Petechiae are pinpoint hemorrhages that have a round shape and occur when small blood vessels under the skin rupture.
Red, purple and violet spots appear as a result of the release of red blood cells from the bloodstream into the interstitial space. Petechiae are like tiny bruises, reaching 1 or 2 mm in diameter. They are not palpable and do not stand out above the surface of the skin. Petechial hemorrhages can be single or multiple. Several flat spots appear at once, which do not change their color and do not disappear when pressed with a finger or stretched the skin.
Petechiae is a symptom of a number of pathologies, among which blood diseases, systemic autoimmune diseases, and some infections predominate.
In healthy people, rashes may appear due to excessive stress. Over time, the spots turn pale and disappear, leaving behind a slight pigmentation. The localization of petechiae is different: the skin of the arms, legs, torso, face, oral mucosa, conjunctiva of the eyes.
It could be syphilis
Small red dots clustered on the soles and palms of a small child may indicate a disease such as neonatal syphilis.
After redness, small blisters with serous fluid appear, which quickly fester and become cloudy. An enlargement of the spleen and liver is often observed. To confirm the diagnosis, serological tests are performed. A child who has contracted pseudofurunculosis will have to be treated with antibacterial drugs and immunotropic drugs, since this disease affects the hair follicles of the skin. It all starts with small redness, which then turns into small blisters with pus, and these, in turn, when penetrating into the deeper layers of the skin lead to the appearance of mini-abscesses.
What to do?
If minor hemorrhages are detected on the skin, it is necessary to determine the exact cause of the rash. It is worth noting that this problem can be successfully solved by a doctor with sufficient qualifications and practical experience. Since only a specialist can find out the cause of the appearance of petechiae and prescribe appropriate treatment.
For petechial rash
Treatment of petechial rashes on the skin directly depends on the cause that triggered the appearance of this rash. Let's look at a few common situations:
- If the petechiae were caused by injury, apply cold to the damaged area. Using a cold compress will help reduce swelling and pain. You need to apply cold (ice) for 10-15 minutes, then take a short break, after which we resume the procedure.
- In case of infection, specific medications are used (antibiotics, antiviral, antimycotic) depending on the type of pathogenic microorganism that caused the development of the disease. In addition, detoxification, sensitizing, immunostimulating and symptomatic therapies are often necessary.
- If the petechial rash is of allergic origin, antihistamines (Tavegil, Suprastin, Zyrtec) are prescribed.
- Systemic autoimmune pathology is mainly treated with glucocorticosteroid drugs. In most cases, to achieve remission, you have to undergo long therapeutic courses lasting several months.
- If a deficiency of essential vitamins is detected in the patient’s body, medications containing ascorbic acid, rutin, etc. are prescribed.
If there is dried blood under the skin
You can quite successfully deal with dried blood under the skin, which is an ordinary bruise, on your own at home. To do this, it is recommended to use medicinal ointments, creams, balms, “talks”, compresses, etc. Several of the most popular drugs that help cure subcutaneous hematomas (hemorrhages, bruises):
- Heparin ointment.
- Lavenum.
- Lyoton.
- Troxevasin.
- Badyaga.
- Gel Bruise Off.
Heparin-based ointments are considered one of the most effective means for treating hematomas. For example, Heparin ointment can be purchased for 60 rubles. At the same time, Lavenum will already cost about 200 rubles. Thanks to the presence of heparin in external agents, the rapid resorption of clotted blood under the skin that forms after hemorrhage is ensured. In addition to the absorbable effect, ointments also have analgesic, antiseptic and other effects.
However, there are some peculiarities in the use of external heparin-based products. The frequency of application per day should be at least five times. In addition, these drugs have a considerable number of contraindications, which significantly limits their use. However, a good advantage of Heparin ointment is its affordable price.
Troxevasin gel is widely used in the treatment of bruises. The active component troxerutin eliminates and reduces the fragility of small blood vessels by strengthening their walls. It also helps eliminate swelling and local inflammation. Successfully prevents the spread of hematoma (increase in volume). It is recommended to lubricate the affected areas with Troxevasin twice a day, which makes it convenient to use. Currently, the cost of the gel is approximately 180 rubles.
