The mechanism of development of sinus arrhythmia
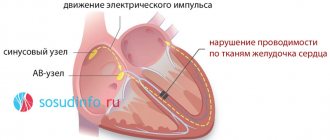
The sinus node is a group of cells in the wall of the heart that produce an electrical impulse.
It is in the sinus node that a normal heartbeat impulse begins to form. It flows along fibers of the heart wall called the conduction system. This system diverges into many fibers, and the smallest of them end in each fiber of the heart wall. This mechanism ensures rhythmic and harmonious functioning of the heart (contractions occur at equal intervals, maintaining the optimal frequency within 60-90 per minute). It is the conduction system that ensures the correct sequence of contractions of the heart chambers. Failures in this system provoke the development of heart diseases, against the background of which heart rhythm disturbances develop.
According to the severity, this pathology is of two types - moderate and severe.
Moderate sinus arrhythmia is characterized by mild symptoms or occurs without obvious signs, and is more often recorded in childhood and adolescence.
Severe sinus arrhythmia is more common in older people, is characterized by obvious clinical manifestations, and is combined with various diseases.
Sinus rhythm disorders
Deviations in the rhythm, frequency and sequence of heart contractions indicate the development of pathological processes in the main organ. The pacemaker migrates - a periodic change in the center of impulse formation. At this time, the activity of the sinus node is suppressed and then restored again.
Table "Deviations in sinus contraction"
| Violations | Signs of change | Possible diseases |
| Increased heart rate | The pulse increases to 110 or higher beats per minute, while the general cardiogram does not change and the main indicators on the ECG remain normal | Tachysystole or ventricular tachycardia |
| Slow heart rate | Decreased activity of the sinus node, resulting in decreased ventricular oscillation | Bradysystole |
| Change the number of heartbeats to 45 and below in 60 seconds. Rhythm indicators on the ECG do not change, with the exception of the P-P intervals (increases to 0.21 seconds) | Bradycardia | |
| Irregular rhythm | Heart rhythm disturbances. Unstable pulse on the ECG can be seen by the difference in the intervals between RR | Arrhythmia |
| Rigid rhythm | Accelerated contraction of the heart, in which there are no natural vibrations and reactions | Autonomic regulation disorders |
| Sinus node damage |
Tachycardia and bradycardia can be temporary and represent a reaction to external stimuli (physical activity, emotional stress, stress). In this case, a slow or accelerated pulse is not considered pathological. If deviations are observed on an ongoing basis, we are talking about heart rate disorders that require medical intervention.
The phenomenon when a ventricular rhythm appears on the cardiogram is also considered a pathology. This suggests that the impulses do not come from the sinus node, but are formed in the atria or atrioventricular node (development of blockades and disruption of the main functions of the main organ).
Causes of sinus arrhythmia
There are several groups of causes that provoke this pathology. The key provoking factor in the development of severe sinus arrhythmia is disturbances in the functioning of the heart, especially coronary artery disease. During ischemia, the heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen, resulting in hypoxia. It is usually accompanied by pain in the heart area.
Another common precipitating factor is myocardial infarction. With this pathology, as a result of hypoxia, part of the heart muscle dies. Subsequently, scarring occurs in this area of the heart.
Heart failure causes the heart's pumping mechanism to become disrupted. This phenomenon is also accompanied by disturbances in heart rhythm. Cardiomyopathy causes structural changes in the heart muscle and provokes arrhythmia.
Heart rhythm disturbances are possible for reasons not related to the functioning of the cardiovascular system (for example, as a result of bronchitis, asthma, vegetative-vascular dystonia). In cases of dysfunction of the nervous system, sinus arrhythmia is usually moderate. Also, non-cardiac provoking factors include pathologies of the adrenal glands and diabetes mellitus.
Often reversible sinus arrhythmia develops due to the use of glycosides, diuretics and antiarrhythmic drugs. The peculiarity of sinus arrhythmia of the heart provoked by alcohol or smoking is that this is an irreversible disorder, which means that it will not go away, even if the patient completely gives up bad habits. However, in people who have stopped smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages, this pathology is mild.
During pregnancy, sinus arrhythmia is provoked by physiological characteristics; treatment is usually not necessary, since the pathology goes away on its own after childbirth.
Causes of sinus arrhythmia in children and adolescents
In children, the factors that provoke this disease are usually heredity, congenital disorders of the heart, acquired pathologies of cardiac activity, and the consequences of previous diseases.
