Popular vitamins
Famous doppel herz vitamins - active Omega 3-6-9. The content of polyunsaturated acids in the drug has a complex positive effect on the human body. In particular:
- Omega-3s obtained from fish oil minimize the risk of increasing cholesterol levels in the blood. This reduces the likelihood of developing atherosclerosis. When the substance is administered, it is possible to normalize blood pressure.
- Omega-6, which is obtained from flaxseed oil, reduces blood clotting, which reduces the risk of blood clots. Substances are important for the processes of transformation of lipids and proteins.
- Omega-9 or oleic acid reduces the risk of developing coronary disease and normalizes glucose levels, which is important if you are predisposed to diabetes or diagnosed with it.
The vitamin complex Active Cardio Hawthorn Potassium + Magnesium is highly effective. The combination of substances regulates metabolism in the myocardium. The balanced composition of the complex allows you to restore the ratio of the main blood electrolytes. In addition, the presence in the vitamin preparation Active Cardio Hawthorn Potassium + Magnesium contains important vitamins and minerals that protect against the effects of free radicals. When taking the drug it is possible to:
- Improve the conduction of biological impulses and improve the excitability of the heart.
- Dilate the coronary arteries.
- Reduce heart rate tachycardia.
- Reduce the effect of stress hormones on the heart muscle.
The vitamin preparation Active Magnesium + B vitamins is effective. It is recommended to buy it if you cannot eat a balanced diet, which does not allow you to ensure that your body receives substances important for heart health. These doppelhertz vitamins are indicated for people who are excessively addicted to alcohol and smoking. They also provide support to the human body under conditions of stress and increased physical activity, in particular during professional sports training.
For older people, it is recommended to take Vitamin and Mineral Complex 50+. It has a balanced composition and is optimally suited for use in order to preserve not only health, but also youth for a long time. The vitamin complex contains vitamins and minerals in optimal combination that improve vitality and maintain good mood. Taking vitamins allows you to maintain good health under increased stress and gives you energy for the whole day.
The German manufacturer also offers other effective complexes for heart health. Buying Doppelhertz vitamins is recommended for inclusion in the therapeutic regimen for treating many diseases. All necessary recommendations are indicated in the operating instructions.
Vitamin and mineral complex for the prevention of atherosclerosis and stroke
The relationship between cardiovascular and cerebral pathology is especially obvious in the example of acute cerebrovascular accidents (ACVA) - stroke, transient ischemic attacks, the main predisposing factors to which in adults are atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension [1]. It should be remembered not only that there are many other etiological causes of stroke (in particular, diabetes mellitus, arteriovenous malformations, systemic and autoimmune diseases, vasculitis, hematological diseases and prothrombotic disorders, heart defects and abnormalities of cerebral vessels, congenital and acquired metabolic diseases etc.), but also about the possibility of developing strokes/transient ischemic attacks in children and adolescents [1, 2].
Today, there is no doubt that dietary approaches are not only widely used in the prevention of acute cerebrovascular accidents, but are also effective, as proven from the standpoint of evidence-based medicine. In particular, the use of vitamin-mineral complexes is one of the tools of neurodietology [3, 4].
In this regard, the English vitamin and mineral complex Cardioace deserves attention, which contains water- and fat-soluble vitamins (ascorbic acid, thiamine, niacin, pyridoxine, cyanocobalamin, folic acid, tocopherol, cholecalciferol), macro- and microelements (Mg , Fe, Zn, Mn, Cr, Se, Cu), as well as biologically active substances (coenzyme Q10, carotenoids, L-carnitine, lecithin) and extracts of edible medicinal plants (garlic and flax seeds).
Vitamins
Ascorbic acid
This water-soluble vitamin is an organic compound related to glucose. In the body, vitamin C functions as an antioxidant, a reducing agent, and a coenzyme for certain metabolic processes.
Ascorbic acid has general strengthening and immunostimulating effects (stimulates the synthesis of endogenous interferon), normalizes redox processes in the body. Vitamin C takes part in the formation of collagen, serotonin (from tryptophan), catecholamines, as well as in the synthesis of corticosteroids; ascorbic acid restores coenzyme Q10 and vitamin E (see below).
