Uric acid diathesis: causes
In the development of this condition (please note that arthritic diathesis is not a disease), hereditary predisposition, multiplied by the action of environmental factors, is of great importance. First, a few words about the genetic factor. It has been established that children with a family history of gout, urolithiasis, atherosclerosis and diseases of the endocrine system suffer much more often from neuro-arthritic diathesis.
Aggressive environmental factors that can cause uric acid diathesis include a diet overloaded with foods that contain a lot of protein and purine bases. An increase in the proportion of such foods in the diet of a pregnant woman, nursing mother and child increases the likelihood of developing arthritic diathesis. The most important are meat and meat by-products, broths, chocolate and cocoa.
Physiological conditions of newborns: normal or pathological?
Home Articles Popular information articles Our children
Neonatology in medical institutions of Chelyabinsk:
Maternity hospital of the South UGMU clinic Maternity hospital of the City Clinical Hospital No. 8 Maternity hospital of the City Clinical Hospital No. 9
When a little person is born, he experiences enormous stress. It passes through the birth canal, which in itself is not easy, and the birth may not be entirely successful. Then the newborn finds himself in a world where it is not as comfortable as in his mother’s belly. Therefore, during adaptation to the environment, the child may experience so-called “physiological states”. They are also called transitional, as they reflect the baby’s transition from intrauterine to extrauterine life. All these conditions are temporary and disappear with the end of the neonatal period (during the first month of life) and do not require treatment. Nevertheless, young mothers may be concerned about changes in the baby’s condition, so it is important to be able to distinguish the physiological conditions of the newborn from the onset of the disease.
CARE FOR A CHILD UP TO ONE YEAR OF AGE
Weight loss
On the 2-3rd day of a baby’s life, his weight decreases by 5-10 percent of his birth weight - this is a physiological loss of body weight. After all, in utero the baby received all the nutrients from the mother’s blood through the umbilical cord. To make adaptation to a different type of nutrition more favorable for the baby, early breastfeeding is recommended (in the first 30 minutes after birth). By 6-7 days the baby regains its original weight.
Transient fever
Simultaneously with physiological weight loss, a transient fever occurs in the newborn on the 3rd-4th day of life. There are several reasons for this transitional state. This is an insufficient intake of fluids into the child’s body (at this time the baby still receives colostrum, which is much thicker than “mature” milk and contains a large amount of protein). Also, the baby’s thermoregulation system has not yet been adjusted and the skin evaporates more fluid than the body receives from food and drink. The result is dry skin, mucous membranes and general dehydration of the body.
A transient fever manifests itself with an increase in body temperature to 38-40 degrees, the child becomes excited and restless. This condition lasts 1-2 days, and then the temperature returns to normal.
Antipyretic drugs have no effect for transient fever. Treatment consists of feeding the baby (you can give warm boiled water or saline) and creating a comfortable temperature and humidity. It is important that the child does not overheat or become hypothermic (you can use a humidifier).
Uric acid infarction
On the 5th-6th day of a newborn’s life, the mother may notice that the baby’s urine has become cloudy and orange-brown in color, and reddish spots remain on the diaper. This physiological condition is called uric acid infarction. It is associated with immaturity of metabolism, increased formation of uric acid and its salts and increased excretion in the urine.
Uric acid infarction resolves spontaneously as fluid intake (including breast milk) increases by 10-12 days of the baby’s life.
Physiological jaundice
This transitional state manifests itself in most newborns from 2-3 days of life - the skin becomes jaundiced; With physiological jaundice, stool and urine do not change color; the sclera does not turn yellow. The reasons for this condition are the enzymatic immaturity of the liver, which is not yet able to cope with the processing and excretion of bilirubin; it accumulates in the body, giving a yellow color to the skin. In order for bilirubin metabolism to normalize, it takes 1-2 weeks, so physiological jaundice “disappears” by the 10-4th day of life and does not require treatment.
