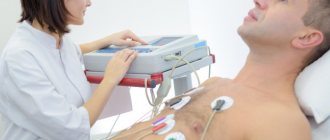
In our pharmacies, it has recently become impossible to buy antibiotics without a prescription and cough medicines with codeine. But there are still a lot of other drugs that we can purchase without going to the doctor. “AiF” learned about some of the most dangerous consequences of self-administration of popular tablets from a professor at the Department of Hospital Therapy of the First Moscow State Medical University. Sechenov Sergei Yakovlev .
Nasal drops, cough medicines
Many cold medicines contain herbal ingredients. You need to be careful when prescribing such drugs to people with bronchial asthma and other allergic diseases. Quite often, the course of bronchial asthma worsens when taking various herbal antitussives and expectorants. It should also be remembered that antitussive drugs can slow down recovery from acute bronchopulmonary infections - bronchitis, pneumonia: cough suppression inhibits the cleansing of the bronchi from pathogenic microbes. Nasal drops with long-term uncontrolled use can cause atrophy of the nasal mucosa, which can lead to chronic ENT diseases. In addition, in hypertensive patients, uncontrolled use of nasal drops may reduce the effect of antihypertensive drugs, and the pressure may ultimately increase.
Pathophysiological mechanisms of high blood pressure in CKD
The relationship between arterial hypertension and renal pathology always develops in two directions. It is known that patients with CKD are most often people with high-risk hypertension phenotypes (we are talking about resistant forms, “nocturnal” hypertension and its latent course). If hypertension occurs latently, target organs are affected. Thanks to recent research, a number of patterns have been identified. For example, if hypertension has a latent course, this is usually associated with:
- with a high risk of left ventricular hypertrophy;
- with the appearance of proteinuria;
- with a decrease in GFR.
In addition, latent forms of arterial hypertension are always associated with:
- with diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- with chronic kidney failure in the terminal stage;
- with any cause of death.
In any case, latent hypertension must continue to be carefully studied, with the constant introduction of rational diagnostic and therapeutic methods.
It is customary to talk about resistant arterial hypertension in cases where, when prescribing at least three antihypertensive drugs (subject to optimal dosage), the pressure remains at the same high level and the target level cannot be achieved during therapy.
As for the pathophysiological mechanisms of the development of arterial hypertension in CKD, it is complex and has many predisposing factors, in particular:
- sodium retention in the body;
- increased intracellular volume;
- intensive work of the parasympathetic nervous system;
- intensive operation of the RAA system;
- endothelial dysfunction.
Recently, researchers have been providing a lot of information about the homeostasis and regulation processes of water and sodium in the body. No less relevant is the discussion of multi-organ effects that cause:
- limiting water consumption;
- prescribing a diet with a high salt content;
- drug vasopressin;
- level of sodium accumulation;
- excretion of sodium by the kidneys.
It has been proven that the kidneys and cardiovascular system are negatively affected by impaired sodium and water metabolism. If the body reacts poorly to a high-salt diet, it is most often associated with an increase in the incidence of both hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Prescription of drugs containing erythropoietin is also associated with both hypertension and CKD. Research shows the multifactorial mechanisms of this connection. For example, there are patients with CKD who cannot quickly adapt to the fact that the red blood cell volume becomes higher due to:
- decreased glomerular filtration rate;
- strong vascular resistance;
- hypertrophy of the left ventricle of the heart.
When using EPA, physicians should be extremely careful, regularly monitoring the rate at which hemoglobin levels in the blood increase (in this case, it can be difficult to control blood pressure).
Arterial hypertension in patients on dialysis occurs due to a number of reasons:
- high volume of fluid in the body;
- increase in sympathetic hyperactivity;
- intensity of operation of the RAA system;
- atherosclerotic changes, etc.
In chronic kidney disease, uremic toxins constantly accumulate in the intestine, negatively affecting its microflora, as well as metabolic processes. Once in the blood, endotoxins aggravate the inflammatory process and damage the kidney structure, which, unfortunately, worsens the prognosis of the disease.
