Home — For the public
- Map of medical organizations
- Vaccination
- Clinical examination
- Fluorography
- Addresses and opening hours of clinics
- Emergency rooms
- Oncology
- Where to take an HIV test
- Healthy child's office
- Services
- Prevention of CVD
- Disease Prevention
- World Patient Safety Day
- Newspaper "Medical News"
- specialist
- School of Health
— Disease prevention
- HIV infection
- All about vaccination
- All about proper nutrition
- Hepatitis
- Flu
- Dementia
- Schoolchildren's health
- STD
- Tick-borne encephalitis
- Whooping cough
- Measles
- Legionellosis
- Meningococcal infection
- Oncology
- Acute intestinal infection
- Pediculosis
- First aid
- Pneumococcal infection
- Pneumonia
- Prevention of rabies
- Dependency Prevention
- Rotavirus infection
- Diabetes
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Injuries
- Tuberculosis
- Tularemia
- Physical activity
- Obstructive pulmonary disease
- Exotic infections
- Ecology
- Why is swimming in ponds dangerous?
— Cardiovascular diseases — Symptoms of cardiovascular diseases
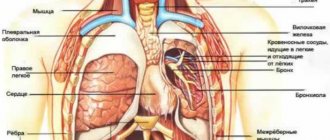
The main function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood to all tissues and cells of the body. The circulatory system is represented by the heart and a closed network of blood vessels - arteries, veins, capillaries, which penetrate all tissues and organs of the body.
The heart consists of muscular chambers (atria and ventricles) that move blood through the vascular system and a series of valves in the desired direction. The heart's self-regulating electrical system sets the heart rate and coordinates the sequence of contraction and relaxation of the atria and ventricles.
The cardiovascular system ensures uninterrupted blood circulation through a closed system of blood vessels, without which it would be impossible to maintain a constant internal environment. Together with blood, oxygen, nutrients, hormones and other vital components are delivered to each cell of the body; the cells are cleansed of toxins and metabolic products, the accumulation of which would lead to the death of both an individual organ and the body as a whole.
It becomes clear that a violation in any part of a complex structure, such as the cardiovascular system, will lead to a breakdown of all functions of the body, which can result in death. That is why cardiovascular diseases are recognized as the most dangerous in the world.
As the pathological process progresses, the heart ceases to perform its functions, and other organs and systems of the body begin to suffer.
How to distinguish heart pain from others?
If unpleasant sensations appear in the area of the heart, pay attention to where it hurts, where it radiates, how exactly and for how long it hurts
.
Localization and irradiation of pain.
Heart pain occurs in the chest region and, as a rule, radiates to the left shoulder and left arm. Less commonly, it radiates to the jaw, upper wall of the stomach and to the area between the shoulder blades.
Duration and nature of pain.
An attack of heart pain lasts from 5 to 10 minutes. Most often it occurs after physical activity: before a trip, say, you loaded heavy bags into the trunk or changed a tire along the way. As for the nature of the sensations, the “prick” and “shot” are definitely not about the heart. Heart pain is pressing, burning. It is sometimes confused with heartburn. If something seems to be “gurgling and turning over” in your chest, it may be due to a heart rhythm disorder.
Which categories of people are more likely to experience cardioneurosis?
The key reason for the development of heart neurosis is the effect of a stressful situation on the body. The first question that a psychiatrist asks a patient with suspected cardiac neurosis concerns the presence of problems in life and recent psychological trauma experienced. Perhaps a person’s loved one has died or fallen ill, problems have arisen in school or at work, or financial difficulties have arisen.
Heart neurosis often occurs in people in adolescence against the background of hormonal changes and a negative stressful environment. In most cases, the disorder occurs in women and girls.
The problem with neurosis is that a person, when it manifests itself for a long time, considers himself truly sick. He spends a lot of time, effort and financial resources traveling to doctors and trying to establish the correct diagnosis. But the solution to the problem lies exclusively in psychological treatment using properly selected drugs and techniques.
What to do first
To alleviate the condition yourself, you need to do the following:
- stop physical work, try to calm down;
- open a window to let in fresh air or go outside;
- put something cold on your forehead (a wet napkin or towel, a bottle of water);
- relax, take a comfortable position;
- breathe deeply, with quick inhalations and slow exhalations;
- you can try to reduce your heart rate by coughing;
- You need to hold your breath for a few minutes and tense your abdominal muscles;
- induce vomiting by pressing on the root of the tongue;
- immerse your face in cold water;
- apply strong and sharp pressure at the angle of the lower jaw;
- take drops (Corvalol, valerian or Valocordin);
- if a person has difficulty breathing, you need to give him an oxygen bag;
- if the condition does not improve, call an ambulance.
