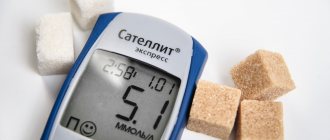
Diabetes mellitus is an irreversible pathology characterized by persistently elevated blood glucose levels. The occurrence of the disease is caused by a failure of the intrasecretory function of the pancreas and a disruption of metabolic processes. Diabetics are prescribed medication and diet therapy for life.
Proper catering involves separating foods and drinks into three categories: prohibited, permitted and limited. The latter includes food that can be consumed in a limited manner, based on the level of glycemia and overall well-being. The main criteria for choosing each product for a diabetic table are the glycemic index (GI) and energy value.
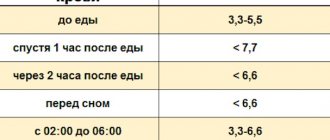
Reference: GI is an indicator of the rate of glucose formation and the speed of its absorption into the bloodstream. Foods with a high GI (⩾ 70 units) are not included in the diet of diabetics. Products indexed from 30 to 70 are considered limited. The basis of diabetic nutrition is drinks and dishes with an index of ⩽ 30 units. Before drinking beer if you have diabetes or consuming other alcoholic beverages, you need to find out how safe it is for your health.
Strong and weak alcohol for diabetes
Vodka, cognac and other drinks contain more than 40% ethanol and are practically devoid of sugar. The glycemic index of these liquids is zero, so their consumption does not cause an increase in sugar levels. In the first hours after drinking, strong alcohol can lower blood sugar levels.
The danger is the correlation of strong alcohol with the drug therapy that the patient receives (insulin injections for type 1 diabetes, and hypoglycemic tablets for type 2 of the disease). With excessive consumption of forty-degree drinks, the risk of developing a hypoglycemic crisis (critical decrease in glucose), accompanied by severe intoxication, progresses.
The next negative aspect of “breastfeeding” is the high calorie content of strong alcohol. The energy value of vodka is 235 kcal/100 g, cognac – 240 kcal/100 g. This is especially true for type 2 diabetics who are overweight. Wines are low-alcohol drinks. They are not as rich in calories as cognac and vodka. Different types of wine contain, on average, from 60 to 80 kcal.
Sweet and sparkling wines are excluded for diabetes
Their glycemic index corresponds to the average, that is, for diabetes, they are limited products. Red blended wine with an alcohol content of 9–13% vol. and sugar content of up to 3 g/l is permitted as a prophylactic against atherosclerosis. For diabetics, the main condition is to comply with a single dose - no more than 200 ml (one glass). Beer, like wine, is listed in the low-alcohol category, but the answer to the question of whether beer can be consumed if you have diagnosed diabetes is not so clear-cut.
Important! Ideally, diabetics should avoid drinking alcoholic beverages altogether.
But if you really want
If you have an irresistible desire to drink or under a combination of circumstances when it is extremely difficult to give up drinking, you must be guided by the following tactics - choose the lesser of two evils. To quickly figure out which drinks should be completely excluded and which can still be consumed in small quantities, the following factors must be taken into account:
- Strength of the drink. Fluctuations in blood glucose directly depend on the strength.
- The amount of sugars in the drink. Many drinks contain quite a lot of sugars, especially wines and liqueurs.
- Calorie content of booze. Many diabetics are overweight, and most alcoholic drinks are high in calories.
If you allow drinking alcohol with such a complex endocrine disease, then preference should be given to the following drinks.
- Wines based on natural grapes. Dry or semi-dry wine made from dark grape varieties is best tolerated by the body. You should not drink more than 200 ml of wine at one time.
- Strong alcoholic drinks such as fortified wine, vermouth, cognac, whiskey and vodka. This drink lowers blood sugar.
Wine made from dark grape varieties is the best choice for diabetes
Characteristics of beer and its effect on the body
Beer contains no fats, the protein component is scanty (only half a gram per 100 g), but it contains a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals. The leading positions are occupied by:
- choline (vitamin B4) – takes an active part in metabolic processes;
- folic acid (B9) – helps accelerate tissue regeneration;
- fluoride – maintains the health of tooth enamel;
- potassium – regulates water balance and stabilizes cardiac activity;
- phosphorus – stimulates the functioning of the brain and muscles, participates in metabolic processes.
