High diastolic pressure usually indicates pathology associated with peripheral vessels. Why can it increase in a person without an increase or with a slight increase in systolic, and what to do in such a situation? Let's try to figure it out.
Increased lower diastolic pressure may be a sign of kidney disease
Blood pressure – systolic and diastolic
Blood pressure (BP) is the force with which blood presses against the walls of the arteries. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and includes two indicators that are written across a line as a fraction. The upper, or systolic, pressure shows the force with which the blood acts on the walls of the blood vessels at the moment of systole, i.e., contraction of the heart muscle, and the lower, or diastolic, shows the force of the peripheral resistance of the vessels at the moment of relaxation of the heart, i.e., diastole.
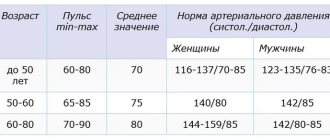
Normally, in a healthy person, diastolic pressure is in the range of 60–90 mmHg. Art.
Diastolic pressure is often elevated in patients with kidney disease, which is why it is also called “renal pressure,” although in fact it can be caused by other factors, such as atherosclerosis.
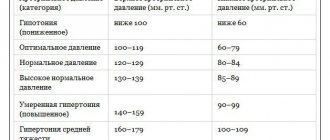
The development of arterial hypertension is indicated in cases where three control measurements recorded blood pressure above 140/90 mmHg. Art. More often there is a simultaneous increase in both systolic and diastolic pressure, but sometimes there is an increase in only the lower indicator.
What does high blood pressure mean?
The cause of high diastolic pressure is usually diseases of the internal organs (kidneys, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, heart). It often happens that high lower pressure becomes one of the first symptoms of these pathologies. Therefore, if it is elevated, you should definitely undergo a medical examination.
Diastolic pressure is often elevated in patients with kidney disease, which is why it is also called “renal pressure,” although in fact it can be caused by other factors, such as atherosclerosis.
Other causes of increased diastolic pressure may include:
- psycho-emotional disorders (depression, manic psychosis, stress);
- abuse of drinks containing caffeine (strong tea, coffee, cola, energy drinks);
- alcohol abuse.
Another reason for high lower pressure is fluid retention in the body caused by overeating, eating large amounts of salty foods, and smoking.
In pregnant women, increased lower blood pressure is often one of the first symptoms of a dangerous complication of pregnancy - OPG-preeclampsia.
How to protect yourself from blood pressure changes
A healthy lifestyle is what can raise low and lower high blood pressure, bringing it closer to normal levels. This does not mean that a chronic hypertensive patient who stops consuming salt will become absolutely healthy, but he will be able to reduce the number of attacks.
The best foods for heart and vascular health
Measures to prevent both low and high diastolic pressure are as follows:
- Complete cessation of smoking, which makes blood vessels fragile and reduces lung capacity.
- Mandatory physical activity appropriate to the person’s age and health status.
- Reducing the amount of salt in the diet (relevant for hypertensive patients).
- Losing weight if you are overweight, which is one of the main factors that increases the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
- Regular walks in the fresh air allow you to saturate your blood with oxygen.
- Maintain a sleep schedule (at least 8 hours at night).
- Proper nutrition, taking into account the body's needs for proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements. Thus, by increasing the level of unsaturated fats in the diet and reducing the amount of saturated fats, you can prevent the formation of cholesterol plaques that accompany almost any vascular pathology.
Why is high diastolic pressure dangerous?
Increased diastolic pressure with normal systolic pressure indicates the presence of some pathology of the vascular system, leading to difficulty in normal blood flow through the vessels.
Normally, in a healthy person, diastolic pressure is in the range of 60–90 mmHg. Art.
If you do not take measures aimed at normalizing blood pressure, then the internal organs and brain do not receive enough nutrients and oxygen. This leads to the development of ischemia and tissue hypoxia, increasing the risk of myocardial infarction and cerebral stroke. An increase in diastolic pressure in older people is especially dangerous, since their blood vessels are significantly altered (atherosclerotic plaques, decreased elasticity of the walls) and the risk of complications of arterial hypertension is higher.
