The Euroonko clinic in Moscow regularly installs vena cava filters for patients with cancer to prevent the development of pulmonary embolism (PE). We also install vena cava filters in patients with a high risk of developing pulmonary embolism who do not suffer from cancer, for example, with deep vein thrombosis of the leg, with various types of blood clotting disorders and a number of other diseases. The information below will be useful for all patients requiring vena cava filters.
There is no single generally accepted concept regarding surgical prevention of pulmonary embolism in international practice. In the USA, a radical approach has been adopted with the installation of vena cava filters, taking into account the embologenicity of the thrombus. In Western European countries, implantation is recommended only if it is impossible to carry out anticoagulant therapy for pulmonary embolism.
Timely placement of vena cava filters in patients with cancer is part of complex therapy for late stages of cancer, and is quite widely used in routine clinical practice in Western Europe. Depending on the form of cancer and the stage of cancer, vena cava filters are installed in approximately 1.5–6.5% of all patients.
Unfortunately, in domestic clinical practice, due to the low financial resources of the healthcare system, the indications for the placement of vena cava filters are significantly narrowed, which contributes to a high mortality rate and a higher incidence of sudden death compared to data from the US Cancer Registry and leading national cancer registries. countries of Western Europe.
Placement of vena cava filters in the inferior vena cava in the early stages of cancer in patients undergoing active chemotherapy, including high-dose chemotherapy, can reduce the risk of sudden death due to the development of thromboembolism, including pulmonary embolism, by approximately 10–15%.
Installation of a vena cava filter allows not only to avoid pulmonary embolism during therapy with a number of chemotherapy drugs, but also to perform thrombolysis of previously occurring blood clots.
The doctors of the Interventional Surgery Department at Euroonko have accumulated extensive experience in the prevention and treatment of venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, thrombophlebitis against the background of varicose veins in cancer. The interventional surgery department uses both temporary and permanent venous filters.
What is a vena cava filter?
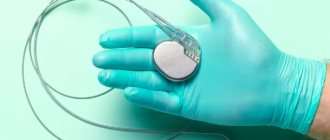
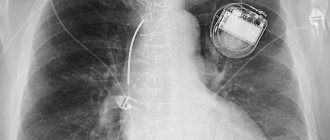
A vena cava filter is a high-tech mesh on a complexly modeled frame or other complex structure. Using X-ray vascular intervention, a vena cava filter is installed into the lumen of the inferior vena cava, just below the entry of the renal arteries into it (infrarenal position).
A vena cava filter installed in the inferior vena cava filters all particles larger than 2–4 mm (depending on design). This allows venous blood flow from the lower extremities and all internal organs to pass freely through the filter, while retaining large clots that could potentially lead to significant thrombosis or PE.
Under the influence of the blood anticoagulation system and anticoagulation drugs taken, for example, warfarin, stuck blood clots dissolve directly on the vena cava filter. If the filter is installed correctly, there is no need for repeated intervention. Modern designs of vena cava filters rarely thrombose.
Treatment methods for pulmonary embolism
In the acute period of PE, it is important to preserve the patient’s life; in the long-term period, treatment is based on preventing possible complications and preventing recurrent cases of PE.
Main directions in the treatment of pulmonary embolism:
- correction of hemodynamic disorders;
- process of removing thrombotic masses;
- restoration of pulmonary blood flow;
- prevention of recurrent thromboembolism.
When diagnosing PE of segmental branches, accompanied by minor hemodynamic disturbances, anticoagulant therapy is sufficient.
Anticoagulants can stop the progression of existing thrombosis.
In hospital settings, it is recommended to use low-molecular-weight heparins, which are free of hemorrhagic complications, have high bioavailability, do not affect the functioning of platelets and are easily dosed when used.
What vena cava filters are installed?
We use the most modern filter models, such as:
- permanent filter TrapEase (Cordis, USA),
- removable filters OptEase (Cordis, USA),
- Guenther Tulip (Cook, USA).
One of the latest innovations in the field of PE prevention is the ALN vena cava filter (ALN, France). This is the world's first vena cava filter that can be left in the vein for life or removed within up to 500 days. This is the longest possible removal period for removable vena cava filters.
The vena cava filter is securely fixed in the vessel wall under the influence of body temperature. The filter has radiopaque markers made of gold rings built into the catheter introducer, which allow you to easily track the movement of the vena cava filter through tortuous vessels. The two-level structure of the filter allows you to effectively capture emboli of various sizes without disturbing the blood flow.
The presence of a vena cava filter in the vena cava does not affect the operation of the magnetic resonance imaging scanner, so a patient with a filter can undergo an MRI examination if necessary.