In the absence of any medications at home, you can use alternating compresses. In the first day after receiving a bruise, it is necessary to apply cold to the damaged area. Especially, it will be useful in the first 30 minutes after injury and will significantly reduce the size of the hematoma. Starting from the second or third day, we switch to a warm compress, which will facilitate faster resorption of the bruise. Do not forget that premature application of heat to the site of injury will only aggravate the matter and intensify the inflammatory process.
If a blood clot under the skin persists for a long time, you should contact a qualified medical specialist.
Preventive measures
The main method of prevention can be called avoiding the causes that can trigger the development of underlying diseases. To minimize the risk, you should follow these simple tips:
- play sports;
- avoid infection;
- observe the rules of hygiene;
- practice only protected sex;
- Avoid taking medications that can cause petechiae.
Of course, you cannot avoid all the factors that can trigger the problem, but these simple tips will help reduce the risk of developing many diseases.
Purpura and petechiae on the skin causes, treatment
Purpura is a purplish-red pathological formation that does not fade when pressed.
Those that are less than 1 cm in diameter are called petechiae, while larger ones are called ecchymoses. Patients often complain of “susceptibility to bruising”—a typical example of the complaint “and more.” " In most cases, they are not dangerous and are the result of a forgotten or unnoticed minor injury.
Causes of purpura and petechiae on the skin
Common reasons:
- injuries,
- senile (senile) purpura,
- liver diseases (especially alcoholic cirrhosis),
- increase in intravascular pressure, for example, with coughing, vomiting, sudden changes in barometric pressure (gravitational effects),
- medications such as steroids, warfarin, aspirin.
Possible reasons:
- vasculitis, such as Henoch-Schönlein purpura, connective tissue diseases,
- thrombocytopenia, for example idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, lesions of the hematopoietic system (for example, lymphoma, leukemia, cytostatics), aplastic anemia,
- renal failure,
- infective endocarditis.
Rare reasons:
- paraproteinemia, such as cryoglobulinemia,
- hereditary bleeding disorder, such as hemophilia, Christmas disease, von Willebrand disease,
- infections such as meningococcal septicemia, rocky mountain spotted fever,
- deficiency of vitamins C and K,
- disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome,
- congenital anomalies of the vascular wall, for example Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
comparison table
Diagnosis of purpura and petechiae on the skin
Examination methods
Basic: OAK, ESR/CRP, MHO (when taking warfarin).
Additional: liver function assessment, urea, creatinine and electrolytes, coagulogram, plasma protein electrophoresis.
Auxiliary: autoimmune tests, further examination in the hospital.
- OAK, ESR/CRP: a general blood test may reveal thrombocytopenia or signs of blood dyscrasia. ESR/CRP and leukocyte count may be increased in dyscrasias, connective tissue diseases and infectious diseases.
- Liver tests, blood tests for urea and electrolytes: if liver or kidney disease is suspected.
- MHO: when taking warfarin.
- Autoimmune tests: for connective tissue diseases as a possible cause of vasculitis.
- Coagulogram: to evaluate hemostatic function (eg, bleeding time, prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time).
- Plasma protein electrophoresis: for hypergammaglobulinemia, paraproteinemia and cryoglobulinemia.
- Further studies (in hospital): to identify the cause, for example, skin biopsy, to confirm the presence of vasculitis, bone marrow biopsy, if there is an infiltrate.
Multiple bruises of varying duration on the legs of children, without other abnormalities and stigmas of blood clotting disorders, are most likely not pathological.
Senile purpura is easily diagnosed based on examination and history. Reassuring the patient is more important than conducting additional research.
Single petechiae on or around a child's eyelids may occur with severe coughing or vomiting. If purpura occurs for these reasons, it is worth telling parents about it, but emphasize that the appearance of an identical rash in other places requires close attention.
Localization of purpura can help in making a diagnosis. The appearance of purpura on the legs is characteristic of thrombocytopathy, paraproteinemia, Henoch-Schönlein purpura or meningococcal septicemia, lesions on the fingers and toes are characteristic of vasculitis, senile and steroid purpura usually occurs on the back and arms.
Purpura with vasculitis, as a rule, rises above the skin and is palpable.
Remember that in children, a rash due to meningococcal septicemia may appear even before the general deterioration of health. If this diagnosis is suspected, penicillin should be administered parenterally and the patient should be hospitalized immediately.
The absence of a family history of bleeding disorders does not exclude their congenital nature. These diseases can occur spontaneously.
