Normal pressure readings are 120 to 80 mmHg. Art. These values change under the influence of various factors: during excessive physical exertion, during periods of stress, during excitement, in the heat. There are many factors influencing changes in blood pressure parameters; a slight change up or down does not indicate serious pathologies. When identifying cardiovascular abnormalities, doctors look at pulse pressure (PP). PD refers to the difference between the upper and lower values. This is a key factor that indicates violations.
What is pulse pressure
Pulse pressure is the difference between systolic and diastolic values. To calculate PD, you need to subtract the lower value from the upper value. The result will be pulse pressure.
The formula looks like this:
Systolic value – Diastolic value = Pulse pressure .
There is a standard pulse pressure that specialists rely on when making a diagnosis. Pulse pressure normally ranges from 40 to 60 points. Deviations from this value are permissible, but they cannot be more than 10 units.
Pulse pressure should not depend on arterial values on the tonometer. When blood pressure surges, the difference between the upper and lower values should remain unchanged.
Pulse pressure is the difference between the upper and lower readings
Calculation formulas
First formula: (2 ×DAD SAD) ÷ 3
Diastolic blood pressure is multiplied by 2, systolic blood pressure is added, and the result is divided by 3.
With indicators of 120/80, the calculations look like this: (2 × 80 120) ÷ 3 = 93 mm Hg. Art.
Diastolic blood pressure is subtracted from systolic blood pressure, the difference is divided by 3, and diastolic blood pressure is added to the result.
Calculation based on indicators 120/80: (120 – 80) ÷ 3 80 = 93 mm Hg. Art.
(0.42 × SBP) (0.58 × DBP)
The upper pressure is multiplied by a factor of 0.42; lower - by 0.58. The works are added up.
Calculation using the example of blood pressure 120/80: (120 × 0.42) (80 × 0.58) = 96.8 mm Hg. st
The result of calculations using this formula is less accurate than in the first two options.
In hospitals, a person’s average pressure is calculated using the formula: CO × OPSS.
What indicators are considered normal?
Pulse pressure can normally fluctuate between 40-60 units. There is no general indicator, since this is an individual value for each person. The normal pulse pressure changes over the years. In youth, the PD value will be 40-45 units, in adults it is 50 points, and in adulthood it will reach 60 points.
The maximum value of pulse pressure is observed at 50-60 years of age, then the indicator decreases. Changes in PD are influenced by hormonal levels.
Table of pulse pressure by age:
| Age limits | Average PP for men | Average PD for women | Normal blood pressure indicators for men | Normal blood pressure indicators for women |
| 20 | 45 | 43 | 123/76 | 116/72 |
| 21-30 | 51 | 44 | 126/79 | 120/75 |
| 31-40 | 47 | 46 | 129/81 | 127/80 |
| 41-50 | 51 | 52 | 135/83 | 137/84 |
| 51-65 | 50 | 51 | 142/85 | 144/85 |
| Over 65 | 45 | 47 | 142/80 | 159/85 |
The table is compiled based on many years of research. Deviations from the table are permissible within minor limits.
RESULTS
RESPONSIBILITY ´Ð°Ð²Ð»ÐµÐ½Ð¸Ðµ в ноÑме â 40 мм. RESULTS, RESULTS, RESULTS, RESULTS °ÐµÑÑÑ. RESPONSIBILITY, RESPONSIBILITY Ð¼ÐµÐ¶Ð´Ñ Ð½Ð¸Ð¼Ð¸ и ÑиÑÑамР¸, коÑоÑÑе ÑказÑÐ²Ð°ÐµÑ ÑаблиÑа, не более 10 мм. RESULTS, RESULTS RESULTS Ð ¸Ñии возÑаÑÑнÑÑ Ð±Ð¾Ð»ÐµÐ·Ð½ÐµÐ¹. RESULTS RESULTS.
››› ROYALTY ››› SYSTEM ÑÑ ÑÑо оÑобенной Ñизиологией и не оÑноÑÑÑ ÑÑÑай к паÑоДогиÑм. RESULTS, RESULTS, RESEARCH Ñ ÑÑевожноÑÑи, паѰлиÑа дÑÑаниÑ.
Causes of high pulse pressure
Pulse pressure reflects disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. High pulse pressure can be caused by a number of factors:
- increase in temperature, overheating of the body: the systolic value increases, which leads to an increase in the difference in values;
- inflammatory processes in individual structures of the heart muscle caused by infections or autoimmune reactions, inflammation of the inner lining of the heart, myocardial damage;
- congenital or acquired heart defects;
- long-term drug therapy for hypertension: a high difference between the upper and lower values will be a protective reaction of the body;
- kidney failure;
- ischemia, heart failure;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- atherosclerotic vascular lesions;
- lack of vitamins in the body.
As body temperature rises, the difference between upper and lower pressure also increases.
Blood pressure control
The highest blood pressure is in the aorta, and as you move away from it, the pressure in the arteries decreases. The lowest blood pressure in the veins! It depends on the volume of blood entering the arteries as a result of the work of the heart and the diameter of the lumen of the vessels.
