Causes of leg vein thrombosis
Thrombosis (vein blockage) is the process of blood clots forming inside the veins, which attach to their walls and interfere with normal blood flow. Depending on the location, thrombosis of superficial and deep veins is distinguished. Interestingly, the process of blood clot formation is not initially pathological: a blood clot should form in response to vessel injury, preventing the development of bleeding. In such a situation, the body intensively synthesizes platelets and fibrin, “sealing” the damage. However, in some cases, this mechanism is triggered even if the vein wall has not been injured. What situations are we talking about?
- Hypercoagulation.
Expert opinionViolation of the drinking regime, poor nutrition, metabolic failures, elevated body temperature, the presence of cancer and chronic inflammatory processes in a person, taking oral contraceptives and some other medications - all this leads to the blood coagulation system over the anticoagulation system, increased blood viscosity and the possible formation of blood clots.
Vascular surgeon, phlebologist
Osipova Ekaterina Yakovlevna
- Narrowing of the lumen of the arteries. The development of this problem can be caused by the presence of atherosclerotic plaques in a person.
- Heart diseases. Atrial fibrillation, heart failure and other cardiac pathologies can negatively affect the condition of blood vessels and the composition of the blood.
- Inflammatory processes and injuries to the walls of blood vessels. The walls of the veins can become inflamed as a result of a violation of their integrity due to frequent injections, catheter installation, bone fractures, bruises and burns, and surgical interventions.
- Hypercoagulation. If a person remains in a sitting/lying position for a long time, there is a risk of developing blood clots in the veins of the legs.
- Overweight. Excessive body weight increases the load on the lower extremities, leading to poor circulation and creating preconditions for the development of thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities.
why are blood vessels blocked?
Causes of blood clots
Several factors play a role in the mechanism of thrombosis, consideration of which is necessary to understand the essence of the process and determine the principles of treatment of thrombosis. These factors are:
- increased blood clotting;
- slowing down the speed of venous blood flow;
- damage to the walls of blood vessels.
High blood clotting can be caused by hereditary and age-related factors, and can also be a companion to certain diseases (autoimmune processes, thrombophilia, acute respiratory infections) and physiological conditions of the body (pregnancy). Increased clotting is also caused by low physical activity, taking oral contraceptives and diuretics.
Disruption of venous blood flow is observed with varicose veins, narrowing of their lumen due to the development of inflammatory processes, as well as with various types of cardiac pathology (heart failure, arrhythmias). A sedentary lifestyle and sedentary work also contribute to a decrease in venous outflow.
Violation of the integrity of the inner lining of blood vessels occurs due to mechanical injuries, including surgical, infectious and inflammatory lesions. Damage to the vascular intima is not a prerequisite for the formation of a blood clot. The first two reasons are often sufficient for this. However, it significantly accelerates the process of thrombus formation.
Blockage (thrombosis) of veins in the legs: symptoms
The initial stage of the pathological process is usually asymptomatic, so many patients seek medical help when the disease reaches a late stage. The intensity of symptoms depends on a number of factors: the size of the blood clot, the number of thrombosed veins, lifestyle and the general health of the person.
Blocked veins in the legs: symptoms
The presence of thrombosis can be suspected by the following signs:
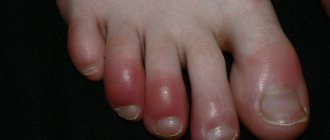
- Swelling and swelling of the lower extremities.
- Swelling of veins.
- The appearance of a pronounced vascular network and “stars”.
- The appearance of small pinpoint hemorrhages on the affected leg - petechial rash.
- A feeling of fullness and heaviness in the legs, increasing in the evening or after a long stay in an upright position. Unpleasant sensations are reduced if a person lies on his back and raises his legs above the level of his heart.
- The lower extremities acquire a bluish tint, and sometimes there is a feeling of numbness and tingling. The affected leg may also appear pale and cold to the touch.
- If thrombosis is accompanied by an inflammatory process and a person develops thrombophlebitis, an increase in local and general body temperature is possible.
What are the symptoms of vein blockage?
Both thrombophlebitis and deep vein thrombosis are characterized by similar symptoms, which include:
- Redness of the affected limb;
- Pain in the area where the veins are blocked (with thrombosis, the pain may be mild);
- Swelling of the leg;
- Local increase in skin temperature.
Deep vein thrombosis in some cases can be completely asymptomatic.