Physical methods for preventing the development and exacerbations of hypertension
Hydrotherapy
Hydrotherapy (hydrotherapy) is a powerful means of recovery, prevention and treatment of hypertension. Water can affect the body as a temperature, mechanical or chemical irritant, and the choice depends on the need for one or another factor of influence.
The temperature factor is the most important in choosing a hydrotherapy technique. Skin capillaries expand and contract in response to exposure to water of varying temperatures. In this case, either an increase in blood flow or a decrease in it occurs. Cold water also slows and increases heart rate and increases blood pressure. Hot water lowers blood pressure, speeds up the heart rate and weakens heart contractions
Most often, to prevent exacerbations of hypertension, water at an indifferent temperature is used, which is indicated for excessive nervous excitability, irritability, cardiac dysfunction, and insomnia.
Hydrotherapy procedures are contraindicated for stage III hypertension.
Before using water procedures as a treatment, you should consult your doctor.
For hypertension stages I-II, rain, dust and circular showers are used using indifferent or warm water with moderate pressure from water jets.
Baths can be general and local; in case of hypertension they are used for therapeutic and preventive purposes. Medicinal baths for hypertension are limited to the use of pine extract.
You can see about the types of hydrotherapy at the Peredelkino Cultural Center here
Drug electrophoresis
This is the use of galvanic current for the purpose of interstitial non-invasive administration of various drugs. Under the influence of galvanic current, drug ions enter the skin and are retained under the anode area, which creates a kind of drug depot. The drug enters the bloodstream rather slowly, which increases the duration of its effect on the body. The body is also affected by the positive effects of galvanic current.
Electrophoresis is indicated in the initial stages of hypertension. At stage III, it is contraindicated. In addition, contraindications are neoplasms, acute inflammatory processes of any location, disorders of blood clotting processes, pronounced atherosclerosis, decompensated diseases of the cardiovascular system, kidneys, pregnancy, individual intolerance to galvanic current.
At the Peredelkino Cultural Center, various types of physiotherapy are used. More details can be found here
Therapeutic exercise (physical therapy)
Therapeutic exercise is used at all stages of hypertension to prevent hypertensive crises and complications of the disease. It includes any available types of physical exercise - dosed walking, morning exercises, health path, swimming.
The best way of prevention is morning exercises or exercises, which allows you to prepare the body for a working day, stimulates the processes of nervous regulation of blood circulation and the reactivity of the vascular system as a whole.
If the disease has already developed, then you should add a daily complex of therapeutic exercises to the morning exercises.
At the Peredelkino Sports and Fitness Center, individual and group physical therapy classes are conducted under the guidance of professional exercise therapy instructors.
Drug therapy
The selection of medications for the treatment and prevention of exacerbations of hypertension should be carried out only by a doctor.
Drug therapy becomes necessary already at the second stage of the disease, when blood pressure reaches significant levels with regular measurements.
The main principle is the individual selection of antihypertensive drugs for each patient.
Dear readers, the articles are for informational purposes only. Before using the recommendations, you should consult your doctor.
Diagnostics
Increased diastolic pressure is not an independent disease, but develops as a symptom of one or another pathology of the internal organs or endocrine system. Therefore, if an increased lower blood pressure is repeatedly noted, the patient must undergo a detailed medical examination, including:
- consultations with a therapist, cardiologist, nephrologist and endocrinologist;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and thyroid gland;
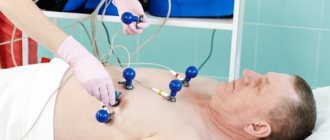
- ECG;
- Echo-CG;
- Dopplerography of cerebral vessels;
- clinical (general) blood and urine analysis;
- determination of the level of thyroid hormones in the blood;
- excretory urography;
- Rehberg's test.
Depending on the results obtained, additional studies of certain organs and systems may be prescribed.