Vitamin C is involved in the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism, blood clotting and tissue regeneration, reduces vascular permeability, reduces the need for vitamins B1, B2, A, E, folic and pantothenic acids. Ascorbic acid inhibits the release of histamine and accelerates its degradation, inhibits the formation of prostaglandins and other mediators of inflammation and allergic reactions [5].
Vitamin B1
A water-soluble vitamin that plays an important role in the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats. Thiamine is essential for normal growth and development and helps maintain proper functioning of the heart, nervous and digestive systems.
Systemic thiamine deficiency is the cause of the development of a number of severe disorders, the leading place in which is occupied by lesions of the nervous system (neuropathy, intellectual impairment, paresis and/or paralysis, etc.) [5].
Vitamin B6
A water-soluble vitamin used as a metabolic stimulant. Pyridoxine is a coenzyme of proteins involved in the processing of amino acids and the regulation of protein utilization; takes part in the production of red blood cells and hemoglobin, and also ensures a uniform supply of glucose to cells and its uptake by neurons, and has hypocholesterolemic and lipotropic effects; Vitamin B6 is necessary for protein metabolism and transamination of amino acids.
Vitamin B6 improves metabolism in brain tissue, increases brain performance, and helps improve memory and mood. Its deficiency is accompanied by disturbances in glutamine metabolism, which may be accompanied by seizures [5].
Vitamin B12
A water-soluble vitamin that has the most complex structure of all vitamins (the basis of the latter is the corrin ring). Cyanocobalamin deficiency is the cause of pernicious megaloblastic anemia; With vitamin B12 deficiency (with or without anemia), neurological disorders such as demyelination and irreversible neuronal death may occur, accompanied by numbness and/or tingling in the extremities, as well as ataxia. There are indications that vitamin B12 deficiency has an impact on the occurrence of depression [5].
Folic acid
A water-soluble vitamin that is practically not synthesized in the human body, but is necessary for the growth and development of the circulatory and immune systems, as well as for DNA replication processes.
Folate deficiency can cause megaloblastic anemia (red blood cell precursor cells produced in the bone marrow enlarge to become megaloblasts).
The main function of folic acid is the transfer of one-carbon groups (for example, methyl and formyl) from one organic compound to another [5].
It is worth noting that vitamin therapy with pyridoxine, cyanocobalamin and folic acid has been used (in combination) for a relatively long time as a preventive treatment for strokes (to reduce homocysteine levels in the blood).
Niacin
A water-soluble vitamin that takes part in many oxidative reactions in living cells. Niacin has a hypolipidemic effect; it normalizes the concentration of lipoproteins in the blood, reduces the concentration of total cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins, reduces the cholesterol/phospholipids index, increases the content of high-density lipoproteins, dilates small blood vessels (including cerebral ones), improves microcirculation; has a weak anticoagulant effect, increasing the fibrinolytic activity of the blood, and has detoxification properties.
Niacin deficiency can lead to dementia (an example is pellagra). Niacin is used by neurologists not only for ischemic cerebrovascular accidents, but also for microangiopathy, diabetic polyneuropathy, prolonged stress and in other clinical situations [5].
Vitamin E
Fat-soluble vitamin (tocopherol). It has pronounced antioxidant properties (the main food antioxidant), improves cell trophism and strengthens the walls of blood vessels, prevents the formation of blood clots and promotes their resorption.
Tocopherol deficiency can lead to neurological disorders such as areflexia, dysfunction of the dorsal horns of the spinal cord, gait disturbances, muscle hypotonia, paresis of the extraocular muscles, etc. [5].
Vitamin D3
Fat-soluble vitamin (cholecalciferol). Vitamin D3 is an essential vitamin, which is also a hormone (prohormone) and has numerous immunotropic and other functions (including cognitive-modulating). This essential vitamin is necessary for the body to ensure normal hemocoagulation, blood pressure regulation and adequate functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Vitamin D3 deficiency is widespread in many parts of the world and is not influenced by race, gender or age. In turn, adequate supplementation of vitamin D3 has a positive effect on the neurological health and immune functions of the individual [2, 5].