Diagnosis of these conditions is made using Dopplerography of the vessels of the legs. This method is the gold standard in the study of venous pathology.
Blockage (thrombosis) of veins in the legs: treatment
blockage of blood vessels
Therapy should begin with a consultation with a phlebologist and an examination. Diagnosis usually requires a visual examination, checking for pulsation, assessing the color, temperature of the limbs and their diameter. To detect the number of blood clots and assess their size, it is necessary to perform duplex ultrasound of blood vessels or, in some cases, perform MSCT with the introduction of a contrast agent.
!
To assess blood composition and the tendency to thrombus formation, a general blood test and coagulogram are prescribed.
Based on the data obtained, the doctor decides how to treat venous thrombosis in this particular case.
Treatment is designed to solve the following problems:
- Reduce blood viscosity.
- A safe way to eliminate a blood clot.
- If there is an inflammatory process, relieve inflammation.
For these purposes, medical and surgical methods are used:
- Anticoagulants. These drugs thin the blood and prevent the formation of new blood clots. They must be taken according to an individually developed regimen under the constant supervision of a physician, since an incorrectly selected dosage can lead to the development of bleeding. Some anticoagulants (such as warfarin) require regular INR blood tests.
- Thrombolytics. The action of drugs in this group is aimed at lysis (dissolution) of the blood clot and restoration of normal blood flow. It should be taken into account that treatment with thrombolytics has contraindications. They should not be taken after recent operations on internal organs, with severe arterial hypertension, the risk of internal bleeding, or in the presence of vascular diseases of the brain.
Blocked veins in the legs, treatment
- Venotonics. Drugs in this group are aimed at increasing vascular tone, eliminating congestion, and relieving swelling. They can be prescribed both for oral administration (in the form of tablets) and for external use (in the form of creams, gels and ointments). Particularly popular are products based on rutin and plant extracts (for example, horse chestnut).
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These drugs are prescribed if thrombosis is accompanied by an inflammatory process and the patient develops thrombophlebitis.
- Surgical intervention.
Expert opinion
In modern medical practice, surgical treatment of thrombosis (thrombectomy) is resorted to if vein thrombosis cannot be eliminated by other methods. The operation should be performed under the guidance of experienced vascular surgeons. It is also possible to install a vena cava filter into the vein - a mesh trap that blocks the penetration of blood clots into the lungs.
Vascular surgeon, phlebologist
Osipova Ekaterina Yakovlevna
vein blockage
Thrombosis of the lower extremities - symptoms
An additional danger of thrombosis is that the disease may not manifest itself for a long time. Symptoms appear when the blood clot reaches a large size and spreads up the vessel. Then the patient begins to complain of pain, which decreases at rest and increases with physical activity. Then, due to the deterioration of blood outflow, swelling is added to the pain. The skin on the leg turns pale (to the point of cyanosis) and “tightens”, acquiring a glossy shine.
To diagnose the localization of a blood clot, an ultrasound of the veins is performed, and in particularly difficult cases, angiography, an X-ray examination with the introduction of a contrast agent into the vessels.
How to treat blockage (thrombosis) of veins in the legs at home?
You should not completely replace medications prescribed by your doctor with the use of traditional recipes. “Grandmother’s” advice can act as an additional measure, but treatment of vein thrombosis should in no case be based solely on them.
blocked veins in the legs
To treat thrombosis at home, decoctions and infusions of herbs are used, which are taken orally and applied externally to the affected areas of the legs - as applications. Herbal medicines can also be used to prepare homemade ointments. What plants are suitable for fighting blood clots?
- Horse chestnut. This is one of the most famous traditional medicines that prevents the formation of blood clots. To prepare the tincture, wash a glass of chestnuts, chop them and pour 800 ml of vodka, then put them away in a dark place for 3 weeks. When the infusion is ready, it is used for oral administration. You can also prepare an ointment from chestnut cores. To do this, the horse chestnut fruits are peeled from the brown shell, the resulting kernels are dried in the oven, crushed and mixed with butter. The resulting ointment is stored in the refrigerator and used to rub the feet.
- Lemon and garlic. These products help thin the blood, so they are actively used in folk medicine to combat blood clots. To prepare the tincture, take a medium head of garlic and a large lemon, grind it in a blender or pass it through a meat grinder. The resulting pulp is placed in a jar, filled with warm water (not boiling water) and left for several days, after which a few sips are taken before each meal.
