For those who are faced with venous disease, it is often unclear how a phlebologist differs from a vascular surgeon. After all, both of these specialists work with different forms of venous diseases and complications. Each of them has specifics, which actually divided the profile of these doctors.
Phlebeurysm
The cause of varicose veins is a malfunction of the venous valves. With this disease, the walls of the vessels of the legs expand and deform, as a result of which the veins cease to function normally. Most often, the disease affects the thin saphenous veins, which over time stretch and become visible under the skin (like lumps).
This is what varicose veins look like
Both women and men are at risk (and they get sick quite often). The main symptoms of varicose veins are swelling, heaviness in the legs, night cramps, and pain. Swelling usually increases in the evening and goes away after rest. In the last stages of varicose veins, pain and swelling are constantly present. A competent angiologist is able to diagnose the disease at an early stage and prescribe treatment in a timely manner.
Contraindications
Despite the apparent safety and gentleness of the main diagnostic methods, they have a number of absolute and relative contraindications. Doctors use in-depth research techniques with caution when:
- Decompensated heart, liver and kidney failure;
- Allergic reactions to the components of the contrast solution;
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- Infections and inflammations;
- Mental disorders.
Studies are carried out with the utmost caution in pregnant and lactating women, elderly patients and patients with disorders of natural coagulation.
Atherosclerosis
With atherosclerosis, the vessels of the whole body suffer, most of all the vessels of the legs, heart, kidneys, and brain. Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease in which plaques of fat and cholesterol are deposited on the inner walls of blood vessels. At the same time, the walls of blood vessels lose their elasticity and become denser. As a result, the lumen through which blood flows narrows and blood flow becomes difficult. The first symptoms of the disease are forgetfulness, memory lapses, then the person’s mood often changes, depression may set in, sleep is disturbed, coordination of movements becomes worse, concentration and attention weaken, headaches often occur and mental abilities deteriorate. The task of the angiologist in this case is to take control of the process as soon as possible and relieve unpleasant symptoms.
Treatment methods
Treatment of blood vessels can be conservative or surgical. Medical tactics depend on the severity of the clinical manifestations of the disease, the patient’s age and general health. When the veins of the extremities are affected, experts prescribe the use of compression hosiery and local agents with a venotonic effect.
It is important to reduce the load on the legs and eliminate the effects of predisposing factors. Shoes should be as loose and comfortable as possible. For varicose veins, the phlebologist must prescribe therapeutic exercises and recommends resting with the leg end elevated at least several times a day to ensure blood flow and normal functioning of the lymphatic system.
For atherosclerosis and high cholesterol, it is recommended to follow a diet limited in fats and simple carbohydrates. Medicines prescribed include nicotinic acid, statins, bile acid sequestrants and other drugs that inhibit the formation of cholesterol plaques and restore fat metabolism.
With the onset of menopause, the risk of developing atherosclerosis in women increases sharply. To prevent vascular damage, hormone replacement therapy is prescribed. The entry into the body of a small amount of estrogens plays a protective role, preventing the occurrence of angina pectoris, coronary heart disease, and atherosclerotic damage to the vascular walls.
If conservative therapy is ineffective and there is a threat to the patient’s life, specialists perform surgical treatment. It involves installing stents at the site of pathological narrowing of the vessel. In case of atherosclerosis of the heart vessels and an increased risk of myocardial infarction, vascular surgeons perform coronary artery bypass grafting.
Aneurysm
With an aneurysm, the wall of an artery of the heart (in rare cases, a vein) bulges because it has become too thin and stretched. Because of this, an aneurysmal sac appears, which compresses nearby tissues. A ruptured aneurysm causes hemorrhage, which often leads to death. At the first symptoms, it is important to consult an angiologist as soon as possible, who will prescribe treatment.
Important! When an aneurysm ruptures, the patient feels pain and his blood pressure rapidly drops. In this case, the person needs urgent medical attention.
Aneurysm can be congenital or acquired. If it is present in a child, then from the first days of his life the disease may not be noticed, because the child grows and develops normally until a rupture occurs. Acquired aneurysm is a consequence of atherosclerosis, hypertension, late stage of syphilis; the risk of the disease increases when the vessel is injured and when infected blood clots form.