Pale patients with purpura require special attention: there is a high probability of bone marrow damage. There is an urgent need to perform OAK or hospitalize the patient.
Always examine the entire surface of the body in a child with bruises, not forgetting the anogenital area. Be aware of the possibility of violent injury.
Never prescribe intramuscular injections for severe bleeding disorders.
Spots on the face are a symptom of dermatoses
The child's body overreacts to chemicals, insect bites, and other external factors. One hot spot or blister against the background of reddened skin is a local reaction to the poison and saliva of mosquitoes, bees, wasps and fleas. If parents notice red spots on the lips and around the mouth in a child, then the list of the most likely causes should be sought among allergic, viral and fungal diseases, and vitamin deficiencies.
Allergies are the most likely cause of spotty rashes and itchy blisters.
The name “dermatoses” is given to a group of diseases. The cause of negative processes in the dermis is usually external and internal factors. The first group includes infections, various injuries and physical effects. The inflammatory process occurs in response to the release of toxins by viruses, microbes, as well as substances in the saliva of stinging and biting animals.
Types of dermatoses
- allergic - contact dermatitis, urticaria, toxicerma, atopic dermatitis, reactions to animal bites;
- itchy – eczema, neurodermatitis;
- bullous or blistering - herpes, impetigo, blistering dermatitis;
- skin pathologies caused by overexertion and strong emotions.
If a child has red, rough spots on his face, then you should pay attention to a violation of metabolic processes in his body and a decrease in immunity. Endogenous factors in the appearance of red spots and nodules - pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, nervous, cardiovascular, hematopoietic systems
Can complications arise?
The formation of subcutaneous hemorrhages of the petechial type does not provoke the appearance of any complications. As a rule, such manifestations disappear without any trace and do not even leave scars.
But if a petechial rash occurs as a result of an underlying pathology, then certain complications may arise, for example:
- damage to internal organs;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- infections begin to develop in other parts of the body.
Peculiarities
Vasculitis is considered one of the most common types of pathology. The clinical picture of this defect is characterized by the appearance of erythematous hemorrhagic spots rising above the level of the epithelium. The appearance of small blisters and nodes is observed, instead of which, over time, ulcers and erosions with serous secretion form. When dry, the new growths become covered with crusts.
The rash spreads mainly along the legs, especially in the joint area. In some cases, the stains are localized on the body. In this case, the general condition of the victim, as a rule, does not change. You can visually identify erythematous hemorrhagic spots from the photo
It is very important to pay attention to the external manifestations of the disease in time and begin treatment immediately. Typically, this pathology is chronic and recurs regularly.
Depending on the cause that provoked the appearance of the anomaly, its symptoms can vary significantly. With meningitis, the rash is usually star-shaped with areas of necrosis in the center. When a tick bites, the rashes are profuse and accompanied by fever. You can visually determine the pathology yourself by looking at photos of hemorrhagic spots.
When the pathology worsens, blood may appear in damaged areas. And during moments of remission, the skin can clear up.
If star-shaped rashes occur, the patient must be immediately admitted to the hospital. After all, spots of this kind indicate the generalization of the phenomenon.
Diagnostics
The examination is carried out under the supervision of a hematologist. A sample list of events is:
- Patient interview. All possible complaints must be identified. A person’s task is to talk about his own well-being in as much detail as possible. The doctor draws up a complete clinical picture, analyzes the symptomatic complex and puts forward hypotheses regarding the disease. This is one of the most valuable diagnostic methods in such a case.
- Anamnesis collection. Past diseases, current pathologies and other important points, including family history, habits, and lifestyle. It makes sense to evaluate all factors to identify the likely origin of the pathological process.
- General blood analysis. The picture can be very different. Depends on the type of disorder, primary diagnosis.
- Coagulogram. An informative technique, the essence of which is to study the rate of blood clotting.
- Bone marrow sampling and biopsy. Used as a last resort. If other methods did not provide a complete answer and an accurate picture of what was happening.
There are not so many methods, however, not all diagnostic methods are named. Depending on the expected primary diagnosis, the list is expanded. It is possible to involve third-party specialists other than a hematologist.