- Cranberries or blueberries. The berries are crushed in a blender or passed through a meat grinder, mixed with honey to taste and taken a tablespoon several times a day.
- Vinegar. For 50-60 ml of apple or grape cider vinegar, take 4 tablespoons of honey, mix until smooth, lubricate the legs with the resulting mixture, wrap with cling film and hold for about 15-20 minutes.
!
Thrombosis is a serious pathology and traditional medicine alone will not be enough to combat it. So if you decide to undergo treatment at home, do not forget to consult your doctor first.
Preventing vein blockages
It is much easier to prevent such a complication of varicose veins as blockage of veins than to cure it. Today, treatment of varicose veins is a matter of one day. There is no long recovery, pain or other problems after vein removal using modern technologies.
An appointment with a phlebologist and the choice of treatment tactics such as Endovasal Laser Ablation, Radiofrequency coagulation, Miniflebectomy or Sclerotherapy will allow you to forget not only about varicose veins and its manifestations, but also about terrible complications.
What is the danger of blockage (thrombosis) of the veins in the legs if it is not treated?
Diagnosis of leg vein thrombosis and timely initiation of treatment are extremely important not only for maintaining health, but also for the life of the patient. After all, if a blood clot formed in a vein completely blocks its lumen, this can lead to an embolism. In turn, this condition can cause insufficient blood flow to the organs. For example, a blood clot that breaks off and blocks a pulmonary artery can lead to the development of a pulmonary embolism, a life-threatening condition that is often fatal.
What other complications should you be aware of in order to start treatment of thrombosis on time?
blockage of blood vessels
- If left untreated, chronic venous insufficiency may develop.
- The situation may be aggravated by the addition of inflammation to thrombosis - in this case, the patient develops thrombophlebitis.
- We should not exclude the possibility of developing decompensation of varicose veins - a condition that occurs when the deep veins in the legs are completely blocked. As a result, a person develops trophic ulcers - long-healing wounds that cause pain and serious discomfort.
blood vessels, disease
- The presence of blood clots negatively affects the appearance of the lower extremities, causing psychological discomfort to patients (especially women). Swelling and bluish tint of the legs can interfere with your personal life and negatively affect social adaptation. This creates a vicious circle: a person begins to feel embarrassed about his condition, tries to limit his social circle and go out as little as possible - as a result, this leads to a decrease in physical activity, which further aggravates the symptoms of thrombosis.
Correlation between diseases of the circulatory system and mortality from them
Consequence #1. Violation of tissue trophism
Trophic disorders are a common consequence in many patients with clearly visible varicose veins in the legs. Often the pathological process involves the skin of the legs, subcutaneous tissue and even underlying soft tissues (1, English).
Trophic changes in varicose veins are a consequence of venous stasis, which is caused by insufficiency of valves in the affected superficial vessels, perforators. Natural development of events during the progression of varicose veins. It is the functional inferiority of the vein valves that determines the appearance and increase of the main symptoms of varicose veins of the legs. (2, English)
Trophic ulcer is a dangerous complication of varicose veins. Redness of the skin in the lower leg area is a symptom for which you should immediately contact a phlebologist.
The involvement of perforators plays a major role in the development of venous insufficiency. These are vessels that normally provide horizontal outflow of blood into the deep venous system. Clinical practice shows that the most pronounced changes in the soft tissues of the legs develop just below the affected large perforator.
The pathogenesis of trophic disorders includes (3, English):
- The formation of venous stagnation in the distal parts of the affected limb, where blood is deposited under the influence of gravity in the presence of vertical reflux (reverse pathological blood flow). This leads to a slowdown in the excretion of metabolic products from the lower extremities and disruption of gas exchange, which has a toxic effect on cells.
- Pathological disturbance of blood circulation in the vessels, which leads to persistent dysfunction of the capillary walls. The functioning of the histohematic barrier, the natural “filter” between tissues and the vascular bed, is disrupted, as a result the physicochemical properties and composition of the intercellular fluid change, and the excretion of metabolic products worsens. The functioning of cell membranes is secondarily disrupted, which negatively affects the condition of all tissues.
- Pathological opening of arteriovenous anastomoses, provoked by increased venous pressure, disrupts the supply of soft tissues with nutrients and oxygen.
