Not always indicators of the content of erythrocytes and hemoglobin can provide answers to the questions posed. In such cases, determining MCV, RDW and some other indicators, which we will talk about, will help when making a diagnosis.
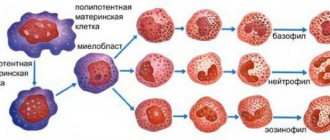
MCV – mean erythrocyte volume, or mean corpuscular volume (Mean Corpuscular Volume). An indicator characterizing the average size of cells (in volumetric terms). The unit of MCV is femtoliter (fl) or cubic micrometer (µm3).
Determined by a hematology analyzer by dividing the cellular volume by the number of blood cells. You should be aware that in some situations it may be unreliable. For example, in the presence of irregularly shaped red blood cells in patients with sickle cell anemia.
On the right in the image is a modified red blood cell in the shape of a sickle
Indications for analysis
MCV blood test is not the only one. To clarify the diagnosis, the therapist may require a retake or refer it for additional tests.
MCV is informative in two cases:
- in order to diagnose one of the types of anemia;
- to determine the type of water-salt imbalance. People are often sent for such an analysis if they have various intestinal infections, acute respiratory diseases and ARVI.
Other, no less serious, reasons for getting tested may be:
- failure of the hormonal system;
- metabolic problems;
- overweight;
- increased blood sugar or diabetes;
- a sharp and causeless decrease in the level of the immune system.
MCV analysis results often help identify such deviations:
- anemia of normochromic type. It is fixed when pathologies appear in the bone marrow, sometimes caused by chronic diseases;
- macrocytic type anemia. It is characterized by an excessive increase in mcv. Red blood cells increase in size due to insufficient amounts of vitamin B and folic acid;
- microcytic anemia. In this case, the disease occurs due to a lack of iron in the blood.
What is the norm and what is considered a deviation
A normal value is considered when the MCV is between 80 and 100 femtoliters. The red blood cell in this case is a normocyte.
If the average volume of a red cell is less than 80 fl, it is a microcyte. Well, if the volume is more than 100, then such an erythrocyte is called a macrocyte.
Accordingly, microcytosis is distinguished when a large number of microcytes are detected in the blood. Low hemoglobin is characteristic. Macrocytosis is characterized by an increased content of macrocytes in the analysis.
Anisocytosis is the presence of red blood cells of different sizes and shapes.
In newborns and children under one year old, the norm is 70-110 femtoliters. With age, this indicator is compared with that of adults
Normal MCV values
| Age, gender | Mean erythrocyte volume, MCV, fl | |
| Children | ||
| 1 day - 14 days | 88,0 — 140,0 | |
| 14 days - 4.3 weeks | 91,0 — 112,0 | |
| 4.3 weeks - 8.6 weeks | 84,0 — 106,0 | |
| 8.6 weeks - 4 months | 76,0 — 97,0 | |
| 4 months – 6 months | 68,0 — 85,0 | |
| 6 months – 9 months | 70,0 — 85,0 | |
| 9 months - 12 months | 71,0 — 84,0 | |
| 12 months - 5 years | 73,0 — 85,0 | |
| 5 years - 10 years | 75,0 — 87,0 | |
| 10 years - 12 years | 76,0 — 90,0 | |
| 12 years - 15 years | Women | 73,0 — 95,0 |
| Men | 77,0 — 94,0 | |
| 15 years - 18 years | Women | 78,0 — 98,0 |
| Men | 79,0 — 95,0 | |
| 18 years - 45 years | Women | 81,0 — 100,0 |
| Men | 80,0 — 99,0 | |
| 45 years - 65 years | Women | 81,0 — 101,0 |
| Men | 81,0 — 101,0 | |
| 65 years - 120 years | Women | 81,0 — 102,0 |
| Men | 83,0 — 103,0 | |
In children under 10 years of age, the index may fluctuate and be inaccurate; later it returns to normal (80-100 fl).
MCHC increased
The hemoglobin concentration in red blood cells may be increased in the following cases:
- hyperchromic anemia (ovalocytosis, folate deficiency, B12 deficiency, spherocytosis, including congenital);
- water-electrolyte metabolism is impaired;
- may be high in newborns, which is considered normal.
Elevated concentrations of iron-containing protein are quite rare. If MCHC has increased to 380 grams per liter and continues to rise, hemoglobin may begin to crystallize.