Multiple red dots in viral and autoimmune diseases
Some diseases are accompanied by multiple skin rashes. Small red dots may appear in adults and children with pathologies such as:
Allergic dermatitis is the body's reaction to allergens. Most often, the rash affects the skin on the head, face, arms and chest. Patients experience severe itching, swelling and peeling of the skin can be observed.
Manifestations of allergic dermatitis
Follicular keratosis. It often occurs in boys and girls during puberty, as well as in pregnant women. Red rashes form in the area of the hair follicles. This phenomenon is popularly called “crow’s feet.” Another name for the disease is lichen pilaris. Most often, the rash is localized on the stomach, back and arms, less often on the face. Keratosis pilaris is not dangerous to others and is considered more as a cosmetic defect. The pathogenesis of the disease is not fully understood. Doctors suggest that the predisposition to keratosis is inherited.
Red dots on the skin due to keratosis pilaris
Rosacea. Small red dots cover the face, neck and chest area. Over time, the rash may increase in size. The disease is accompanied by hyperemia, peeling and swelling of the skin in the affected areas.
Rosacea on the face
Rubella. This viral disease appears as a red, dotted rash. Sometimes there is muscle weakness, headaches and slight itching. The rashes are most often localized on the back, arms, legs, and buttocks. Rubella is transmitted by airborne droplets, the incubation period lasts 10-20 days.
Rubella rash
Scarlet fever. The causative agent of the disease is group A streptococcus. Scarlet fever most often occurs in children, the incubation period is 5 days. The disease is characterized by an acute onset. Small red dots in the plural appear along with general malaise and headache. It is rare to observe the formation of vesicles with serous fluid. After 2-3 days, symptoms may completely disappear.
Scarlet fever rash
Chicken pox. A viral disease, the main symptoms of which are a sharp increase in temperature and the formation of small red blisters filled with clear liquid. As the pathological process develops, the rashes spread throughout the body and increase in size to 2-5 mm. Within 1-2 weeks, the blisters burst and become crusty.
Chickenpox rash
Lupus erythematosus. The rash is localized on the cheekbones and bridge of the nose. It has a specific form called “butterfly syndrome”. The rash also spreads to the back, chest and arms. There are several types of rash for lupus erythematosus, including edematous, with signs of red pimples.
Facial skin lesions due to lupus erythematosus
Dermatomyositis is a systemic disease that affects the skin and muscles. One of the first signs of pathology is an erythematous rash from red to purple. Clusters of dots can be observed on the cheeks, upper eyelids, décolleté and in the joint area.
Symptoms of dermatomyositis
Red dots on the skin can be a sign of serious pathologies such as leukemia or meningitis. Therefore, if a rash of unknown origin occurs, you need to visit a therapist or other specialist.
Petechiae on the skin and mucous membranes: photos, causes, treatment
Petechiae are tiny, round spots that appear on the skin, mucous membrane, or serous membrane. They occur as a result of bleeding under the skin.
Typically, petechiae appear on the surface of the skin, eyelids, or oral mucosa.
Petechiae usually look like a rash. The appearance of petechiae can be caused by many different reasons. It is advisable to make an appointment with a doctor if petechiae appear.
Petechiae occur when tiny blood vessels (capillaries) burst. When this happens, blood leaks under the skin.
Some of the reasons that can lead to petechiae include:
- local trauma or trauma in which the skin is damaged;
- sunburn;
- allergic reactions to insect bites;
- various autoimmune diseases;
- viral and bacterial infections;
- decreased level of platelets in the blood;
- medical treatments for cancer, such as radiation or chemotherapy;
- leukemia or bone marrow cancer, which leads to a reduction in platelets;
- after severe vomiting or coughing - especially in newborns;
- strenuous activity, such as heavy lifting or childbirth;
- sepsis;
- scurvy;
- vasculitis;
- viral fevers such as dengue, ebola and yellow fever can interfere with blood clotting, causing bleeding under the skin.
The use of certain medications can also cause petechiae. Drugs that can cause petechiae as a side effect:
- antibiotics;
- antidepressants;
- contraceptives;
- blood thinners;
- drugs to normalize heart rhythm;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs);
- sedatives.
Almost 50% of newborns develop physiological erythema in the first days of life. In this case, the baby develops red spots of varying sizes and irregular shapes on the face and other parts of the body. This condition is caused by the expansion of skin capillaries and is one of the mechanisms of adaptation to life outside the maternal body.
