Which method is the most reliable?
Hemorrhoids are a disease that occurs as a result of expansion of the arterial collectors of the rectum.
In addition to a hereditary predisposition to the development of hemorrhoids, the following lead to: ___• stool disorders (constipation, diarrhea), ___• sedentary lifestyle, ___• sedentary work, ___• overweight, ___• heavy physical activity, ___• diseases of the digestive system, ___• pathologies, increasing intra-abdominal pressure (ascites, emphysema, chronic cough, etc.), ___• pregnancy.
The duration of the relapse-free period for hemorrhoids does not depend on the method of eliminating the enlarged node. To prevent the disease from returning, it is necessary to eliminate all factors contributing to the development of pathology - this is a necessary and sufficient condition for maintaining your health.
Hemorrhoids in women
Contrary to popular belief that men are more likely to suffer from hemorrhoids, they often occur in women as well. Predisposition to the disease is inherited, and its occurrence is also determined by the patient’s lifestyle. In patients it often occurs for the following reasons:
- constipation;
- passive lifestyle;
- pregnancy;
- as a complication during childbirth;
- due to vascular pathologies.
Hemorrhoids in women occur due to pathologies in the pelvic cavity, digestive disorders and tumors.
When is treatment without surgery prescribed?
Acute hemorrhoids
It is possible to cure hemorrhoids without surgery using conservative methods of therapy if we are talking about an exacerbation of the disease. Acute hemorrhoids, as a rule, develop in response to the influence of a resolving factor: ___• errors in diet (spicy food, alcohol), ___• bowel disorders (constipation or diarrhea), ___• heavy physical labor.
Thrombosis of the hemorrhoidal node is clinically manifested in the appearance of a subcutaneous painful formation in the projection of the anus. The pain increases with bowel movements, and in severe cases, with walking, coughing and sneezing.
The pain may radiate down the leg and/or be accompanied by a sensation of a foreign body in the rectum. Another characteristic complaint of patients with acute hemorrhoids is blood on the surface of the stool during bowel movements. In severe cases, serious bleeding may occur.
Pregnancy
Conservative therapy methods are used to treat hemorrhoids during pregnancy. The expansion of hemorrhoidal veins during pregnancy is associated with physiological changes in the body of the expectant mother.
The enlarged uterus puts pressure on the rectum, as a result, blood circulation is disrupted and conditions are created for stagnation of blood in the hemorrhoidal vessels. The situation is aggravated by the hormonal background of pregnant women that provokes chronic constipation.
After the birth of a child, all factors contributing to the development of hemorrhoids are successfully eliminated - intra-abdominal pressure decreases, hormonal levels stabilize, and stool normalizes. All conditions are created to eliminate hemorrhoids using conservative methods.
But, if the process started before pregnancy, the doctor may offer treatment using minimally invasive methods.
If surgery is contraindicated
Conservative therapy in the later stages of development of hemorrhoids is prescribed if the patient’s health condition does not allow radical surgery: ___• acute infection, ___• exacerbation of chronic pathology, ___• acute vascular accidents, ___• general weakened state of health, ___• oncological diseases.
In such cases, conservative therapy successfully solves the following problems: ___• improving the patient’s quality of life (elimination of pain, anal itching and other unpleasant sensations), ___• preventing further development of the disease, ___• combating complications (iron supplements for anemia, etc.) .
However, the prognosis for getting rid of the disease remains questionable, and the risk of complications is quite high. Therefore, proctologists recommend carrying out intervention immediately after the patient’s health condition has stabilized.
Types of hemorrhoids
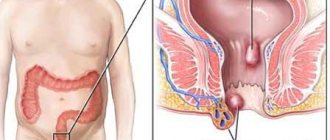
There are three types of pathology - external, internal and mixed hemorrhoids.
Interior
Internal hemorrhoids are considered to be the presence of varicose veins inside the ampulla. Nodes are formed inside on its walls. The formations lie in the thickness of the mucous ampulla of the rectum, located above the dentate zone. Here is the internal venous plexus.
The inner ties are quite treacherous. They do not show themselves in anything for a long time. Small lumps remain asymptomatically inside the intestine for a long time. Only later, when the process decompensates, do clinical manifestations become obvious - discomfort, burning in the anal area, swelling in this area, painful bowel movements, blood on toilet paper.
Outer
External hemorrhoids are a pathology that forms when blood circulation in the anal venous network is impaired. Vasodilation occurs in certain areas of the vessels - cavernous bodies, followed by the formation of nodes. They are located directly under the skin in the area below the rectal-anal line.
There are common and complicated forms of the disease. With it, hemorrhoids bleed, fall out, become pinched and ulcerate. This type of damage to the venous vessels in the anal area manifests itself with striking clinical manifestations. External hemorrhoids almost immediately after their appearance introduce discomfort into the patient’s usual lifestyle.
The patient is concerned about pain in the anal area and itching. They appear first during bowel movement, and then are present constantly. Symptoms intensify with physical activity, sneezing, and sitting for long periods of time.
Methods of conservative therapy
Protective regime and non-drug treatment methods
A protective regime and physical procedures are prescribed as part of the general range of measures for conservative treatment of hemorrhoids, as well as in preparation for surgery and during the rehabilitation period after traditional surgery or low-traumatic procedures.