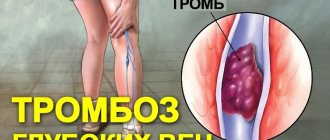
A blood clot lurking against the wall
Under normal conditions, blood clots do not form inside blood vessels. However, if the vascular wall is injured or inflamed, the ability to clot blood increases, or blood flow through the vessels slows down, blood clots can form near the vessel wall (mural thrombus) or even completely block the vessel. A “fresh” thrombus slows down the blood flow even more, promoting the growth of the clot, which quickly increases, acquiring a loose and mobile “tail”. If part of the blood clot or all of it breaks off, then it becomes a dangerous “projectile” carried by the bloodstream throughout the human body.
How is a vena cava filter installed?
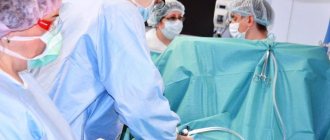
The procedure of implantation of a vena cava filter is currently a common endovascular intervention. The conductor with which the vena cava filter is implanted is inserted through the femoral access and the great saphenous vein, or into the jugular and subclavian veins under X-ray television control. The choice of access is determined by the intended location of the thrombus, since inserting a catheter through thrombosed veins is fraught with fragmentation of the thrombus with the development of pulmonary embolism. As a rule, the vena cava filter is installed at a level below the orifices of the renal veins.
Typically, the operation is performed in an X-ray operating room under short-term anesthesia (superficial anesthesia with propofol). During the implantation procedure, the patient does not feel any pain or discomfort.
Once the catheter reaches the desired level, the vena cava filter opens and the guidewire is removed. No stitches are placed on the skin. The duration of the placement procedure is usually about 1 hour. After implantation of the vena cava filter, a control x-ray is performed to confirm the correct installation and control its location.
We recommend limiting physical activity, preferably bed rest for 1–2 days after vena cava filter implantation. The patient is prescribed antibiotics and anticoagulants for 5–6 days.
After operation
In the first days, the patient must remain in bed. In addition, he is prescribed heparin and antibacterial agents. When puncturing the veins of the neck, the patient’s usual level of activity is allowed after 24 hours, when inserting a filter through the femoral vein - after 48 hours.
After installing the filter, the patient must inform the doctor if the following symptoms occur:
- fever;
- prolonged headache and nausea;
- discomfort and pain in the chest;
- numbness or coldness of the leg;
- bleeding, swelling, pain or redness at the vein puncture site.
What are the indications for installing vena cava filters?
The generally accepted indications for the installation of vena cava filters are:
- Deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities with the presence of non-occlusive (floating) thrombi - a permanent vena cava filter is installed.
- Deep vein thrombosis of the legs with concomitant atrial fibrillation, coronary heart disease, heart failure, as well as in patients with cancer, especially in the later stages.
- Episodes of pulmonary embolism (PE) in the past in the presence of venous thrombosis of the lower extremities at the present time - a permanent vena cava filter is installed.
- Carrying out operations on the veins, laparoscopic interventions for thrombosis of the pelvic veins. At the time of surgery and the immediate postoperative period, a temporary vena cava filter is installed.
The vena cava filter itself does not affect the risk of blood clots, since it does not eliminate the cause of the blood clots. However, it prevents pulmonary embolism from a detached thrombus and reduces the risk of sudden death.
We install more than 20 different types of vena cava filters for patients, both temporary and permanent, from the world's leading manufacturers.
Preparing for surgery
- The doctor will give detailed instructions on how to prepare for the procedure.
- Do not eat or drink anything after midnight before your procedure.
- If you regularly take any important medications, you can take them with a sip of water.
- Do not smoke before and after the procedure. Smokers have a slower recovery after the procedure and are also more likely to have breathing problems during surgery. For this reason, if you are a smoker, you should quit smoking at least 2 weeks (preferably 6-8) before the procedure.
- Tell your doctor if you have any kidney problems or reactions to foods that contain iodine.
What restrictions do patients face after installing a vena cava filter?
When installing universal removable vena cava filters, the patient is under the dynamic supervision of an angiosurgeon or phlebologist for 6 months. If a vena cava filter is installed, taking warfarin is mandatory.
Once the risk of thromboembolism has been reduced, the temporary vena cava filter is removed using an intervention similar to inserting a filter. This operation is also performed in an X-ray operating room by an angiosurgeon under X-ray control.
The fundamental decision to remove the vena cava filter is made after a repeat study of hemodynamics in the inferior vena cava system (including both limbs), when the dynamics of thrombosis resolution is assessed.