According to nutritionists, for a healthy person, drinking beer in small quantities is not only not dangerous, but also beneficial. When you have diabetes, not everything is so rosy. The energy value of the foamy drink, depending on the variety, ranges from 45 to 60 kcal per 100 ml. With a simple comparison of calorie content, a half-liter bottle of beer can be equated to a full-fledged cheeseburger, which is unacceptable under diabetic dietary restrictions.
The percentage of alcohol in beer is small, different varieties contain from 3.5 to 5.5%. The alcohol component is formed through the fermentation of brewer's yeast and sugars, in particular glucose. During a chemical reaction, molecules break down, releasing ethanol and carbon dioxide, which turns beer into a carbonated liquid, dangerous for people with diabetes. First, soda speeds up the penetration of alcohol and glucose into the bloodstream. Secondly, it promotes the manifestation of polyphagia (increased appetite). It is not always possible for a person to resist the desire to snack heavily. This leads to a set of extra pounds that are unacceptable for diabetics.
Does drinking beer increase blood sugar? Undoubtedly. The glycemic index of the drink reaches 110 units. Considering that diabetics are not allowed products indexed over 70 units, foam is, a priori, excluded from the diet. In type 1 diabetes, an important criterion for the ability to eat (drink) a particular product is the number of bread units (1 XE = 12 g of carbohydrates). Patients are allowed no more than 24 XE per day (290 g of net carbohydrates). 100 grams of foam, 4.5% strength, contains 3.8 g of carbohydrates.
When calculating bread units per half-liter bottle (3.8:100*500:12), it turns out about 1.6 XE. This number increases blood glucose levels by approximately 4 mmol/l from the initial values. Type 2 disease is characterized by the ability of the pancreas to synthesize insulin, but the inability of cells and tissues to perceive it. Beer has a high insulin index (108 units), indicating the degree of response to the product of the endocrine function of the pancreas.
When drinking beer, the body begins to intensively produce insulin, which the body is not able to use rationally. Against the background of glucose-lowering drugs, this can lead to hypoglycemia (a drop in blood glucose levels to the maximum possible levels). This is another reason why diabetics should avoid the foamy drink. Drinking beer if you have diabetes is extremely undesirable based on the traditions of drinking this drink. As a rule, beer libations are not limited to one half-liter bottle.
For example, in the company of friends while watching a football match, preliminary plans from the “I’m a little bit” series do not work out. For a diabetic patient, excessive drinking can pose a real threat to life and health. When asked whether or not to drink alcohol, everyone answers independently. If a diabetic makes a positive decision in favor of beer, it is necessary to know the rules for drinking an intoxicating drink and be clearly aware of the possible negative consequences.
Additionally
An alternative to beer can be homemade kvass made from rye bread and sweeteners. Chicory, nettle, and hops are suitable as useful additives.
To prepare kvass you need 450 g of rye bread, 3 liters of water, 150 g of sweetener
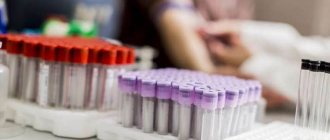
The effect of alcohol on blood tests
Drinking alcohol can reduce the reliability of blood test results. If clinical blood tests are prescribed, you must refrain from drinking alcoholic beverages, both low and strong, preferably for two days.
The low reliability of blood test results is due not only to the fact that alcohol reduces blood glucose, but also due to its effect on the reagents that are used during the analysis.
Most often, alcohol enters into a chemical reaction, thereby distorting general blood counts. Even minor consumption of low-alcohol drinks can distort a clinical blood test.
Conditions for drinking beer with diabetes
The lifestyle that an endocrinologist’s patient leads plays a big role. With strict adherence to dietary rules and constant monitoring of the amount of carbohydrates eaten, a diabetic can adjust the menu so that a glass of foam does not exceed the daily carbohydrate load on the body. The main rule is a sense of proportion. It is strictly forbidden to exceed the theoretically permissible dose of an alcohol-containing drink.
Other conditions that must be met:
What can't you eat if you have diabetes?
- Give preference to light varieties of the drink.
- Do not neglect the permissible portion of all alcoholic beverages consumed, including beer. A single dose of alcohol for diabetics is 20 g of alcohol. In beer equivalent, this is 0.33 liters.
- Do not include foam in your diet more than once every seven days.