The factor of heredity is of particular importance. If one of the parents has a predisposition to heart disease, then there is a high probability that this tendency has been passed on to the child. Children at risk are under special supervision by a doctor.
Congenital heart rhythm disorders are often associated with problems that arose during fetal development. Acquired arrhythmias can develop as a result of severe emotional shocks.
In adolescents, this pathology is recorded during puberty. The reason for the phenomenon is the increased function of hormone-producing organs. In this case, treatment for sinus arrhythmia is also not necessary, since after puberty it goes away on its own.
Respiratory and non-respiratory sinus arrhythmia in children
This pathology in children can be respiratory or non-respiratory in nature. The peculiarity of respiratory sinus arrhythmia in children is that this phenomenon is associated with respiratory movements: inhalation is accompanied by an increase in heart rate, and exhalation is accompanied by a decrease. Such rhythm disturbances are often observed in infants with intracranial hypertension syndrome, postnatal encephalopathy, as well as in premature infants.
In overweight children, arrhythmia can manifest itself during physical activity. Provoking factors include rickets, which affects the excitability of the nervous system. Sinus arrhythmia in a child at 6-7 years old and 9-10 years old, that is, during rapid growth, is a fairly common occurrence.
Sinus respiratory arrhythmia in children does not affect their well-being and does not require treatment with medications.
Non-respiratory arrhythmia is less common and is usually provoked by various diseases. This disorder can be constant and paroxysmal. An attack of sinus arrhythmia in a child can occur once every 1 year or several times a day. Typically, in such conditions, the main pacemaker continues to provide the heart with the correct rhythm, and changes leading to arrhythmia occur in the conduction system of the heart or in its cells.
Heredity may be a factor in the development of non-respiratory sinus arrhythmia. If the mother or father is susceptible to heart rhythm disturbances, then there is a fairly high probability that this disease will be passed on to the child.
Infectious diseases accompanied by fever, intoxication or dehydration also provoke the development of non-respiratory arrhythmia in children. This is due to changes in the water-electrolyte composition of the blood. Another provoking factor is neurocirculatory dystonia: in this case, rhythm disturbances are associated with the fact that the vessels supplying the heart are not able to change their lumen adequately to the oxygen demand of the tissues.
During inflammatory processes in the heart muscle (of bacterial or viral origin), sinus arrhythmia, atrial fibrillation, extrasystolic arrhythmia, and heart block may occur. Rheumatism affects the valve apparatus of the heart and can cause myocarditis, which provokes the development of arrhythmia in the child. The onset of the disease may be associated with a sore throat, accompanied by high fever. Also, non-respiratory arrhythmia in children develops against the background of congenital heart defects.
Moderate and severe sinus arrhythmia in a child
Based on severity, this disease is divided into two categories. Moderate sinus arrhythmia in a child manifests itself mildly or occurs without symptoms at all. Most often it is detected by chance. Severe sinus arrhythmia in a child manifests itself quite clearly and can be combined with serious heart diseases.
Symptoms that will help recognize sinus arrhythmia in a baby: poor sleep, frequent crying at night, refusal to eat, shortness of breath, blue or pale skin.
Older children may develop symptoms such as chest pain, fatigue, poor tolerance to physical activity, and fainting. Parents should be wary if their child begins to play less active games and tries to avoid other physical activities.
Sinus arrhythmia and sports
Often, the parents of a child who has sinus arrhythmia try in every possible way to protect him from physical education, believing that it was they who provoked the problem. However, if a child does not have a predisposition to heart rhythm pathologies, then even playing professional sports will not lead to the development of arrhythmia. At the same time, if there is a predisposition, the onset of the disease can be triggered by any physical activity.
In most cases, it makes no sense to completely protect your child from physical education, since moderate physical activity is very important for health. Respiratory arrhythmia is not a contraindication even for sports activities. However, the child must be under the supervision of a cardiologist and undergo a control electrocardiographic examination. Children who participate in professional sports must be observed by a sports doctor and undergo an ECG every 3 months.
If a child has a non-respiratory arrhythmia, then sports activities are strictly limited. In such a situation, physical activity is really dangerous.