- Decreased activity of local immunity, which contributes to the development of nonspecific inflammatory reactions under conditions of tissue hypoxia. Relative immune deficiency is the main factor in reducing the activity of the skin barrier. Dysbiosis on the surface of the epidermis that develops against this background significantly increases the likelihood of secondary infection of the skin.
Trophic disorders are an almost constant companion to complicated varicose veins of the lower extremities. An exception is cosmetic varicose veins, in which very small valveless intradermal veins undergo changes. They have a limited blood drainage basin, so a change in their functioning does not affect the general process of venous outflow from the lower extremities.
What do trophic disorders look like?
Trophic disorders are changes that occur as a result of malnutrition (trophism) of soft tissues. In the case of varicose veins, they are caused by microcirculatory disorders against the background of long-term venostasis. Such changes are chronic in nature and are often associated with inflammation, an allergic reaction, and infection.
First, patients with varicose veins develop tissue compaction and peeling of the skin, which is called lipodermatosclerosis. As a rule, the inner surface of the lower leg is affected. Such trophic disorders develop gradually, do not cause obvious discomfort to patients and do not disfigure the limb, and therefore often remain without due attention.
As the disease progresses and microcirculatory disorders worsen, trophic disorders become more and more obvious. Tissue hyperpigmentation develops, and lipodermatosclerosis worsens. At this stage, venous eczema may form. Subsequently, severe complications arise: an ulcerative-necrotic defect is formed, and secondary tissue infection occurs. Such trophic disorders usually already act as the main reason for visiting a doctor.
Trophic complications with varicose veins are understood (4, English):
- Increased dryness of the skin of the legs, not associated with external causes. The epidermis loses its proper elasticity and becomes prone to irritation and microdamage. Dry skin is often accompanied by itching, pigmentation and insufficient hair growth in the affected area.
- Development of aseptic cellulite (nonspecific inflammation of subcutaneous fat) with subsequent formation of lipodermatosclerosis. Accompanied by uneven compaction of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue due to the appearance of connective tissue areas. The consequences of lipodermatosclerosis persist even after the elimination of chronic venous insufficiency, significantly worsening the appearance of the limb.
- The appearance of venous eczema is an infectious and inflammatory lesion of the dermis. Most often, the skin in the affected area becomes wet, itchy, and covered with bursting blisters, erosions, crusts and scales. An area of hyperpigmentation and dense edema forms around the eczematous lesion. In place of resolved severe eczema, an area of sclerosis remains; the skin remains brownish-brown, dry, and thinned. And these changes are irreversible.
- Formation of a venous trophic ulcer - a persistent open rounded skin defect with a depression in the subcutaneous tissue. Around it there is an area of edema, eczematous dermatitis, the edges are scarring and quite rough. The bottom of the ulcer may be dry or rotting-wet.
The typical localization of such disorders is the lower third of the leg above the inner malleolus; lesions in the retromalleolar region are slightly less common. With severe varicose veins, almost the entire limb below the knee is subject to trophic changes, but they reach the greatest intensity precisely in these zones - this is explained by the peculiarities of vascularization of the lower leg and especially the course of the perforating veins.
Eczema and trophic ulcers are very serious complications of varicose veins. Their appearance indicates severe persistent decompensation of venous insufficiency, which requires prompt specialized treatment.
Treatment of trophic disorders
Trophic disorders due to chronic venous insufficiency develop gradually, so patients rarely consult a doctor immediately after the appearance of unpleasant symptoms.
Unjustified watchful waiting tactics and inadequate treatment when trophic disorders appear are fraught with the development of severe complications. The consequences will be irreversible, persisting even after venous insufficiency is eliminated.
The development of eczema and ulcers should be considered as an indication for the use of radical treatment. It can be carried out simultaneously or in stages.
Surgical treatment of trophic disorders in varicose veins may include classical surgical procedures (combined phlebectomy, miniphlebectomy, dissection of perforators).
Preference is given to gentle, minimally invasive techniques:
- Endovenous laser coagulation.
- Sclerotherapy.
- Radiofrequency obliteration of veins.
If necessary, pathogenetically targeted interventions are supplemented with autodermoplasty to quickly close the skin defect.
Is it possible to completely cure ulcers and venous eczema without surgery? The answer is clear - no: conservative therapy (both local and systemic) is not able to eliminate the root cause of trophic disorders - pathological reflux with the development of venostasis. It can somewhat alleviate the patient’s condition and stabilize the situation, which is used in the preoperative period.
Components of conservative therapy:
- Disaggregants.
