A blood test is the first test that is prescribed during a preventive examination or in the presence of various complaints for patients of any age. Deviation of individual indicators from the norm may indicate a certain disease or be a consequence of a pathological or physiological process. One of the important blood indicators is ESR - erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Its increase may indicate the presence of inflammation.
ESR is usually determined during a general or abbreviated blood test, and not as an independent study. In most cases, the analysis is used to detect inflammation of various types at an early stage. To make an accurate diagnosis, one analysis is usually not enough. Diagnosis usually involves a comprehensive examination.
When elevated ESR is not dangerous
ESR depends on the characteristics of the erythrocyte membrane and the concentration of certain proteins in the blood. Sometimes their number changes, but this is not associated with the disease, but is the norm. For example, the following people may have elevated values:
- In pregnant women Pregnancy and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. The longer the period, the higher the ESR. In the first half, the indicator can increase to 18–48 mm/h, and in the later period - up to 30–70 mm/h. If a woman suffers from anemia, the results will be even higher - up to 95 mm/h.
- In the elderly Erythrocyte sedimentation rate and disease in the elderly. ESR increases with age. Even in healthy people after 60 years of age, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate can be 35–40 mm/h.
- For those who like fatty foods. Clinical assessment of laboratory test results. Because of this diet, there are more lipids in the blood, and the ESR also increases.
This does not mean that you do not need to pay attention to an increased ESR. In some cases, this is a sign of illness, so it is better to entrust the interpretation of the analysis to a therapist.
ESR: norm and pathology
Reference values are differentiated by age and gender of patients. There is a special norm for pregnant women. For the age category up to 10 years, the reference ESR values are 0-10 mm/hour. At the age of 10-50 years, the norm for women is 0-20 mm/hour, and for male patients 0-15 mm/hour. For people over 50, the reference values for men are 0-20 mm/hour, and for women the norm is up to 30 mm/hour. An increase in indicators during pregnancy is usually explained by physiological processes. In infants, ESR values are low. As they grow older, they gradually increase in size.
It is important to remember that deviations from the generally accepted norm do not always indicate the presence of a disease. They may be explained by the individual characteristics of the patient. When interpreting test results, the doctor takes into account the patient's medical history, clinical picture and a number of other factors.
What diseases can an elevated ESR indicate?
Most often, an increase in erythrocyte sedimentation rate is associated with various inflammatory processes. But remember: the indicator does not help determine what disease a person has. ESR is needed only to monitor the condition. And its increase may indicate a certain group of pathologies.
Infections
ESR increases Nursing care in therapy for any infectious disease. This could be a simple acute respiratory viral infection, acute inflammatory processes in the genitourinary organs or intestines. After recovery, this figure usually gradually decreases. But in people with chronic or severe infections, abnormalities may persist for a long time. For example, with mononucleosis Clinical and laboratory features of infectious mononucleosis depending on the etiological factor in children, tuberculosis.
Aseptic inflammation
In some diseases, tissues are destroyed and inflamed, but this is not associated with the action of microorganisms. Such pathologies include:
- heart attack;
- stroke The erythrocyte sedimentation rate: old and new clinical applications;
- cirrhosis Features of hemogram indicators in liver cirrhosis;
- nonspecific Analysis of laboratory parameters in patients with nonspecific ulcerative colitis ulcerative colitis.
Immune disorders
If a person has a condition in which immune cells attack their own tissues or foreign proteins, it causes immune disorders and leads to an increase in ESR. Due to pathology, there is more immunoglobulin and fibrinogen protein in the blood, which are involved in inflammatory reactions and increase erythrocyte sedimentation.
ESR may increase with diabetes. Changes in the functional state of the immune system in patients with various types of diabetes, allergies, TYPES OF ALLERGIC REACTIONS, MECHANISMS OF THEIR DEVELOPMENT. IV TYPE OF ALLERGIC REACTIONS PART I and the following autoimmune pathologies:
- systemic lupus erythematosus A case of cutaneous lupus erythematosus induced by golimumab;
- rheumatoid arthritis Erythrocyte aggregation in rheumatoid arthritis: Cell and plasma factor's role;
- giant cell arteritis Sed rate (erythrocyte sedimentation rate);
- polymyalgia rheumatica;
- glomerulonephritis Clinical assessment of laboratory results.
Blood diseases
Changes in blood composition, cell shape or concentration can cause the ESR to accelerate. Is this happening? Blood sedimentation—a simple and useful test? in such cases:
- with iron deficiency anemia, when the level of hemoglobin decreases;
- with sickle cell anemia, when red blood cells take on a crescent shape;
- for macrocytosis Blood sedimentation—a simple and useful test? - a disease in which the volume of the red blood cell increases.
Oncology
With malignant tumors, various antibodies, inflammatory proteins, and toxic substances appear in the blood, which are the result of tumor disintegration. They significantly accelerate ESR. Changes in the blood test will appear in case of myeloma Sed rate (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) disease, acute leukemia, lymphoma The erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Still a helpful test when used judiciously, prostate cancer The erythrocyte sedimentation rate: old and new clinical applications or other organ.
Rare diseases and conditions
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate may also increase for other reasons. Clinical evaluation of laboratory results. Sometimes this happens with high cholesterol, hyper- or hypothyroidism, or protein deficiency. In some people, an increase in ESR is a side effect of certain medications. For example, morphine, vitamin A supplements, blood pressure medications.
What is ESR
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is an indicator whose determination is included in a general blood test. This is a nonspecific laboratory screening test, changes in which can serve as an indirect sign of ongoing inflammatory or other pathological processes, such as malignant tumors and diffuse connective tissue diseases
FACTORS AFFECTING ESR INDICATOR
The ESR indicator varies depending on many physiological and pathological factors.