The installation of non-removable permanent vena cava filters, even in patients with advanced stages of cancer, is currently practiced relatively little, since a permanent vena cava filter, along with its positive role - preventing thromboembolism - causes obstruction of blood flow in the inferior vena cava basin and the formation of secondary venous insufficiency.
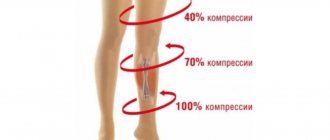
After installing a vena cava filter, the patient lives a normal life. We recommend taking indirect anticoagulants in maintenance dosages. In the presence of concomitant chronic venous insufficiency, it is advisable to undergo clinical observation with a visit to the doctor at least once a month, use phlebotonics and wear compression stockings. In addition, it is advisable to undergo a control duplex scan of the veins of the legs and the inferior vena cava.
Sections of medicine
- Treatment in Israel
- Cancer treatment in Israel
- Andrology
- Urology
- Proctology
- Phlebology
- Cardiology
- Plastic surgery
- Mammalogy
- Gynecology
- ENT diseases
- Ophthalmology
- Neurosurgery
- Orthopedics
- Dentistry
- Cardiac surgery
- Vertebrology
- Oncology
- Bariatric surgery
- Overweight treatment
- Obesity surgery in Israel
- Bariatric surgery in Estonia
- Thoracic surgery
- Rehabilitation medicine
- Medical check up
- Treatment in Germany
- Cardiology in Germany
- Neurosurgery in Germany
- Oncology center Sofia in Moscow
- Proton therapy
- Surgery with the Da Vinci robot
- Sanaviation
- Treatment in Turkey
- Treatment in India
- European Oncology Clinic in Moscow
- Clinic of Neurology and Oncology in Moscow
- Treatment in Finland
- Treatment in Switzerland
- Surgery in Germany – Saxenhausen Hospital
What is the cost of installing a vena cava filter in Moscow?
We bring to your attention a price list from which you can find out the cost of installing vena cava filters at Euroonko:
- Implantation of a permanent vena cava filter made in the USA - 137,500 rubles.
- Implantation of a vena cava filter (made in the USA) with retrograde iliocavagraphy – RUB 179,300.
- Removal of a removable vena cava filter - 117,600 rub.
- Implantation of a removable vena cava filter made in the USA or France - 176,000 rubles.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Blood to protect the body
From a chemical point of view, blood is a solution and suspension consisting of water and many water-soluble and insoluble substances and cells. But blood is also a living tissue, and it has unique properties. It can change viscosity, fluidity, gas and cellular composition depending on the situation.
One of the most important functions of blood is its ability to clot, the ability to quickly form clots called thrombi when necessary. On the other hand, after a certain time, blood enzymes can dissolve clots.
The main function of the blood coagulation system is protective. It allows you not to lose a significant amount of this unique fluid during injuries and wounds. A thrombotic “plug” helps prevent serious complications that arise from bleeding. But, unfortunately, with some congenital or, more often, acquired pathologies, thrombus formation in the body becomes excessive, and, as a rule, in the wrong place and at the wrong time.
Pros and cons of laparoscopy
When using this method of treatment, the body recovers in a short time. The period of hospitalization usually does not exceed 3 days from the moment of the manipulation. The number of incisions is minimal, so they heal quickly without causing severe pain or discomfort.
After laparoscopy, bleeding and other complications caused by mechanical damage rarely develop. No scars appear, so rehabilitation after laparoscopy is much faster than after abdominal surgery.
Among the disadvantages are noted:
- limited working space for the surgeon to work, so difficulties may arise during the operation;
- the use of sharp objects during research or treatment, which require experience and skill, otherwise careless handling can result in damage to vital organs;
- the instruments are inserted without the help of hands, so it is difficult to assess the effort applied to the organ;
- In rare cases, the image on the monitor screen is distorted, so the perception of the picture may differ.
But do not worry about the possible disadvantages of laparoscopic manipulation. Instruments improve, and experienced specialists often work with minimally invasive operating techniques, so they have advanced surgical skills.
Many patients are nervous when surgical diagnostics are prescribed. But fears are in vain - this method most accurately establishes a diagnosis if other data is insufficient. A significant plus is that if a pathology is detected during the examination, the surgeon can immediately remove the tumor or affected organ.
Our doctors
Malakhov Yuri Stanislavovich
Doctor - cardiovascular surgeon, phlebologist, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Doctor of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
Experience 36 years
Make an appointment
Drozdov Sergey Alexandrovich
Cardiovascular surgeon, phlebologist, Doctor of Medical Sciences
47 years of experience
Make an appointment