Physiological erythema does not require treatment; in most cases it goes away on its own within 10-14 days. Sometimes physiological erythema can become toxic. If the erythema does not go away for more than a month, then the baby may be prescribed antihistamines, Bifidobacterin to strengthen the intestinal microflora, vitamins B, E and C. The rash can be treated with brilliant green, a weak solution of potassium permanganate or zinc oxide.
Pemphigus of newborns is a serious disease. The causative agent of this disease is most often Staphylococcus aureus, but it can also be streptococcus and filterable virus. An infant can become infected from unsterile instruments or medical personnel. Exfoliative dermatitis begins 3-4 days after birth. When symptoms of this disease appear, the newborn is immediately isolated and treatment is started.
Redness and skin rash, as a rule, occur against the background of allergization of the body or infectious diseases. Atopic dermatitis, eczema, measles - the list of diseases and conditions that cause red spots on a child’s face includes several dozen names. The doctor prescribes treatment only after determining the underlying cause. In various situations, antihistamines, disinfectant solutions and soothing ointments are used.
Red spots on the face are a symptom of meningitis, scarlet fever and impetigo (bacterial infections).
Causes of red spots under the eyes of a child:
- allergies to foods in the diet, pollen, secretions of household mites;
- focus of chronic infection in the body;
- helminthic infestation;
- adenoids.
Redness of the eyes occurs with allergic conjunctivitis. A red spot may appear on the eyelid due to a reaction to the use of eye or nasal drops, even with antihistamine components in the composition. Allergies or hypersensitivity manifest themselves both in relation to medications and when consuming certain foods, the action of pollen and the juice of certain plants.
Redness and enlargement of the area around the eyes or swollen lips are a symptom of Quincke's edema.
The allergic component is the leading one in the development of dermatoses. This is a group of diseases dangerous for the development of angioedema, anaphylaxis, and asphyxia. Scratching itchy spots often leads to bacterial infection.
Petechiae in a child
The disease in a baby is represented by small, round subcutaneous spots of blood that occur after the rupture of blood vessels, as well as blood leakage under the very surface of the skin or mucous membranes. The subcutaneous layer of petechiae affects a point, and their diameter reaches up to 1-2 mm. A feature of these formations is that they cover a fairly large area of the skin and mucous membrane. The rashes appear as flat spots and do not change color even when pressed. Petechiae appear on all kinds of skin areas, including the oral cavity.
Causes of petechiae in children
One of the main causes of the disease in children is trauma, as well as damage to the capillaries, after which they rupture, as well as blood leakage, which spreads into the subcutaneous surface.
Petechiae in children occur during play, and the causes are accidental falls. The disease can occur with septicemia - this is an infection of the blood due to the ingress of pathogenic bacteria. Septicemia occurs against the background of any disease. Young children often suffer, because their immunity is not sufficiently developed to contain the pathological process.
Petechiae on the palate appear due to injury when eating solid food. Poor care of the baby and insufficient nutrition can provoke childhood scurvy, which is characterized by scattered pinpoint hemorrhage of the skin and oral mucosa. The cause of hemorrhage in the skin in children is a lack of vitamin K.
Petechiae in children and their symptoms: high temperature, difficulty breathing, rapid pulse, development of pulmonary failure and fever. Toxic substances produced by microbes injure blood vessels and cause the formation of a rash, which is called hemorrhagic. With septicemia, the rash grows during the day. The severe course is accompanied by fainting and delirium. The development of septicemia occurs very quickly and its timely diagnosis, as well as treatment, are necessary conditions for saving the child’s life.
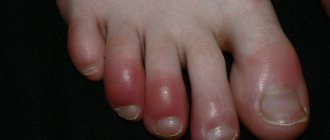
photo of petechiae on legsWhen should you contact a specialist?
In any case, immediately after the appearance of the rash, you need to consult a specialist, because this rash can signal the development of quite serious diseases. The doctor will examine the mucous membranes and skin, after which he will be able to tell you what causes the problem and whether they can be classified as serious.
Along with the formation of petechiae, some other symptoms may appear that will indicate a serious condition of the person or child. These include the following:
- loss of consciousness or confusion;
- very high body temperature rises;
- bleeding begins;
- I constantly have a severe headache.
If any of these symptoms are present along with the rash, then you should consult a doctor immediately, because this may be a signal of the development of a very serious pathology.