At this time, the child’s well-being, as a rule, does not suffer. Jaundice that appears in the first days after birth, rapidly progresses and lasts longer than 14-16 days may indicate a serious deviation in the baby’s health. In any case, if there is anything alarming about the color of your child’s skin, regardless of age, be sure to consult your pediatrician.
Erythema of the newborn
This physiological condition is characterized by redness of the skin after removal of vernix lubrication by the end of the first day after birth. It is also called physiological catarrh and can intensify for 2-3 days. Erythema usually subsides by 4-5 days of life, followed by peeling. This does not affect the baby’s well-being in any way.
Sometimes it is possible to develop toxic erythema on days 4-5 of life. A rash appears on the skin in the form of small red spots and bumps, and bubbles with transparent contents may also appear on bright red inflamed skin. Toxic erythema is the result of an allergic reaction of the child’s body to environmental factors. It is important to prevent further development of toxic erythema: for this you need to ensure maximum cleanliness. Do not lubricate or open blisters on the skin - this will lead to the development of purulent inflammation. Under favorable and comfortable conditions for the baby, toxic erythema disappears on its own after 2-3 days.
Sexual crisis
In utero, the baby receives the mother's hormones through the placenta - estrogens, which are necessary for the proper development of the baby. After birth, the child no longer receives them. Visible changes in girls occur in estrogen-dependent organs: mammary glands, vagina and uterus, although manifestations of a sexual crisis are observed in children of both sexes.
The mammary glands increase in volume from 2-4 days of life and reach maximum engorgement by 7-8 days. Breast engorgement is always bilateral, symmetrical, the color and temperature of the skin near the nipples do not change, the mammary glands can increase up to 3 cm in diameter. Breast engorgement usually disappears by 2-3 weeks of life, sometimes it can persist until one month of age. This condition does not require treatment.
On the 3rd-4th day of life, newborn girls experience grayish-white discharge from the genital tract - this is the exfoliation of a large number of vaginal epithelial cells. They disappear in the second week of life. This condition also does not require treatment. You just need to wash the girl several times a day from front to back (that is, hold the child with her tummy up so that the water washes first the genitals and then the buttocks). You should not try to remove all the mucus from the genital slit, the main thing is that there are no excessive accumulations. It is important to follow the rules of hygiene when caring for a newborn girl, otherwise an infection may also occur. In case of heavy and prolonged bleeding, additional examination is necessary to exclude the disease. On the contrary, the absence of manifestations of a sexual crisis (vaginal discharge) may indicate a fusion of the labia in the baby. Therefore, any deviation from the physiological norm, any doubt a mother has about her baby must be resolved by a pediatrician.
In boys, on the 3-4th day of life, the appearance of the genital organs changes: the scrotum becomes swollen and increased in volume. By 7-8 days, these manifestations usually fade away, although in some cases the genitals take on normal size only by the age of one month. These changes do not require anything other than ordinary hygiene.
In a newborn baby, you can notice whitish-yellow rashes on the face - this is a consequence of blockage of the excretory ducts of the sebaceous glands, which work most actively during a sexual crisis. The rash is called milia and can be located on the forehead, wings of the nose, or chin. After a few days, the milia disappear on their own and do not cause concern to the baby.
As you can see, there are many physiological conditions in newborns, and most of them appear at the same time - on the 2-4th day of the baby’s life. It is in your power to provide your child with the greatest possible comfort, cleanliness, compliance with all hygienic rules of care and, of course, breastfeeding. Then your baby will easily and quickly adapt to the world around him.
Author: T.V. Karikh, pediatrician at HCMP.
Based on materials from the newspaper “On Health” (issue No. 5, May 2009)
Print version
Uric acid diathesis: symptoms
This condition is accompanied by clinical manifestations of the central nervous system, kidneys and joints, and in later stages the respiratory and cardiovascular systems are involved in the process.