Minerals
Magnesium
An essential macronutrient necessary for the full functioning of nervous tissue. Magnesium (Mg) is a regulator of many physiological functions and biochemical processes in the body, but the most important of them seems to be ensuring the transmission and speed of nerve impulses from the brain to peripheral nerve endings and muscles, as well as antioxidant properties.
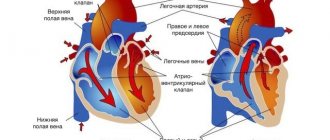
Mg supports the structures of ribosomes, nucleic acids and individual proteins; it is involved in oxidative phosphorylation reactions, protein synthesis, lipid and nucleic acid metabolism, and the formation of energy-rich phosphates. Mg controls the normal functioning of myocardiocytes and regulates the contractile function of the myocardium (individual cells and parts of the heart - the atria and ventricles).
Up to 30% of the world's population regularly lacks magnesium in food, which is partly due to modern technologies and mineral fertilizers, leading to a deficiency of this mineral in the soil. Excessive elimination of magnesium from the body is facilitated by the consumption of refined foods, as well as excess salt and sugar. Magnesium deficiency is caused not only by insufficient dietary intake of this macroelement, but also by insufficient sun exposure, taking certain medications (corticosteroids, aminoglycosides, diuretics), as well as situations with an increased need for Mg. Mg deficiency does not allow one to resist the effects of oxidative stress and other pathological phenomena that lead to significant damage to the endothelium and mitochondria. The need for Mg increases with increasing physical and intellectual stress, under stress and in other situations. This macronutrient is not produced in the body and comes from food or special medications.
The main manifestations of Mg deficiency include increased blood pressure, a tendency to thrombus formation, cardiac arrhythmias, spastic (painful) contractions of the intestines, esophagus, apnea, bronchospasm, etc. Psychoneurological manifestations of Mg deficiency are tremor, chorea-like movements, ataxia, skeletal muscle spasms, headaches , tetany, cephalalgia, hearing loss, etc.
Mg preparations are used in the treatment of migraine and acute cerebrovascular accidents (especially ischemic stroke) as a means of providing neuroprotection [2, 5, 6].
Iron
Iron (Fe) is a trace element that has long been recognized as an essential nutrient. Iron is a catalyst for oxygen exchange processes and the main active element of blood hemoglobin; the microelement is part of the enzymes of other cells (in the form of heme) [5].
Zinc
Zinc (Zn) is a trace element with the properties of an adaptogen, antioxidant, neuroprotector and immunomodulator [7]. Other positive effects of zinc are an anti-stress effect, the ability to stabilize the blood-brain barrier during intoxication (an antagonist of heavy metals in the development of neuronal death) and an obstacle to the induction of apoptosis by the latter, that is, it is an antagonist of heavy metals in the development of neuronal death. In addition, Zn is a stabilizer of the D1-dopamine receptor.
Symptoms of zinc deficiency include not only behavioral disorders and damage to the organ of vision (photophobia, night blindness), hypogeusia, but also intention tremor, nystagmus, dysarthria, emotional lability, impaired ability to concentrate, etc. [5, 7, 8 ].
Manganese
Manganese (Mn) is a trace element that is found in very small doses in the bodies of all living organisms, but has an impact on vital processes (growth, blood formation, gonadal functions). Mn affects redox processes, protein metabolism, activates the activity of enzymes and is a necessary element for the natural development of the skeleton. It is necessary to maintain the tone of the cardiovascular system, helps strengthen memory and the nervous system, and activates the body's protective functions. Mn deficiency may be accompanied by paralysis, convulsions, disturbances of consciousness, vision and/or hearing [5].
The inclusion of Mn in the vitamin-mineral complex Cardiois aims to help normalize metabolism and energy metabolism.