Causes of petechiae on the skin with photos
There are several generating factors in terms of the formation of petechiae. The main reasons for the formation will be discussed below.
- Capillary traumatic phenomena and damage. As a result of this lesion, rupture of bodies and particles is observed, blood flows under the surface of the skin. In children, due to the weakness and underdevelopment of the body, the phenomenon can manifest itself during a fall, the same applies to people with fragile skin. In adults, a more severe blow will be required.
- A deficiency of vitamin K leads to the occurrence of these phenomena. The fact is that failure to comply with the subtleties of caring for the baby and lack of healthy nutrition can cause childhood scurvy, represented by scattered skin hemorrhage and damage to the oral mucosa.
- If a child or adult suffers significantly from coughing attacks and similar phenomena, formations can manifest themselves in the mucous membranes of the throat, as well as on the face.
- One of the side effects responsible for the occurrence of affected areas may be the use of acetylsalicylic acid, used to eliminate respiratory and viral diseases, including influenza.
- Often, a rash appears as a result of treatment for varicose veins, so therapy is aimed not only at eliminating the consequences in the form of unsightly spots, but also at the use of drugs that thin the blood.
- If the patient experiences frequent bouts of vomiting, the rash forms in the upper chest area and can also be observed on the face, neck and other parts of the body.
- Regular or constant wearing of tight clothing may lead to the formation of petechiae on the skin anywhere. The situation can be eliminated by eliminating the object in close contact with the skin.
There are quite a lot of reasons for the formation of phenomena, so the therapeutic complex consists of combating not only the consequences, but also the primary sources of the disease.
Pathological causes of the formation of the disease
There are situations when petechiae on the skin (photos can be seen in the article) appear as separate symptoms against the background of other manifestations and diseases. In this case, efforts will need to be made not only to eliminate the consequences, but also to remove the causes of the disease.
- Thrombocytopenia is a disease caused by impaired blood clotting. If the skin suffers minor damage, you can become a victim of serious bleeding. The disease occurs with constant complications in soft tissue areas.
- Lupus erythematosus is a disease accompanied by a serious blood disorder. During such failures, the DNA structure changes through antibodies. In this situation, petechiae can act as signs of a serious autoimmune process.
- Diseases that promote the destruction of connective tissue, which can provoke sudden changes in temperature. Due to this phenomenon, capillaries burst, and a rash may appear on the body, face, and limbs.
- Abscess and sepsis are ailments represented by an infected blood process, which can lead to the formation of a rash. In this case, therapy can be prescribed by several specialists at the same time.
- Gonococci and staphylococci are diseases that are responsible for processes affecting blood circulation and occur against the background of diseases in which a rash forms in the extremities. In the second case, a purulent rash appears as a sign of the disease; sometimes it can degenerate into gangrene (in the absence of timely qualified assistance from doctors).
Timely receipt of help from competent doctors in case of pathological processes guarantees a quick recovery.
Symptoms
Soldatenkov Ilya Vitalievich, general practitioner
Petechiae are pinpoint hemorrhages that have a round shape and occur when small blood vessels under the skin rupture. Red, purple and violet spots appear as a result of the release of red blood cells from the bloodstream into the interstitial space.
Petechiae are like tiny bruises, reaching 1 or 2 mm in diameter. They are not palpable and do not stand out above the surface of the skin. Petechial hemorrhages can be single or multiple.
Several flat spots appear at once, which do not change their color and do not disappear when pressed with a finger or stretched the skin.
In healthy people, rashes may appear due to excessive stress. Over time, the spots turn pale and disappear, leaving behind a slight pigmentation. The localization of petechiae is different: the skin of the arms, legs, torso, face, oral mucosa, conjunctiva of the eyes.
Etiology
Before you begin treatment for petechiae, it is necessary to identify and eliminate the causes of their appearance!
The appearance of spots is the only sign of petechiae. However, since they are often a sign of an underlying condition, the patient may experience other symptoms along with the petechial rash:
- hematomas;
- bleeding or bruising;
- bleeding gums;
- hemorrhage into the joint cavity (hemarthrosis);
- unusually heavy menstrual periods (menorrhagia);
- nose bleed.
