An occasional headache is familiar to all people, since it can appear as a consequence of ordinary fatigue or the body’s reaction to changes in meteorological conditions. Usually this condition does not require medical intervention and stops on its own, you just need to rest a little or wait for the weather to change. However, constant pain in the temples, forehead or eyes this is a clear reason to think about your own health, since regular headaches (chronic cephalgia) can be one of the symptoms of a serious illness.
Causes of headaches
Insufficient time for rest, nervous stress, city noise, and an overly intense rhythm of life are often the root causes of constant headaches. If the cause of stress or discomfort is eliminated for a certain period of time, your health will improve significantly. While persistent cephalgia may be a sign of a serious disease that requires medical intervention:
- allergy;
- high intracranial pressure caused by vascular diseases;
- migraine accompanied by nausea, sound and light sensitivity;
- hematomas in the head caused by injury;
- tumor formations;
- aneurysms;
- the presence of inflammatory foci in brain tissue;
- nasal congestion, infectious diseases of the respiratory system;
- critical days of the menstrual cycle or pregnancy;
- damage to the trigeminal nerve.
Chronic headaches in the temporal region and forehead with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, as a rule, are chronic. This is a consequence of pinched vessels supplying the neck and irritation of the nerve endings. After the underlying disease is cured, the patient’s well-being improves. If no other reasons related to physiology can be traced, the whole issue may be a disorder of the vegetative-vascular system.
Non-hazardous conditions
Cephalgia often manifests itself during pregnancy, often at the beginning, as a result of hormonal imbalance, a drop in immune defense occurs, and the emotional reaction becomes difficult to control. Women are often under mental stress, feel pressure drops, forgotten chronic diseases appear, and catch a cold.
These reasons influence the appearance of pain in the temples and forehead, which has an aching, squeezing nature. The following factors can worsen the situation:
- fatigue, poor sleep;
- change in climate zone;
- unhealthy diet (consumption of sweets, citrus fruits, strong drinks, overeating, hunger);
- physical stimuli (bright lights, smells, sharp sounds).
The cause of painful sensations can be various everyday moments associated with prolonged exposure to the open air in the heat or, conversely, in the cold, in a strong wind.
If you wear contact lenses, they can lead to headaches or dry eyes. Also, a person’s well-being is influenced by what he eats. By eliminating harmful components from the diet (smoked meats, processed foods, fast food, alcohol, caffeine), the feeling of discomfort may go away on its own.
Dangerous reasons
When you first seek medical help with a complaint of headaches, your blood pressure is usually checked, since this is the most likely cause for cephalalgia. The cause of high blood pressure (BP) can be an inactive lifestyle and changes in atmospheric conditions, lack of sleep, long-term drug therapy, troubles, and unhealthy habits.
Headache can be caused by a common cold, as well as various infectious diseases. Meningitis is considered among the most dangerous. This disease leads to inflammation of the meninges and can only be treated in a hospital.
Severe anomalies include benign or malignant neoplasms in the skull. At certain stages, the tumor causes severe pain in the head. At the first suspicion of this disease, it is necessary to conduct a neurological diagnosis and contact an oncologist.
What to do if you have a headache when you move your eyes?
Headache when moving the eyes and at rest (whether it is pain in the eyes when reading or working on a computer) is an extremely unpleasant condition for a person. Therefore, it is urgent to take a painkiller from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The next step in helping a person is to see a doctor. If there are signs of a general infectious disease (flu, acute respiratory infections), then a general practitioner will be able to provide adequate medical care. In other cases, consultation with an ophthalmologist and often a neurologist is necessary. If the cause of pain in the eye is a foreign object or injury, in no case should you rub your eyes or try to reach such an object directly with your fingers. It is necessary to rinse your eyes generously with clean water. If this does not produce results, seek medical help immediately.
Research methods
Headache is a symptom, not a pathology. This symptom is not specific, and for this reason, its presence is difficult to make a correct diagnosis. It is necessary to take into account the accompanying manifestations and perform diagnostics using appropriate equipment to identify the underlying cause of this condition. The following procedures are prescribed for diagnosis:
- Blood pressure measurement.