The earliest symptoms of uric acid diathesis are changes in nervous activity. This feature of the clinic of arthritic diathesis is explained by the fact that urates have an irritating effect on the centers of the nervous system, which leads to excitement and increased activity of the latter.
Neuro-arthritic diathesis is accompanied by constant overexcitation of the central nervous system. Before the age of one year, this is manifested by the constant cry of the baby, who asks to be held by his parents, falls asleep poorly or does not sleep at all in their absence. The positive side of these features of the nervous system is that a child with uric acid diathesis is ahead of his peers in mental development, he masters speech faster and begins to read early, has an excellent memory, is inquisitive and actively interested in everything that happens around him.
The negative side of uric acid diathesis in children is their emotional lability, the manifestations of which often acquire features of neurotic symptoms. The baby sleeps poorly, is anxious, and enuresis and night terrors often accompany diathesis. Children with neuro-arthritic diathesis slowly gain weight, and they have an extremely persistent decrease in appetite.
In addition to the central nervous system, the target organs for uric acid diathesis are the kidneys and joints. A high concentration of uric acid salts in the blood leads to an increase in their excretion by the renal tubules, and this leads to an increase in urate content in the urine (hyperuricosuria) and the formation of crystals. Crystalluria and saluria themselves are not a pathology, however, these symptoms of uric acid diathesis can subsequently cause urolithiasis (urolithiasis).
Uric acid salts affect joints. In childhood, we do not see persistent morphological changes in the joint tissues (as, for example, with gout); diathesis manifests itself only as joint pain, which bothers children at night. Much less often, with neuro-arthritic diathesis, the clinical picture contains signs of damage to the respiratory system with an asthmatic component, the digestive tract (tendency to constipation, colitis) and allergic dermatitis.
Laboratory symptoms of uric acid diathesis include uraturia, a predisposition to acidosis and a periodic increase in the level of acetone and ketone bodies in the blood. Such metabolic disorders (tendency to ketoacidosis) pose a serious danger, because against the background of errors in diet, intense physical or mental stress, they become the cause of acetonemic vomiting in children with uric acid diathesis.
Acetonemic vomiting in arthritic diathesis is highly intense and quickly leads to dehydration and disruption of water-electrolyte balance; in severe clinical cases, it is accompanied by convulsive syndrome and the appearance of meningeal symptoms.
In the treatment of uric acid diathesis, the clinical picture of which includes acetonemic syndrome, heavy drinking and saline solutions are used to correct metabolic disorders, and cleansing enemas and enterosorbents are prescribed to remove ketone bodies. Enterosgel is recognized as the best sorbent, which has a high affinity for toxic elements, but does not interfere with the absorption of nutritional components of food.
Symptoms
Since this disease manifests itself and progresses in the first days of a baby’s life, when he and his mother are in the hospital, determining its presence is not difficult. The main symptoms include:
- Change in urine color. It takes on a dark red hue.
- Brick-colored stains left by urine may form on a diaper or diaper. Also sometimes small crystals appear, very similar to salt crystals. They have a similar color - brick.
- Despite all these changes, the newborn’s well-being does not deteriorate.
- The symptoms do not progress and disappear within a week.
There should be no other symptoms. If a child exhibits symptoms such as fever or vomiting, this indicates the development or already manifestation of another disease. It is necessary to monitor the child’s condition (see point 4 of the list above). The fact is that the outpatient period may be prolonged. Do not think that in this case there is no likelihood of complications. In this case, it is recommended to consult a specialized pediatrician for advice.
Consequences of uric acid diathesis
We have repeatedly said that diathesis itself is not a disease. Any diathesis is a constitutional feature that, under the influence of unfavorable environmental factors, leads to the development of a certain pathology. Arthritic diathesis can transform into kidney pathology (urolithiasis, urate nephropathy and interstitial nephritis), and increased levels of uric acid in the blood can cause gout and arthritis.
