Upper pressure indicators
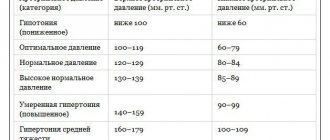
| Age (years) | Upper pressure indicators | ||
| lower | upper | dangerous | |
| 15 | 70-79 | 110-120 | 121-130 |
| 16-29 | 80-89 | 120-130 | 131-140 |
| 30-39 | 80-89 | 120-130 | 131-140 |
| 40-59 | 85-90 | 135-140 | 141-150 |
| 60-69 | 91-99 | 145-150 | 151-160 |
What is pressure
Pressure is usually understood as the force with which the blood acts on the arterial walls at the time of circulation. The biological fluid is moved by the contractions of the heart. There are two types of blood pressure: systolic and diastolic. The first characterizes the effect of blood on the arteries at the time of myocardial contraction. Diastole shows the pressure in the arteries when the heart muscles relax.
A person’s well-being and the state of his internal organs depend on the level of blood pressure. If the myocardium pushes out an insufficient amount of blood, then the organs and systems will be in a state of hypoxia and function incorrectly. High blood pressure increases the load on the entire body.
There is no single standard for pressure. Medical scientists were able to determine the optimal systole and diastole indicators for people of different age categories. For middle-aged people (30-40 years old), blood pressure is considered normal within the range of 110-139 per 70-89 mmHg. The classification of pressure levels is shown in the table below.
| Pressure level | Systolic indicator, mmHg | Diastolic indicator, mmHg |
| Optimal | 110-120 | 70-80 |
| Normal | 120-129 | 80-84 |
| Increased normal | 130-139 | 85-89 |
| High (hypertension) | above 140 | more than 90 |
Don't bog me down with statistics!
40% men and 41% of women in Russia suffer from high blood pressure.
45% premature deaths occur due to strokes and heart attacks caused by hypertension. That is, almost every second person in Russia dies due to diseases that began with just high blood pressure.
12% of men and 25% of women after 45 years of age are interested in their blood pressure and measure it regularly, the rest simply do not pay attention to the alarming symptoms.
Heart pressure is the top or bottom
People who are faced with the problem of low or high blood pressure for the first time are interested in whether their heart pressure is high or low. The tonometer shows two numbers: the first is the value of systole, the second is diastole. Upper pressure is formed due to contractions of the myocardial ventricles. The left side plays a particularly important role. It is responsible for supplying the vascular system with blood. Heart pressure is usually called the top number of the tonometer. It characterizes the force of myocardial contraction, the degree of vascular tension, and heart rate. Lower blood pressure is usually called renal blood pressure, since it reflects the state of the vessels supplying blood to the paired organ.
Today, most people have problems with blood pressure. Heart pressure may rise or fall below normal. There are various reasons for such jumps.
Some doctors note that it is incorrect to separate pressure into cardiac and renal pressure, since systole and diastole are formed by the myocardium and arteries.
Possible complications of isolated hypertension
The situation when the upper pressure is high and the lower pressure is normal is called isolated hypertension by experts. The disorder is associated with a decrease in the degree of distensibility of the arteries, including the most important one - the aorta. It is she who is normally responsible for receiving blood and suppressing pressure during cardiac output. Elasticity allows blood flow to pass smoothly, but as the rigidity of the arterial walls increases, this ability is lost. Blood cannot circulate through the vessels at an optimal speed, which provokes pressure surges. Small vessels are not affected, so lower pressure readings remain normal.
Over time, this condition can lead to a number of additional disorders, among which the following can be noted:
- heart failure;
- decreased left ventricular function;
- disturbance of the speed of blood flow through large vessels;
- damage to the endothelium and subsequent replacement of deformed areas with rigid connective tissue;
- increased production of enzymes that negatively affect the vascular walls - nitric oxide, angiotensin, renin.