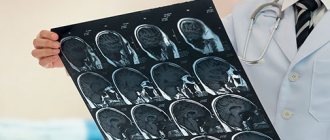
- MRI of the brain.
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and head.
- Laboratory blood analysis.
- Cardiogram.
- CT scan of the skull and brain.
- Dopplerography.
Causes of ocular migraine
The main cause of atrial scotoma is a series of neurological disorders, the roots of which lie in a local decrease in the tone of the posterior cerebral artery. Against this background, ischemia (insufficient blood supply) develops in areas of the cerebral cortex involved in the analysis of visual signals, as well as in the retina itself. Alternatively, ocular migraine occurs due to compression of the 3rd pair of cranial nerves by the dilated cavernous sinuses or carotid arteries.
An attack of atrial scotoma can be triggered by:
- violation or prolonged non-compliance with the work and rest regime;
- sleep disorders;
- change of place of residence, especially with a change in time zones;
- suffered stress, emotional tension;
- hormonal imbalances, including cyclical changes in women;
- long-term stay in rooms with high gas pollution;
- exposure to flickering light sources, including older PC monitors.
The risk of experiencing an ocular migraine attack is higher in patients with abnormalities in the structure of blood vessels: aneurysms, malformations. In adolescents, an attack can be triggered by academic stress and a growth spurt.
Treatment of sinusitis
Depending on the patient’s condition and the course of the disease, the doctor prescribes therapy and selects antibacterial, decongestant and anti-inflammatory drugs. Treatment can be conservative or surgical.
Conservative treatment
For mild sinusitis, in addition to drug treatment, according to indications, nasal cavity lavage according to Proetz, or “cuckoo”, is performed. A special solution is injected into the nose of the patient lying on his back. It passes through the nasal cavity, sinuses, after which it is pumped out with a vacuum pump. “Cuckoo” is carried out in a course of 2 to 10 procedures.
For moderate and severe cases of the disease, antibiotics are prescribed in the form of tablets, solution for injection or inhalation.
Surgical treatment (puncture of the maxillary sinus)
In case of severe purulent sinusitis or lack of effect from conservative therapy, a puncture is used. This allows you to quickly remove pus from the sinus, clean it and treat it with an anti-inflammatory drug. Sometimes several similar manipulations are required. Punctures are performed under local anesthesia.
When sinusitis cannot be treated or is in an advanced stage, surgery is performed under general anesthesia. The period of complete recovery after surgery can take up to two weeks.
Diagnosis of sinusitis
Treatment of sinusitis will be effective if the patient contacts an ENT specialist in time, the specialist will diagnose and prescribe treatment. The examination includes a number of procedures:
- examination of the nasal cavity;
- palpation or feeling the area around the nose and under the eyes;
- clinical blood test;
- X-ray of the paranasal (paranasal) sinuses - according to indications;
- computed tomography of the sinuses.
X-rays can detect the accumulation of mucus in the sinuses and swelling of the mucous membrane of the sinuses. With sinusitis, a darkening will be visible in the picture, since the mucus and swelling of the tissues in the cavities do not allow x-rays to pass through.
CT scan of the paranasal sinuses is necessary to identify polyps, cysts and anatomical changes. The examination is painless and lasts no more than 5 minutes.
If you feel heaviness when you tilt your head down, and the discomfort subsides some time after you raise your head, contact an ENT specialist. Self-medication with folk remedies, randomly selected antibiotics and nasal drops causes serious complications. Sinusitis can become chronic and cause more severe diseases: otitis media, meningitis, brain abscess, orbital phlegmon (inflammation of the tissue around the eyeball).
Forecast and prevention of ocular migraine
Patients diagnosed with atrial scotoma must carefully observe the daily routine, work and rest. Harmonious distribution of the load on the physical body and psyche helps reduce the risk of an attack by 2-3 times. Nutrition also plays a role - some foods provoke constriction or dilation of blood vessels. These include:
- red tomatoes and products made from them;
- milk;
- red grape wines;
- celery;
- cocoa and chocolate.
