What is low blood pressure anyway?
Blood pressure is the force with which blood pushes against the walls of the arteries. At the moment when the heart contracts, the pressure is highest - it is called upper, or systolic. In the interval between heartbeats, the pressure in the vessels drops - it is called lower, or diastolic.
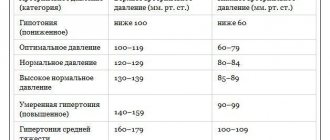
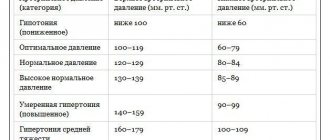
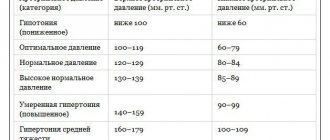
Normal blood pressure ranges from 90/60 to 120/80 mmHg. The numbers 90 and 120 indicate systolic pressure, and 60 and 80 indicate diastolic pressure. If the readings are less than 90/60, the blood pressure is considered low. This condition is called hypotension.
Diagnostic measures
When contacting specialists with a problem of low blood pressure (for example, 100–106 to 60–66), patients are interested in the question of whether this is normal, and if not, how to improve the readings. The doctor must ask the patient about the following points:
- When were such pressure indicators first noticed?
- Associated symptoms.
- What is the patient’s “working” pressure?
- Do the patient and his relatives have any diseases of the cardiovascular system?
- The presence of pathologies of other systems.
- Does the person take any medications, etc.
Hypotension can cause fainting
Blood pressure must be measured several times at intervals of 5–10 minutes. If necessary, daily monitoring of blood pressure with monitoring of pulse and other indicators of heart function is prescribed. Additional methods include ECG, echocardiography, electro- and rheoencephalography, and examination by an ophthalmologist.
Is low blood pressure dangerous?
Many people - most often thin women - live with hypotension for years and feel great. Doctors believe that these people are lucky: they are less likely to suffer from cardiovascular diseases.
However, if your blood pressure suddenly drops below normal levels, unpleasant symptoms may appear:
- blurred vision;
- dizziness;
- fainting;
- nausea or vomiting;
- drowsiness;
- feeling of weakness.
As a rule, at a young age, the health risk is associated not with low blood pressure itself, but with the reasons due to which it falls. The exception is fainting. “This is the most alarming symptom, since it often leads to injuries and accidents,” says Oksana Dikur, general practitioner, cardiologist at the Rassvet clinic. “If hypotension is accompanied by loss of consciousness, you should definitely consult a doctor.”
But for older people, low blood pressure can be really dangerous. Moreover, a drop in diastolic pressure is more dangerous than a decrease in systolic pressure.
“This can lead to deterioration of blood supply to the kidneys and brain, increasing the risk of stroke and kidney failure,” explains Oksana Dikur.
Feeling good with blood pressure 100/60
If the pressure drops sharply, the patient complains of headache, dizziness, pulsation in the back of the head, rapid heartbeat (at a pressure of 100 to 60, the pulse can reach 100 beats/min). Cold sweat, severe weakness appear, trembling in the limbs may occur, and body temperature decreases. The result of a critical drop in indicators is a fainting state requiring emergency assistance.
With chronic hypotension, the patient complains of daily weakness, fatigue, emotional lability, depression, and shortness of breath. With a chronic type of pathology, people get used to attributing their poor health to all sorts of factors, but not to a drop in pressure. The problem is associated with changes in weather conditions, fatigue at work, stress, overeating or, conversely, diet abuse.
What causes hypotension?
If you suddenly change your body position
Get up quickly or, for example, sit up sharply in bed. This is called orthostatic hypotension. When a person assumes a vertical position, blood, under the influence of gravity, rushes to the legs and abdominal area, and the pressure in the vessels drops. In order to raise blood from the legs and normalize blood pressure, the autonomic nervous system increases the heart rate and constricts blood vessels.
Healthy people do not experience discomfort, since this mechanism works very quickly. But in some cases, the autonomic nervous system fails. As a result, the pressure drops, the blood does not have time to rise from the legs, the brain lacks oxygen, and symptoms of hypotension appear. This happens, for example, in pregnant women, in people with certain diseases such as diabetes, and in every fifth elderly person.