How is sinus arrhythmia treated in children? The child must undergo a control electrocardiographic examination and ultrasound of the heart, a general urine test and a clinical blood test. If the only detected disorder is sinus arrhythmia, the child will be observed by a cardiologist with follow-up examinations every six months. If the arrhythmia is not respiratory in nature, then it is necessary to cure the cardiac pathologies that provoked it. Mild sinus arrhythmia in a child goes away on its own over time.
Tachyarrhythmia: when is the condition urgent?
The heart rate of a healthy person is normal when he practically does not feel the heartbeat. Exposure to a number of negative factors (stress, excitement, anxiety, anxiety) leads to a disruption of the heart rhythm. A pathological condition develops - tachyarrhythmia, as a type of arrhythmia in which the heartbeat remains disturbed, even if there are no prerequisites for this.
A person’s constant presence in such a state is fraught with serious consequences, so it becomes a reason to make an appointment with a cardiologist. Lack of treatment for tachyarrhythmia can lead to dysfunction of systems and organs.
Risk factors
Tachyarrhythmia is not an independent disease. This is a secondary symptom caused by thyroid imbalance, heart problems. More often observed in patients over 45 years of age.
Pathology is at risk for people who abuse alcohol, drugs, and medications. The risk group includes patients with diabetes mellitus and diseases of the cardiovascular system:
- ischemia;
- myocarditis;
- arterial hypertension;
- myocardial infarction;
- previous heart defect.
8
24/7
Types of pathology
Tachyarrhythmia is a sign of impending danger or the development of a pathological process in the body. The disease has 6 varieties. The pathology is classified depending on the location of development and the degree of impairment of cardiac contractility.
- Paroxysmal arrhythmia: characterized by a chronic course, sudden sharp attacks or regular episodes of heart rhythm disturbances.
- Supraventricular: characterized by a sudden increase in heart rate (over 100 beats/min), attacks of tachycardia from several minutes to 7 days in a row. Pathology is more often detected in children and adolescents.
- Ventricular arrhythmia: acceleration of heart rate to 200-240 beats/minute. It is life-threatening - the pathology can lead to ventricular fibrillation and death.
- Atrial fibrillation: accompanied by an accelerated heartbeat, the frequency of which can reach 700 beats every minute. The condition requires urgent hospitalization and resuscitation.
- Atrioventricular tachyarrhythmia: localization of the pathological focus in the atrium is manifested by an attack lasting up to 3 minutes, although it happens that disturbances persist for up to several days.
- Sinus form: heart rate 80-120 beats/minute. This is the most common condition, occurring even in healthy people during periods of anxiety and intense physical training. Sinus tachyarrhythmia is a normal variant, but gradually the heart begins to lack the required volume of blood, which leads to deterioration of blood circulation in the myocardium and other systems and organs. The functioning of the thyroid gland and autonomic nervous system is disrupted. Patients should consult an endocrinologist, cardiologist, undergo tests, and undergo hardware examinations.
Causes
If the heart rate during tachyarrhythmia stays within 100-140 beats/minute, this is a consequence of pathological processes in the lower ventricles or upper parts of the heart chamber. The heart begins to work intermittently: it either freezes or beats faster. The condition is caused by internal reasons:
- heart failure;
- cardiomyopathy;
- atherosclerosis;
- dysfunction of the heart valves (incomplete closure of the valves);
- tumor or infectious lesion of the heart muscle;
- heart disease;
- myocarditis;
- hypertension;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- diseases of the lungs, thyroid gland;
- electrolyte imbalance;
- infectious diseases: botulism, influenza, ARVI;
- anemia.
Or external:
- physical, emotional stress;
- excessive physical activity;
- abuse of drugs and alcohol, which provoke surges in blood pressure and increased heart rate.
Symptoms
Variations of symptoms are different. Depends on the form of the pathology: acute, chronic, recurrent. In acute cases, the signs are aggressive and bright. The chronic stage proceeds slowly, sometimes secretly. But even banal, minor shortness of breath can foreshadow an approaching cardiac crisis.
Main symptoms:
- attacks of suffocation;
- weakness;
- fainting state;
- pulmonary edema;
- dizziness.
Attacks from the vegetative-vascular system are observed as:
- feverish condition;
- muscle cramps;
- increased urge to urinate;
- loss of coordination of movements.