The result is obtained using modern hematology analyzers
Most often, a significant increase in MCHC is not associated with any disease, but indicates an error during a laboratory test, since a high concentration of hemoglobin in red blood cells will lead to morphological changes in red cells and their complete destruction. There is only one disease in which this indicator is increased. This is a hereditary pathology - spherocytosis. Refers to hemolytic anemia and is characterized by a defect in the cell membrane of red cells.
In most cases, the following technical errors are the basis for increased MCHM:
- incorrect determination of hematocrit and hemoglobin;
- violation of the conditions for blood collection and storage, which is why partial disintegration of red blood cells occurred.
MCV is higher than normal
If the results are above normal, this indicates the development of macrocytic anemia. It can be directly related to diseases such as:
- drug intoxication;
- food poisoning;
- problems with the thyroid gland;
- lack of iodine or iron in the body;
- liver dysfunction;
- oncological process of red bone marrow;
- long-term alcoholism;
- disruption of the pancreas.
An increase in mcv can be caused by:
- long-term use of birth control pills that affect hormonal levels;
- addiction to cigarettes and tobacco products;
- prolonged contact with toxic substances (work in hazardous industries);
- taking medications that increase the level of mcv in the blood.
If left untreated, macrocytic anemia can lead to frequent fainting, poor health, and low hemoglobin levels in the blood. Particularly at risk are:
- people who eat poorly, lead a sedentary lifestyle and ignore exercise;
- patients with chronic liver failure;
- people with a genetic predisposition to the disease;
- men over fifty-five years of age who abuse alcohol.
Experts identify some signs by which one can understand that a person’s red blood cell volume is too high:
- unhealthy pale lips;
- abdominal pain for no particular reason, which appears very often;
- the presence of tachycardia (heartbeat too fast), even when the person is at rest;
- skin with a yellowish tint.
If you notice similar symptoms or detect an increased level of mcv in the blood, you must immediately consult a general practitioner for appropriate treatment.
Why is MCV lowered?
If the MCV indicator in a blood test is low (does not reach the required 80 fl), most often this indicates that the child or adult is developing some form of anemia, that is, a lack of hemoglobin in red blood cells. Thanks to the compensatory properties of blood, the number of red blood cells themselves can increase, but all of them will poorly supply oxygen to the tissues and organs of a sick person.
The reasons for the decrease in the average volume of red blood cells may be the following conditions and pathologies:
- Iron deficiency anemia (grade 2-3) is a lack of iron, which the body receives from food or in the form of vitamin-mineral complexes. Often develops against the background of gastrointestinal diseases and microelement absorption disorders, intestinal tumors, gastritis with low acidity. Pregnancy can also lead to iron deficiency.
- Lack of folic acid, often also associated with pregnancy.
- Chronic diseases associated with constant blood loss: hemorrhoids, nosebleeds, peptic ulcers, etc.
- If the indicator in women is below normal, this may indicate the development of uterine tumors (fibroids, fibroids, or malignant ones). These diseases are characterized by frequent bleeding not associated with menstruation.
- A pathology of the red bone marrow that results in insufficient production of normal blood cells (congenital sideroblastic anemia). In addition to the congenital form, the disease can develop due to lead poisoning and taking a number of medications.
- Thalassemia, hemoglobinopathy and other hereditary blood diseases. Characterized by a decrease in the average size of red blood cells to 65 fl.
- Hemolytic anemia associated with increased destruction of blood cells (transfusion of blood incompatible with the patient’s group or rhesus, hereditary forms, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome).
Important information: What does low or decreased ESR mean in a blood test in women?
When the MCV value in the blood is below normal, but no pathologies are detected, the cause may be conditions associated with blood loss in large quantities:
- surgical intervention;
- trauma with injury to soft tissues and blood vessels;
- donation
Often, a decrease in the volume of red blood cells is also caused by metabolic disorders or endocrinological disorders (increased thyroid function, etc.). These conditions are distinguished from anemia by the normal hemoglobin content. Only a doctor can correctly decipher a blood test and determine the presence of any abnormality.
If you find a reduced reading of the average volume of red blood cells, it is recommended to visit a physician, especially if you have painful symptoms.