Sometimes healthy people experience similar sensations, for example due to heat, and there is nothing to worry about. But if you feel dizzy every time you change position, you need to see a doctor.
If you eat
After eating, blood rushes to the gastrointestinal tract, and to prevent pressure from dropping too much, the autonomic nervous system constricts blood vessels and increases the heart rate. However, in about a third of older people it cannot cope with such a load. This condition is called postprandial hypotension. If this happens, you need the help of a doctor.
If you grow too fast
As you might guess, the problem most often occurs in children and adolescents: due to rapid growth, a malfunction occurs in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. As a result, when you change your posture or bend over, symptoms such as dizziness and fainting appear. This is called nerve-mediated hypotension. Children usually outgrow the problem, and hypotension goes away on its own.
But sometimes neurally mediated hypotension is a sign of serious neurological diseases. In this case, the person needs the help of a doctor.
If you get sick
Blood pressure may drop in people who are dehydrated, those who have had shock, diabetics, and patients with arrhythmias and heart failure. In this situation, doctors seek to cure or control the disease that is causing hypotension.
If you take certain medications
Sometimes hypotension is a side effect of anti-anxiety medications, diuretics, painkillers, or blood pressure pills. In order to solve the problem, it is usually enough for the doctor to adjust the dose of the medication.
Correction of indicators and first aid
To increase the pressure, you must follow the following algorithm:
- Call a team of medical workers.
- Lie on a horizontal surface with the leg end raised or lay the victim down in this way.
- Open a window or direct a fan to provide fresh air.
- Drink sweet warm tea or give the victim something to drink. You can add 10 drops of tincture of eleutherococcus, ginseng or Rhodiola rosea.
- Rub your whiskey with lemon essential oil.
What does blood pressure 120/70 mean during pregnancy?
Monitoring blood pressure is an integral part of monitoring the condition of a pregnant woman, which is carried out already from the 12th week of gestation. Many women experience fluctuations in blood pressure, which is associated with changes in hormonal levels. Thus, the first trimester is characterized by a slight decrease in indicators. Then it increases, reaching a level of 122/75 mm. rt. Art., and lasts about 3 months. The second trimester is characterized by activation of placental blood circulation, which causes increased heart rate and increased blood pressure. If your blood pressure level is 140/90 mm. rt. Art., then it is regarded as normal.
In the third trimester of pregnancy, indicators of 120/70 are regarded as slightly reduced. If a woman suffered from hypotension before pregnancy, then these values may be elevated for her. Warning signs are:
- severe headache, dizziness;
- tinnitus, spots before the eyes;
- weakness;
- lack of coordination;
- feeling of lack of air.
If pathological symptoms appear, you must immediately seek medical help to clarify the cause of the disorder.
Treatment tactics
Dual. It consists of eliminating symptoms and improving the quality of life on the one hand, and on the other hand, fighting the root cause, and this is the most important point.
The list of methods varies from prescribing tonic medications to surgical interventions and the use of hormone replacement therapy. Lower blood pressure can be increased using selective methods, by selecting the right combination of corticosteroid-based drugs and classical tonic drugs.
An important role is played by the normalization of sleep and wakefulness, diet, and the use of vitamin and mineral complexes. Quitting smoking and drinking alcohol will have a positive effect (there is nothing useful in alcohol).
Treatment lasts from several months to a year, followed by a period of maintenance therapy. As a rule, hypotension does not recede on its own and is kept within limits only thanks to medications.
A blood pressure of 120 over 60 is a pathological level. Systemic correction is required under the control of a whole council of specialists.
Conclusion
The optimal difference between systolic and diastolic pressure is 70
is 40 mmHg. But a slight deviation of 10 units up or down is also within acceptable limits.
blood pressure prevention
If the pressure changes by 20 more or less, and you feel normal, most likely there was an incorrect pressure measurement. If your health really gets worse, you should immediately consult a doctor.
In case of difference between systolic and diastolic pressure
is sixty or more, this is the risk of developing heart and vascular diseases. In this case, you must constantly consult your doctor. To make an appointment with our specialist, leave a request on the website or call.
