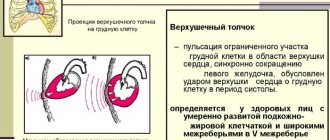
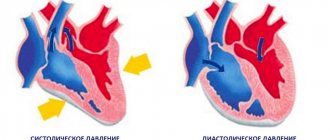
A cardiac impulse is a vibration in a limited area of the chest in the area where the heart is located, caused by contraction of the organ and is an external manifestation of its activity.
The altered shape and size of the heart when it is tense leads to oscillations at the moment the apex of the heart comes into contact with the chest.
During the period of diastole (relaxation) of the ventricles, the heart decreases in size and moves somewhat away from the sternum, which leads to the disappearance of the protrusion.
Method of determination
Determination of the cardiac impulse occurs through inspection and palpation and precedes listening to the sounds it makes.
Properly performed percussion is also a fairly informative method, but at the moment it is practically not used.
With the help of cardiography, it is also possible to record vibrations that occur in the chest and are a consequence of cardiac activity.
To examine a patient using cardiography, specialists use a Frank mirror cardiograph
However, the results of cardiography in determining the cardiac impulse may not always be accurate and depend on the different projection of the impulse on the chest, the thickness of the subcutaneous layer, the perceptive properties of the device, etc.
1. Heart rhythm disturbances
Normal heart function is, as a rule, subjectively imperceptible. Only when you are scared, rise sharply or jog do you feel a palpitation. If there are objective reasons for changes in heart rate, then this is a harmless and transient physiological reaction to internal and external changes. Unfortunately, interruptions in heart rhythm
can occur for no apparent reason, and the average age of onset of cardiac dysfunction is steadily decreasing.
Evolutionarily, it so happened that the work of the heart becomes noticeable to the person himself only when cardiac arrhythmias occur. Even a single freezing of the heart or its too strong contraction is felt as an interruption or a jolt. Arrhythmia
It can be an independent cardiac disease (congenital or acquired), accompany other diseases, or represent a reaction to external factors or internal conditions.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Visual inspection and palpation
Visual inspection and palpation are only suitable for detecting the apex beat. It occurs when the left ventricle and interventricular septum move toward the chest.
Additional heart beats are possible with pathological changes in the ventricles, atria and large vessels. It is important to systematically detect these symptoms.
Visual examination of the patient is the initial stage of the study of cardiac activity and in some cases is more effective than palpation.
It is necessary to direct a beam of light tangentially to the expected place of pulsation, which will facilitate the best detection of tremors during cardiac activity.
It should be taken into account that with some features of the human body, visual observation of the push may be absent, for example:
- overweight;
- small spaces between ribs;
- developed muscles;
- mammary glands are large or contain implants.
In people of asthenic physique, vibrations are most noticeable.
Palpation is a diagnostic method carried out by palpating tissues and organs with the hands. The examination has no contraindications and is used for all categories of patients
After the examination, they move on to the palpation method, which includes the following steps:
- The location of the right hand in the area of the intended push (between the 3rd and 6th ribs in the area of the upper part of the organ).
- Initially, the pulsation is determined by the entire palm with further localization by the index finger (pad).
- Widespread pulsation involves identifying its leftmost area at the bottom. This is where the push actually appears.
The most effective palpation is when the patient bends over or lies on his left side after a deep exhalation. If a person is positioned on the right side, the left lung moves the heart away from the chest, making it impossible to hear the beats.
Examination of women involves elevation of the left breast.
As a result, under the finger there is a feeling of rhythmic vibrations that occur when the left ventricle hits the chest.
Next, the specialist analyzes the results obtained during palpation and the need for additional examination of the patient.
Classification of beats in the heart
The problem in most cases begins in the ventricle (60% of diagnosed cases) or atrium (25%). With pathology of the heart muscle, an incorrect impulse leaves the sinus-atrial node, which is responsible for the coordinated functioning of the organ. Attacks vary in frequency:
- rare (less than 5 times in 1 minute);
- medium (from 6 to 15 times);
- frequent (more than 15 times per minute).
The medical classification of tremors in the heart area is based on the affected area, from which the irregular rhythm emerges:
- Supraventricular : freezing is provoked by an area outside the organ. The atrium and the valves that regulate blood flow are responsible for the problem.