The child's body overreacts to chemicals, insect bites, and other external factors. One hot spot or blister against a background of reddened skin is a local reaction to the venom and saliva of mosquitoes, bees, wasps and fleas. If parents notice red spots on the lips and around the mouth in a child, then the list of the most likely causes should be sought among allergic, viral and fungal diseases, and vitamin deficiencies.
The name “dermatoses” is given to a group of diseases. The cause of negative processes in the dermis is usually external and internal factors. The first group includes infections, various injuries and physical effects. The inflammatory process occurs in response to the release of toxins by viruses, microbes, as well as substances in the saliva of stinging and biting animals.
Types of dermatoses
- allergic - contact dermatitis, urticaria, toxicerma, atopic dermatitis, reactions to animal bites;
- itchy - eczema, neurodermatitis;
- bullous or blistering - herpes, impetigo, blistering dermatitis;
- skin pathologies caused by overexertion and strong emotions.
If a child has red, rough spots on his face, then you should pay attention to a violation of metabolic processes in his body and a decrease in immunity. Endogenous factors in the appearance of red spots and nodules - pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, nervous, cardiovascular, hematopoietic systems
Mechanisms of development of the disorder
The development of the disorder is based on a whole group of factors. As a rule, they do not occur in a single system, at least this is not observed so often.
If we talk about pathogenetic aspects in more detail, we can name the following typical mechanisms:
Autoimmune or infectious inflammatory processes
Affecting small vessels throughout the body. As a rule, these are severe disorders such as vasculitis, less dangerous, for example, thrombocytopenic purpura.
As part of these anomalies, increased vascular fragility occurs. A slight physical impact on the tissue is enough to provoke destruction and bleeding under the skin.
Spontaneous outpourings are also possible, for no apparent reason. This is most typical for severe disorders at advanced stages.
Blood clotting problems
Insufficient synthesis of specialized substances responsible for platelet aggregation also leads to their inferiority.
This is how hemophilia can manifest itself, and in the same way malignant diseases of the hematological profile make themselves known (we are not talking about cancer processes). All of these conditions require mandatory treatment in a hospital.
Disturbances in the formation or functional activity of platelets and blood cells
Thrombocytopathies of various types. Pathognomonic (characteristic) signs within the framework of the mechanism are a decrease in the number of these structures or their normal number with a significant drop in functional activity. As a result, the blood becomes too liquid and comes out through the walls of the capillaries, accumulating under the skin.
One way or another, the diseases in question pose a danger to health and life; petechiae on the skin themselves do not threaten anything; moreover, they are informative from the point of view of early diagnosis.
Spontaneous factors
Which do not need to be eliminated by any separate methods. For example, the use of certain medications: thrombolytics, antiplatelet agents, hormonal drugs, oral contraceptives, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, glucocorticoids and many others. Up to and including antibiotics if used uncontrolled.
Hemorrhages on the skin develop as a result of insufficient coagulation and destruction of blood vessels (as a result of their abnormal fragility).
Such disorders in the early stages may seem not dangerous, but in fact there are a lot of diseases manifested by a petechial rash that can affect health or take life: from hemophilia to cancer processes.
Why does a petechial rash appear - causes of petechiae
Localization sites are divided into skin and mucous membranes. In infectious diseases, petechiae can appear on the upper palate, tonsils, and inner surfaces of the cheeks. On the legs, petechial rash is often associated with diseases of the vascular wall and systemic pathologies of connective tissue. Elements can appear on the abdomen with measles, scarlet fever and cirrhosis of the liver.
The main cause of petechiae is small, pinpoint ruptures of capillaries, around which a microscopic hematoma forms. Why does a petechial rash appear in children and adults with various pathologies? Let's look at this issue in more detail.
So, the main provocative factor is physical traumatic exposure. This can be a blow, bruise, maceration, non-penetrating injections with blunt objects.
Other risk factors include:
- severe coughing attacks - the appearance of elements on the face, throat, on the wings of the nose;
- use of acetylsalicylic acid during influenza virus infection - widespread multi-point rash throughout the body;
- the use of drugs to treat varicose veins - blood clotting worsens;
- disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome - most often occurs with cold viral diseases;
- vomiting due to intestinal infections - rashes may occur on the face, chest, and in the area of the front wall of the neck.
Sometimes petechiae appear after wearing incorrectly sized underwear, golf stockings, or socks. In this case, the elements appear in the areas where pressure was applied.