Reasons for a persistently low diastolic reading
The factors for the development of isolated hypotension are diverse. Among the most common are a number of physiological and pathological ones.
Natural. Caused by non-pathogenic changes in the body
- Temporary hormonal imbalances. They develop as a result of several reasons. Puberty. Puberty. Associated with surges in estrogen or androgens. The period falls on the age from 12 to 18-19 years. All this time, the teenager’s blood pressure is in an unstable state, either increasing or decreasing throughout the day. Menstrual cycle, pregnancy. It is difficult for representatives of the fairer sex to tolerate precisely because of vegetative manifestations. A blood pressure of 120 over 60 during pregnancy may be normal. But in any case, diagnosis is necessary. Climax. Both men and women. It is accompanied by a total hormonal imbalance, which can only be corrected by medication.
- Sex and age characteristics. Young girls have a smaller heart size, so their blood pressure is, on average, higher than that of men. This is observed throughout life. The individual norm regarding pulse pressure, however, cannot be more than 40 mmHg for a long period. This is an indication of a pathological process. What kind - you have to find out with your doctor.
- Overwork. This affects the release of stress hormones and the production of toxins that are dangerous to the nervous system. A proper rest is necessary if your own working pressure has not been restored at the end of sleep.
- Heavy physical overload, emotional component. The factor in the development of the problem is the same. You need to come to your senses and take a few tablets of a sedative of plant origin (valerian, motherwort).
- Meteosensitivity. From 20% to 40% of the population suffers from a pronounced reaction to changing weather. This is due to the instability of the nervous system, which cannot regulate the state of the body and adequately increase or decrease blood pressure levels in response to changes in the barometer. This can be solved by taking medications that improve brain nutrition and blood circulation.
These factors are taken into account first. Only then do they look for pathological causes. The latter are more common. Natural ones can be dismissed in the process of initial diagnosis.
Pathological. Associated with the course of a particular disease
The list of such is wide:
- Hypothyroidism. A decrease in the concentration of thyroid hormones as a result of insufficiently active functioning of the organ. Tumors, other neoplasias, injuries and poor nutrition have an effect. A whole complex of symptoms of various kinds arises, which are difficult not to pay attention to. On the other hand, this is at least a small plus. The patient has time to react. The manifestations force one to go to the doctor, since the standard of living is significantly reduced.
- Diabetes. A systemic endocrine disease that destroys the entire body to its core. Both the nervous and circulatory systems suffer. In addition, the excretory tract, connective tissue, bones, etc. It is treated for life. The pressure in such a situation is corrected by constant intake of tonic drugs.
- Pathologies of the adrenal glands based on the type of deficiency of cortisol synthesis. Induced Addison's disease. Occurs with injuries, tumors, and operations on the anatomical site. Requires replacement treatment under the supervision of an endocrinologist. Without the use of medications, blood pressure can drop to critical levels in a short time.
- Pituitary pathologies. Associated with insufficient secretion of corticotropin. The factors causing the problem are different: neoplasia, mechanical damage, etc.
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine and other systemic diseases of the musculoskeletal system and muscle fibers. They cause compression of arteries located in the anatomical area. They provoke a violation of the trophism of brain structures that regulate the normal tone of vascular formations. The body begins to give chaotic signals, provoking jumps in the level of the tonometer, so 120/60 is still a mild option. The process is not always symmetrical; it all depends on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
- Anemia. Develops as a result of bleeding, poor nutrition, and genetic abnormalities. Accompanied by a decrease in hemoglobin concentration and, accordingly, a change in the properties of liquid connective tissue and organ hypoxia. The heart has to work harder to pump blood as it becomes thicker. An important element is the presence of additional, unusual symptoms: brittle nails, hair, cracking and dry skin, problems with teeth, vision, addiction to inedible things.
- Problems with the excretory system. There are a lot of disease options. Ultrasound diagnostics is needed to put an end to the issue. Arterial hypotension with a pressure level of 120 to 60 is the result of a decrease in renin production and disturbances in general hemodynamics (fluid comes out too actively, dehydration is possible).
- Pathologies of the central nervous system. Dyscirculatory changes lead to generalized problems with blood pressure.