8
24/7
Insufficient blood saturation of the heart is fraught with the development of ischemia, myocarditis, and myocardial infarction. When tachyarrhythmia is detected, urgent emergency care is required, since a prolonged course of, for example, paroxysmal tachycardia, can cause:
- heart failure;
- formation of a blood clot in the heart chamber;
- accumulation of blood clots in the atria;
- inability of blood to flow out into the brain, aorta.
The consequences can be extremely severe.
Diagnostics
An electrocardiogram can detect any type of tachyarrhythmia. Additional diagnostic methods prescribed by the attending physician:
- Holter method: electrodes connected to a device are attached to the patient’s body, which allows monitoring the heart rate over a certain period of time;
- duplex scanning of the aorta;
- blood test (general clinical, biochemical);
- echocardiography by connecting ultrasound equipment: allows you to analyze the condition of internal organs (kidneys, thyroid gland, liver).
Treatment in the early stages
If the cases of manifestation of signs of tachyarrhythmia are isolated, then treatment is not carried out. The advisability of therapeutic measures is determined by the cardiologist. If the signs have become intrusive and are repeated in frequent episodes, then you need to undergo an examination or emergency procedures to restore blood circulation and heart rhythm.
Treatment is inpatient. Patients are placed in the cardiology department, where IVs are placed and intravenous injections are given (glucose, insulin, potassium chloride). Additionally, enhanced rehabilitation therapy is carried out to relieve attacks of arrhythmia:
- cardiac glycosides (Ligoxin, Coronal, Egilok);
- antiarrhythmic drugs;
- sedatives (Panangin, Cordarone, Novocainamide) to suppress irritated receptors - give drugs for emergency care if ventricular tachyarrhythmia is suspected;
- antispasmodics (Lidocaine, Novocaine).
Oxygen therapy in combination with light massage on the heart area is effective.
If paroxysmal, ventricular arrhythmia is detected by ECG results, the patient should be urgently admitted to a hospital for intensive, emergency therapy to restore heart rhythm.
Features of treatment of tachyarrhythmia in children
If isolated cases of sinus arrhythmia are identified, then treatment as such is not carried out. The child is not even protected from physical education. For serious heart rhythm disturbances and concomitant diseases (myocarditis, heart disease, tumor-like neoplasm), the following are prescribed:
- antiarrhythmic drugs (Mildronat, Mexidol);
- vitamin complexes;
- preparations containing zinc, magnesium, iron, ascorbic acid.
Herbal preparations will help improve the functioning of the heart muscle and normalize blood flow:
- valerian officinalis;
- Cardiomagnyl;
- Corvalment;
- Corvaltab;
- Asparkam;
- Panangin;
- Corvalol.
It is recommended to take Barboval at night.
The drug Egolok helps to correct the condition and normalize the heart rate - a frequently prescribed drug for tachyarrhythmia, which provides relief within 2-3 minutes. It is taken in conjunction with a diet that involves the introduction of foods high in magnesium, potassium, and vitamin E.
Forecast
Tachyarrhythmia is a pathological condition of the heart muscle, in which doctors do not undertake to give any predictions. At the initial stage, the body is able to independently prevent the progression of the disease.
The type of pathology plays a big role. With sinus arrhythmia, the prognosis is favorable, since the course of the disease is uncomplicated. The most dangerous is ventricular arrhythmia and can result in sudden death.
In general, with timely detection of pathology, doctors are able to stop cardiac collapse and achieve an improvement in the quality of life.
With tachyarrhythmia, a rapid heartbeat is observed, which does not have the best effect on the tissues and blood vessels in the body. The pathological condition is not considered fatal, but requires constant monitoring by doctors and periodic treatment procedures.
If tachyarrhythmia is not treated on time, complications are inevitable:
- arrhythmogenic shock;
- cardiac ischemia;
- stroke;
- myocardial infarction;
- pulmonary embolism.
The prognosis is favorable only in the absence of complications.
Disease prevention
Regardless of the type of heart pathology detected, it is important for patients to adhere to a number of recommendations:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- review your diet;
- exclude intensive physical activities, athletes should leave their professional activities;
- comply with all doctor’s appointments and instructions;
- suppress stress, nervousness, mental and physical stress;
- combine work and rest;
- normalize sleep;
- walk more in the fresh air.
- Visit a cardiologist regularly if you are diagnosed with tachyarrhythmia.