Chromium
Chromium (Cr) is a microelement involved in glucose metabolism and necessary for energy supply to the body, sometimes called the “glucose tolerance factor.” Cr is essential for adequate synthesis of cholesterol, fats and proteins; Maintains stable blood glucose levels. Low Cr supply (low Cr content in the blood) may be a reflection of coronary insufficiency.
In a standard (average) diet, the Cr content is usually insufficient, which is facilitated by a number of factors (low level of absorption, comparative scarcity of nutritional sources, significant loss during cooking, increased dietary intake of sucrose, etc.).
Cr deficiency can lead not only to anxiety, fatigue, glucose intolerance and disorders of amino acid metabolism, but also to an increased risk of atherosclerosis. The ideal form of the microelement is considered to be picolinate, in which Cr easily penetrates into cells and ensures the effective action of insulin [5]. Cr, as one of the constituent components of the Cardioace vitamin-mineral complex, is responsible for the transport of another microelement - iron (Fe ensures the formation of red blood cells and hemoglobin).
Selenium
Selenium (Se) is a microelement that actively interacts in the body with vitamins, enzymes and biological membranes, participating in the regulation of fats, proteins and carbohydrates, as well as in redox processes. Se is a component of more than 30 vital biologically active compounds in the body.
Se has been proven to be an antioxidant; it is used for the prevention and treatment of a wide range of diseases. Small concentrations of Se suppress histamine, have an antidystrophic effect and antiallergic effect, stimulate tissue proliferation and improve the functions of the immune system. Approximately 80% of Russians have Se deficiency [5].
Biologically active substances
Coenzyme Q10
Coenzyme Q10 is a coenzyme (benzoquinone) containing a quinoid group (hence the designation Q) and 10 isoprenyl groups; A synonym for coenzyme Q10 is ubiquinone. Coenzyme Q10 is necessary for the normal functioning of living organisms, especially for the functioning of tissues with a high level of energy metabolism. It takes part in oxidative phosphorylation reactions, is a component of the electron transport chain in mitochondria, and is involved in the transfer of electrons from the NADH dehydrogenase complex (complex I) and the succinate dehydrogenase complex (complex II) to complex III (promotes ATP synthesis).
Coenzyme Q10 is not only an antioxidant, but also restores the antioxidant activity of vitamin E. By its chemical nature, coenzyme Q10 is similar to vitamins E and K; it has been relatively widely used in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases since 1965 (in particular, in the treatment of atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension). It is also used in pediatric and therapeutic practice to improve energy exchange in cells [5].
Carotenoids
Carotenoids are a group of natural fat-soluble organic pigments (isoprenoids) present in the chloroplasts and chromoplasts of plants and some photosynthetic organisms. Carotenoids are unsaturated hydrocarbons (carotenes proper) or their oxidized derivatives (xanthophylls), they are chemically close to the important chromophore - retinal.
Carotenoids are powerful antioxidants that provide protection against the harmful effects of free radicals and fatty acid oxidation, which is most important in the composition of the described vitamin-mineral complex [5].
L-carnitine
L-carnitine is a trimethylammonium (betaine) derivative of γ-amino-β-hydroxybutyric acid; acyl-coenzyme A transporter across the mitochondrial membrane. It is a stimulator of energy metabolism in the human body. This natural compound is an essential substance and is related to B vitamins. The metabolic functions of L-carnitine are extremely numerous (providing and maintaining the activity of coenzyme A, detoxification properties, anabolic functions, antioxidant, lipolytic and neuroprotective effects, etc.).
L-carnitine is used for cerebroendocrine syndrome, many types of mitochondrial pathology, intense physical/psycho-emotional stress; vascular, toxic and traumatic lesions of the central nervous system, disorders of β-oxidation of short- and medium-chain fatty acids, organic aciduria (acidemia), aminoacidopathy, etc. L-carnitine has biological activity that is in demand in various fields of medicine, but its main function is is the transfer of long-chain fatty acids across the inner membrane into the mitochondria. In this case, normalization of mitochondrial structure and functions is achieved, and long-chain fatty acids penetrate from the cytoplasm into the mitochondria and their β-oxidation occurs with the formation of adenosine 5'-triphosphate and acetyl coenzyme A [5].