Phlebitis
Phlebitis is an inflammation of the vein wall with its gradual destruction; it can be acute or chronic. The main danger of the disease is the high risk of blood clot formation and complete blockage of the vessel. Most often, phlebitis is caused by past infections and inflammation. However, the inflammatory process can also begin if a substance that irritates the vessel wall enters the bloodstream. Phlebitis can affect deep and superficial veins.
Depending on which particular vessel wall is inflamed, phlebitis is divided into three types:
- endophlebitis – inner wall;
- periphlebitis – outer wall;
- Panphlebitis is a common form, all membranes are affected.
An angiologist treats any form of this disease; you need to go to a doctor if there are any signs of unhealthy veins, and he will accurately determine the disease.
Treatment of vein diseases
After carrying out diagnostic measures, the doctor decides which treatment is most effective in a particular case. Treatment is conservative or surgical. In our clinic, treatment is carried out using modern and individual methods, using high-tech equipment.
Conservative treatment includes prescription of medications, selection of compression garments and stockings.
Also in our clinic we offer the following range of services:
- Sclerotherapy (introduction of a special agent into the altered vein - a sclerosant, which promotes its gluing and, subsequently, resorption);
- Cosmetic phlebology
- Compression therapy
- Non-surgical techniques - laser removal of capillaries on the face, nose, eyelids
In our clinic, for the treatment of venous diseases, we use the entire arsenal of high-tech and modern techniques, and we provide a guarantee for the operation. Our patients immediately return to their normal lifestyle.
Thrombophlebitis
This is inflammation that occurs due to varicose veins. If left untreated, the inflammation will spread to the deep veins, and as a result, the risk of blood clots moving through the bloodstream increases, causing a pulmonary embolism - a fatal disease. Superficial thrombophlebitis is first felt as a worsening of varicose veins, to which a person is already accustomed, so many do not pay attention to the alarming symptoms. However, you need to urgently consult an angiologist if you:
- it hurts where varicose veins are present;
- the pattern of the saphenous veins becomes clear, it hurts to touch it;
- seals appear around the vein, they are painful and noticeable;
- body temperature rises sharply to 39℃, you feel feverish and shivering;
- near the veins it swells sharply, turns red, and swells.
If necessary (depending on the stage of the disease), the patient is referred to an angiologist surgeon for further treatment.
Phlebothrombosis
Phlebothrombosis is the primary formation of a blood clot in the deep vessels of the legs; the vein is blocked by a blood clot, but no inflammation is observed. Usually the disease focuses on the deep veins of the leg, its back surface. Phlebothrombosis is dangerous because it increases the risk of developing pulmonary embolism and postthrombophlebitis syndrome. This disease is typical for older people, but now it is rapidly getting younger. Phlebothrombosis can be caused by blood stagnation, damage to the vessel wall, and increased blood clotting. The main triggers are oncology and chemotherapy, pregnancy, cardiovascular disorders, the postpartum period, obesity, hormone therapy or oral contraceptives.
Symptoms are pain in the legs, which becomes stronger with movement, slight swelling, and the pain is bursting in nature. If several vein trunks are affected, the skin may turn blue and swelling may increase. After physical activity, the condition worsens, the person tries to move the affected leg less. When the femoral vein is damaged, swelling quickly increases, the venous pattern becomes clearly visible, that is, the veins become full, the skin turns blue, body temperature rises, and the lymph nodes enlarge. With the listed symptoms, the patient urgently needs the help of an angiologist who treats this disease in the initial stages or gives a referral to an angiologist surgeon.
Phlebothrombosis
Prevention
Measures to prevent deep vein thrombosis include the following:
- Don't sit still. If you have had surgery or were on bed rest for other reasons, try to get back to work as soon as possible. If you sit for any period of time, do not cross your legs as this can block blood flow. If you are traveling long distances by car, stop every hour or so and take a walk. If you're on an airplane, stand or walk occasionally. If you can't do this, stretch your shins. Do some exercises. Try raising and lowering your heels while keeping your toes on the floor, then lifting your toes while pressing your heels into the floor.
- Do not smoke. Smoking increases the risk of developing DVT.