Painkillers
We almost always assign them to ourselves. The most popular antipyretic and pain reliever is paracetamol. Often their temperature is reduced, but they do not look at the maximum allowed daily dose and take it for more than 3 days. As a result, acute toxic liver damage can develop - drug-induced hepatitis, sometimes with severe liver failure.
Painkillers from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - diclofenac, ibuprofen, ketorolac, indomethacin, etc., which are often used to treat headaches, pain in the joints, and spine, should not be taken independently for more than 2-3 days. If the pain does not go away, you should consult a doctor. One of the most common complications is erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract. A person took a pill - it didn’t help, took 2-3 without reading the instructions, and developed an ulcer or even worse - bleeding from this ulcer.
In patients with bronchial asthma, taking NSAIDs can provoke asthmatic attacks. NSAIDs, in particular painkillers, reduce the effect of antihypertensive drugs - this should be taken into account by hypertensive patients. All NSAIDs can cause acute drug-induced liver or kidney damage, sometimes severe, although the risk of these complications varies between drugs in this group. In recent years, evidence has emerged that regular use of certain NSAIDs increases the risk of acute myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke.
Problems of chronic kidney disease
Now CKD represents a real epidemiological problem, since the number of patients suffering from it is increasing. Prolonged and recurrent course of the disease leads to the development of end-stage renal failure, resulting in huge costs for the healthcare system.
As kidney function gradually decreases, arterial hypertension also increases, which, as a rule, always accompanies CKD.
Hypertension is an equally serious medical problem, since it is the main cause of the development of:
- all types of strokes;
- pathologies of the heart and blood vessels.
In this case, chronic kidney disease can act both as a cause of arterial hypertension and as its complication if the disease proceeds uncontrolled.
The prevalence of hypertension and CKD among adult patients looks something like this:
- AH - from 25 to 30%;
- CKD - about 15%.
If a person already suffers from chronic kidney disease, he is also diagnosed with arterial hypertension. Conducted epidemiological studies indicate that from 67 to 71% of patients suffer from hypertension, and the percentage of elderly people makes up 82% of the total number of clinical cases. When CKD progresses to the later stages of its course, hypertension is observed in 90% of patients.
When a patient is on dialysis, the frequency of hypertension changes, since the methods of controlling blood pressure are different (pre-, post-dialysis, outpatient, etc.). However, research shows that hypertension affects:
- from 50 to 80% percent of patients undergoing hemodialysis;
- about 30% of those undergoing peritoneal dialysis.
It has been said many times that arterial hypertension can be both a cause and a result of the development of chronic kidney disease.
The prevalence, severity level and ability to control the disease are influenced by:
- causes of renal pathology;
- albumin level in urine;
- hereditary factor;
- socioeconomic reasons.
Ethnic and racial factors should also be taken into account.
Blood pressure tablets
Many people treat hypertension on their own. I took my blood pressure and went to the pharmacy and bought pills from my neighbor. Usually these are drugs from the group of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (enalapril, captopril, etc.). Doctors themselves prescribe them most often. Before taking it, you need to make sure that there are no kidney diseases that may not manifest themselves in any way. Otherwise, the medicine will become a catalyst for the disease. If there is bilateral stenosis of the renal arteries, then taking the drug can lead to a sharp decrease in pressure, up to loss of consciousness and threat to life. Such drugs can increase creatinine levels. This is fraught with serious complications in case of undiagnosed kidney diseases. The patient may develop kidney failure with retention of urine and all toxins in the body, which is also deadly.
According to modern recommendations, doctors avoid prescribing short-acting drugs (captopril, nifedipine, etc.). They quickly reduce blood pressure, but after an hour or two the pressure rises sharply again, which can lead to strokes and heart attacks. It is preferable to take drugs that reduce blood pressure gradually, over a long period of time, and are taken 1-2 times a day.