MCV below normal
Tests showing that the volume of red blood cells is below normal also indicates pathology. Experts name a number of reasons that can lead to such results:
- genetic predisposition;
- insufficient amount of water consumed;
- development of various types of anemia;
- lead intoxication;
- the presence of malignant formations, tumors in the body;
- taking medications that affect test results.
In medical circles, a disease in which the level of red blood cells in the body decreases is commonly called microcytic anemia. The peculiarity of the disease is that red blood cells do not perform their transport function, i.e. they do not deliver oxygen and other useful substances to the body’s cells in the required quantities.
With this pathology, a characteristic clinical picture is observed:
- constant fatigue;
- increased irritability, nervousness;
- decreased concentration and performance;
- absent-mindedness;
- memory impairment.
A decrease in the volume of red blood cells is always observed with various types of blood loss.
Pregnancy and mcv
During pregnancy, due to the body's increased consumption of iron, microcytic anemia can develop. This condition can negatively affect both the health of the unborn child and the well-being of the mother.
Some experts are convinced that mcv indicators are directly related to a person’s psychological state.
Causes of elevated MCV
The average volume of red cells is increased when:
- liver diseases;
- hemolytic anemia;
- development of water-electrolyte imbalance in the form of hypotonic overhydration, which is possible with kidney diseases;
- macrocytic and megaloblastic anemia;
- deficiency of folic acid and vitamin B12;
- myelodysplastic syndrome.
Anemia cannot be ruled out when MCV is not higher than normal. For example:
- after bleeding;
- with hemolytic anemia;
- for some acute poisonings.
Features of the analysis
Today, the mcv test is included in the general blood test or can be performed separately from other indicators. To donate blood, the patient must come to the treatment room, where a laboratory technician or nurse will take blood samples from a finger or vein. Blood sampling is carried out in accordance with all sanitary and epidemiological regulations (SanPiN).
The patient is required to comply with the following rules:
- You need to donate blood on an empty stomach (5-12 hours after your last meal);
- at the time of donation, the woman should not be menstruating;
- feeling normal. It is prohibited to take blood samples if the patient is not feeling well, is in a coma or is in cardiac shock.
What is it used for?
This indicator is one of the most constant in blood tests. In this regard, it is used to identify errors during laboratory tests. The MCHC red blood cell index is used in the following cases:
- when assessing the effectiveness of anemia therapy;
- in the differential diagnosis of anemia;
- when diagnosing hypochromia.
Signs of iron deficiency anemia
Iron deficiency anemia is a common pathology in our time. It is caused by insufficient intake of iron from food or its difficult absorption in the gastrointestinal tract, and may also be associated with some chronic diseases and blood loss. Characterized by a decreased level of red blood cells, it occurs due to severe bleeding, increased destruction of red blood cells or impaired formation of blood cells. Anemia is popularly called anemia. To diagnose it, an analysis to determine the level of red blood cells and hemoglobin is usually not enough. The following blood parameters are usually examined, which together give a more complete picture:
- mean red cell hemoglobin concentration (MCHC);
- average hemoglobin content in one red blood cell (MCH);
- red blood cell distribution width (RDW);
- mean erythrocyte volume (MCV);
- color index (CP).
MCHC reduced
A reduced MCHC indicates a condition such as hypochromia, that is, the red cells are not sufficiently saturated with hemoglobin. This condition is associated with pathologies in which the production of iron-containing protein is impaired. Hypochromia can be caused by various types of anemia, hypovitaminosis, lead poisoning, some hereditary congenital diseases, and is also associated with a disorder of iron metabolism in the body. A decrease in the concentration of iron-containing protein in erythrocytes has the following reasons:
- sideroblastic and hypochromic iron deficiency anemia;
- chronic posthemorrhagic anemia;
- hemoglobinopathies, in which hemoglobin synthesis is impaired and some amino acids are replaced in its chains;
- disturbance of water-electrolyte metabolism;
- thalassemia (some types) is a hereditary disease associated with mutations in genes that are responsible for the synthesis of iron-containing protein;
- megaloblastic anemia, in which red cells increase in volume more significantly than they are saturated with iron-containing protein.
When hemoglobin synthesis is impaired, MCHC decreases last. Therefore, a decrease in the concentration of iron-containing protein with normal values of other blood parameters (erythrocyte and hemoglobin content) indicates an erroneous laboratory test result.