- Ventricular : a more severe form of pathology, which is often complicated by failure and arrhythmia. Excitation begins inside the organ and spreads in waves along the walls.
Depending on the cause of the tremors, cardiologists offer the following division, which facilitates diagnosis:
- Organic : the risk factor is always diseases of the internal organs, pathologies of heart development. In this case, extrasystole can be congenital and accompany defects, or acquired during a heart attack or ischemia.
- Functional : tremors provoke problems of the human nervous system, exacerbation of autonomic pathologies. The reasons may lie in malnutrition, lack of essential vitamins and amino acids.
If the patient feels a single blow from the inside, we are talking about a single focus - monotropic. With multiple spasms, a polytropic form of the disorder is suspected.
Localization of the shock
When the apex of the heart contracts, it creates vibrations in the chest. The top is quite freely located and moves rhythmically. When the body moves, the position of the pendulum also deviates accordingly.
Inspection and palpation of contractions of the right ventricle is impossible, since they do not lead to visible and felt vibrations of the chest. In some cases, weak palpation of movements of the right ventricle is observed in childhood or adolescence with small anteroposterior dimensions of the chest.
The normal location of the push is considered to be the fifth intercostal space medial to the left mamillary line by 1–1.5 cm.
A shift in vibrations may indicate pathological processes in the body or be observed during pregnancy, flatulence, or excessive weight loss.
The apex beat, shifted to the left, occurs due to:
- diseases, one of the symptoms of which is an enlarged left ventricle: aortic stenosis, hypertension, mitral valve insufficiency;
- pushing the left ventricle to the left side by the right one with an increased size of the latter;
- filling of the pleural cavity with fluid or air on the right side;
- high standing of the diaphragm, which shifts the left ventricle to the left side during pregnancy, with excess body weight, increased gas content in the intestines, and accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
Aortic insufficiency leads to a displacement of oscillations to the left and down.
A displaced push to the right side and down causes a low position of the diaphragm, which can lead to emphysema and low body weight.
Exudative pericarditis and left-sided exudative pleurisy do not allow cardiac impulses to appear at all.
Interpretation of results
What can palpation of the apex beat tell you? For an experienced doctor who has the skills to physically examine a patient and has discovered, for example, a weakened apical impulse, it will not be difficult to associate this symptom with the presence of effusion pericarditis , characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the cavity of the heart sac, or pericardium. In this case, the vibrations caused by heart beats are simply not able to pass through the layer of fluid and are felt as a push of weak force.
In the case when a doctor diagnoses a diffuse apical impulse, he may think about the presence of left or right ventricular hypertrophy . Moreover, an increase in myocardial mass is likely if there is a displacement of the impulse to the right or left. Thus, with left ventricular hypertrophy, the impulse shifts to the left. This is due to the fact that the heart, increasing in mass, must find a place for itself in the chest cavity and it will shift to the left side. Accordingly, the apex of the heart, creating a push, will be determined on the left.
Thus, palpation of the heart, when performed by an experienced doctor, can bring undoubted benefit to the patient, since during a routine examination the doctor is able to suspect any disease and promptly refer the patient for further examination using instrumental diagnostic methods.
Square
The area of the heart impulse should normally be 2 square meters. see Deviations from it may indicate pathology. As a rule, the ideal area for a person lying on his left side is 1.8 square meters. cm.
An increase in this indicator indicates a diffuse apex shock, which is observed:
- with an enlarged heart, mainly the left ventricle;
- thin chest;
- wide intercostal spaces;
- wrinkled lower edge of the left lung;
- displacement of the heart forward by neoplasms in the middle parts of the chest cavity;
- high diaphragm position.
If the vibrations have an area of less than 2 square meters. cm, we can talk about a limited push that is inherent:
- emphysema;
- low diaphragm;
- exudative pericarditis;
- hydro- or pneumopericarditis.
Cardiomegaly can contribute to an increase in the vibration area of more than 4 cm.
Treatment of heart beats
If sharp tremors in the heart area are caused by a lack of potassium and sodium, the doctor adjusts the diet, recommends taking vitamin complexes, and saline-based injections. The specialist calculates the amount of salt and prescribes a course of therapy with Narzan mineral water. In case of incomplete absorption of nutrients, an examination of the digestive system and consultation with a gastroenterologist is required.