An acceleration of the heart rate up to 140 beats/minute is a consequence of pathological processes in the lower ventricles or upper chambers of the heart. Sudden death can be caused by the ventricular form of pathology. Fatal heart rate is also observed with thromboembolism, accompanied by symptoms - loss of consciousness, drop in pressure, shortness of breath, suffocation, bluish skin, pain or burning in the chest.
The patients' condition is on the verge of clinical death and only timely intensive care will help save life. Therefore, regular examinations and routine examinations are mandatory, especially for people who have prerequisites for the development of cardiac pathologies.
8
24/7
Symptoms of sinus arrhythmia
This pathology can have various signs. An increase in heart rate is accompanied by shortness of breath, a feeling of lack of air, a feeling of pulsation in the temples, and pain in the chest. Against the background of a decrease in heart rate, headaches, weakness, and dizziness occur. With severe sinus arrhythmia of the heart, the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, so the patient may lose consciousness. Moderate pathology occurs without severe symptoms.
In a newborn baby, sinus arrhythmia can manifest itself with the following symptoms: changes in skin color (skin becomes pale or bluish), refusal to eat, frequent crying, shortness of breath. Older children experience symptoms such as fatigue and poor exercise tolerance, and in some cases fainting.
How is this disease diagnosed? The diagnosis is made based on the patient's complaints and examination results. Changes in heart rate are detected using electrocardiography.
The Holter monitoring technique is used: the patient wears a small ECG-type device for 24 hours. At the same time, records are kept, that is, the patient’s daily activities are recorded: lifting weights, eating, climbing stairs, waking up and going to bed, etc. After removing the device and deciphering the data obtained, the results are entered into the conclusion sheet.
Sometimes diagnosis is made using ultrasound. A biochemical analysis of blood and urine is performed, and sex hormones are examined.
Arrhythmia in children
Medicine considers the concept of respiratory arrhythmia, and this is perhaps the only case of cardiac arrhythmia in a child when there is no reason to worry. In approximately thirty percent of the remaining cases, it is necessary to pay close attention to a child with arrhythmia and conduct a comprehensive examination of the body as early as possible in order to identify the cause of the rhythm disturbance.
Arrhythmias in children are divided into acquired and congenital, and in cases where a disturbance in the normal frequency or rhythm of heart contractions begins at an early age, say, in the presence of arrhythmia in a 7-year-old child, there is a high probability that an organic pathology is occurring. Based on clinical manifestations, the following types of cardiac arrhythmias in children are distinguished:
- Tachycardia;
- Bradycardia;
- Extrasystole;
- Sinus arrhythmia;
- Migrating source of rhythm;
- Paroxysmal tachycardia;
- Atrial fibrillation;
- Sick sinus syndrome.
The reasons why arrhythmia occurs in children vary from psychogenic reactions to organic pathology. This includes infectious diseases, heart disease, endocrine pathology, and functional conditions as well. Each specific type of arrhythmia can be provoked by a number of reasons from those listed, various combinations of them, or may appear due to a single disturbance in the homeostasis of the body. Sinus tachycardia is an increase in heart rate of more than 160 beats per minute at rest in young children and 140 beats in older children, provided that other elements of the electrocardiogram are located in the normal sequence. This type of arrhythmia implies a normal mechanism of contraction of the heart muscle with shortening, but within normal limits, of all intervals between the elements of the ECG.
Sinus tachycardia can occur under conditions of psychoemotional stress or physical exertion, while acting as an adaptive mechanism of the body to changing environmental conditions. However, this arrhythmia in children can also occur against the background of organic heart pathology of various origins. Also, the heart rate may increase in response to an increase in body temperature, a decrease in blood pressure, significant blood loss, and a decrease in myocardial contractile function, which can be inflammatory, dystrophic, toxic or ischemic in nature.
In addition, the presence of concomitant diseases, such as thyrotoxicosis, vegetative-vascular dysfunction or a state of shock, increases the heart rate. Some medications increase heart rate, examples of which are methylxanthines, anticholinergics, sympathomimetics, arteriolar vasodilators, etc.
The opposite rhythm disorder to tachycardia is called bradycardia, and the heart rate decreases to less than 80 beats per minute in newborns and less than 70 beats per minute in older children. All electrocardiogram intervals are kept within normal limits, as in the case of tachyarrhythmia, but, unlike the latter, bradycardia is characterized by a prolongation of all elements of the contraction cycle of the heart muscle. Physiological bradycardia is typical for children whose heart muscle is trained, so if your child attends sports clubs or enjoys another hobby that trains his body in terms of physical endurance, there is nothing to fear.