Statins, cholesterol-lowering medications, can also be purchased freely at pharmacies. It has been proven that lowering cholesterol and normalizing lipids helps reduce the risk of developing acute myocardial infarction, stroke, and certain arterial diseases. However, with self-prescription and uncontrolled use of statins, liver damage and severe muscle damage can develop. A connection has been established between long-term use of statins and serious brain damage - memory loss, impaired thinking, even dementia. Not all patients should be treated with statins, and sometimes the risks of complications outweigh the potential benefits. It is safer to reduce high cholesterol with diet and physical activity.
Rational combinations of antihypertensive drugs
Lecture transcript
XXVI All-Russian Educational Internet Session for doctors
Total duration: 20:10
Oksana Mikhailovna Drapkina, executive director of the Internet Session, secretary of the interdepartmental council on therapy of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences: - It is with great pleasure that I give the floor to Professor Maria Genrikhovna Glezer. "Rational combinations of antihypertensive drugs"
00:10
Glezer Maria Genrikhovna, Doctor of Medical Sciences:
– Dear colleagues. Arterial hypertension is currently the No. 1 risk factor. In 2010, it was recognized by the World Health Organization as the No. 1 killer. It is high blood pressure that determines more than 50% of all cases of coronary heart disease and strokes.
What are the classes of drugs for long-term treatment of arterial hypertension. 8 classes. But we must first use the first 5 classes:
- diuretics;
- beta blockers;
- ACE inhibitors;
- sartans;
- calcium channel blockers.
Alone or in combination, these drugs are used to reduce the risk of complications.
There is a sufficient evidence base for these first five drugs. These classes of drugs may reduce cardiovascular morbidity and death.
What are the main pathophysiological mechanisms involved in increased blood pressure?
This is the activation of the renin-angiotensin system. Activation of the sympathetic nervous system. Increase in circulating blood volumes (changes in water and electrolyte balance).
Ultimately, these systems will lead to changes in intracellular calcium transport. The drugs that we have affect different stages of pathogenesis.
Beta blockers, sympatholytics, imidazoline receptor agonists - for increased activity of the sympathetic nervous system. Diuretics – for increased circulating blood volume, lipid metabolism disorders. Calcium antagonists – to change intracellular calcium transport. 3 groups of drugs (inhibitors, sartans and direct renin inhibitors) - on the activated rhinin-angiotensin system.
We know well from clinical practice that all patients with arterial hypertension are different. The contribution of each pathogenetic mechanism may vary from person to person. For some, an increase in circulating blood volume prevails. Some people have predominantly increased activity of the renin-angiotensin system. Some people (especially young people) experience an increase in the activity of the sympathetic nervous system.
It is clear that it is most often impossible to solve the problem with one class of drugs.
02:34
Athena Study.
More than 2,000 women in the Russian Federation were analyzed. Where hypertension was controlled, 2-component, 3-component or more drugs were more often used to treat high blood pressure.
Where there was no control (in fact, this was the majority), either these patients were not treated at all, or monotherapy was used. This is further evidence that different classes of drugs need to be combined in order to achieve blood pressure goals.
Categories of patients most likely to require combination therapy:
- persons who have a significant increase in blood pressure (above 160/100 mm Hg);
- patients with diabetes mellitus (DM);
- people who have certain lesions of organ systems. For example, kidney damage;
- left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH);
- people who smoke, are obese, have sleep disordered breathing.
Combination therapy is the key to success in achieving the goal (based on the pathogenetic mechanisms that I have already mentioned and the complications that often occur in patients).
What do we call a goal? The best evidence to date is that the goal is to achieve target blood pressure values.
In September 2010, there were some changes to the target values. Now, regardless of the degree of risk, they try to keep the pressure below 140 and 130. Up to 140 mm Hg. Art. systolic and 90 – 80 mm Hg. Art. by diastolic.
Not a single large study (probably how they were structured) has proven that a decrease of less than 130 and 80 mm Hg. Art. provides an additional reduction in morbidity and mortality. At the same time, a decrease from 130 is a very difficult moment, requiring a lot of effort and financial costs.
In persons over 80 years of age, based on data from the HYVET study, target values for systolic pressure are set at less than 150 mmHg. Art. Low numbers remain with significant proteinuria.