What to do in this case? Treat. Moreover, not only relieve a person from unpleasant symptoms, but also eliminate the cause that caused the disorder. The sooner the problem is diagnosed, the answer is given to the question of why the upper pressure is high and the lower pressure is low, and a treatment regimen is drawn up, the faster you can get rid of the disease and the lower the risk of developing all kinds of complications.
Important! You cannot take medications or be treated with traditional methods without consulting your doctor.
Causes and symptoms of increased heart pressure
All reasons for increased systole are divided into physiological, psychological and pathological. Sometimes an increase in blood pressure is simultaneously provoked by all these factors. A condition in which blood pressure remains above normal for a long period of time is called hypertension.
Physiological reasons for the increase in cardiac blood pressure:
- bad heredity;
- binge eating;
- lack of physical activity;
- abuse of salt in dishes, coffee, strong tea;
- aging of the body;
- excess body weight;
- overwork;
- addiction to tobacco and alcohol;
- taking medications that have a hypertensive effect.
Among women under 50 years of age, there are far fewer hypertensive patients than men of the same age. But the onset of menopause changes the situation: most representatives of the fairer sex have problems with fluctuations in blood pressure.
The psychological reasons for the increase in heart pressure are experiences and stress. Pathological factors of hypertension include:
- atherosclerosis;
- adrenal tumor;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- hormonal imbalances;
- diabetes;
- left ventricular hypertrophy;
- vegetative-vascular imbalance of the hypertensive type;
- kidney diseases (organ failure, pyelonephritis);
- malfunction of the aortic valve.
While a person is young, his arteries and heart are in good condition, compensatory mechanisms are immediately activated when blood pressure deviates from the norm. As we age, all organs and systems wear out and begin to function worse. Many elderly people are diagnosed with atherosclerosis and left ventricular hypertrophy. Therefore, as you age, heart pressure standards increase. So, for an elderly person, a systole in the range of 140-155 units will be considered optimal.
Systolic hypertension is manifested by the following symptoms:
- pain in the occipital area and temples;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- numbness of the limbs;
- fear of death;
- weakness;
- heart rhythm disturbance (tachycardia);
- increased irritability;
- redness of the epidermis;
- deterioration in the quality of vision;
- insomnia;
- tinnitus.
Treatment methods
In cases of secondary ISAH, the disease that causes the high blood pressure is treated.
Therapy of the primary form is carried out with a combination of drugs from several groups:
| Group of drugs | Examples |
| Diuretics | Indapamide Hypothiazide |
| Beta blockers | Atenolol Bisoprolol |
| Calcium antagonists | Amlodipine Verapamil |
| Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors | Enalapril Lisinopril |
| Angiotensin receptor blockers | Losartan Valsartan |
In the case of the primary form, treatment is long-term (sometimes lifelong).
Causes and symptoms of decreased heart pressure
The tonometer numbers decrease for various reasons. People whose heart pressure is below 110 units are called hypotensive. Some people have lower than normal heart pressure from birth, but are completely healthy.
All factors of low systolic blood pressure can be classified into physiological, psychological, and pathological. The first group includes the following negative factors:
- bad heredity;
- strict low-calorie diet, fasting;
- physical fatigue;
- bad habits;
- taking drugs that have a hypotensive effect.
Psychological reasons lie in worries and worries. It happens that the central nervous system cannot cope with stress. Nervous fatigue can lead to a decrease in tonometer numbers.
Pathological factors for a drop in heart pressure are represented by the following conditions:
- hypofunction of the thyroid gland;
- hypoxia;
- diseases of the central nervous system;
- abnormalities in the structure of the myocardium;
- vegetative-vascular imbalance of the hypotonic type;
- bleeding (external or internal);
- hormonal imbalances;
- disruption of the functioning of the endocrine glands;
- dehydration;
- stomach ulcer;
- anemia;
- infectious damage to the body;
- oncopathology.