Constant smoking, alcohol abuse and other factors of a similar subjective nature also have an effect. It is necessary to understand in more detail.
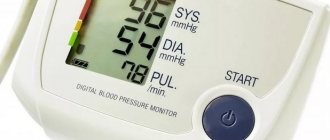
How to measure blood pressure correctly
A special device is used to measure blood pressure - a tonometer. Tonometers are manual (mechanical), semi-automatic and automatic.
Selecting a tonometer
The manual one consists of a shoulder cuff, an air pump (bulb), a stethoscope, and a pressure gauge. The semi-automatic tonometer contains a cuff, a bulb and an electronic unit. An automatic tonometer pumps air on its own and consists only of a cuff and an electronic unit.
It is difficult to measure pressure on your own with a manual tonometer; you will need the help of a person with the necessary skill. However, measurement with a manual tonometer is considered the most accurate. Most often it is used by doctors. Semi-automatic and automatic devices allow you to monitor blood pressure at home or at work without difficulty and outside assistance.
Rules for measuring blood pressure
To obtain the most accurate result, the following rules must be observed:
- the measurement should be carried out in a quiet environment, in a quiet room at room temperature;
- After eating, physical activity, smoking, at least 30 minutes must pass before the procedure;
- Do not drink tea or coffee before measurement;
- Blood pressure should be measured while sitting in a comfortable natural position, the hand should rest on a support approximately at the level of the heart, and be as relaxed as possible;
- During the measurement, you cannot keep your legs crossed, move or talk;
- Blood pressure should be measured on both arms with a break of 10-15 minutes;
- When taking antihypertensive drugs, 1-2 hours should pass before measuring blood pressure.
The results must be recorded in a special diary, noting the date, time of measurement, circumstances that may affect the result - poor sleep, malaise, taking medications.
Why can pressure “jump”?
There are actually many reasons for high blood pressure, but here is a list of the most common:
- The heart does not work as before, its strength is reduced.
- The quality of the blood has changed. The older a person is, the thicker his blood is, which makes it difficult for it to pass through the vessels. Blood thickening can be caused, for example, by diabetes or autoimmune diseases.
- The vessels have become less elastic. Possible causes are poor diet, excessive exercise, and taking certain medications.
- Atherosclerotic plaques due to increased levels of “bad” cholesterol.
- A sharp narrowing of blood vessels due to hormonal imbalance.
- Malfunctions of the endocrine system.
- Hereditary factor.
In most cases, high blood pressure can be stabilized on your own by starting to eat right, eliminating bad habits and stress, and starting to move more. This will allow you to stay healthy for as long as possible and avoid the dangerous complications of hypertension (stroke, heart attack).
If lifestyle changes do not affect the situation, the doctor prescribes antihypertensive drugs that must be taken on an ongoing basis so that the blood pressure remains normal.
Symptoms that require you to see a doctor
As a rule, physiological hypotension does not make itself known by specific symptoms. The maximum that the patient feels is slight weakness and drowsiness. In all other cases, a clinical picture of varying completeness develops.
You can define a list of manifestations as follows:
- Low-grade fever or increased body temperature (this also happens, the exact etiology of the process is not clear).
- Headache (or cephalgia). It is explained by insufficient nutrition of brain structures.
- Dizziness. The vestibular apparatus, centered in the cerebellum, is affected.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting that does not bring relief.
- Intolerance to travel by transport, including water (motion sickness).
- Palpitations (tachycardia) or the reverse process of baracardia.
- Weakness, mental impairment, decreased cognitive function up to dementia, if the process has been going on for a long time.
- Orthostatic fainting with sudden movements and changes in body position.
- Shortness of breath even at rest. Increases with physical activity.
Any of the symptoms presented is a reason to be wary and call an ambulance.
Additional symptoms
Low diastolic pressure against a background of normal systolic pressure is usually accompanied by characteristic symptoms:
- A man has a headache.
- Your heart rate slows or your pulse becomes irregular.
- Dizziness occurs when you suddenly turn your head or come out of the dark into the light.
- Fainting, starting with darkening of the eyes, is possible.
- Memory deteriorates.
- Activity decreases, fatigue occurs even at rest.