The essence of the protective regime is to eliminate all factors that increase intra-abdominal pressure and contribute to stagnation of blood in the pelvic veins: ___• prohibition of heavy physical labor and prolonged sitting, ___• dosed exercise (walking on level ground), ___• restriction thermal procedures (baths, saunas), ___• combating excess weight, ___• treatment of chronic diseases that aggravate the process (pathologies of the digestive tract, lungs, genitourinary system), ___• refusal to drink alcohol and spicy foods.
To relieve pain, proctologists prescribe baths with potassium permanganate and/or decoctions of medicinal herbs, which have an astringent, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effect.
In the subacute period, as well as as an anti-relapse treatment, special complexes of physical therapy are recommended that strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, have a beneficial effect on intestinal motility and restore blood circulation in the pelvis.
Fighting bowel dysfunction
Impaired bowel regularity (constipation, diarrhea, and constipation alternating with diarrhea) is the main cause of exacerbations of hemorrhoids. To stimulate intestinal function, a diet high in fiber (apples, oranges, wholemeal bread, prunes) is recommended. Products that help to consolidate stool are excluded from the diet: ___• potatoes, ___• rice, ___• semolina, ___• pears, ___• quince, ___• pomegranate, ___• wheat products: white bread, pasta.
Also prohibited are foods that irritate the intestines: ___• pickles and smoked meats, ___• spices, onions, garlic, ___• carbonated and alcoholic drinks, ___• strong coffee.
Food should be soft and sufficiently heat-treated (steamed, boiled or baked food). It is recommended to include in the diet a sufficient amount of liquid foods and drinks that will ensure that the body is saturated with water (more than 2 liters per day).
If the diet does not help achieve regular bowel movements, natural laxatives are prescribed, the principle of which is to soften the stool (for example, Forlax).
Drug treatment: suppositories and ointments
Treatment of hemorrhoids without surgery involves the use of medications for external use. For nodes located externally, ointments are prescribed, and for pathological elements located inside the intestine, suppositories are prescribed.
Preparations used for hemorrhoids may contain one or more active ingredients: ___• painkillers, ___• antispasmodics, ___• anti-inflammatory, ___• antimicrobial, ___• blood thinners, ___• strengthening capillaries, ___• astringents, drying agents, etc.
Some patients believe that the more actions a drug performs simultaneously, the better, but a large number of components means an increased risk of side effects and a longer list of contraindications. Therefore, we recommend contacting a proctologist who will select the drug individually based on your specific situation.
Minimally invasive methods
Mechanism of action of low-traumatic interventions
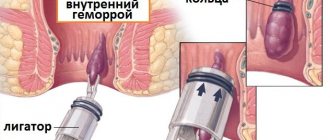
Minimally invasive (low-traumatic) treatment methods involve the removal of hemorrhoids without the use of a traditional surgical scalpel. Such procedures are well tolerated by patients, so they are often called the treatment of hemorrhoids without surgery. ___1. Sclerotherapy of hemorrhoids is the introduction of a chemical substance into the lumen of the vessel feeding the node, which burns the inner lining of the vessel. As a result, the pathological element decreases in size. ___2. During coagulation of hemorrhoids, “gluing” of the internal walls of the vein feeding the node occurs under the thermal influence of wave radiation. ___3. Ligation of nodes with latex rings is a mechanical ligation of the feeding arteries.
Thus, the mechanism of action of minimally invasive methods is the same: the pathological element is “disconnected” from the vascular network, becomes necrosis and is excreted from the body with feces.
Advantages and disadvantages of low-impact methods
The advantages of low-traumatic methods of treating hemorrhoids are expressed in the name itself. An injury that is insignificant to the body does not impose increased demands on the patient’s health, so such treatment can be carried out even in old age in patients aggravated by many chronic diseases.
In addition, minimally invasive intervention assumes: ___• outpatient nature (does not require hospitalization), ___• a short recovery period with minor restrictions (prohibition of physical activity and thermal procedures), ___• mild postoperative pain syndrome, easily relieved with standard painkillers.
Minimally invasive methods have one single, but serious drawback : they are not effective for all patients. At stages IV and V of the development of the process (unremovable nodes), as well as in cases of complicated hemorrhoids, it is necessary to resort to traditional surgery to remove hemorrhoids
Diagnosis of hemorrhoids
Diagnosis of this disease is not difficult. It is performed by a proctologist or surgeon. The doctor interviews the patient, finds out his complaints and information about the course of the disease. Then carries out the following activities:
- Inspection. They examine patients in a chair. To do this, bring your knees as close to your stomach as possible. If there is no chair, the examination is carried out in the knee-elbow position. The doctor examines the anus area. Reveals his anal deformation. He evaluates the skin around it and examines the hemorrhoids.
- Finger examination. The condition of the external and internal sphincters, as well as the mucous membrane, is studied. The doctor determines the location and size of hemorrhoids. He evaluates the possibility of their reduction.
- Anoscopy. This endoscopic method allows you to examine up to 12 cm of the anal canal. Patients easily tolerate this procedure. With its help, the location of internal nodes is determined.
- Sigmoidoscopy. It is prescribed to exclude pathology of the upper intestines.
If it is necessary to identify complications and concomitant pathologies, the patient is referred to other types of examination - ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and gastroscopy.