Few Kaliningrad residents know that a pathological condition in the form of ringing or noise in the ears is quite common in childhood and adolescence. This symptom worries children both with normal hearing and with various hearing impairments. In this regard, parents should understand: if a child actively complains of “buzzing”, “buzzing” or “machine noise” in the ears in the absence of an external sound source, this may be associated not only with hearing aid disorders, but also signal more serious problems in the child's body. Let's look together at the important nuances of this “noisy” issue...
general characteristics
Patients describe their subjective sound sensations differently: as a constant monotonous noise, a low hum, similar to the operation of an engine.
Patients often say that they hear ringing or squeaking in their ears. Some people compare the auditory sensation to a rumble or crackling sound. The noise occurs suddenly, and it is not always possible to trace the connection between its appearance and the influence of external factors. It lasts from several minutes to several days and even weeks, which significantly reduces performance and causes negative emotions, including the development of depression. Tinnitus can be either unilateral or bilateral. Sometimes the symptom is accompanied by severe pain in the ear and temples, hearing loss, dizziness and balance problems. For some people, the noise is so strong that it completely drowns out the sounds of the surrounding world. Since subjectively unpleasant sound sensations can be caused by serious neurological or vascular disorders, it is necessary to urgently visit a specialist to determine the cause of the symptom and select an adequate treatment regimen.
Potential Complications
If tinnitus appears suddenly and bothers a person for a long time, it is necessary to consult a specialist. The clinical syndrome may become chronic. The causes of noise can be depression and stress. In the absence of adequate treatment, there is a high risk of developing panic attacks, various phobias and the appearance of suicidal tendencies.
If the root cause of tinnitus is pathology of the cardiovascular system, then if left untreated, a heart attack, stroke and other serious complications may develop (including cardiac arrest and death).
Knocking without pain in the ears is a common complaint from patients to the otolaryngologist. Experts do not recommend self-medication: after the examination, the exact cause of the discomfort should be identified. Uncontrolled use of medications, the use of folk remedies, selected independently, without the knowledge of the doctor, can aggravate the situation.
Classification
According to the sound characteristics, tinnitus is divided into tonal - continuous sounds of the same frequency (ringing, whistling, low-frequency hum) and non-tonal - periodic unpleasant auditory sensations in the form of clicks, crackling, rumble. According to the duration, the symptom is divided into acute (up to 3 months), subacute (from 3 to 12 months) and chronic (lasting more than 1 year). In clinical practice, tinnitus is classified depending on the cause of its occurrence:
- Subjective noise
. Often caused by prolonged exposure to loud sounds on the auditory analyzer. Extraneous sounds are heard only by the patient, which prevents the person from concentrating on the actions being performed or talking. - Neurological noise
. This type of tinnitus is caused by damage to specific nerve receptors in the inner ear, as occurs in Meniere's disease. Patients experience a strong buzzing sensation, usually accompanied by dizziness. - Somatic noise
. It can be associated with damage to any organ, pathological impulses from which excite the auditory analyzer. Somatic tinnitus is in some cases triggered by movements and touches. - Objective noise
. The rarest type of disorder, which is caused by deformations of the ear vessels and pathology of the muscular system. Extraneous “pulsating” sounds can be heard by the doctor when using a stethoscope.
To assess discomfort, Soldatov’s classification is used, which subdivides ear noise according to severity. At grade 1, performance is preserved, the person is adapted to extraneous sounds. The appearance of intense noise at night indicates a transition to stage 2. A constant strong hum, which interferes with the performance of usual duties, is disturbing at stage 3; with a complete loss of performance, stage 4 of the disease is diagnosed.
Types of tinnitus
Otorhinolaryngologists distinguish several types of sound effect:
- Objective (vibrator noise) is pulsating or continuous in nature and occurs due to vibrations of an anatomical formation or pulsation of blood vessels. This type of sound can be heard with a phonendoscope and is quite rare.
- Subjective (non-vibratory noise) is heard only by the patient. It is formed when the impulse of the auditory analyzer (auditory nerve, cochlea) is interrupted for some reason, that is, the sound-conducting pathways are affected. This noise effect is recorded in the presence of cerumen, otitis media, intoxication, acoustic trauma and dysfunction of the auditory tube.
According to localization, noises can be generated in the center of the skull, shifted to one ear, or heard simultaneously in both ears. Note that noise in the head, as a rule, excludes pathology of the ears, while noise in the ear does not at all exclude the possibility of the formation of a pathological process inside the skull.
The clinical classification provides for 4 degrees of noise manifestation: from subtle manifestations that do not cause discomfort, to an obsessive constant symptom with sleep disturbance and the psycho-emotional state of the child.
Causes of tinnitus
Acoustic trauma
The appearance of noise is provoked both by a single sound impact of prohibitive volume (shots from large-caliber weapons, fireworks, rock concerts), and by the constant influence of sounds, which is often found among people listening to loud music through headphones, workers in factories and sewing workshops. In case of acute injury, a person temporarily loses hearing, which causes a monotonous ringing or squeaking in the ears. May cause severe throbbing pain in the temporal part of the head and dizziness.