- Do not drink on an empty stomach. Before drinking beer, you need to have a snack. It is advisable that this be a balanced dish of protein foods and fiber-rich vegetables.
- When drinking beer, type 1 diabetics should reduce the dose of insulin; patients of non-insulin-dependent type should strictly monitor the intake of carbohydrates into the body on the day of drinking alcohol, and adjust the dosage of hypoglycemic drugs.
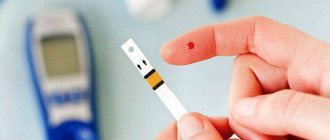
- Strictly control blood sugar. If the glucometer indicates a significant increase in readings, you should stop drinking beer. To assess the body's response to a foamy drink, you need to measure your glucose 2 hours after drinking it. To objectively assess the effects of alcohol, you can measure the glycemic level at night.
- On the day when beer is included in the diet, it is necessary to exclude visiting the bathhouse and sauna, sports training and other physical activities. In combination with alcohol, this can cause hypoglycemia.
- Avoid traditional beer snacks (flavored snacks and crackers, chips, etc.). Such products contain a lot of salt, chemical additives, and have high energy and glycemic value. In a diabetic diet, they are included in the category of prohibited foods. It is not recommended to eat salted fish. Excessive amounts of salt increase blood pressure (BP).
- Do not buy questionable products. Counterfeit alcohol leads to serious poisoning.
Light beer has a lower percentage of carbohydrates
Absolute contraindications to the use of ethanol of any concentration are:
- inflammatory diseases of the pancreas;
- chronic diseases of the hepatobiliary system;
- gout;
- perinatal and lactation period in diabetic women;
- diabetic angiopathy (complication associated with vascular damage);
- psychopathic disorders;
- third degree hypertension.
Important! A minimum portion of beer is allowed only for stable compensated diabetes. In a state of decompensated disease, ethanol can kill a person.
Dangerous consequences
Excessive one-time consumption of alcohol is manifested by signs of intoxication:
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness;
- visual impairment;
- weakness.
In diabetics, this condition is aggravated by a drop in blood glucose levels. If you are very intoxicated, the patient may not feel a rapid decrease in sugar levels and fall into a hypoglycemic coma. It’s a mistake to think: “It won’t affect me, I’ll just get over the hangover.” A body weakened by diabetes may react inadequately to alcohol. It is important that there is someone close to you who can provide first aid.
With regular abuse of alcohol-containing drinks, the following actively progress:
- toxic hepatitis, hepatosis, cirrhosis;
- depletion of glycogen reserves;
- polyneuropathy and angiopathy of the lower extremities with further development of diabetic foot;
- DKA (diabetic ketoacidosis);
- severe ischemia.
Chronic alcoholization of the body in diabetes is a guarantee of early complications.
The dangers of alcohol for diabetics
Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages may increase the risk of diabetes.
They have a toxic effect on the pancreas, which is responsible for the secretion of insulin.
Resistance to the hormone increases, carbohydrate metabolism is disrupted, the patient becomes obese and liver activity is impaired. Such conditions are dangerous for people already dependent on insulin, because the liver cannot cope with the production of glycogen, which prevents glucose levels from falling under the influence of the hormone.
Alcohol has a detrimental effect on the liver within a few hours. If the patient abused it the night before, hypoglycemia may occur at night.
Alcohol has a negative effect on the activity of the peripheral nervous system, destroying its neurons. It wears out the muscles of the heart, the walls and arteries of blood vessels. Diabetes also contributes to disruption of the nervous system. Drinking alcoholic beverages by a pregnant woman suffering from diabetic disease can be fatal.
The potion has a negative effect on sugar in the presence of an inflammatory process in the pancreas, especially if the patient has decreased organ function and lipid metabolism is disturbed.
Vodka lowers blood sugar levels, while other drinks raise it. Both conditions are potentially dangerous for a diabetic, leading to various negative consequences.
- Alcohol and rheumatoid arthritis. What do you need to know?
Results
Diabetes mellitus does not tolerate neglect. Beer, as an exception, is allowed only in the stage of compensation of the disease, no more than once a week, in a dosage of no more than 0.33 liters. When drinking beer, it is necessary to strictly control glycemia and adjust the dose of medications used (insulin or hypoglycemic drugs). How and how long the patient can live largely depends on compliance with nutritional rules. Since beer is not considered an essential food, diabetics should avoid it.