ESR values in women are slightly higher than in men .
Changes in the protein composition of the blood during pregnancy lead to an increase in ESR during this period.
A decrease in the content of erythrocytes (anemia) in the blood leads to an acceleration of ESR and, on the contrary , an increase in the content of erythrocytes in the blood slows down the sedimentation rate.
The values may fluctuate during the day ; the maximum level is observed during the daytime.
The main factor influencing the formation of “coin columns” during erythrocyte sedimentation is the protein composition of the blood plasma.
Acute-phase proteins, adsorbed on the surface of erythrocytes, reduce their charge and repulsion from each other, promote the formation of coin columns and accelerated sedimentation of erythrocytes.
An increase in acute phase proteins , for example, C-reactive protein, haptoglobin, alpha-1-antitrypsin, during acute inflammation leads to an increase in ESR.
In acute inflammatory and infectious processes, a change in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is observed 24 hours after an increase in temperature and an increase in the number of leukocytes.
In chronic inflammation, an increase in ESR is caused by an increase in the concentration of fibrinogen and immunoglobulins.
Some morphological variants of red blood cells can also affect ESR. Anisocytosis and spherocytosis inhibit red blood cell aggregation. Macrocytes have a charge corresponding to their mass and settle faster.
In anemia, drepanocytes influence the ESR so that even with inflammation, the ESR does not increase.
REASONS FOR CHANGES IN ESR INDICATORS
Normal ESR value
Depends on gender and age:
- in newborns, the ESR is very slow - about 2 mm, which is associated with a high hematocrit and low globulin content
- by 4 weeks the ESR accelerates slightly
- by 2 years it reaches 4-17 mm
- in adults and children over 10 years of age, ESR ranges from 2 to 10 mm for men and from 2 to 15 mm for women, which can be explained by different levels of androgenic steroids
- in older people, normal ESR levels range from 2 to 38 in men and from 2 to 53 in women.
Increase in ESR value
The most common reason for an increase in ESR is an increase in the plasma content of coarse proteins (fibrinogen, a- and g-globulins, paraproteins), as well as a decrease in albumin content. Coarse proteins have less negative charge. By adsorbing on negatively charged erythrocytes, they reduce their surface charge and promote the convergence of erythrocytes and their faster agglomeration.
- Infections, inflammatory diseases, tissue destruction.
- Other conditions leading to increased levels of fibrinogen and globulins in plasma, such as malignant tumors, paraproteinemia (for example, macroglobulinemia, multiple myeloma).
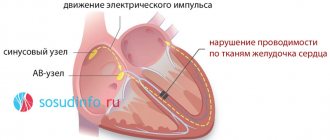
- Myocardial infarction.
- Pneumonia.
- Liver diseases - hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, cancer, etc., leading to severe dysproteinemia, immune inflammation and necrosis of liver tissue.
- Kidney diseases (especially those accompanied by nephrotic syndrome (hypoalbuminemia) and others).
- Collagenoses.
- Diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes).
- Anemia (ESR increases depending on severity), various injuries.
- Pregnancy.
- Poisoning by chemical agents.
- Elderly age.
- Intoxication.
- Injuries, bone fractures.
- Condition after shock, surgical interventions.
The most significant increase in ESR (up to 50–80 mm/h) is most often observed with:
- paraproteinemic hemoblastoses - myeloma, Waldenström's disease
- connective tissue diseases and systemic vasculitis - systemic lupus erythematosus, periarteritis nodosa, scleroderma, etc.
Decrease in ESR value
- blood thickening
- acidosis
- Polycythemia.
- Sickle cell anemia.
- Spherocytosis.
- Hypofibrinogenemia.
- Hyperbilirubinemia.
- Fasting, decreased muscle mass.
- Taking corticosteroids.
- Pregnancy (especially 1st and 2nd semester).
- Vegetarian diet.
- Overhydration.
- Myodystrophies.
- Severe symptoms of circulatory failure
The most common reason for a significant decrease in ESR is an increase in blood viscosity in diseases and syndromes accompanied by an increase in the number of red blood cells (erythremia, secondary erythrocytosis).
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, it should be noted that, despite its widespread use in clinical practice, the determination of ESR has limited diagnostic value. At the same time, most authoritative experts in the field of clinical medicine clearly point out that the diagnostic capabilities of this method are far from being fully used, and the main problem for the practice of domestic CDL lies in the methodological features of the test. The two methods presented, the Panchenkov method and the Westergren method for determining ESR, are very necessary methods, because with their help you can confirm various inflammations. But you need to be careful, because for research you need to strictly follow the rules of analysis using modern developments, which not only improve the quality of test results, but also significantly increase the safety of the patient and staff when taking blood samples. In the near future, it is planned to release multi-parameter smart cards, along with ESR, allowing to evaluate the anemia factor, aggregation factor, viscosity, hematocrit index and hemoglobin index.
Conclusions:
ESR is a nonspecific laboratory blood indicator; a change in ESR can serve as an indirect sign of the current inflammatory process and is relevant to this day;
When studying ESR using different methods, different results are obtained;
The ESR from venous blood is significantly higher than from capillary blood;
The Panchenkov method is technologically outdated and takes longer than other methods for determining ESR;
When performing ESR using the Panchenkov method, it is more difficult to comply with the sanitary and epidemiological regime.
Head of the Clinical Diagnostic Laboratory Tatyana Shah
What to do if ESR is elevated
If a person took a blood test during a routine medical examination and found an elevated ESR, but there were no other deviations from the norm, most likely this is not a big deal. To get rid of doubts, the doctor should prescribe The erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Still a helpful test when used judiciously retest after a few months.
But those who have other changes in their blood may need further testing. Which one will be decided by the specialist who noticed the increased ESR.