However, there is often another reason for bradycardia, and it may be an increase in the influence of the vagus nerve, which often accompanies peptic ulcer disease; head injuries, increased intracranial pressure also lead to a decrease in heart rate; hypothyroidism, hypothermia and severe hypoxia can cause a decrease in heart rate. Among external interventions, the cause of bradycardia may be excessive administration of potassium preparations into the body, the use of beta-blockers, opioid analgesics, some tranquilizers and cardiac glycosides. Infectious lesions of the heart muscle (myocarditis), sick sinus syndrome are also causes of bradycardia.
How to treat sinus arrhythmia
If the pathology is severe, then there is a need for drug therapy. Therapeutic methods and cardiac pacing are used. The choice of medications is made by a cardiologist, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
If the pathology is provoked by a stressful situation or emotional instability, then a neurologist can prescribe treatment. For such sinus arrhythmia, sedatives and nootropics are used. In some cases, tranquilizers and antipsychotics are necessary. These drugs are prescribed by a psychiatrist.
If the heart rate is below 50 per minute and pronounced disturbances in central hemodynamics are recorded, then installation of a pacemaker is indicated. This miniature device is inserted under the skin in the collarbone area.
When treating sinus arrhythmia, it is important to avoid physical overload and stress, and adhere to a diet limiting sweets, flour and fatty foods.
If this pathology is detected in a pregnant woman, then the following measures are taken: the patient is registered with a perinatologist and visits him according to a certain schedule, undergoes examinations, takes multivitamins, and adheres to the rules of a balanced diet.
Treatment of sinus arrhythmia in children necessarily implies a rational organization of work and rest. If the pathology is severe, then it is necessary to be treated in pediatric cardiology. The amount of simple carbohydrates in the child’s diet is limited, the emphasis is on vegetables and fruits, which will provide a large amount of fiber. Also an important condition for recovery is the use of psychotherapeutic methods of influence: it is necessary to restore the child’s normal emotional state and protect him from stress. Having diagnosed sinus arrhythmia, the doctor will tell you in detail what it is and explain how to behave to avoid complications.
Diet for respiratory arrhythmia
The diet should be balanced and varied, with a predominance of raw fruits and vegetables, herbs, dairy products, and fish. It is necessary to limit the consumption of sweet, starchy and too fatty foods, as well as products containing caffeine. Also useful are walks, trips to nature, and engaging in any hobby that will fill the patient’s life with positive emotions and help avoid stress.
What foods are most useful for heart rhythm disorders? Watermelon and melon remove excess cholesterol. Turnips are great for calming heart palpitations. Grapes eliminate swelling and shortness of breath, improve the tone of the heart muscle. Apples reduce the risk of developing tumors, normalize blood pressure, and improve digestion.
Avocado contains enzymes that help the body absorb substances necessary for the correct functioning of the heart. Potatoes and cabbage are sources of potassium, which normalize the functions of the heart muscle. Cereals effectively inhibit the absorption of cholesterol. Pumpkin corrects the water-salt balance and helps reduce blood pressure.
If a person who has been diagnosed with respiratory arrhythmia eats right, devotes time to moderate physical activity and avoids stress, then he will not feel any discomfort.
Prevention of sinus arrhythmia
General preventive measures include regular exercise without excessive overload, walks in the fresh air, and control of body weight.
An integral part of the prevention of sinus arrhythmia is dosed physical activity, especially for people suffering from diabetes, obesity, and thyroid pathologies. The optimal forms of physical activity are walking and swimming.
In a state of tension and anxiety, a fifteen-minute walk in the fresh air is often more effective than mild sedatives. While walking, the brain produces endorphins, which improve your mood, calm you down, and relieve pain. An exercise such as walking can be performed by absolutely anyone, including children, and does not require a special suit or equipment.
With the doctor's permission, walking can be supplemented with running, skiing or other more active sports.
Often the source of heart rhythm disturbances is neuroses, lack of adequate sleep, overwork, and stress. In this regard, a key component of prevention is adequate rest and sleep at least 8 hours a day. Automotive training, aromatherapy, and herbal medicine (decoctions and infusions of valerian, motherwort, calendula, mint, and hawthorn) help control stress.
