, st. Dzerzhinsky, 41
Drug therapy
To get rid of dyslipidemia, it is necessary to correct lipid metabolism disorders with the help of medications. For this purpose, patients are prescribed statins, fibrates, vitamins and other drugs.
1. Statins
is a group of drugs that reduce the biosynthesis of cholesterol in the liver and destroy it inside the cell.
They have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect and improve vascular endothelial function. "Rosuvastatin", "Atorvastatin", "Simvastatin", "Fluvastatin
" prolong the life of patients with atherosclerosis and prevent the development of severe complications. They do not affect carbohydrate metabolism and inhibit platelet aggregation.
2. Fibrates
- medications used for high levels of triglycerides in the blood.
Fenofibrate
increases the level of HDL, which prevents the development of atherosclerosis. Sometimes they are prescribed together with statins.
3. Cholesterol absorption inhibitors
block its absorption in the small intestine.
The only officially approved drug in this group is Ezitimib.
4. Bile acid binding resins
-
"Colestipol" and "Cholestyramine"
. They do not dissolve in water and bind bile acids in the lumen of the small intestine, preventing their reabsorption. Drugs in this group are prescribed to patients with familial hyperlipidemia as monotherapy or in combination with other cholesterol-lowering drugs.
5. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
found in large quantities in fish oil. They reduce the content of lipids, cholesterol, LDL, VLDL in the blood and have an antiatherogenic effect. Omega-3 is an effective means for the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis, improving the rheological properties of blood and inhibiting thrombus formation.
6. A nicotinic acid
-
“Niacin”, “Enduracin”
. These drugs belong to the B vitamins and have a pronounced lipid-lowering effect.
Extracorporeal therapy is used in severe cases when other treatments have become ineffective. The main methods of extracorporeal detoxification: hemosorption, plasmapheresis, ultraviolet irradiation of blood, ultrafiltration, cryoprecipitation.
You need to remember that:
- Only a doctor can prescribe the drug and select the dose!
- In some cases, it is necessary to take medications, while diet therapy is a secondary, additional means of influencing cholesterol!
Prescription of statins is mandatory for persons with hypercholesterolemia concomitant with the following diseases
, since their use in combination with other drugs prescribed by a doctor significantly
reduces the risk of sudden cardiac death:
- Persons over 40 years of age with a high risk of cardiovascular pathology,
- Coronary heart disease, angina pectoris,
- Previous myocardial infarction,
- Coronary artery bypass surgery or stent installation for myocardial ischemia,
- Stroke,
- Obesity,
- Diabetes,
- Cases of sudden cardiac death in close relatives under the age of 50 years.
Contact Clinic-NM, Orekhovo-Zuevo, st. Dzerzhinsky, 41
Tel: +7(496)4-290-888, +7(910)4-290-88
How do you donate blood?
Cholesterol levels are determined during a biochemical blood test. Where is blood taken from? Typically, blood is taken from a vein to determine total cholesterol levels. The unit of change is usually taken to be mmol per liter of blood.
Before donating blood for cholesterol, you need to know the rules to avoid unreliable results.
- Donate blood on an empty stomach in the morning, with the last meal no later than 12-14 hours before the test.
- It is better to avoid fatty foods a few days before the examination.
- You cannot drink alcoholic beverages during the day.
- An hour before the procedure you will have to stop smoking.
- Before taking the test, you can drink plain water.
- During the day before donating blood, it is advisable not to be nervous and avoid physical activity.
- You should tell your doctor in advance if you are taking any medications that may affect your cholesterol levels. These are statins, NSAIDs, fibrates, hormones, diuretics, vitamins, antihypertensive drugs and others. Usually the appointment is canceled before the analysis.
Norm
The normal level of total cholesterol in the blood is 5.2 mmol per liter. If the indicator is in the range from 5.2 to 6.5 mmol per liter, we are talking about borderline values. Elevated values are indicated if the cholesterol level in the blood is more than 6.5 mmol.
To prevent plaque deposits on the walls of blood vessels, you need to eat right
HDL should normally be between 0.7 and 2.2 mmol per liter. LDL – not higher than 3.3 mmol.
Cholesterol levels can change throughout life. As a rule, they increase with age. This indicator is not the same for men (2.2-4.8) and women (1.9-4.5). In young and middle age it is higher in men, in older age (after 50 years) – in women. The norm for children is 2.9-5.2 mmol.
If the cholesterol level exceeds the norm, a detailed analysis is prescribed - a lipid profile.
Price
The price of devices starts from 4890 rubles for MultiCare-in to 11600-11700 rubles for the Accutrend Plus analyzer. This difference in the lower and upper range is explained by the build quality, country of origin and functionality.
The presence of additional functions makes the device even more expensive (for example, the ability to do several types of analyzes or increased memory). Fame and brand recognition leads to an increase in price, but it is better to focus on the technical characteristics and take into account the reviews of patients who have already used the device for a long time.
How to reduce with folk remedies?
It is best to reduce cholesterol through diet and traditional medicine. Many effective remedies are offered, the preparation of which will require affordable products and medicinal plants.
Flax seed
It can be purchased at any pharmacy and immediately crushed. Add powder to food. Flaxseed will not only help lower cholesterol, but also improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and normalize blood pressure.
Oats are one of the effective means for lowering cholesterol.
Oats
Pour a glass of oatmeal into a liter of boiling water in a thermos. The next morning, strain the prepared broth and drink throughout the day. Every day you need to prepare a new decoction.
Beet
To reduce cholesterol, beet kvass is prepared. Peel a few medium-sized vegetables and cut into strips. Fill half a three-liter jar with beets and fill to the top with cold boiled water. Place the container in a cool place until it ferments. As soon as fermentation has begun, kvass can be drunk.
Lemon, garlic, horseradish
To prepare, you will need 250 grams of all ingredients. They need to be passed through a meat grinder and filled with 750 grams of boiled water. Place in a cool place for a day. Then you can take a tablespoon half an hour before meals in the morning and evening. The mixture should be topped with honey.
Herbal collection
In equal quantities, take St. John's wort, dill seeds, coltsfoot, dried strawberries, horsetail, and motherwort. Pour a glass of boiling water over a teaspoon of the mixture and let it brew for 20 minutes. Drink a third of a glass three times a day for about 30 minutes. before meals. Treatment lasts one month.
Garlic tincture
This is one of the most effective means to combat bad cholesterol. One head of garlic needs to be peeled, grated and poured with vodka (1 liter). Close the container tightly, place in a dark corner and leave for ten days, shaking daily. When the tincture is ready, strain it and place it in the refrigerator. Drink 15 drops daily, twice a day.
Honey
If you are prone to high cholesterol, it is recommended to eat honey regularly. There is a very effective remedy for cleansing blood vessels, the preparation of which also requires cinnamon. Mix honey (2 tablespoons) and cinnamon (3 teaspoons), pour two glasses of warm water. Drink three times daily.