05:04
A meta-analysis of 147 studies in older people aged 60–69 years showed that while one standard-dose drug reduces the risk of coronary heart disease by 25% and stroke by 35%, then a combination of three drugs at half the dosage reduces the risk of developing both coronary heart disease and stroke is almost twice as high.
A very interesting analysis was published in 2009. A 2-drug combination has been shown to be 5 times more effective in lowering systolic blood pressure (SBP) than doubling the dose of either drug class. Be it beta blockers, diuretics, inhibitors, calcium antagonists. This is proof that it is combination therapy that allows you to achieve the desired values.
In addition, combination therapy can undoubtedly lead to a faster, more pronounced reduction in blood pressure.
The VALUE study clearly showed: if during the first month from the start of treatment the pressure decreases by more than 10 mm Hg. Art., then the number of fatal/non-fatal cardiovascular events, strokes and death from all causes becomes significantly less than in those people who did not achieve a reduction during the first month.
06:29
The second point that you should pay attention to: you should still strive to achieve the target numbers within 6 months. This is less than 140 mmHg. Art. Then all outcomes, including fatal events, heart attacks, strokes, deaths from all causes, and hospitalization will be significantly lower.
In my opinion, how should the decision-making process proceed when treating patients with arterial hypertension.
Certainly. We can start with monotherapy. This ensures the safety of treatment for our patients. If you see a person for the first time and you do not know what the reaction will be to antihypertensive therapy, you can start with monotherapy.
But you don’t need to go further in this vicious circle: you reached the maximum increase in dose, you became convinced that it was ineffective, you changed the drug, and so on. Patients stop this treatment, they leave the doctor.
Correct decision-making process: Tried monotherapy. We realized that it was quite effective and safe, and switched to combination therapy. We are moving further along the path of increasing doses of combination drugs. This is the principle I preach.
Plus one: the patient came - the treatment was not effective enough - the next class of drugs was added. If something else doesn’t suit you, the next class is added. Then you will be more likely to succeed.
When it comes to combination therapy, they always say: “This is polypharmacy, it is bad for patients, and so on.” Correct, because combination therapy must undoubtedly be rational.
What is rational therapy? This is when the effectiveness of treatment increases, while the incidence of side effects decreases.
This can lead to an increase in efficiency. We use different classes of drugs, influence different parts of the pathogenesis of the disease and eliminate the activation of counter-regulatory systems. If you use drugs in smaller dosages, then dose-related side effects may, of course, be reduced.
The side effects of one of the components can be eliminated by using another component.
08:51
Recommended combinations of drugs for hypertension.
Diuretics plus inhibitors or sartans. Best time to use: Where there is a high risk of heart failure.
Beta blockers and dihydropyridine calcium antagonists. When is it best to use: for ischemic heart disease.
Metabolically neutral class of drugs, sartan inhibitors, calcium antagonists. In persons at high metabolic risk.
Today, this is probably how one can imagine rational combinations. It's a diuretic plus something. Anything – these are inhibitors or sartans.
Another type of combination. Calcium antagonists plus ACE inhibitor or calcium antagonists plus sartans. Dihydropyridine calcium antagonists are used with beta blockers in patients with coronary artery disease.
Currently, the combination of diuretics plus calcium antagonists is considered irrational because this combination almost doubles the risk of myocardial infarction. Diuretics plus beta blockers had the best effect in this case.
The final picture looks like this: 1) calcium antagonists plus inhibitors or sartans and 2) diuretics, inhibitors and sartans.
The slide shows the recommended combinations of antihypertensive drugs in a trapezoid.
This trapezoid is considered the most rational today.
I took the liberty of slightly modifying the picture shown in the European recommendations. I drew a triangle. At the top I put a group of drugs that inhibit the activity of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) plus diuretics or plus calcium antagonists. Or the three of us together in the center of the class. There will be effective treatment.
What is the rationale for saying that a combination of diuretics, inhibitors or sartans is an effective and rational combination. It is known that diuretics and inhibitors (sartans) are powerful antihypertensive drugs with pronounced organoprotective properties that can reduce the incidence of morbidity and mortality in arterial hypertension (AH).