- Phlebotonics.
- Phleboprotectors.
- Local products with cleansing, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and regenerating effects.
- Modern dressings (wound dressings).
- Physiotherapy.
- Compression therapy.
The onset of scarring of the ulcer and the subsidence of the symptoms of eczematous dermatitis during conservative treatment should not lead to refusal of minimally invasive treatment. Without a radical solution to the problem, one can expect a recurrence and aggravation of severe trophic complications.
World clinical practice shows that intervention with the complete elimination of vertical and horizontal reflux (or at least one of them at the first stage) allows for rapid resolution of eczema and good scarring of the ulcer. Such radical treatment has a long-term effect. Elimination of venostasis prevents not only relapses of severe trophic disorders, but also other complications of varicose veins.
Blockage (thrombosis) of a vein in the leg: what to do for prevention?
Rationalization of work and rest schedules, wearing special compression garments and correcting nutrition - all this has a beneficial effect on the condition of blood vessels and helps reduce the risk of thrombosis of the leg veins.
Preventative exercise
When the first symptoms of thrombosis appear, the patient is advised to reconsider his attitude towards physical activity. It is advisable to avoid staying in any static position for a long time - either sitting or standing, or lying down. During the day, you need to perform not very difficult physical exercises, and if this is not possible, then at least change your body position as often as possible.
Massage
As a preventive measure, you can practice self-massage, as it relieves the feeling of tightness and improves blood flow. However, remember that if you have thrombophlebitis with dilated and painful veins, you cannot do a massage.
foot massage
Compression underwear
Since one of the reasons for the development of blockage (thrombosis) of the veins of the lower extremities is varicose veins, wearing special compression products - stockings, tights, knee socks, elastic bandages - gives good results in the fight against this problem. Their use has a beneficial effect on the speed of venous blood movement. Each patient can choose the type of compression garment that suits them, depending on the level of pressure exerted by the product on the lower extremities.
compression underwear
Hirudotherapy
Installing medical leeches is an effective means of preventing varicose veins on the legs. The saliva of leeches contains a special component - hirudin, which is a natural anticoagulant. This substance reduces blood viscosity, improves blood flow in the lower extremities, and increases local and general immunity.
!
It is worth considering that hirudotherapy has contraindications (oncology, purulent processes, etc.)
In addition, the placement of leeches cannot be combined with the use of medicinal anticoagulants, as this can lead to complications, such as the development of bleeding.
Nutritional Features
A properly formulated diet allows you to lose excess weight, which puts additional pressure on the lower limbs, and also reduce blood viscosity. To achieve these goals, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- Drink enough clean drinking water daily (up to 2 liters per day). Reduce coffee consumption, give up alcohol, limit, or better yet completely eliminate, milk and dairy products.
- Eat foods rich in heavy animal fats: fatty meats, butter, lard. Healthy sources of fat and protein are sea fish, seafood, vegetable oils (olive, flaxseed, MCT oil), replace milk with soy, almond, coconut.
- Completely exclude from the diet trans fats, margarine, smoked and salty foods, fatty sauces, chips and snacks, sweet carbonated drinks, milk chocolate, baked goods, bread, fast food.
- The daily menu should include vegetables, herbs, and fruits, which contain fiber.
- It is recommended to further enrich the diet with foods that include vitamins C, E and Beta-carotene. They are natural antioxidants that help reduce blood hypercoagulability. Such products include citrus fruits, kiwi, cranberries, raspberries, blueberries, apples, spinach, sea buckthorn, green tea, carrots, bell peppers, red beans, nuts, sunflower seeds. It is also worth eating foods that contain vitamin P (rutin). It maintains vascular tone at a high level, ensures their strength and elasticity. Contained in cherries, tomatoes, garlic, chokeberries, sorrel, buckwheat.
- Don’t forget about foods that increase the production of elastin, a protein that ensures the elasticity and strength of blood vessels. These include seafood, red grapes, and beef liver.
PLEASE NOTE: The recommendations described above are general guidelines. Therefore, it is advisable that the daily diet be compiled by a doctor taking into account an assessment of the patient’s general health.
Thrombosis development process
In a healthy body, blood clots perform a regenerative function and are designed to restore damaged vessel walls. However, a number of unfavorable factors can cause uncontrolled thrombus formation and, as a consequence, the occurrence of diseases such as:
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Ischemic stroke of the brain.