With chronic exposure to sound stimuli, symptoms increase gradually. First, complaints appear about short-term noise (within 1-2 hours), which begins after being in a room with loud sounds or using headphones. As the condition progresses, the ringing in the ears becomes constant and is accompanied by hearing loss. The frequent occurrence of noise, which disrupts performance, is combined with headaches and hearing loss, is an indication for seeking medical help.
Age-related changes
Among people 55-65 years old, every fifth person periodically notes the appearance of extraneous sounds; after 65 years, the number of people suffering from humming and ringing in the ears increases to 40%. Typical complaints are bilateral noise, which at first feels very quiet and practically does not interfere with everyday activities. Then the sounds seem more intense. Due to the intensification of symptoms at night, patients usually suffer from insomnia. Tinnitus in the elderly is caused by degenerative changes in the inner ear and is combined with decreased hearing, which requires consultation with a doctor.
Hypertonic disease
The appearance of tinnitus is typical for patients suffering from high blood pressure, and the intensity of auditory sensations depends on blood pressure levels. Extraneous sounds are caused by the turbulent movement of blood through narrowed vessels with thickened walls. Hypertensive patients periodically hear a slight hum, which usually occurs against the background of a headache and a deterioration in their general condition. Increased noise, accompanied by painful nausea, flashing “spots” before the eyes, is a symptom of an incipient hypertensive crisis.
Pathological processes in the ear
Ear noise may indicate damage to the auditory analyzer, which is caused by disturbances in the perception and analysis of sounds, and discoordination of the work of different parts of the hearing organ. These reasons often cause temporary sensations of humming or ringing, which cease to bother you after the underlying pathology is relieved. With some lesions of the inner ear that are difficult to treat, the noise becomes constant. Tinnitus is caused by:
- Inflammatory diseases
: external and otitis media, eustachitis, labyrinthitis. - Blockage of the ear canal
: wax plugs, foreign bodies, water ingress. - Inner ear diseases
: Meniere's disease, otosclerosis.
Vascular disorders
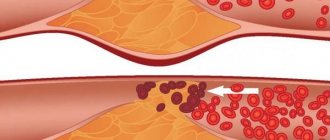
Most often, the symptom occurs with atherosclerosis: the deposition of lipid plaques on the walls of the vessels of the inner ear disrupts the normal movement of blood, which is felt as a moderately intense “pulsating” noise. In most patients, the hum is more pronounced on one side, which is associated with the degree of damage to the vascular wall. Unilateral loud ear noise is observed in patients suffering from temporal artery aneurysm. In this case, uncomfortable auditory sensations are combined with periodic headaches and dizziness.
Tumor causes
Tinnitus is most characteristic of a benign formation—acoustic neuroma. With this neoplasia, unilateral tinnitus becomes the first symptom. A person notices the appearance of a weak constant hum in one ear, which does not disappear even at night. As the disease progresses, hearing on the affected side gradually deteriorates, and sound sensations become more intense. Pulsating one-sided noise in combination with swallowing disorders and asymmetry of the palpebral fissure occurs with glomus tumor of the ear.
Cervical osteochondrosis
In case of problems with the spine, the occurrence of ringing or humming in the ears is associated with sharp turns or tilts of the head, or prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position. The causes of noise are compression of individual vessels that go from the neck to the ear and brain. The symptom is observed periodically, the intensity of the sounds is low, so the performance of most patients does not suffer. With severe deformation of the cervical vertebrae, a monotonous strong ear noise is possible, combined with dizziness, fainting, and sharp pain in the neck.
Traumatic brain injuries
Mild head injuries may be accompanied by a short-term noise or ringing in the ears, which does not cause severe discomfort. With more significant damage, unusual auditory sensations are detected against the background of severe nausea and vomiting, intense headaches. Sometimes the symptom does not appear immediately after the injury, but several days later. The noise that occurs after hitting the head is grounds for an urgent visit to the doctor, since with a traumatic brain injury there is a risk of destruction of bone structures and intracranial hemorrhages.
Complications of pharmacotherapy
Tinnitus most often develops 1-2 weeks after the start of etiotropic treatment of severe bacterial infections, which is due to the strong ototoxic effect of drugs. The symptom also occurs in patients with hypertension who are forced to take medications from several groups daily. Side effects from the auditory analyzer are provoked by such groups of medications as:
- Antibiotics
: aminoglycosides, tetracyclines, macrolides. - Diuretics
: furosemide, ethacrynic acid, hydrochlorothiazide. - NSAIDs in high doses
: indomethacin, diclofenac, aspirin. - Tranquilizers
: flurazepam, tranxene, phenazepam.