The enhancement of the hypotensive effect is due to the fact that conditions are created for the most pronounced action of both components. The activation of counter-regulatory mechanisms is eliminated: diuretics reduce sodium levels, thereby stimulating the production of renin. This leads to a more pronounced antihypertensive effect of drugs that inhibit the activity of the angiotensin system.
At the same time, inhibitors or sartans, by reducing the production of aldosterone, reduce the excretion of potassium from the body, which is always not good when prescribing diuretics. In addition, inhibitors and sartans have a beneficial effect on purine metabolism and reduce the severity of hyperuricemia.
11:50
The combination with diuretics allows you to achieve the same reduction in blood pressure 4 weeks earlier compared to monotherapy with any of the drugs. This leads to the fact that better treatment results can be achieved.
ACE inhibitors (in general, probably the same with sartans) are drugs with pronounced organotensive properties. They influence vascular remodeling, reducing or normalizing the ratio between the lumen of blood vessels and the intima-media complex. This is very important for persistently maintaining blood pressure at normal levels and avoiding crises. The data are given for one of the long-acting ACE inhibitors - the drug Lisinopril. In our country it is often used in the form of the drug “Diroton”. Normalization of the vascular ratio in arterial hypertension.
Indicators related to heart function improve. In particular, improving the diastolic function of the heart. The ratio of peak E to peak A returns to almost normal. The time of isovolumic relaxation improves, the diameter of cardiomyocytes decreases. It is very important that myocardial fibrosis is reduced in patients with arterial hypertension. This is one of the first steps to developing a particular form of heart failure. Heart failure, which is caused by hypertension with preserved ejection fraction.
13:27
ACE inhibitors are known to work very well in obesity because the activity of the renin-angiotensin system is increased in obesity. Each fat cell produces the angiotensin gene in an amount equal to 70 liver cells.
One of the first studies that was conducted demonstrated that lisinopril was effective in approximately 60 patients. Hydrochlorothiazide (HTC) is less effective. The most important thing is that this effect is detected at doses of “Lisinopril” of 10 mg, and “Hydrochlorothiazide” - 50 mg. The side effects of Hydrochlorothiazide may already be quite pronounced.
A very interesting study was conducted in Russia - the Desire study. This study showed that the use of lisinopril can normalize the abnormal daily blood pressure profile. In particular, Lisinopril in women halved the night-picker type when there is a sharp increase in blood pressure at night.
Another achievement that was shown in this study. The use of the drug in the evening allows to normalize blood pressure to a greater extent and reduce the disturbed profile. This is important because night-pickers have a higher incidence of strokes, adverse events, and so on.
Combination with diuretics. Diuretics are one of the most important classes of drugs for the treatment of arterial hypertension. Returning to the Athena study, I would like to say that the difference is in the prescription of drugs where it was ineffective: diuretics were used less often. All other classes were used approximately equally. If diuretics are not prescribed, then it is even difficult to say that something is effective or ineffective.
15:22
Two studies: UKPDS and LIFE. In the UKPDS study, the target blood pressure was 160/90 mmHg. Art. 60% of patients were already on diuretics. In the LIFE study, where the target numbers were 140/90 mmHg. Art. 90% of patients required diuretics.
In our country, the use of diuretics is somewhere around 30%. This is not a sufficient purpose. According to the LIFE study, people who received diuretic drugs had a 30-40% lower risk of various adverse events (cardiovascular death, heart attack, stroke), and a 45% lower overall mortality rate. This is a very important class of drugs that should be used in combination therapy.
I'll say it again. We can say that hypertension is resistant to treatment if a combination of three antihypertensive drugs prescribed in adequate dosages does not reduce blood pressure, but one of these drugs is a diuretic. Thus, this is a very important way to achieve target blood pressure values.
The use of ready-made combination forms is an easier path to success in treating patients with arterial hypertension.
Where hypertension was controlled, a higher percentage of cases used preformed combination dosage forms than in groups where there was no sufficient effect.