- Do exercises and control your weight. Obesity is a risk factor for DVT. Regular exercise reduces the risk of blood clots, which is especially important for people who sit a lot or travel frequently.
Obliterating endarteritis
Obliterating endarteritis is a chronic inflammation of peripheral vessels, due to which their lumen gradually narrows, and blood flows worse to the legs. As a result, ischemia appears in the legs, and this is a direct path to gangrene. The prognosis depends on the stage of the disease at which the patient came to the doctor, concomitant diseases and a number of other factors are important. In the worst case scenario, the leg is amputated.
This disease affects men more often, 10 times more often women, the vulnerable age is 20-40 years. Usually it all starts with a spasm of the peripheral arteries. In the first stages, blood flows poorly to the limbs only during physical activity, and over time, the deficiency worsens. In the last phase, the vessel is completely closed, necrosis begins in the legs and gangrene develops. Moreover, other vessels may also be involved in the process; in this case, they speak of a generalized form of obliterating endarteritis.
Symptoms depend on the stage, and in total the disease has 4 stages of development:
- I – after a walk of 1 km, pain appears;
- IIa – pain appears when walking 200 meters or more;
- IIb – pain occurs when walking distances of less than 200 meters;
- III – pain appears at rest and when walking 25 meters;
- IV – ulcers and foci of necrosis appear.
The task of the angiologist is to prevent the disease from progressing to later stages. If this has already happened, then an angiologist surgeon treats this disease.
Recommendations before visiting a doctor
At the beginning of the appointment, the patient must voice his complaints to the specialist. To provide your doctor with more complete information, it is recommended to keep a diary of pain attacks. It should note the nature of the pain, its location, strength, frequency of occurrence, and duration. It is also necessary to pay attention to the factors that provoke attacks and, conversely, contribute to their cessation.
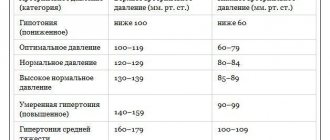
If the patient suffers from pressure changes, you need to draw up a table of blood pressure readings in the morning and evening for the last 2-3 days.
The neurologist should be shown a list of medications taken (with exact names and dosage).
It is also advisable to write down questions for yourself that will be asked to the doctor after diagnosis (about the cost and duration of the therapeutic course, prognosis of the disease, the need for consultation with related specialists, etc.).
Before the examination, you should take a shower and put on clean and comfortable clothes.
Raynaud's syndrome
With this syndrome, a spasm of the hands occurs in the cold or under stress; it is reversible, as is a change in skin color. During an attack, one or more fingers may turn pale, blue, etc. One finger may have one manifestation, another may have another. Sometimes Raynaud's syndrome affects the tongue or nose. Although the symptoms sometimes frighten people, treatment is simple - protection from the cold, quitting smoking, working with a psychologist, taking medications. This disease is treated by an angiologist who prescribes medications and, if necessary, refers to a psychologist.
Women are more susceptible to Raynaud's syndrome, and young women are more likely to suffer from the disease. This disease is caused by excessive α2-adrenergic activity, due to which vasospasm occurs, the mechanism of which has not yet been established by medicine.
The primary form occurs most often - in approximately 80% of cases. It develops without signs of another disease, and in case of secondary disease, patients are diagnosed with various concomitant conditions and diseases, mainly related to connective tissue.
Symptoms, in addition to changes in skin color, are a feeling of cold, goose bumps, burning sensation, a clear boundary of color change appears on the fingers, transitions can be one-, two- and three-phase, often the changes are symmetrical.
Hematologist: who is he, for what symptoms and diseases should you make an appointment with a doctor?
Table of contents
- Hematologist: what does it treat?
- Pediatric hematologist: who is he and what does he treat?
- Help from a hematologist during pregnancy
- When to go to a hematologist?
- Preparing for a consultation
- Blood tests to be taken before consultation
- Stages of consultation with a hematologist
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Advantages of visiting a hematologist at MEDSI
A hematologist is a doctor who deals with the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the blood and hematopoietic organs.
This specialist works with children and adults and uses both traditional and modern techniques in his practice. It can successfully identify even hidden pathologies that do not manifest significant symptoms.