If there is not enough air and your heart rate increases, you need to consult a therapist or cardiologist. Perhaps the patient will be referred to another specialist, since these symptoms are not always characteristic of cardiac diseases.
Sedatives will help you calm down and reduce your heart rate.
Diagnostics
A thorough examination and an equally detailed collection of anamnesis and complaints are the most important components of the diagnosis of hyperventilation syndrome. The disease always causes a large number of complaints about the functioning of certain systems and organs, which can immediately lead to the idea of hyperventilation syndrome. However, a final diagnosis can only be made if organic diseases of the organs and systems that the patient complains about are excluded. To confirm their absence, additional procedures are prescribed: ultrasound of the abdominal organs, ECG, ultrasound of the heart, spirography and others.
Careful questioning of the patient usually reveals certain anxieties, high emotional stress and other changes. This is called a positive psychogenic analysis, which also leads the doctor to think about hyperventilation syndrome.
The disease can be detected using a simple and free method that does not require special equipment. The patient needs to breathe frequently and deeply for 5 minutes. If hyperventilation syndrome is truly present, then the symptoms will begin to manifest themselves. Since when symptoms of the disease appear, the amount of carbon dioxide in the exhaled air and blood decreases, after the onset of symptoms the patient needs to breathe air with a 5% carbon dioxide content (in a clinical setting) or breathe into a plastic bag. This will help relieve symptoms.
Medical researchers have developed a unique questionnaire, the results of which can diagnose the disease in 9 out of 10 cases.
The diagnosis of hyperventilation syndrome cannot be made on the basis of one specific symptom and the results of additional studies that refute the problem with the disturbing organ or system. After all, disorders of the respiratory system may also indicate the presence of a number of other diseases, much more terrible (heart failure, bronchial asthma, and so on). Only the doctor’s individual approach to the patient, combined with modern research techniques and a complete comprehensive examination, will help make the only correct diagnosis.
How to treat
Frequent heartbeat and at the same time lack of air is a manifestation of another disease. To get rid of tachycardia with shortness of breath, it is necessary to treat primary pathologies. To do this, you need to be examined by a cardiologist or therapist and find the cause of such symptoms. You may need to consult other specialists (neurologist, endocrinologist). In some cases, drug treatment is not required; it will be enough to change your lifestyle, diet, and drink soothing herbal teas and infusions.
Symptomatic treatment
Medicines may be prescribed to lower your heart rate. Usually two groups of drugs are used:
- Antiarrhythmic drugs (intravenous and oral). They not only reduce the heartbeat, but also prevent the occurrence of tachycardia attacks. These include Verapamil, Propranolol, Adenosine, Flecainide and others. You cannot take the pills on your own; they are selected individually, taking into account other diseases and contraindications.
- Sedatives (calming). They help especially effectively if rapid heartbeat is associated with disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system. The most well-known drugs in this group: valerian (tablets, tincture), Persen, Novopassit, Deazepam and others.
If the cause of palpitations is serious pathologies of the cardiovascular system, antiarrhythmic drugs, oral or intravenous, are prescribed
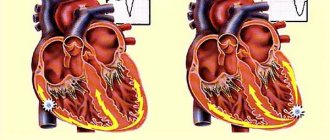
Heart failure
Shortness of breath and tachycardia are companions of heart failure. The goal of treatment is to reduce symptoms, limit disease progression, and increase life expectancy. Particular difficulties arise in the treatment of cardiac cough.
Treatment of heart failure is complex and includes:
- Regime and diet. With the help of a diet, they improve the nutrition of the heart muscle and reduce the volume of fluid in the body. It is important to limit salt and liquid intake, give up alcohol, and include more vitamins and protein foods in your diet.
- Drug treatment. Several groups of drugs are prescribed: ACE inhibitors, cardiac glycosides, beta blockers, potassium-sparing diuretics, aldactone antagonists, vasodilators, calcium channel blockers, anticoagulants.
- Surgical intervention. Without surgery, it is often not possible to achieve positive results. The most common procedure is to install a pacemaker.
Vegetovascular dystonia
With VSD, patients have a lot of complaints, including difficulty breathing and rapid heartbeat. She is being treated by a neurologist. Depending on the symptoms, other specialists may also be involved: cardiologist, therapist, endocrinologist, urologist, gastroenterologist.
Basic principles of therapy for vegetative-vascular dystonia:
- Observe the daily routine, work and rest.
- Sleep at least 8 hours a day.
- Eat properly. The products must contain all the necessary nutritional elements. You need to give up processed foods, fatty, smoked, hot, spicy, canned foods, salt, and strong drinks with caffeine.