During the treatment of diseases that can provoke heart rhythm disturbances, drug prevention of arrhythmia can be carried out.
Sinus arrhythmia during pregnancy
Causes of sinus arrhythmia during pregnancy
Among the processes that cause the development of this pathology, the following can be distinguished:
- the appearance of an additional blood circulation that connects the fetus with the maternal body;
- increased emotionality and reduced stress resistance of the expectant mother;
- high activity of the sympathetic nervous system;
- electrolyte disorders;
- anemia.
Expectant mothers with heart defects are at risk. For them, the risk of developing arrhythmia during pregnancy is very high, even after successful surgery. Heart rhythm disturbances are also very often recorded in women with congenital diseases of the cardiac conduction system.
Symptoms of sinus arrhythmia during pregnancy
The most common signs of this heart rhythm disorder are sensations of frequent beats in the chest, pounding in the temples and dizziness, shortness of breath and high fatigue even with minimal exertion, a frequent and even pulse rhythm without interruptions.
Malfunctions in the heart of the expectant mother can lead to a deterioration in the blood supply to the fetus, and this is fraught with negative consequences for its development. That is why, at the first signs of heart rhythm disturbances, it is necessary to consult a specialist. The doctor, having diagnosed “sinus arrhythmia” based on the ECG and tests, will explain what this means and how to fix the problem.
Complications of sinus arrhythmia during pregnancy
Serious consequences of heart rhythm disturbances include:
- thromboembolism;
- tachycardia;
- heart failure.
Thromboembolism is characterized by the appearance of blood clots as a result of blood stagnation. To prevent blood clots, medications that reduce blood clotting are prescribed.
Tachycardia is accompanied by shortness of breath, weakness and a sharp decrease in pressure. This pathology is due to the fact that the heart, contracting too often, cannot pump the required volume of blood.
Heart failure develops due to the fact that due to disturbances in normal blood circulation, excess fluid is retained in the body. As a result, breathing becomes difficult, gas exchange disorders in the lungs and hypoxia occur.
Treatment of sinus arrhythmia in pregnant women
All substances entering the blood of the expectant mother are transferred to the fetus. Taking medications during pregnancy is permitted only for strict indications.
A pregnant woman needs to control her weight: if she gains more than 300 grams in a week, then she needs to reconsider her diet. It is especially important to limit the consumption of flour, fried and salty foods. As for sports, physical exercises such as walking and swimming, as well as gentle yoga, are recommended during pregnancy.
Sinus arrhythmia during pregnancy requires consultation with doctors of various specialties: cardiologist, gynecologist, pediatrician. Even a slight disturbance in the heart of the expectant mother can provoke oxygen starvation and delayed fetal development. For preventive purposes, it is recommended to undergo examination at the stage of pregnancy planning. If any serious pathology is identified, it will be possible to carry out a course of effective treatment in advance.
To prevent heart rhythm disturbances during pregnancy, measures such as a balanced diet, avoidance of caffeine-containing products, and moderate exercise are necessary. You should also avoid stressful situations and nervous tension.
Pharmacies where you need to search for medications are located on our website in the “Pharmacy” tab. There you can book medical products online and see all the necessary information about them, the types of available dosages.
Possible reasons for deviations
Negative processes in the functioning of the sinus node can be caused by a number of internal and external factors.
Table “Causes of heart rhythm disturbances”
| Pathological | Organic myocardial disorders (infarction, ischemia, myocarditis, cardiosclerosis) |
| Congenital anomalies in the structure of the main organ (underdevelopment of the valve apparatus, disorders in the AV node) | |
| Diseases of the cardiovascular system caused by infection | |
| Heart failure (acute and chronic form) | |
| Problems in the endocrine system (hypertrophy of the thyroid gland) | |
| Nervous system diseases | |
| Chronic hypoxia | |
| Anemia | |
| Physiological | Abuse of alcohol, cigarettes |
| Drug overdose | |
| Insufficient intake of vitamins and microelements into the body (lack of calcium, magnesium, potassium) | |
| Long-term use of cardiac glycosides | |
| Excessive exercise | |
| Constant stress, emotional fatigue | |
| Poor nutrition (abuse of fatty, salty, spicy foods, flour products) |
Important! If changes in sinus contractions are caused by external factors, then eliminating them will improve cardiac activity. In case of pathological abnormalities, complex therapy will be required to normalize the functioning of the main organ.