Other causes of petechial rash that require seeing a doctor:
- thrombocytopenia or poor blood clotting (characterized by prolonged and heavy bleeding, even with minor cuts and abrasions of the skin);
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- rheumatoid lesions of joints and connective tissue (body temperature rises, pain occurs in the knee and elbow joints);
- endocarditis of infectious origin (spontaneous pressing pain in the heart and behind the sternum may occur, accompanied by deterioration of the condition, increased body temperature);
- blood poisoning - sepsis against the background of long-term inflammatory diseases (refers to serious conditions and requires immediate hospitalization);
- purpura and periarteritis nodosa, septicemia and typhoid fever.
Consequences
The main complications, especially without treatment, are:
- Severe massive bleeding.
- Acute shock conditions. For example, when developing sepsis, which quickly takes a person’s life.
- Neurological deficit. Against the background of infections, autoimmune diagnoses.
- Heart problems. IHD, chronic cardiac failure, severe dysfunction.
- Disability. As a result of damage to nerve tissue.
- Death.
Petechiae (intradermal hemorrhages) in themselves are not diseases; they are not an independent diagnosis. Only a symptom, but extremely informative.
It makes sense to undergo a full comprehensive diagnosis as quickly as possible; it is important to urgently identify the probable cause. The prognosis, and possibly the patient’s life, depends on this.
Causes not related to diseases
Petechiae are not always the result of the course of diseases. These hemorrhages also occur as a result of the influence of a number of natural, safe factors.
- Injuries. Mechanical tissue damage. Mainly bruises. In fractures, petechiae are extremely rare due to the large volume of bleeding. Restoration is carried out immediately, in which case there is a chance to reduce cosmetic defects to a minimum.
- Wearing tight clothes. Compression of the skin and mechanical trauma affect it. The same goes for uncomfortable shoes.
- Compression of tissues with a tourniquet. When carrying out routine diagnostic or therapeutic measures. Intravenous infusion of drugs.
- Physical overexertion. Including labor. Coughing, playing sports, crying, vomiting and other similar phenomena also cause subcutaneous hemorrhages.
- Natural skin aging processes.
The reasons are assessed separately. It makes sense to first exclude pathological factors, only then look for natural ones. This is a matter of timely diagnosis and human safety.
Forecast
Generally favorable, unless we are talking about serious illnesses.
Autoimmune processes such as systemic vasculitis, pathologies of hematopoietic structures, sepsis, and some forms of infectious disorders pose a great threat to health and life. They are deadly.
Attention:
It is impossible to provide information on prospects without analyzing a specific situation, since there are many diseases that cause hemorrhagic rash.
It is better to address the question to the treating specialist. He will be able to say anything specific only after the diagnosis has been carried out.
Types of rash
1. Bubble
, which is filled with liquid (diameter - 0.5 cm). Most often, this indicates diseases such as: herpes, eczema, allergic dermatitis, chicken pox, shingles.
2. Pustule
, inside of which there is purulent contents. This is how folliculitis, furunculosis, impetigo, pyoderma, and acne manifest themselves.
3. Blisters
They usually occur as an allergic reaction and go away after some time. They appear as a reaction to an insect bite, a nettle burn, and occur with urticaria and toxicoderma.
4. Stains
- This is redness or discoloration of certain areas of the skin. They occur with syphilitic roseola, dermatitis, leukoderma, vitiligo, typhoid and typhus. Moles, freckles and tans are pigmented spots.
5. Erythema
- This is a sharply limited area of red skin that is slightly raised. Occurs in people with hypersensitivity to certain foods (for example, strawberries, eggs), medications, after sunbathing, and with erysipelas. In the case of an infectious disease or rheumatism, exudative or erythema nodosum is possible.
6. Purpura
– hemorrhages on the skin of various sizes (small, pinpoint or large bruises). This is possible with hemophilia (when blood clotting is impaired), Werlhof's disease, capillary toxicosis, leukemia, scurvy.
7. Nodule
– this is a change in the relief, color and consistency of the skin. The dimensions of the nodule are 1-3 mm – 1-3 cm in diameter. This could be psoriasis, lichen planus, warts, atopic dermatitis, papilloma, eczema.
8. Knot
differs from the nodule in size. It can reach a diameter of up to 10 cm and be located deep in the skin. When the nodule disappears, it often leaves behind a scar.