Rare causes
- Malformations of the auditory analyzer
: Goldenhar syndrome, microotia, congenital sensorineural hearing loss. - Endocrine pathology
: hypothyroidism, pituitary adenoma. - Diseases of internal organs
: digestive system, kidneys. - Neurological causes
: multiple sclerosis, age-related degenerative processes in the brain. - Damage to the temporomandibular joint
. - Allergy
.
Diagnostics
When tinnitus occurs, the patient is referred for examination to an otolaryngologist, who identifies the otogenic causes of the symptom. The diagnostic search is aimed at a detailed study of the functionality of the auditory analyzer and the structure of all parts of the ear. A comprehensive examination involves instrumental and laboratory methods, the most informative of which are:
- Instrumental examination of the ear canal
. Otoscopy is necessary to exclude inflammatory diseases of the outer and middle ear, ruptures of the eardrum. To assess the degree of mobility of the tympanic membrane, a pneumatic Siegle funnel is used. The method is complemented by determining the patency of the auditory tubes. - Audiometry
. To detect hearing impairment, special devices are used that generate sounds of a given frequency. Speech audiometry is intended for rapid assessment of the function of the auditory analyzer. Using tuning fork tests, pathologies of the middle and inner ear are differentiated. - X-ray studies
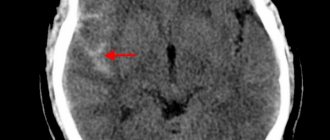
. Ear noise is often caused by neurological causes, so patients usually undergo x-rays of the skull bones. In patients with symptoms of osteochondrosis, it is necessary to examine the spine. For more detailed visualization of space-occupying formations and structural disorders of the brain, MRI of the head is also prescribed. - Angiography.
If an aneurysm or atherosclerotic lesion of the cerebral vessels is suspected, a contrast angiogram is recommended, which allows one to visualize the structure of the vascular bed and establish the exact localization of pathological changes. An even more modern method of examining blood vessels is MR angiography.
Laboratory methods are used as auxiliary methods; the examination plan includes general and biochemical blood tests; if there is a possible infectious cause of the disorder, serological tests (ELISA, RIF, PCR). In inflammatory processes accompanied by discharge from the ear, bacteriological culture is performed. In complex diagnostic cases, to establish the cause of ear noise, consultations with other specialists (neurologist, oncologist) are required; some patients are indicated for a psychiatric examination.
Otoscopy - instrumental examination of the ear canal
Is it common?
The description of tinnitus historically dates back to the time of Hippocrates. Beethoven, Van Gogh, Goya, E.K. Tsiolkovsky, B. Streisand and other famous figures suffered from these sensations against the background of severe hearing loss. Ear noise occurs in 13% of people with normal hearing. In audiology patients, tinnitus occurs in an average of 82-85% (varies from 16.5 to 93%). It is believed that this disease affects about 10% of the adult population in the world. According to some data, about 80% of people with tinnitus do not report any discomfort, and 20% report that the noise forces them to seek medical help.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
You can completely get rid of tinnitus only after treating the underlying disease that caused the discomfort. Therefore, if extraneous sounds appear for no reason, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor. To reduce discomfort until the cause of the disorder is identified, mild herbal sedatives and soothing herbal teas are recommended. In some cases, self-massage of the ears helps: rubbing movements, pressing with your palms on the ears.
Conservative therapy
Since tinnitus is caused by various causes, treatment regimens are selected strictly individually, taking into account the underlying disease and concomitant pathology. A prerequisite for the effectiveness of therapy is the elimination of provoking factors (refusing loud music on headphones, changing jobs, avoiding noisy parties and visiting nightclubs). Etiotropic therapy includes antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and antihistamines, angioprotectors, other groups of drugs, and their combinations. For the symptomatic treatment of tinnitus, use:
- Sedatives
. Herbal and synthetic drugs reduce the excitability of the brain and the speed of nerve impulses. Medicines also normalize the emotional state. - Antidepressants
. Medicines are effective for constant noise, which is caused by chronic diseases, Meniere's disease. The drugs affect centers in the brain and increase the concentration of serotonin. - Tranquilizers
. Indicated for severe ringing or buzzing in the ears, leading to insomnia and reducing performance. The effectiveness of the drugs is due to their sedative and hypnotic effects.
Experimental treatment
Tinnitus retraining therapy (TRT) is an innovative direction that is a type of cognitive behavioral therapy. The program involves individual sessions using psychotherapeutic methods, during which a person is taught ways to relax and techniques for switching attention. A component of the treatment is individually selected sound therapy. The patient is asked to listen to a pleasant noise (the splashing of waves, the rustling of leaves, the sound of rain). Over time, the brain learns to block these sounds, while the perception of pathological noise decreases.
Surgery
If humming, ringing, or tinnitus are associated with purulent inflammatory diseases, it is necessary to open and drain the tympanic cavity, which significantly speeds up the healing process. If tumors of the auditory analyzer are detected as the main cause of the disorder, they are removed with mandatory cytomorphological examination. Treatment of malignant neoplasms involves a combination of surgery with chemotherapy and radiation therapy. In aneurysms, the affected vessel is clipped.