The presence of psychogenic factors must be treated using different methods:
- Eliminate bad habits, stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Take natural herbs to relieve tension, stress, and improve sleep. Instead of tea and coffee, you can drink a decoction of motherwort, mint, chamomile, or peony infusion.
- For frequent attacks of extrasystole (more than 200 beats per day), it is necessary to select sedative medications to normalize the functioning of the nervous system: Persen, Sedofyton, Novo-Passit.
Often the cause of tremors is cervical osteochondrosis. His treatment is carried out by a neurologist together with a cardiologist. The therapeutic course includes therapeutic massage, physiotherapy, taking anti-inflammatory drugs: Movalis, Diclofenac, Nimesulide. Muscle relaxants help relieve tension and reduce discomfort in the heart area: Mydocalm, Sirdalud, Tizalud.
Prevention of tremors in the heart is to prevent diseases that can disrupt its functioning: colds, flu, sore throat, internal infections. Moderate cardio exercises are recommended, which strengthen the heart muscle well and stimulate its stable functioning. Proper nutrition and a nutritious diet maintain electrolyte balance and prevent complications due to stress.
FacebookvKontakteTwitterWhatsApp
Duration
In the normal state, the apex beat does not differ in duration and lasts until mid-systole. Longer vibrations are considered pathological and require more detailed medical examination.
As a rule, an increase in the duration of vibrations is caused by an enlargement of the heart, or an increased load on it, both in pressure and volume.
If there are no pathological murmurs, cardiomegaly may develop or a decrease in the volume of blood pushed by the left ventricle into the aortic lumen during systole.
The appearance of a systolic murmur can be caused by pressure overload of the myocardium.
Aortic regurgitation, leading to a diastolic murmur with an intermittent impulse, usually indicates mild lesions.
Causes of heart beats
In most cases, the sensation of tremors in the heart area in patients under 50 years of age provokes a disruption of the heart rhythm caused by psychogenic factors. This group includes uncontrolled use of many medications, drugs, and alcohol. Common causes of such extrasystole:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- osteochondrosis in the cervical spine;
- stressful conditions;
- depression;
- neuroses;
- working in unfavorable conditions;
- living in a region with a polluted environment.
Rare attacks occur in women during periods of hormonal imbalance: menstruation, pregnancy, taking contraceptive medications. This is a common problem among people who overindulge in coffee, strong tea, or energy drinks.
Organic causes of unpleasant tremors occur when the myocardial muscle is inflamed or damaged, which is caused by the following health problems:
- previous heart attack;
- chronic ischemia;
- infectious pericarditis;
- myocarditis;
- any vices;
- congenital deficiency.
For some people, the problem appears when the heart muscle is depleted, which is caused by hard work, physical activity: athletes, hot shop workers, miners. It becomes a complication of a sore throat, pneumonia, or purulent otitis media.
The toxic form of the pathology is distinguished separately. It appears with long-term use of medications that a person has to take constantly: sedatives, diuretics to lower blood pressure, glucocorticoids. Tremors in the heart area are provoked by the use of Euphyllin and Furosemide. Their components wash away sodium and potassium ions, which extinguishes conductive signals and weakens muscles.
Amplitude
An increase in the force of the push is observed when he lifts the specialist’s finger. The indicators are influenced by the contractility of the myocardium, the structural features of the chest, the width of the ribs, etc.
The appearance of hyperdynamic pulsation can be facilitated by:
- myocardial overload with volume and increased cardiac output (aortic regurgitation, defects between the right and left ventricles);
- congestive cardiomyopathy;
- obesity;
- thin chest wall without accompanying pathologies;
- physical and nervous overload;
- tachycardia.
Vibrations can be weakened by:
- wide chest structure;
- pericarditis;
- expansion of the heart;
- emphysema, etc.
"Cat Purr"
Aortic and mitral stenoses lead to palpation of a peculiar trembling of the chest, the so-called cat purring. It is caused by shocks as blood moves through the narrowed vessels of the heart.
Occurrence is observed:
- systole-diastolic tremors;
- diastolic tremor;
- systolic tremor.