You can suspect low heart pressure by the appearance of the following unpleasant symptoms:
- weakness;
- drowsiness;
- pallor of the epidermis;
- cold extremities;
- dizziness;
- pain in different parts of the head;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- abnormal heartbeat (bradycardia);
- sweating;
- loss of consciousness;
- deterioration in the quality of vision.
It must be taken into account that there is a concept of working blood pressure. It means those tonometer numbers at which a person has no unpleasant symptoms of hypotension or hypertension, and performance is at a high level.
What do the indicators depend on?
Despite the fact that upper blood pressure is called cardiac blood pressure, the numbers are influenced by several factors, namely
Hypertensive crisis - what is it?
- heart rate;
- blood ejection rate;
- left ventricular stroke volume;
- distensibility of the aortic walls.
Thus, the upper blood pressure is affected not only by the heart, but also by the blood vessels (large).
Most often, surges in systolic blood pressure are encountered by elderly people, whose vascular elasticity decreases due to age-related changes. But today, hypertension is also diagnosed in young people. The reasons causing the violation may be the following:
- unhealthy diet, replete with fatty, salty, spicy foods;
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol;
- sedentary lifestyle);
- increased physical or mental stress;
- stressful situations;
- chronic fatigue;
- sleep disorders;
- weather;
- some medicines and traditional medicine.
Obese people suffer from hypertension in 90% of cases
How to keep your heart pressure within normal limits
It is important to remember that even a minimal deviation of heart pressure from the norm, upward or downward, can lead to negative consequences. At first, the pathology may not manifest itself in any way. But then the disease progresses, becomes chronic, and begins to disrupt the functioning of all organs and systems. Therefore, it is important to keep your heart pressure within normal limits. To achieve this, prevention should be carried out.
Doctors give the following recommendations:
- Stop smoking.
- Limit your consumption of alcoholic beverages. Only dry red wine is considered beneficial for blood vessels, but it should be drunk in small doses.
- Normalize body weight if there are deviations.
- Start eating right. It is necessary to eat food often, in small portions. It is important to calculate the optimal daily caloric intake and take it into account when creating a menu. Fatty, spicy, salty foods, foods containing preservatives, flavors and dyes should be excluded from the diet. You can't overeat and starve.
- Increase physical activity. Exercises in the morning and walking in the evenings are useful. You can sign up for group classes in fitness, yoga, and step aerobics. Cardio exercise helps strengthen blood vessels and the heart.
- Minimize the impact of stress. You need to learn to think and approach life positively. If you cannot cope with anxiety, then you should take sedatives (leonwort tincture, valerian tablets).
- Periodically undergo preventive examinations (ECG, duplex scanning of blood vessels, etc.). This will help to identify disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system in a timely manner and take measures to normalize the state of health.
Thus, cardiac is the upper pressure, it is also called systolic. It shows the force with which biological fluid acts on the arterial walls when the heart contracts. The norm for upper blood pressure is within the range of 110-139 units. It is important to try to lead a healthy and active lifestyle, eat high-quality and healthy food. This will help keep your heart pressure at normal levels.
Classification
| Classification according to changes in diastolic pressure levels | Classification by stream |
| Type 1 (60%) – no increase. Type 2 (40%), or “burnt-out hypertension” - a gradual transition of the form with increased numbers of upper and lower pressure into ISAH. | Stable – fluctuations in upper pressure are insignificant, a crisis increase is extremely rare. Labile or crisis - pronounced fluctuations in systolic pressure with frequent hypertensive crises. |
Prevention
{banner_banstat9}
The patient’s lifestyle is important: giving up bad habits, diet, dosed exercise, walking, proper rest. It is necessary to calculate the daily drinking ration together with your doctor, at least 2 liters of clean water daily. Instead of saunas and hot baths, take a contrast shower. The diet should consist of vegetables, fruits, and foods containing iron: liver, tomatoes, fish, apples. A healthy lifestyle is especially relevant for those who have crossed the forty-year mark.