Hematologist: what does it treat?
These specialists provide therapy for the following diseases:
- Anemia.
This pathology is characterized by a decrease in red blood cells and hemoglobin. Anemia is not a separate disease! This is a symptom of mycosis, pyelonephritis, tuberculosis and other dangerous conditions. It is usually accompanied by weakness, general malaise, appetite and sleep disturbances, shortness of breath even with moderate exertion, and poor concentration. - Lymphocytic leukemia.
This disease is malignant and is characterized by the proliferation of atypical B lymphocytes that accumulate in the bone marrow, spleen, liver and lymph nodes. A predisposition to the pathology is inherited, and its main symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, excessive sweating, weakness and sudden weight loss. As lymphocytic leukemia develops, an enlarged spleen and liver, anemia, dizziness, and spontaneous bleeding are detected - Multiple myeloma.
This pathology is malignant and is distinguished by the ability of tumor cells to synthesize homogeneous immunoglobulins or their fragments. The tumor is formed predominantly in the bone marrow and can be focal, diffuse or focal-diffuse - Myeloid leukemia.
This form of leukemia is characterized by the rapid division of special cells in the bone marrow and their accumulation in the blood. Usually it is diagnosed only during a clinical analysis, since often the pathology does not manifest itself in any way. In some cases, patients complain of a slight increase in body temperature, decreased immunity and general malaise. It is also possible to detect anemia and an enlarged spleen - Lymphomas.
This pathology is characterized by enlarged lymph nodes. The primary tumor site usually metastasizes and spreads throughout the body. There are several forms of lymphoma, which differ in symptoms and degree of malignancy.
Specialists also treat other diseases.
Pediatric hematologist: who is he and what does he treat?
This specialist deals with the treatment and prevention of diseases that occur in both children and adults. Working with patients under 18 years of age, he takes into account all the features of their age and development.
They are referred to such doctors if they suspect various forms of anemia, thrombocytopenia (decreased platelet count), hemorrhagic vasculitis (inflammation of microvessels), hemophilia and other congenital hereditary disorders.
Important! If blood diseases are detected at an early age, the patient should be under medical supervision for as long as possible. It is very important not only to detect pathology, but also to control it. Only in this case can the correct growth and development of the child be ensured.
Help from a hematologist during pregnancy
A large number of blood diseases are inherited, for this reason it is very important to visit a doctor when planning a child and during pregnancy. The specialist will provide the necessary genetic tests and determine the likelihood of developing abnormalities. It is especially important to contact a hematologist if one or both future parents have pathologies.
In addition, it is very important for a pregnant woman to monitor all blood parameters, since the supply of oxygen and other nutrients to the fetus largely depends on them. Consultation with a doctor is required for various deviations from the norm. It is especially important to quickly seek medical help if you suspect the development of iron deficiency anemia. This problem is one of the most common and needs correction and observation until birth.
When to go to a hematologist?
Consultation with a doctor is required for the following signs of various disorders:
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Weakness and drowsiness
- Increased body temperature (not due to colds and inflammatory processes)
- Weight loss
- Sleep disorders
- Excessive sweating
- Pale skin
- Decreased appetite
- The appearance of bruises on the body without objective reasons
- Dizziness
Help is required for patients who complain of joint pain, itching, dry skin, tingling and numbness of the fingers. You should make an appointment with a hematologist if you have a hereditary predisposition to blood diseases and low hemoglobin detected as part of a general diagnosis. Both general practitioners, gastroenterologists, neurologists and other doctors can refer you to this specialist.
Preparing for a consultation
No special preparation is required for the standard appointment. Some restrictions are imposed only if the patient must first undergo tests.
Before research you must:
- Try to quit drinking alcohol and smoking for a few days
- Limit fluid intake (per day)
- Refuse to eat (10-12 hours before)
- Avoid the use of medications. If this is not possible, you should tell your doctor what medications are being taken, on what schedule and in what dosages. This will allow you to correctly decipher the diagnostic results
Blood tests to be taken before consultation
Before visiting a hematologist, you should undergo the following tests:
- Common with determination of the number of reticulocytes
(“young” red blood cells). This test will reveal the rate of red blood cell production in the bone marrow - For HIV, hepatitis and other infections
- For ferritin.