- The patient becomes irritable, periods of apathy are replaced by aggression.
With both hypertension and hypotension, a person begins to react sharply to the vagaries of the weather with increased symptoms
The relationship between hypotension and pulse
Normal heart rate also depends on the person's age. In children it is more rapid, but in older people, on the contrary, it is slightly slower. The average heart rate per minute is 60-90 beats. It happens that when blood pressure levels decrease, the heart rate increases, slows down, or remains within acceptable limits. Why and under what conditions does this happen and what does it mean?
What are the reasons for an increase in heart rate (pulse rises to 100 and above) against the background of a drop in pressure:
What does pressure 100 over 40 mean?
- dehydration, for example, due to intestinal infections, stomach upsets;
- bleeding of varying severity;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system (decrease in circulating blood volume, embolism, inflammation of the pericardium);
- acute inflammatory processes of internal organs;
- shock states of various origins;
- pregnancy period;
- taking certain medications.
Bradycardia (decrease in heart rate) against the background of low blood pressure is observed with hypothermia, pregnancy, significant physical activity (professional athletes), certain heart diseases (blockades, arrhythmias), poisoning and pathologies of the thyroid gland. In rare cases, hypotension is accompanied by a normal pulse (70-80 beats per minute).
Blood pressure norms depending on gender and age
Blood pressure is higher in adults than in children; it differs between men and women. In women, changes in blood pressure are affected by pregnancy and menopause.
Blood pressure norms for men and women
Age (years) Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg) male wives husband. wives 10-20 123 116 76 72 20-30 126 129 79 75 30-40 129 127 81 80 40-50 135 137 83 84 50-60 142 144 85 85 60-70 145 159 82 85 70- 80 147 157 82 83 80 -90 145 150 78 79Often young people under 35 years of age do not notice symptoms of high blood pressure. However, they can also develop arterial hypertension, so periodic monitoring in case of existing risk factors and the appearance of complaints is mandatory for timely diagnosis, prevention and treatment if necessary.
In childhood, the walls of blood vessels are more elastic, so normal blood pressure in children is lower than in adults. The indicator increases as the child grows. The most significant change in blood pressure values is observed from birth to one year. Girls and boys have the same blood pressure, the difference appears towards the end of puberty.
Blood pressure norms in children
| Age | Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) | Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg) |
| newborns | 60-96 | 40-50 |
| from 2 months up to a year | 80-112 | 50-74 |
| 1-2 years | 82-115 | 61-75 |
| 2-3 years | 85-116 | 60-76 |
| 3-4 years | 90-118 | 60-78 |
| 4-5 l. | 95-120 | 60-80 |
| 5-6 l. | 100-122 | 60-80 |
| 6-8 l. | 110-122 | 70-82 |
| 8-11 l. | 110-126 | 70-82 |
| 12-15 l. | 110-136 | 70-86 |
| 15-16 l. | 110-136 | 70-90 |
| 16-18 l. | 110-120 | 80-90 |
Treatment recommendations
First of all, it is necessary to normalize your lifestyle. You should do gymnastics daily, preferably in the fresh air. Evening walking, swimming, cycling, and light jogging are excellent options for low blood pressure. You should stop drinking alcohol and smoking and normalize your sleep. And it is also important to correct the diet: give up fried, smoked and fatty foods, include a large amount of vegetables and fruits, grains in the menu.
The prescription of medications depends on the type of hypotension. In the primary form of the pathology, anticholinergics are used, which have a sedative and antispasmodic effect. In order to increase the heart rate (according to indications) and increase the return of blood to the heart, sympathomimetics are prescribed.
And they also use preparations based on herbal and other natural ingredients (tincture of aralia, ginseng, zamanikha, camphor, Pantocrine, Saparal). In the treatment of symptomatic hypotension, attention should be paid to the treatment of the underlying disease that caused the decrease in blood pressure. To regulate blood pressure numbers, it is important to take vitamins:
- Thiamine.
- Riboflavin.
- Niacin.
- Pantothenic acid.
- Pyridoxine.
- Folic acid.
- Cyanocobalamin.
- Ascorbic acid.
- Calciferol.
Important! Hardening helps well, which can be used to prevent a hypotonic state.