To determine high blood pressure, it is necessary not to measure it once, but to measure it three times
Treatment of high diastolic pressure
How to reduce diastolic pressure with normal systolic pressure, since conventional antihypertensive drugs lower both lower and upper pressure? You don’t need to do this yourself; you need to see a doctor. The main treatment will be to eliminate the primary pathology that led to an increase in lower pressure.
In pregnant women, increased lower blood pressure is often one of the first symptoms of a dangerous complication of pregnancy - OPG-preeclampsia.
To normalize blood pressure, the following groups of drugs can be used:
- Diuretics (diuretics) – stimulate diuresis, remove excess fluid from the body and eliminate swelling.
- Beta blockers - block receptors sensitive to adrenaline, resulting in relaxation of blood vessels and lowering blood pressure. The heart rate also decreases. These drugs are contraindicated in patients suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Calcium channel blockers (calcium antagonists). They prevent the flow of calcium ions from the intercellular substance into the muscle cells of blood vessels and the heart. A decrease in Ca2+ concentration in the smooth muscle of blood vessels promotes their dilation and a decrease in blood pressure.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors). They reduce the concentration of angiotensin in the blood, which leads to a decrease in blood pressure.
- Sympatholytics. Normalizes the tone of blood vessels.
- Antispasmodics. Relaxes muscle cells, including those forming the walls of arteries.
Medications for high diastolic blood pressure should be taken in strict accordance with the doctor's prescription. It is unacceptable to independently change the dose of prescribed medications and the schedule for taking them.
Treatment
High diastolic pressure can be reduced by eliminating the cause of the disorder. To do this, you should undergo an examination (blood test, ECG, x-ray), which will determine the causes of the condition. It is important to adhere to the treatment regimen drawn up by your attending physician, taking all prescribed medications and constantly monitoring your well-being using a home blood pressure monitor. Help to lower regularly rising blood pressure:
- ACE inhibitors;
- diuretics;
- calcium antagonists;
- alpha blockers;
- beta blockers;
- angiotensin 2 antagonists.
Blood pressure-lowering drugs are selected by a doctor, as they have a large list of contraindications and side effects that must be taken into account when drawing up a treatment regimen. An integrated approach will allow you to increase the effectiveness of therapy: taking medications, correcting your diet, giving up bad habits, and traditional medicine recipes.
Tablets and other potent medications are practically not used in the treatment of low blood pressure. To correct the condition, the disease that led to it is treated. If no deviations in the functioning of the body are found, then doctors recommend using folk remedies. These are healing herbal decoctions, tinctures of ginseng root and eleutherococcus. Treatment is long-term – at least 40 days. Raising your blood pressure to normal levels, you should regularly monitor your condition by visiting a doctor and measuring blood pressure at home.
No ads 3
Lifestyle change
Speaking about how to treat high blood pressure, it should be said that in the complex treatment regimen for this pathology, considerable importance is given to lifestyle changes.
First of all, this concerns diet. You should eat food 4-5 times a day in small portions. Chocolate, coffee, table salt, marinades, fatty and spicy foods are excluded from the diet (or severely limited).
The development of arterial hypertension is indicated in cases where three control measurements recorded blood pressure above 140/90 mmHg. Art.
The daily menu should include fresh fruits and vegetables, herbs, dried fruits, foods rich in potassium (nuts, cabbage, tomatoes, baked potatoes, dried apricots), magnesium (buckwheat, fish, dairy products, strawberries, bananas) and B vitamins (yeast , liver, meat, pears, apples, oranges). It is advisable to contact a nutritionist to develop a detailed menu that takes into account the energy needs of the body, the general condition of the patient, and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
Physical activity. To improve blood circulation, it is necessary to devote sufficient time to physical activity every day. The level of permissible loads is determined by the attending physician, based on the general condition of the patient. Preferably swimming, walking, cycling. General massage is very useful.
Massage is useful for high blood pressure, as it helps normalize vascular tone.