Numerous enzymopathies and metabolic disorders can become causes of endocrine pathology (diabetes), atherosclerosis, obesity and diseases of the cardiovascular system in uric acid diathesis, and the constant irritating effect of urates on the central nervous system leads to neuralgia, neurotic symptoms and migraines.
To prevent neuro-arthritic diathesis from transforming into one of the above-mentioned diseases, it is necessary to promptly begin treatment of metabolic disorders and follow recommendations regarding lifestyle and nutrition.
Diagnosis of the disease
There should not be any particular difficulties in diagnosis. The main criterion for diagnosis is the characteristic color of urine. In order to make sure, laboratory assistants take it for analysis. They examine and identify common indicators. Most often, an increased protein content is observed. There should be no other symptoms. When identifying side symptoms, it is necessary to look for coincidences and correspondence with other diseases. It is also possible to take blood for analysis for the presence of specific bodies in its composition.
Samples are examined under a microscope and factors that are fundamental to making a diagnosis are identified. For example, the presence of microcrystals in urine. There is also the possibility of a small amount of blood in the urine.
The blood test process is slightly different. For this purpose, biochemical analysis is used. The process of adaptation of the kidneys is accompanied by corresponding changes in the tissues of the organs. Therefore, ultrasound methods for identifying symptoms are used for analysis. They make it possible to see these changes.
To exclude the possibility of developing other diseases, computed tomography is used. It allows for more accurate research.
Uric acid diathesis: treatment
For arthritic diathesis, the main focus of therapy is recommendations regarding work, rest and diet. Uric acid diathesis in children requires strict dosing of mental and emotional stress; parents must protect the child from stress; hardening and regular (feasible) physical activity will have a positive effect.
Proper nutrition is even more important for the treatment of uric acid diathesis. The share of animal products in the child’s diet should be reduced. Broths, canned fish and offal are subject to complete elimination. We limit our meat consumption, and dairy products become the main source of animal protein. Also, with neuro-arthritic diathesis, you should avoid chocolate, coffee and cocoa, and it is recommended to reduce your consumption of animal fats. The basis of the diet should be cereals and products of plant origin (except spinach and sorrel).
If arthritic diathesis is diagnosed, it is recommended to give the child enterosorbents to prevent episodes of ketoacidosis, as well as to remove uric acid salts from the body. The drug of choice for uric acid diathesis in children is Enterosgel, which is characterized by sorption and detoxification properties and helps restore the permeability of the intestinal wall, thereby preventing the reabsorption of toxins into the blood.
Complications and consequences
Due to the fact that the disease is a natural transition and the body’s adaptation to life outside the womb, there should be no complications or consequences. However, there may be force majeure circumstances that lead to some complications. Therefore, it is recommended to monitor the child’s condition. His behavior and general well-being can give a sign to his parents. If the condition worsens, it is recommended to consult a pediatrician.
If preventive recommendations are not followed correctly, the child may develop the following complications in the future:
- renal failure;
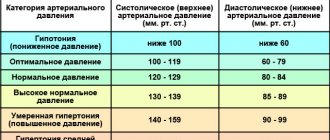
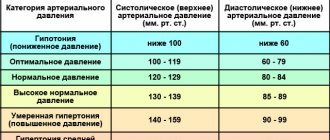
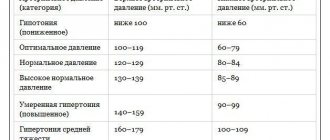
- hypertension.
Prevention
It is important to understand that the child’s condition will primarily depend on his mother. To do this, during pregnancy she needs to take care of herself and avoid stressful situations. Before planning to conceive a child, it is recommended to undergo screening for infectious and other diseases that can subsequently be transmitted to the child. Do not engage in activities that induce premature birth. They can serve as an impetus for the development of the described disease. It is also recommended to breastfeed your baby for as long as possible and, if possible, not switch to artificial feeding.
Based on the information presented, parents will be able to have a general understanding of the disease. This will help either avoid illness altogether, or protect the child as much as possible in case of illness.