High blood pressure destroys blood vessels and damages arteries. Being in this state for a long time, a person is at risk of: cerebral hemorrhage; failure of the kidneys and heart.
Why does blood pressure rise? Most often this is due to lifestyle. Many professions force a person to remain in one position for a long period of time, and for proper blood circulation it is necessary to move. Conversely, people who work in hard and physical jobs often overload the body, which cannot cope with the movement of blood flow in the vascular system.
Another important reason may be stress and emotional disorders. A person who is completely absorbed in work does not even notice that he has high blood pressure. This is due to the fact that the brain is constantly busy with tasks, and the body has little rest and relaxation.
Hypertension is often caused by bad habits. For example, alcohol and smoking. This is not surprising, since alcohol and tobacco destroy the walls of veins and vessels through which blood flows.
Why does pulse pressure drop?
Low pulse pressure is the difference between the upper and lower values of less than 40 units. In this case, doctors diagnose isolated arterial hypotension.
The causes of low human pulse pressure are always caused by pathologies:
- Ischemic nephropathy caused by vascular stenosis. Pulse pressure is regulated by biochemical mechanisms. The body produces the enzyme renin, which regulates vascular tone and the blood supply system. When kidney function is impaired, an imbalance occurs in metabolism, organ nutrition, and synthesis. This leads to a change in the glomerular filtration rate, impaired blood flow, and general destabilization. If left untreated, the condition can worsen and lead to a heart attack or severe kidney failure. Due to disorders occurring in the kidneys, the arterial value increases, which is reflected in the pulse value.
- Myocardial infarction. In case of acute disruption of blood supply, tissues and cells die. This is reflected in the value of pulse pressure, which decreases sharply. arterial parameters also drop to critical values.
- Extreme degree of left ventricular failure. Due to a sharp decrease in arterial parameters, failure develops in the left ventricle of the heart muscle. Factors influencing the development of the disorder are different: from aortic valve stenosis to a heart attack. Without medical intervention, a person can die.
- Heavy bleeding. Blood loss leads to a sharp drop in blood and pulse pressure. This is a protective reaction of the body, which tries to preserve tissue nutrition. Internal organs and vital systems do not receive sufficient nutrition and blood supply, which can lead to necrosis.
- Decompensation of chronic heart failure.
- Damage to the hypothalamus.
- Vegetovascular dystonia.
- A sharp decrease in cardiac output and cerebral ischemia.
A sharp decrease in pulse blood pressure can lead to death, so therapeutic intervention is required.
The lower the pulse pressure indicator, the greater the problems with the person’s condition it indicates
Symptoms of abnormalities
Deviations from the average pulse pressure can be determined by the appearance of characteristic symptomatic signs:
- pain in the head: throbbing pain in the back of the head in time with the heart rhythm;
- dizziness: loss of orientation in space, vestibular disorders, vertigo;
- vomiting: reflex vomiting, which does not bring relief, the feeling of nausea is caused by insufficiency of cerebral blood supply;
- increased sweating: the body receives false signals that force it to start thermoregulation, it produces more sweat due to imaginary cooling;
- clouding of consciousness: disorientation, auditory and visual hallucinations, memory loss, prosopagnosia;
- blue discoloration of the skin around the mouth;
- speech impairment, unintelligibility;
- unsteady gait;
- paralysis, lack of coordination of movements.
These are the main symptoms of dangerous pulse pressure that occur most often. The list of disorders is much wider.
Why are such conditions dangerous?
High and low pulse pressure values are dangerous to human health. Main risks and possible complications:
- a heart attack leading to acute heart failure, which can lead to sudden death;
- acute cerebrovascular accident, which is caused by rupture of a vessel or death of nerve cells, which can be fatal;
- heart failure syndrome;
- ischemia;
- syncope, which can lead to serious internal pathologies or death;
- impaired renal function due to damage to one organ;
- dementia, cognitive disorders, impaired mental activity, high risk of developing schizophrenia, Alzheimer's disease.
If signs of pulse abnormalities appear, you should consult a doctor who will select treatment appropriate to the indications.
If the difference between the upper and lower values is high, the likelihood of complications and severe consequences is much higher.
High pulse pressure can be very dangerous
Features of treatment
Deviations of normal blood pressure in any direction require identification of the root cause of the pathology and its elimination (relief). Without this, treatment is either useless or dangerous, since what helps with one disease can cause death in another.
Minor fluctuations in blood pressure do not require any intervention. They are most often one-time and physiological: temperature changes, climate zone changes, physical or psychological overload. The maximum that needs to be done is to consult a cardiologist in case of recurring abnormalities.
The doctor can prescribe folic acid - vitamin B9, which will support the heart and eliminate overload. The vitamin is produced by intestinal microflora and is responsible for cell growth and DNA preservation. During hyperloads, it is not enough, therefore, to stabilize the immune system, metabolic processes, and vascular elasticity, additional supply from the outside is necessary.