Cat purring syndrome may indicate:
- about stenosis of the aortic mouth;
- pulmonary stenosis;
- mitral and tricuspid stenosis;
- septal defect between the ventricles;
- open ductus arteriosus.
Symptoms of extrasystole
If strong heartbeats are observed in a practically healthy person and are associated with stress or drinking strong coffee, the unpleasant sensations are mild, without pain or burning. In chronic pathologies, the patient describes the following symptoms:
- inside the heart turns around its axis;
- flutter;
- interruptions;
- sweating;
- heat;
- weakness in the limbs;
- dyspnea.
When tremors occur, a person feels anxious, and there is a desire to go out into the air and take a deep breath. If the attack occurs in several stages, your hands begin to tremble and you feel dizzy.
A complication of extrasystole is its degeneration into more severe health problems: arrhythmia, constant tachycardia, cerebrovascular insufficiency. With constant attacks, the atrium muscles do not receive enough blood and oxygen, and necrosis of certain areas occurs. If left untreated, the patient faces a heart attack or death.
Other types of unwanted vibrations
The occurrence of a resistant cardiac impulse is associated with aortic defects or hypertension. Upon palpation, the specialist feels a dense, thick muscle. If the pulsation is characterized by hyperdynamicity and an increased area, we can talk about a dome-shaped apical impulse.
The occurrence of pulsation of large main vessels is observed in the second intercostal space on the right and left sides of the sternum and in the area of the jugular notch may indicate pathologies of the pulmonary artery and thoracic aorta.
Also, the transmission of rhythmic contractions of the heart to the abdominal aorta (pulsation in the epigastric region) should not normally be detected.
Why is heart palpation needed?
There are no clear indications for this physical examination, because it is advisable for each patient to perform a chest examination and palpation of the heart, along with auscultation of the heart and lungs during the initial consultation with a therapist or cardiologist.
These methods suggest hypertrophy of the left or right ventricles, since an increase in the size of the heart chambers leads to expansion of the heart, as a result of which its projection onto the anterior surface of the chest, determined using the hands, also expands. In addition, it is possible to suspect pulmonary hypertension and an aneurysm of the ascending aorta.
After receiving data that differs from the norm, it is necessary to clarify the disease that caused hypertrophy or pulmonary hypertension using further instrumental methods - ECG, ultrasound of the heart, coronary angiography (CAG), etc.
Diseases detected by palpation
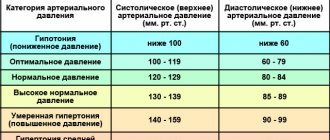
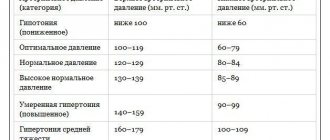
Violations of the location, area, strength, amplitude, rhythm and duration of the cardiac impulse may indicate:
- about congenital and acquired heart defects;
- excessively high blood pressure (over 200 mm Hg);
- aneurysm of the thoracic aorta;
- pericarditis (chronic inflammation of the pericardium);
- diseases of the respiratory system;
- about the increased volume of the abdominal cavity caused by ascites, tumor formations, pregnancy, bloating.
For a more accurate diagnosis of pathological changes in the body identified by palpation, additional examination of the patient using technology is required.
Heart pounding (cardiac arrhythmia)
It happens that “the heart beats in the chest like a bird” or “like an autumn leaf trembles.” And sometimes “it will clog up, then it will freeze.” In medical language, all this is called cardiac arrhythmia. Heart contractions become irregular and irregular. There are different types of arrhythmias, but one of the most common is atrial fibrillation. It is known that with each heartbeat there is a sequential contraction of its parts - first the atria, and then the ventricles. Only such alternation ensures efficient functioning of the heart. With arrhythmia, which has received the beautiful name “atrial fibrillation,” one of the phases of the cardiac cycle disappears, namely, atrial contraction. Their muscle fibers lose the ability to work synchronously. As a result, the atria only twitch chaotically - flicker. As a result, the ventricles begin to contract irregularly.
Why does atrial fibrillation occur?