Rejection of bad habits. The patient is advised to completely quit smoking. Nicotine promotes spasm of blood vessels, and hence an increase in diastolic pressure. It is equally important to give up the abuse of alcoholic beverages (it is permissible to drink no more than 50 ml of cognac or 200 ml of red wine per day).
Normalization of sleep and rest patterns. Night sleep should last at least 8-9 hours. You should try to go to bed no later than 10 pm. It is important to adhere to a daily routine, alternating work and rest.
Spa treatment. It is based on the use of climatic and physical factors that normalize the state of the cardiovascular system and thereby stabilize blood pressure.
An increase in diastolic pressure in older people is especially dangerous, since their blood vessels are significantly altered.
Risk factors for developing hypertension
Stress, mental and mental fatigue
Research shows that hypertension is more common in people whose life is associated with constant nervous tension. For example, in residents of large cities, hypertension is much more common than in people living in rural areas.
Hypertension and stress are inextricably linked, so it is necessary to treat both ailments.
Every fourth man and every fifth woman in the world has high blood pressure
Research shows that hypertension is more common in people whose life is associated with constant nervous tension. For example, in residents of large cities, hypertension is much more common than in people living in rural areas. Hypertension and stress are inextricably linked, so it is necessary to treat both ailments.
Complications of hypertension are responsible for 9.4 million annual deaths worldwide (WHO)
Physical inactivity
Physical inactivity is a decrease in muscle load due to a sedentary lifestyle. A modern city dweller does little physical labor, prefers to use vehicles even for short distances, instead of walking, and spends his free time in front of the computer or TV. Only 1% engage in recreational sports and 5% do morning exercises.
As a consequence, this lifestyle leads to significant changes in all life-supporting systems of the body, especially the cardiovascular and nervous systems.
The combination of physical inactivity and stress makes a person extremely vulnerable to hypertension and its complications. Adrenaline produced during times of stress stimulates the production of glucocorticoids, which, in turn, stimulate an increase in blood sugar and an increase in blood pressure.
In an immobilized body, adrenaline and sugar, instead of “burning out” with the release of energy, remain in the blood vessels for a long time and lead not only to a long-term increase in pressure, but also to heart attacks and strokes.
Overweight
In order to determine whether you are overweight or not, body mass index is used. It is calculated as the ratio of body weight in kilograms to the square of height in meters. If the result obtained exceeds 25 kg/sq.m for young people and 27 kg/sq.m for older people, but does not exceed 30 kg/sq.m, then this means that there is excess weight. If the index value is above 30 kg/sq.m, then in this case we are talking about clinically pronounced obesity.
More than half of patients with hypertension are obese.
Obesity is a chronic metabolic disease in which excess fat accumulates in adipose tissue.
Numerous scientific studies have proven that reducing excess fat mass by 5-10% leads to a decrease in high blood pressure and improved control of the disease.
Other risk factors
Unhealthy diet - excessive salt intake, high content of saturated fats and trans fats in food, insufficient consumption of vegetables and fruits. As well as the use of tobacco and alcohol.
Uncontrollable risk factors include family history, age, and underlying medical conditions such as diabetes or kidney disease.
Folk remedies for normalizing high blood pressure
If diastolic pressure has increased slightly under the influence of stress, overwork, or eating unhealthy foods, then traditional methods of treatment can be used to reduce it:
- Valerian tincture. Take 2-3 times a day, 5-10 drops. Has a mild sedative effect.
- Infusion of black currants, pine cones, chokeberry and peony. Mix plant materials in equal volumes. Pour two teaspoons of the resulting mixture into a glass of cold water and heat over low heat until boiling. Leave for 30 minutes, strain. Take a third of a glass 3 times a day half an hour before meals. The infusion contains a large amount of flavonoids, which have a beneficial effect on the condition of the vascular wall.
- Lemon juice with honey. Squeeze the juice of half a lemon into a glass, add a tablespoon of honey. Add warm water to the brim and stir. This drink allows you to quickly reduce high diastolic pressure.