I want to show you one more study. Where a combination of Lisinopril and Hydrochlorothiazide was used (in our country, the drug Co-Diroton), patient adherence to treatment was higher than when Lisinopril and Hydrochlorothiazide were used in 2- x different tablets.
The creation of finished dosage forms follows the path of rational combinations, that is, a diuretic plus an ACE inhibitor, or a diuretic plus sartan. Or a combination based on calcium antagonists, to which inhibitors, sartans or beta blockers are added in the treatment of patients with coronary heart disease.
Now a drug has been released that contains a combination of 3 groups. This is Amlodipine plus Valsartan plus Hydrochlorothiazide. This is the right direction: when you have selected certain dosages, then you can already use ready-made combined forms.
In a nutshell about the combination of calcium antagonists with inhibitors or sartans. Calcium antagonists are good at reducing the risk of stroke, inhibitors are good at reducing the risk of myocardial infarction. This provides a reduction in the risk of major cardiovascular events.
18:14
Advantages and disadvantages of mono- and combination therapy for arterial hypertension.
Of course, if you use combination therapy, there is always a higher response rate. This is a very high possibility of dose titration, because you can take a quarter of a tablet from one package, a full tablet from another, and so on. The incidence of side effects is lower if we use rational combinations.
But it becomes difficult to accept. Patients with hypertension will not use anything that is complicated. As soon as the necessary dosages have been selected, you need to switch to fixed combinations, which has an advantage in absolutely all positions.
In conclusion, I want to say what rational combination antihypertensive therapy is. This is an impact on different parts of the pathogenesis of hypertension and elimination of the activation of counter-regulatory mechanisms. Based on this, the effectiveness of treatment increases. When it is effective, people will be more committed (commitment increases).
A good combination is a decrease in the frequency of side effects - which means an increase in adherence. Increasing adherence means increasing the effectiveness of treatment.
Let's look at the second part of this circle. Increasing efficiency, increasing adherence means decreasing cost. Any change in therapy entails, of course, an increase in the cost of treatment. And when it’s not so expensive, people will be more committed. They will better follow the doctor's orders. You should always think about this.
Thank you for your attention.
Oksana Drapkina: Thank you very much, Maria Genrikhovna.
Antibiotics
Some macrolide antibiotics (azithromycin, clarithromycin) and fluoroquinolones (levofloxacin, moxifloxacin) are contraindicated for people with heart disease, as they can cause dangerous arrhythmias, especially when taken simultaneously with certain allergy and antifungal medications. Amoxicillin/clavulanate or azithromycin, often prescribed in outpatient practice, can cause liver damage. Fluoroquinolones and macrolides can inhibit the function of the central nervous system, reducing attention and reaction. Taking them is incompatible with driving a car. But we will not find warnings about this in the instructions for the antibiotic. In recent years, severe diarrhea and colitis caused by clostridia have become relevant. And all antibiotics, if taken incorrectly, can cause resistance in microorganisms - next time they may simply not help.
Blood pressure control and its targets
Despite the high level of awareness of patients with CKD about hypertension, it is not always possible to control blood pressure. For diagnostic purposes, blood pressure is most often measured either randomly or in an outpatient setting. Thanks to ambulatory blood pressure measurement, it is possible to further evaluate its variability during the day. Unfortunately, not all patients with CKD regularly monitor their blood pressure; therefore, from 30 to 60% of patients cannot achieve its target values. It is their target organs that may be damaged in the future.
Thus, regular blood pressure monitoring ensures:
- reducing the risk of complications from the heart and blood vessels;
- reduced risk of cerebral complications;
- reduction in mortality rate;
- prevention of irreversible processes associated with kidney failure.
The optimal blood pressure values for people suffering from chronic kidney disease still remain controversial among specialists, despite the fact that clinical studies have already made it possible to give specific and clear recommendations:
- upper “digits” of blood pressure - 140/90 (albuminuria - less than 30 g daily);
- 130/80 (albuminuria - more than 30 mg daily).
For patients with CKD and a high level of cardiovascular risk, the optimal target blood pressure for them is 130/80.