There are many reasons that can lead to this disease. For example, various heart diseases: hypertension and some heart defects, infectious heart disease and heart failure, coronary heart disease (CHD) and its dangerous complication - myocardial infarction. In young people, the cause of arrhythmia is often mitral valve prolapse, that is, sagging, weakness of one of the valve leaflets between the left atrium and the left ventricle. This pathology usually occurs latently and is detected accidentally. Atrial fibrillation may be its first manifestation.
But the cause of arrhythmia is not only a diseased heart. A variety of diseases can give it a start. And not only diseases. · Very often, an attack of atrial fibrillation is provoked by drinking more alcohol than usual. There is even such a concept - “holiday cardiac arrhythmia.” · On any given day, you can expect arrhythmias to appear in people with thyroid disease (especially those with excessive thyroid function) and some other hormonal disorders. · Arrhythmia often develops after surgery, stroke, or various stresses. · Its development can be provoked by rich food, constipation, tight clothing, insect bites, and some medications. · Taking diuretics to lose weight often lands “your own doctor” in a hospital bed. · There is a high risk of developing atrial fibrillation in people with diabetes, especially if diabetes is combined with obesity and high blood pressure. However, doctors are not always able to determine the cause of the arrhythmia. How to find out about the onset of the disease? It is signaled, for example, by palpitations, when the heart is pounding so much that it seems like it is about to jump out of the chest. There may be a feeling of interruptions in the heart. “It will knock, knock, and suddenly freeze,” or “something will turn inside” - this is how patients describe their condition. But often the arrhythmia goes unnoticed. Only by feeling the pulse can you establish the irregularity of heart contractions. Often the disease is detected only during a clinical examination using an ECG. But it can be worse: the first manifestations of the disease are complications. Why is atrial fibrillation dangerous? It is often accompanied by tachycardia, that is, an increase in heart rate. At the same time, a colossal load falls on the heart. As a result, chest pain may appear - symptoms of angina pectoris or even myocardial infarction. Arrhythmia may reduce the efficiency of the heart. This will lead to another complication - heart failure. At the same time, the person feels suffocated; it seems to him that there is not enough air. Can arrhythmia go away on its own? In principle, it can. But if the arrhythmia persists for several hours or complications arise, you should immediately seek medical help. However, even if the arrhythmia disappears on its own, you should not postpone your visit to the doctor. Repeated rhythm disturbance can occur at any time and end tragically. Therefore, self-medication will not help much. As a good song says: “No matter how much you treat the heart with validol, there are still continuous interruptions.” The fact is that restoration of normal rhythm is best done on the first day from the onset of arrhythmia. It is possible to eliminate arrhythmia later than this period, but then additional preparation will be required. With atrial fibrillation, when the atria do not contract normally, the blood flow in them sharply slows down, and therefore blood clots - thrombi - form. This occurs on the second day after the onset of arrhythmia. When the normal rhythm is restored and the atria begin to contract, fragments of blood clots can break off and clog the vessels of any organ. Typically, blood clots “float” into the vessels of the brain. And this leads to a stroke. That is why anyone who consults a doctor more than 24-48 hours after the onset of arrhythmia is prescribed drugs that slow down blood clotting. Only when the effect is obtained, after about 1-2 weeks, is it possible to restore the rhythm. How is normal heart rhythm restored? There are many techniques. The most effective is restoring the rhythm using an electrical discharge. The procedure is performed under anesthesia, so it does not cause any discomfort. Often doctors are able to eliminate arrhythmia with drug injections. It is much more difficult to select an antiarrhythmic drug to maintain a normal heart rhythm. And here a lot depends on you: strictly following the doctor’s instructions is already half the success, since each new attack of arrhythmia is more difficult to bear than the previous one. Can atrial fibrillation persist for a long time and is it dangerous? There are two main forms of arrhythmia: paroxysmal, which manifests itself in individual attacks, and constant, when atrial fibrillation persists for years or even decades. Of course, persistent arrhythmia threatens great complications, especially if accompanied by tachycardia. But here regular use of medications that slow down the heart rate helps. Is it harmful to take pills all the time? It’s a shame that even in our enlightened age people prefer to get sick so as not to “contaminate the body with chemicals.” It is safe to say that refusing treatment will cause much more harm to the body. You need to take special care of your heart. It is not for nothing that it was called the “heart,” that is, the core, the center of life.
Alexey Erlikh, cardiologist Family doctor