Such a study will determine the content of a protein in the blood that preserves iron in cells. - Percentage of transferrin saturation.
This test identifies a protein that binds to iron and distributes it throughout the body.
The research results will allow the specialist to immediately make a diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment. If necessary, other examinations will be recommended.
Stages of consultation with a hematologist
Conversation
It is aimed at collecting anamnesis. The patient is asked about the symptoms of the disease that have arisen. The doctor clarifies the time of appearance of signs of pathologies, their intensity and other features. The specialist also finds out hereditary predisposition to various diseases.
Inspection
The doctor assesses the condition of the skin and mucous membranes. During the examination, signs of disturbances in the functioning of the hematopoietic system may be revealed, such as pale skin, rashes, hematomas, cyanosis (bluish coloration).
Making a diagnosis or ordering additional examinations
If a patient contacts a hematologist with the results of blood tests, a diagnosis can be made immediately. If studies have not been carried out, the doctor will refer you to them. In some cases, not only laboratory but also instrumental examinations are required. The doctor writes out directions for them.
Diagnostics
Blood diseases have a variety of manifestations that are similar to other pathological conditions. Therefore, a wide range of examination techniques are used to identify them. The patient is required to undergo blood tests.
Also held:
- Urine tests
- Coagulogram
- Lymph node puncture
- Scintigraphy
- CT and MRI (computer and magnetic resonance imaging)
- X-ray of flat bones
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and lymph nodes
- Bone marrow puncture, etc.
Comprehensive diagnostics makes it possible to identify even hidden pathologies that have not yet manifested themselves.
Treatment
The treatment regimen and program are developed depending on the individual characteristics of the patient, general current condition, and the presence of concomitant diseases.
The main areas of treatment include:
- Antibacterial.
It is required for patients who suffer from a general decrease in immunity and are more susceptible to various infections than others. - Transfusion.
This therapy involves transfusion of blood and its components. - Supportive.
It is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease and improving the general well-being of the patient. - Chemotherapy.
Prescribed to disrupt the processes of growth and reproduction, as well as necrosis of malignant cells - Medication.
This treatment is carried out to replenish the deficiency of various elements, correct the functioning of the blood coagulation system and accelerate metabolic processes - Radiation therapy.
Prescribed in combination with other manipulations to combat cancer pathologies
Doctors can also resort to hormonal treatment, bone marrow cell transplantation, and surgical interventions.
Important! As a rule, therapy is complex.
Advantages of visiting a hematologist at MEDSI
- Experienced doctors.
Our specialists have all the knowledge and skills necessary to treat pathologies even in advanced cases. If necessary, endocrinologists, gastroenterologists, etc. are involved in the work. - Comprehensive expert-level diagnostics.
We have modern equipment to conduct any examinations. Laboratory research can be performed in Cito mode (urgent) - Application of modern methods of treatment of various identified diseases.
This increases patients' chances of a full recovery. - Comfort of visiting a doctor.
We have ensured that there are no queues and offer to make an appointment for a consultation at a convenient time.
If you want to consult a hematologist, just contact us in any convenient way.
Systemic vasculitis
This is a group of diseases that occur due to inflammation of the walls of blood vessels. Symptoms vary depending on which vessel is affected and the severity of the inflammation.
Vasculitis is:
- Primary – vascular damage as an independent process. They may appear as spots, rashes, ulcers, etc., but there are no other signs of inflammation.
- Secondary is a complication of any cancer or infection, so treatment should be carried out by a specialized specialist, to whom an angiologist refers. Vasculitis often occurs against the background of viral hepatitis.