Patients with extra pounds and high pulse pressure are prescribed diuretics to normalize the total volume of circulating blood: from Furosemide, Diacarb, Hypothiazide to Triampur, Veroshpiron, Spironolactone. The treatment regimen is strictly individual, depending on the degree of obesity, blood pressure levels, and concomitant pathology.
In the presence of atherosclerosis, statins are added that normalize cholesterol metabolism: Atorvastatin, Rosuvastatin, Pitavastatin. They use nicotinic acid (niacin, vitamin PP, vitamin B) - a lipid-lowering agent, ion exchange resins (hemodialysis) or bile acid sequestrants: Cholestyramine, Colestipol, which reduce low-density lipoproteins that can destroy the arterial wall.
Age-related myocardial degeneration is stopped by prescribing cardiac glycosides: Digoxin, Celanide, Strophanthin. To reduce the diastolic index, Papaverine, calcium inhibitors: Amlodipine, Norvasc, Lacidipine, antispasmodics: Platiphylline, Scopolamine, Spazgan are prescribed.
To maintain vital functions, adrenergic drugs are used: Isadrin, Dobutamine, Dopamine. They act quickly, but only for a short time. For acute heart failure - intravenously - Amrinon and Milrinone.
Hormone replacement therapy can be used, and in extreme cases, surgical intervention: heart disease, aneurysms, total vascular atherosclerosis.
How to relieve the condition at home?
If pulse pressure increases or decreases, you must call an ambulance. It is impossible to normalize the condition and help the patient at home.
Before the ambulance arrives, you must follow the general recommendations:
- You should not take pills for hypertension or hypotension without a doctor’s prescription; taking medications not according to indications can lead to a worsening of the condition; before prescribing medications, the doctor will conduct a comprehensive examination, determine the cause of the disease, the severity of the problem, and then draw up a therapeutic treatment plan;
- if pulse pressure is disturbed, the patient should not be allowed to drink or eat, this can lead to loss of consciousness and involuntary vomiting; in this state, the patient may choke on vomit;
- to normalize the condition, you need to take a comfortable position, calm down, take a few deep breaths and exhales, think about the good;
- in the room you need to open a window or window to ensure the flow of fresh air into the room, you need to remove tight clothes from your body, unfasten the collar.
Upon arrival of the ambulance team, you must describe your condition in detail, as well as follow all the recommendations of medical workers. Specialists will provide first aid and decide whether hospitalization is necessary.
First aid
It is impossible to stop a large or small pulse difference on your own; an ambulance is needed. Before her arrival:
| With high blood pressure | At low pressure |
| Do not take any medications unless previously approved by your doctor | |
| Do not drink or eat anything (fainting, vomiting, aspiration of vomit), you can take sedative drops: Corvalol, Valocordin, Valerian | Eat something salty, drink a couple of glasses of water, a cup of coffee, green tea |
| Take a comfortable position, open the windows for oxygen flow, loosen tight clothes | |
| Carry out tonometry, record the results for the doctor | Tonometry every 10 minutes with accurate recording |
The doctor may suggest hospitalization, the patient has the right to refuse, but it is more reasonable to stop the attack inpatiently, under the supervision of specialists.
Diagnostic measures
To diagnose a pulse pressure disorder and the cause of its occurrence, you need to consult a therapist. The therapist will conduct a general examination and write a referral to a cardiologist, endocrinologist, neurologist, nephrologist. A comprehensive examination will help to accurately determine the cause of the deviation of pulse pressure from normal values. After a comprehensive examination, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment according to indications.
Diagnostic methods:
- neuromonitoring, checking the functioning of the kidneys and thyroid gland;
- physical diagnosis;
- collecting information about the development of the disease, concomitant diseases, and other abnormalities;
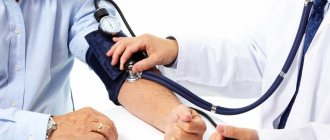
- measuring blood pressure using a tonometer;
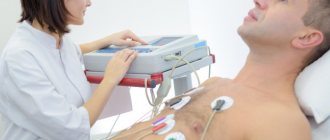
- continuous recording of heart dynamics on ECG throughout the day;
- ECG;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- Doppler examination of the vessels of the neck and head;
- analysis of thyroid hormones;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- clinical urine analysis;
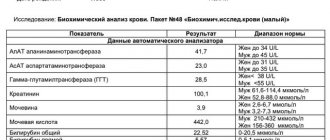
- general blood analysis;
- blood chemistry.
The types of diagnostic tests are determined by the attending physician after assessing the general condition of the patient.
ECG is one of the most accessible diagnostic methods
The danger of chronic reduced PP
A decrease in indicators is characteristic not only of acute conditions; in some diseases, such a deviation takes on a less pronounced, but chronic form. For example, pathology occurs very often with vegetative-vascular dystonia.
There is no immediate danger to human life, but constant monitoring of blood pressure and treatment of the underlying disease are necessary. In another case, VSD will progress, and constantly reduced pressure negatively affects the condition of all organs, not just the heart or kidneys.
Pregnant women especially need to be attentive, since when carrying a child, the load on these organs increases.