Tablets "from the stomach"
The most popular among them are antispasmodics such as no-shpa, drotaverine and analogues. They can mask serious surgical situations called “acute abdomen”: acute appendicitis, acute cholecystitis, which need to be treated under the supervision of a surgeon, perhaps even operated on. If you relieve pain with pills, you can progress surgical pathology to an extremely dangerous state - inflammation of the peritoneum, or peritonitis, which poses a direct threat to life. And don’t forget that the much-loved activated carbon can absorb not only toxins, but also other substances, including tablets. So their effect may be reduced when taken simultaneously with an absorbent.
Link to publication: aif.ru
Diagnostics
The “Clinic of Modern Medicine” has a powerful modern laboratory and technical base, which allows you to quickly conduct a comprehensive study and promptly obtain reliable results. The following studies will help determine whether hypertension has a renal component:
- urine tests (general, according to Nechiporenko, bacterioscopy of urinary sediment),
- blood test (general, urea, creatinine),
- Ultrasound, MRI of the adrenal glands,
- excretory urography,
- angiography of the renal arteries,
- radioisotope radiography,
- kidney biopsy.
Differential diagnosis makes it possible to accurately identify pathology, determine the type of hypertension, its stage and severity, which allows the doctor to select the most effective treatment regimen.
Precautionary measures
- They start taking the prescribed drug with a small dose - for the first couple of days they take a quarter of a tablet. Gradually the dose is increased to normal. This way the body adapts better. The course is completed by reducing the dose.
- The first effect appears only 2 weeks after the start of treatment. Sustained action - after six months. All this time you need to take the drug without skipping or breaks.
- The products cannot be combined with melatonin, St. John's wort, products and dietary supplements based on sibutramine, 5-NTR. The combination of the two can increase serotonin to dangerous levels. They also cannot be combined with monoamine oxidase inhibitors. When writing a prescription , the doctor takes these points into account.
- to take antidepressants in parallel with visits to a psychotherapist. If the drugs normalize the biochemical processes in the body, then this doctor will help normalize the psychological state after depression.
Blood pressure norms by age
There is no definite answer to the question “what is a person’s normal blood pressure?”, since, as we said above, everyone has their own characteristics of the body. According to medical indicators, the normal pressure for people 20-40 years old is 120/80 mm Hg. Art.
At the age of 16-20 years, a person may have slightly low blood pressure (approximately 100/70 mm Hg.
), and this is a physiological norm.
Blood pressure norms by age
Photos from open sources
With age, as shown in the table, both systolic and diastolic pressure increase.
To control your blood pressure and detect problems in time, you need to be able to use a tonometer and keep a special blood pressure diary. It is advisable to have this device at home, no matter what age you are.
What should normal blood pressure be and how to treat hypertension.
October 20, 2021
1387
5
1
Content
- Blood pressure: what is it?
- Pressure standards
- Blood pressure norms by age
- How to measure blood pressure correctly?
- Why can pressure “jump”?
- How to choose blood pressure pills
- The most popular blood pressure pills
- Veroshpiron
- Verapamil
- Captopril
- Bisoprolol
- Losartan
Each person's blood pressure norms are individual; this indicator is influenced by many factors. Nevertheless, there are average medical indicators that need to be guided by. Medical pressure standards help the doctor determine that there is a health problem.
Pressure can change depending on a person’s age, time of day, etc. We tell you what normal blood pressure a person has at a certain age, why it changes, and what is considered a deviation.
What is meant by depression
Doctors have been familiar with it since the times of Ancient Greece and Egypt. Hippocrates described it as melancholy - a condition that is accompanied by anxiety, despondency, insomnia, refusal of food, and irritability. Most often, the cause is childhood trauma or severe, frequent stress in adulthood. There are many provoking factors: the death of a loved one, worsening living conditions, alcoholism, brain diseases. Such cases are referred to as psychogenic depression.
The second type is endogenous. The problem does not arise from major external shocks, but from internal causes. A person is constantly dissatisfied with himself and exposes himself to criticism. Many patients have panic attacks and are haunted by feelings of fear and anxiety.