Plant products
Garlic extract
Regular consumption of garlic is believed to maintain normal blood cholesterol levels and increase high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels while reducing low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and triglyceride levels. These effects explain the preventive action of the beneficial ingredients of garlic against atherosclerosis and stroke [9].
Flax seed oil
Flaxseed oil (oleum lini) is characterized by a high content of unsaturated fatty acids (linoleic, linolenic, oleic). Its beneficial properties are due to the content of essential polyunsaturated fatty acids, in particular linolenic acid triglycerides [5, 9]. Cardioace contains flax seed extract as a plant source of essential fatty acids, including omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (docosahexaenoic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid).
Conclusion
The described vitamin-mineral complex also contains other ingredients (riboflavin, copper, lecithin), each of which has the ability to have a positive effect on the state of the cardiovascular and nervous systems. I would like to express the hope that in the near future, disease-specific complexes like CardioEys will find active use in Russia in the prevention of atherosclerosis and acute disorders in patients of different ages. Currently, the drug is intended for use from 14 years of age.
Literature
- Studenikin V.M., Tursunkhuzhaeva S.Sh., Nechaeva N.L., Kuzenkova L.M., Shelkovsky V.I., Pak L.A. Stroke in children // SVOP. 2012. No. 4, p. 43–52.
- New targets in pediatric neurodietology (collective monograph) / Ed. Studenikina V.M.M.: Dynasty. 2012. 252 p.
- Neurodietology of childhood (collective monograph) / Ed. Studenikina V. M. M.: Dynasty. 2012. 672 p.
- Studenikin V.M., Kurbaytaeva E.M., Borovik T.E., Balkanskaya S.V. Neurodietology - a new direction of neuroscience // Questions of children's dietology. 2008. T. 6. No. 1. P. 40–44.
- Nutrients, conditional nutrients and antinutrients in neurodietology of childhood (Handbook) / Ed. Studenikina V.M.M.: Dynasty. 2013, 188 p.
- Studenikin V.M., Tursunkhuzhaeva S.Sh., Zvonkova N.G., Pak L.A., Shelkovsky V.I. Magnesium and its drugs in psychoneurology // Effective pharmacotherapy. Neurology and psychiatry. 2012. No. 4, p. 8–12; 58–60.
- The physiological role of zinc and correction of its content in the body (Small Encyclopedia of Zinc) // Reference and information publication for doctors. M., 2008. 26 p.
- Studenikin V.M., Tursunkhuzhaeva S.Sh., Shelkovsky V.I. Zinc in neuropediatrics and neurodietology // Attending Physician. 2012. No. 1. pp. 44–47.
V. M. Studenikin, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Corresponding Member of the RAE
FSBI "NTsZD" RAMS, Moscow
Contact Information
Abstract. The possibilities of preventive care for cardiovascular disease and acute cerebral blood flow dist in patients aged > 14 years are examplified by contemporary vitamin/mineral complex. Therapeutic properties of main ingredients in vitamin/mineral complex for atherosclerosis and stroke prevention are described.
Side effects and overdose
Most patients who take Doppelhertz vitamin complexes tolerate the drugs well if they follow the dosage recommendations. But in some cases, negative reactions of the body were recorded due to the use of the products. Most often this is:
- Slowing heart rate.
- Lethargy and drowsiness.
- The occurrence of arterial hypotension.
- An allergy manifested by hives and itching of the skin.
- Allergic manifestations in the form of urticaria and itching.
If these symptoms appear, you should stop taking vitamins and consult a doctor. After assessing the condition, the specialist will make the correct decision.
An overdose of doppelhertz vitamins can cause serious negative consequences and pose a health hazard. When taking a large amount of vitamins at once, there is a risk of developing severe bradycardia. In this case, it is recommended to rinse the stomach urgently. To do this, you need to drink a liter of boiled water to induce vomiting. If after this it is not possible to improve the condition, then you should urgently seek qualified medical help.