Depending on the size of the vessel that is inflamed, vasculitis is divided into three groups: with damage to small vessels (Churg-Strauss syndrome, Wegener's granulomatosis), medium ones (polyarteritis nodosa, Kawasaki disease), large ones (Horton's disease, Takayasu arteritis). Symptoms depend on the type of vessel affected; these can be:
- Hemoptysis, shortness of breath, cough, suffocation - with lung damage;
- Increased blood pressure, edema – kidney damage;
- Ulcers, discoloration of the integument, gangrene, rashes - skin;
- Rashes and ulcers in the mouth - mucous membrane;
- Loss of vision, redness, pain and stinging in the eyes;
- Decreased hearing, discharge from the ears and nose, impaired sense of smell, hoarseness, nosebleeds - ENT organs;
- Convulsions, dizziness and headaches, stroke, epileptic seizure – nervous system;
- Diarrhea, abdominal pain, blood in stool - gastrointestinal tract;
- Irregularities in the functioning of the heart, chest pain, increased blood pressure - cardiovascular system;
- Increased body temperature, weakness, weight loss are common symptoms.
What is the difference between a vascular surgeon and a phlebologist?
When any visible manifestations appear on the veins, the skin of the legs, or heaviness in the legs, the patient is often faced with the question of which specialist should he turn to: an angiosurgeon (vascular surgeon) or a phlebologist?
It seems to the patient that there are no differences in them, but in fact these are two completely different specialists who treat various pathologies of the body’s vascular system. If angiosurgeons are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of the entire vascular system of the body, then phlebologists primarily deal with diseases of the veins of the lower extremities.
Considering the frequency of occurrence (more than 30% of the general population), the high risk of disability and mortality from thromboembolic complications, a separate section of angiosurgery was identified in cardiovascular surgery - phlebology, which made it possible to study venous pathology in more detail and make great progress in the methods of its diagnosis and treatment. and prevention.
Angiosurgeons perform open and endoscopic interventions mainly on arterial vessels, such as bypass surgery, stenting, endoprosthetics, etc. As for the venous system, angiosurgeons take a more radical position, taking into account less awareness in this area.
Unlike angiosurgeons, phlebologists consider the problem in more detail and determine the indications for each type of surgical or conservative treatment depending on the medical history, severity of the disease, the presence of complications, and so on based on the totality of individual characteristics in each individual case.
Phlebologists treat: thrombophlebitis, varicose veins of the lower extremities, trophic ulcers, spider veins, chronic venous insufficiency and phlebopathy. If a patient with obvious manifestations of disease of the veins of the lower extremities turns to a vascular surgeon, then most likely the doctor will refer him to a phlebologist.
Diabetic angiopathy
With this disease, the lumen of the blood vessels narrows or they become completely blocked, blood circulation is disrupted, and various organs, limbs, the retina, and the brain can be affected. In some cases, even amputation of a limb is necessary due to gangrene, which develops against the background of venous or arterial insufficiency.
Impaired blood flow due to blockage of a vessel
The disease can be of several types:
- Microangiopathy – small vessels are affected;
- Macroangiopathy – large vessels are affected;
- Combined – small and large vessels are affected.
Treatment is carried out by an angiologist or an angiologist surgeon, depending on the stage and symptoms.
Due to the narrowing of blood vessels in the lower extremities, ischemia begins, which is a deficiency of blood supply and oxygen. As a result, the function of the legs is impaired, ulcers appear, areas of necrosis, and then gangrene. The feet suffer the most, a person’s legs become numb and cold, goosebumps run throughout the body, cramps and pain occur, ulcers appear on the feet, and the skin changes. When the vessels are not severely affected, a slight tingling sensation is felt.
Symptoms
The location of the disease directly affects its symptoms. When the limbs are affected, lameness develops, pain, sensory disturbances, and tingling appear. Without treatment, the disease develops into gangrene and ultimately leads to amputation.
If the vessels of the heart are affected, coronary artery disease, arrhythmia, angina pectoris, pain and shortness of breath become manifestations.
When cerebral vessels are damaged, the signs are as follows:
- Memory impairment.
- Headache.
- Poor blood circulation in the brain.
- Dizziness.
- Decreased attention, speech impairment.
- Mental changes, dementia.
- Motor impairment.
Get diagnosed with atherosclerosis at Clinic No. 1
- Neurologist appointment
- Doppler ultrasound
- Coronary angiography
For one-time payment for services - 20% discount
Call
Emboli
With this disease, the vessel is blocked by an embolus, which may consist of fat, a blood clot, or an accumulation of air. The causes can be any foreign masses that enter the bloodstream, for example, particles of adipose tissue, detached blood clots, amniotic fluid, parasites, protozoa, and fragments from injury.