All these products contain tyramine, a complex organic polypeptide that affects vascular tone and excitation processes in brain cells.
It is advisable to avoid stressful situations and increased physical activity. To relax the nervous system, swimming, massage, acupuncture, hydrotherapy, and rational psychotherapy are recommended. If preventive measures are taken, ocular migraine does not pose a threat to health and life, although it can periodically reduce their quality.
What is sinusitis?
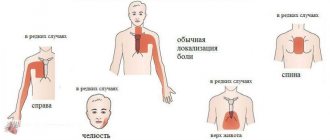
Sinusitis is an inflammation of the maxillary sinuses. It usually develops as a complication of a runny nose. The most characteristic signs:
- temperature rises to 37 - 37.5 C;
- nose is stuffed;
- yellow-green nasal discharge appears;
- the bridge of the nose, cheeks near the wings of the nose and temples hurt;
- headache worsens in the evening;
- the sense of smell disappears;
- the voice becomes nasal;
- feeling of general weakness.
When the maxillary sinuses are inflamed, a person quickly gets tired, it is difficult for him to concentrate, and his memory weakens. It is very difficult to work with sinusitis, so it is better to take sick leave.
Sinusitis can be acute or chronic.
Symptoms of ocular migraine
Based on its clinical manifestations, atrial scotoma is difficult to confuse with other ophthalmological diseases. In the retinal form, provoked by abnormal relaxation of the posterior cerebral artery, the patient is concerned about:
- defects appearing in the field of view - bright flashes, flickering, dark spots and streaks that can merge with each other;
- gradual total decrease in visual acuity;
- the appearance of phosphenes (visual images) in the “blind” zones of the visual field and along its periphery.
As ocular migraine worsens, it becomes complicated by headache localized in the frontal lobe, bridge of the nose, spreading to the orbits. It pulsates, waxes and wanes, like contractions during childbirth, inevitably reaching a peak. At the peak of the attack, pain is complicated by nausea, vomiting, and a feeling of fullness in the head.
Good to know: a characteristic symptom of ocular migraine is increased sensitivity to light, sounds, and touches. They increase the pain, so the patient strives with all his might for solitude and silence.
The average duration of an attack of atrial scotoma is from 30 to 300 minutes. A mild degree of anomaly occurs within 10-20 minutes, sometimes not accompanied by headaches. After the end of the attack, it takes up to 1 hour for complete restoration of vision.
If atrial scotoma is caused by compression of the 3rd pair of cranial nerves, the patient experiences:
- transient drooping of the upper eyelid;
- dilation of the pupil in one eye while maintaining the same size in the other;
- dilation of the pupil against the background of paralysis of the muscles that regulate its diameter;
- divergent strabismus due to paralysis of the extraocular muscles in one eye.
Among the visual impairments with ocular migraine of this form, a split image is observed, when one eye perceives the picture correctly, and the other transmits an image inverted horizontally or vertically. This picture is typical for children and adolescents who have entered puberty.
Good to know: ocular migraine with compression of the cranial nerves has a specific “Alice syndrome”, which consists of the appearance of visual hallucinations visible in peripheral vision.
Symptoms with ophthalmoplegic atrial scotoma last longer than with retinal scotoma - up to 2 weeks. All this time, the anomalies may be accompanied by headaches, but often occur without them.
Prevention of sinusitis
To avoid sinusitis you should:
- spend enough time outdoors;
- strengthen immunity;
- Healthy food;
- take vitamins;
- dress according to the weather;
- seek medical help in a timely manner.
If you have discovered the first symptoms of sinusitis and are looking for a qualified specialist who will diagnose and help you cope with the disease, call the phone number listed on the website or leave a request in the feedback form. Medical staff will answer your questions and conduct all necessary examinations within one business day. Let's take care of your health together!