- Thrombophlebitis.
- Inflammation and atherosclerosis of blood vessels.
- Slowing of blood flow and its disturbances.
- Violation of rheology (qualitative characteristics) of blood.
- Gangrene of the limbs.
It should be remembered that if problems with blood vessels appear, you should not delay visiting a doctor! Only timely and professional treatment will help reduce the risk of thrombotic diseases and their complications.
Advantages of treatment of deep vein thrombosis at the center of Professor Kapranov
The list of advantages of contacting our center includes the following points:
- High level of professionalism. Professor S. A. Kapranov and his colleagues, working at several clinical sites, are the few highly qualified specialists in Russia who have unique experience in successfully performing stenting of the iliac veins.
- Use of modern stents. Innovative products are used for all vascular interventions. They are safe, are not felt by the patient, and do not harm his health.
- An impressive experience. Every year, the center’s specialists perform hundreds of endovascular interventions for deep vein obstruction.
- High, clinically proven effectiveness of any medical manipulation during the therapy we offer. Many patients were able to forget about all the symptoms and limitations associated with their disease.
- No pain. During treatment, after completion of therapy, patients do not experience any noticeable discomfort. All unpleasant sensations are relieved with special medications.
- Comfortable conditions for staying in the clinic.
Rice. 2. Endovascular picture of occlusion of the pelvic veins (left external and common iliac vein).
Rice. 3. Endovascular balloon dilatation of the occluded iliac vein.
Rice. 4. After implantation of a venous stent, complete patency of the pelvic veins, elimination of clinical symptoms of postthrombophlebitis disease.
Main forms of the disease
There are several common forms of deep vein thrombosis.
- Phlebothrombosis is characterized by the occurrence of a blood clot, which is fixed to the venous wall, causing an inflammatory reaction. This disease can lead to a serious complication - pulmonary embolism as a result of a blood clot.
- Thrombophlebitis is inflammation of the venous walls with the formation of blood clots in the lumen of the affected vessel. This pathology affects the deep veins only of the lower extremities and, as a rule, is a complication of varicose veins.
- Deep vein thrombosis of the leg. It is characterized by swelling in the lower part of the leg, pain when bending the leg, and impaired sensitivity in the foot area.
- Thrombosis of the subclavian vessel occurs during prolonged intravenous manipulation using a catheter. The disease manifests itself as increasing swelling in the neck, collarbone, and arm. Painful sensations often occur in the subclavian region.
- The pathology of the mesenteric vessels is caused by a violation of the outflow of blood through the thrombosed vein from the intestinal loops. Usually the patient suffers from dull abdominal pain and bloating. Necrosis of the intestinal wall, peritonitis and phlebitis are indicated by the appearance of nausea and vomiting, and increased pain.
- With occlusion in the portal vein, the outflow of blood from the stomach, liver and pancreas is blocked. This process often occurs in malignant tumors and cirrhosis of the liver. Its main symptoms include increasing pain in the right hypochondrium, vomiting blood. Often the patient has a large belly, which does not arise from overeating, but from the effusion of fluid into the peritoneum during ascites.
- With thrombosis of the deep veins of the hemorrhoidal ring, pain occurs in the anus. In addition, the patient suffers from increased itching around the rectal outlet. An increase in body temperature is also often noted.
One of the most dangerous complications of thrombosis is pulmonary embolism. When this pathology occurs, a blood clot blocks the lumen of the pulmonary artery or its branches. A blood clot that breaks away from the vessel wall travels through the veins to the heart and into the lungs. Symptoms of the condition develop suddenly and include:
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- increased heart rate;
- severe shortness of breath;
- pain in the sternum that radiates to the arm;
- in some cases, hemoptysis appears.
When large vessels are blocked, cyanosis of the upper half of the body occurs. This process is accompanied by a clear swelling of the cervical vessels.
Acute thromboembolism can only be dealt with urgently. If the patient is not treated on time, he dies. Death is possible within 2 hours after the onset of the attack.
An equally dangerous complication of deep vein thrombosis is the formation of chronic venous insufficiency of the lower extremities. With this pathology, blood stagnation develops in the body and within 2-3 years the disease leads to disability of the patient. The venous wall swells, its elasticity decreases, and permeability increases. The patient suffers from severe pain, and lumpy vessels are often visible through the skin. In some cases, trophic ulcers form on the legs, which do not heal for a long time.
Request a call back Get a free consultation