Symptoms vary depending on the type of embolism:
- Fatty – disorientation, increased excitability, delirium, apathy, respiratory dysfunction, acute respiratory failure;
- Air – focal neurological disorders;
- Bacterial – sepsis;
- Pulmonary embolism – pain in the heart area, shortness of breath, fainting, lack of pulse. This is a potentially fatal condition.
This disease is treated by an angiologist surgeon, in some cases simply by an angiologist, but rarely.
Hemangiomas
Hemangioma is a benign vascular tumor that occurs mainly in children, more often in girls. Its type is lymphangioma, that is, a benign tumor of the lymphatic bed. Tumors appear immediately after birth, they are mainly found on the head and neck, sometimes they are found on internal organs.
Both tumors are noticeable visually - it is a thickening that is higher than the level of the skin. When pressed, the formation decreases and then restores its size. Hemangiomas grow quickly, and it is impossible to predict their behavior.
Lymphangioma grows more slowly and is located in places where there are many lymph nodes.
The reasons are hormonal characteristics of childhood, especially with prematurity, viruses that a woman suffered during pregnancy, and side effects of drugs during pregnancy.
If you find a tumor in your child, you need to contact an angiologist who treats this disease or, if necessary, refers you to a vascular surgeon.
Symptoms that should prompt you to contact an angiologist
You should contact an angiologist if you have:
- swelling, heaviness, fatigue in the legs for no apparent reason;
- spider veins and networks;
- the venous pattern has intensified, it hurts to touch, it is hot to the touch;
- veins become inflamed;
- varicose veins;
- trophic ulcers appear;
- the skin of the limbs changes color;
- the general condition worsens – the temperature rises, weakness appears;
- swelling does not go away even after rest and a night’s sleep;
- Legs hurt - with exertion, at rest;
- night cramps in the legs.
How is treatment done by an angiologist?
This doctor deals with conservative treatment and diagnosis of vascular diseases.
How is the examination carried out and what tests are prescribed?
During the examination and interview of the patient, a medical history is compiled, on the basis of which the doctor can already guess what kind of disease the patient has. The doctor asks questions about complaints, the time of their appearance, their nature, and provoking factors. For example, if there is pain, when it intensifies, does it go away on its own or do you need to take medicine? Many vascular diseases are hereditary, so you need to remember whether relatives had similar conditions.
During the examination, the doctor evaluates the patient’s skin, palpates sore spots, and examines the mucous membranes.
Next, tests are prescribed to accurately establish the diagnosis, confirm or refute the doctor’s first assumption. The list of tests depends on the problem, but there are those that are prescribed for almost everyone. This is a clinical blood test, a biochemical blood test, a coagulogram (clotting time test), a general urine test, and an infectious minimum.
A vascular surgeon usually prescribes ultrasound duplex scanning of veins, angiography, plethysmography, venography, and vascular CT.
Treatment methods
The angiologist provides non-surgical treatment and, if necessary, gives a referral to a vascular surgeon. The doctor prescribes various medications, as well as:
- exercise therapy;
- phlebectomy;
- cold therapy;
- compression treatment, which has proven itself to be effective for lymphostasis and varicose veins;
- barotherapy;
- darsonvalization;
- magnetic therapy;
- thermal laser, which eliminates blood reflux;
- special diet.
The patient must change his lifestyle, eliminate bad habits, become more active and eat better, his body must be in constant tone.
What does an appointment with a phlebologist include?
A doctor’s consultation begins with the collection of patient complaints, clarification of circumstances that could lead to the development of phlebological disease, the presence of chronic diseases, work load, and hereditary predisposition are determined.
Next, the doctor examines the patient. During the examination, the phlebologist will ask you to stand up, when the patient is standing, blood fills the veins and varicose nodes and dilated trunks of the saphenous veins are clearly visible. After the examination, the doctor identifies the problem, makes a diagnosis and gives the necessary recommendations. To clarify the diagnosis, the phlebologist will perform an ultrasound scan of the veins of the lower extremities and prescribe a blood test.
If the patient is indicated for conservative treatment, the phlebologist will prescribe the necessary medications or solve the problem using surgical or non-surgical techniques.