- Avoid stress.
- Do auto-training.
- Engage in light sports (swimming, walking), therapeutic exercises.
For VSD, physiotherapy is effective, including antiarrhythmic, vasoconstrictor or vasodilator electrophoresis, as well as relaxing and tonic baths.
For hypertensive form, alcohol tinctures are used:
- motherwort,
- valerian,
- peony,
- hawthorn.
The most famous and often used remedy for palpitations is alcohol tincture of valerian.
For VSD of the hypotonic type:
- infusion of Schisandra chinensis;
- infusion of immortelle;
- tincture of ginseng root;
- tincture of enticement.
Medicines are prescribed in extreme cases if non-drug methods do not help. This is especially true for children and adolescents. Adults are prescribed tablets for symptomatic treatment:
- in the hypertensive form - adrenergic blockers (Bisoprolol, Anaprilin);
- for stress, anxiety, panic attacks - antidepressants, tranquilizers;
- drugs that stimulate cerebral circulation (Cavinton, Tanakan, Oksibral).
Heart pain when inhaling
General information
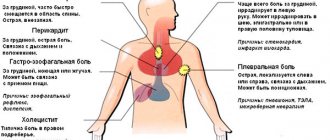
Pain in the heart with inhalation, coughing, or other respiratory movements usually points to the pleura and pericardial region or mediastinum as a possible source of pain, although pain in the chest wall is probably also influenced by respiratory movements and has nothing to do with heart disease. Usually the pain is localized in the left or right side and can be either dull or sharp.
Heart pain when inhaling
Pain in the heart when inhaling occurs due to inflammation of the membrane lining the chest cavity from the inside and covering the lungs. Dry pleurisy can occur with various diseases, but most often with pneumonia.
Pain during dry pleurisy decreases when lying on the affected side. There is a noticeable limitation in the respiratory mobility of the corresponding half of the chest.
With unchanged percussion sound, weakened breathing may be heard due to the patient sparing the affected side, and pleural friction noise. The body temperature is often subfebrile, the patient may experience chills, night sweats, and weakness. Restriction of chest movement or pain in the heart when inhaling and exhaling with shallow breathing is observed with:
- functional disorders of the rib frame or thoracic spine (limited mobility);
- pleural tumors;
- pericarditis.
With dry pericarditis, pain in the heart increases with inhalation and movement, so the depth of breathing decreases, which worsens shortness of breath. The intensity of pain when inhaling varies from slight to severe. When the interpleural ligament is shortened, a constant cough is observed, which intensifies when talking, taking a deep breath, physical activity, stabbing pain when inhaling, or running. With intercostal neuralgia, sharp “shooting” pains occur along the intercostal spaces, sharply intensifying with inhalation.
Neuroses and other causes
With renal colic, the pain is localized in the right hypochondrium and in the epigastric region and then spreads throughout the abdomen. The pain radiates under the right shoulder blade, to the right shoulder, intensifies with inspiration, as well as with palpation of the gallbladder area. There is local pain in the spine. If a rib fracture occurs, the patient feels a sharp pain in the heart when inhaling and coughing. Neuroses cause pain in the heart, which is accompanied by unpleasant sensations and paresthesia in the arms (usually on the left) and other parts of the body.
If you have heart pain, you should consult a neurologist or therapist for help. If the pain is systematic and acute, this is an alarming symptom. Pain in the heart when breathing complicates the process of saturating cells with oxygen, causing an unpleasant state and panic. Treatment will help you cope with fear and overcome an unpleasant disease.
Causes
The development of the disease can be influenced by a number of factors, which are divided into 4 subgroups:
- Diseases of the nervous system that are organic in nature;
- Psychogenic factors: anxiety and stress (chronic), fears, neuroses, hysteria, neurasthenia;
- Lack of magnesium, calcium and other metabolic disorders, as well as intoxication;
- Various diseases: hypertension, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes and others.
Psychogenic factors are the most common. It has been proven that hyperventilation syndrome very often overcomes people who, in childhood and adolescence, had to periodically observe respiratory disorders. There are a lot of examples: suffocation of drowning people, asthma, and so on.
Hyperventilation syndrome from a neurological point of view is a kind of failure of the “inhale-exhale” program. The alternation of inhalation and exhalation becomes unstable, resulting in excessive oxygen supply to the lungs. This process starts from the brain stem, where excessive excitability of the respiratory center occurs. All this leads to increased acidity and a decrease in the amount of carbon dioxide in the blood, and mineral imbalance occurs. Changes occurring in the body cause the symptoms of this disease.