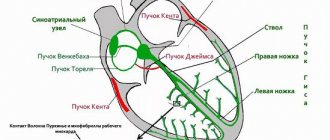
Briefly about the physiology of the fetal heart
The heart is one of the very first organs that is formed in the embryo’s body.
Already at 5 weeks of pregnancy, the first heartbeats can be recorded.
This happens for one simple reason: there are cells in the heart tissue that can independently generate an impulse and cause muscle contractions. They are called pacemakers, or pacemakers. This means that the work of the fetal heart in the early stages of pregnancy is completely independent of the nervous system.
Only by the 18th week of gestation do signals from the vagus nerve arrive to the heart; its fibers are part of the parasympathetic nervous system. Thanks to the influence of the vagus nerve, the heart rate slows down.
stages of fetal heart development
And by the 27th week, the sympathetic innervation of the heart is finally formed, which leads to an acceleration of heart contractions. The influence of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system on the heart is the coordinated work of two antagonists, whose signals are opposite.
Thus, after the 28th week of pregnancy, the heart rhythm is a complex system that obeys certain rules and influences.
For example, as a result of the baby’s physical activity, signals from the sympathetic nervous system predominate, which means that the heart rate accelerates. Conversely, when a baby sleeps, signals from the vagus nerve dominate, which leads to a slower heart rate. Thanks to these processes, the principle of “unity of opposites” is formed, which underlies the myocardial reflex. The essence of this phenomenon is that the work of the fetal heart in the third trimester of pregnancy depends on the motor activity of the baby, as well as the sleep-wake rhythm. Therefore, to adequately assess heart rhythm, it is necessary to take these factors into account.
It is thanks to the peculiarities of the innervation of the heart that it becomes clear why cardiotocography becomes most informative in the third trimester of pregnancy, when the work of the heart obeys certain rules and patterns.
When is the examination done and how often?
The study is carried out no earlier than 32 weeks. It is by this time that the nervous and cardiovascular systems reach a certain maturity. By 8 months, the myocardial reflex is formed - the relationship between cardiac activity and motor activity of the fetus. At the same time, the activity-rest cycle is established. Rhythmic changes in fetal sleep and wakefulness follow each other throughout the remaining period of pregnancy.
Cardiotocography must be performed 2 times during the 3rd semester. However, the frequency of the study is determined by the doctor based on the mother’s medical history, pregnancy history, results of other examinations and risk factors.
How does a cardiotocograph work and what does it show?
This device has the following sensors:
- Ultrasound, which detects the movements of the fetal heart valves (cardiogram);
- Tensometric, determining the tone of the uterus (tocogram);
- In addition, modern cardiac monitors are equipped with a remote control with a button that must be pressed at the moment the fetus moves. This allows you to assess the nature of the baby’s movements (actogram).
Information from these sensors enters the cardiac monitor, where it is processed and displayed on an electronic display in digital equivalent, and is also recorded by a recording device on thermal paper. The speed of the tape drive differs among different types of fetal heart monitors. However, on average, it ranges from 10 to 30 mm per minute. It is important to remember that there is special thermal paper for each cardiotocograph.
example of a CTG tape: above - fetal heartbeat, below - uterine tone values
Fetal reactivity index and non-stress test
The first indicator reflects the state of the fetal nervous system in response to external influences. Such stressful situations primarily affect the state of the cardiovascular system. Points are used for calculation, where:
- 0 – complete absence of response to external stimulus.
- 1 – pronounced decrease in reactivity.
- 2 – noticeable decrease in reactivity.
- 3 – moderately expressed response to external influence.
- 4 – initial degree of pathological reactivity.
- 5 – adequate response to external influences.
Applying a warm or cold object to the pregnant woman's abdomen is used to assess fetal reactivity
A non-stress test is carried out to assess the state of the baby’s cardiovascular system during his voluntary movements. Normally, such a test should be negative, which implies the presence of 2 or 3 increases in heart rate by 15 beats, lasting no more than 20 seconds.
Despite the large number of indicators, cardiotocography is only an additional diagnostic method. For a comprehensive assessment of the condition of the mother and fetus, other instrumental examinations, laboratory test data and consultation with an experienced specialist are necessary.
How is cardiotocography done?
In order for this study to be informative, the following rules must be adhered to:
- CTG recording is carried out for at least 40 minutes.
It is during this time that certain patterns of rhythm changes can be traced. - A pregnant woman should lie on her side during the examination.
If a pregnant woman lies on her back during CTG registration, unreliable results may be obtained, which is associated with the development of the so-called inferior vena cava syndrome. This condition develops as a result of pressure from the pregnant uterus on the abdominal aorta and inferior vena cava, which may result in disruption of uteroplacental blood flow. Thus, if signs of hypoxia are obtained on CTG performed with the pregnant woman lying on her back, it is necessary to redo the study. - The sensor that records the fetal heartbeat must be installed in the projection of the fetal back.
Thus, the location of the sensor’s fixation depends on the position of the fetus in the womb. For example, with a cephalic presentation of the baby, the sensor must be installed below the navel, with a pelvic presentation - above the navel, with a transverse or oblique presentation - at the level of the umbilical ring. - A special gel must be applied to the sensor
to improve the conduction of the ultrasonic wave. - The second sensor (strain gauge) must be installed in the fundus of the uterus.
It is important to know that you do not need to apply gel to it. - During the study, the woman must be given a remote control with a button that must be pressed when the fetus moves.
This allows the doctor to compare rhythm changes with the baby’s motor activity.
Possible reasons for poor results
If at any period after 28 weeks - 35 weeks, 36 weeks or some other period, the result of the CTG reading showed 7 points - this does not mean that everything is bad. A bad result can be obtained erroneously for a number of reasons:
- The results of cardiotocography can be affected by stressful situations and nervous breakdowns. It is possible that to avoid distorting the result, the doctor will recommend taking some sedatives before recording a CTG.
- Excessive exercise before the examination may also give incorrect results. It is more correct to achieve a decrease in muscle tension before starting CTG recording and only then begin diagnostics.
- A poor cardiotocography result can be obtained if the baby is not very active. This problem can be eliminated if the pregnant woman eats something sweet before the examination and is moderately active.
Women do not choose when to have cardiotocography during pregnancy. In this matter, you must strictly adhere to the recommendations of your doctor. In some cases, this procedure has to be repeated several times, and in case of poor performance (7 points and below), it happens every day.
Cardiotocogram indicators
The following indicators are the most informative:
- The basal rhythm
is the main rhythm that predominates on CTG; it can be assessed only after a 30-40 minute recording. In simple words, this is a certain average value that reflects the heart rate that is characteristic of the fetus during the resting period. - Variability
is an indicator that reflects short-term changes in heartbeat from the basal rhythm. In other words, this is the difference between the basal rate and rhythm fluctuations. -
Acceleration
is an acceleration of the rhythm by more than 15 beats per minute, which lasts more than 10 seconds. - Deceleration
– rhythm slowdown more than 15 beats. per minute lasting more than 10 seconds. Decelerations, in turn, are divided according to severity into:- dip 1 – lasts up to 30 seconds, after which the baby’s heartbeat is restored.
- dip 2 – last up to 1 minute, and are characterized by high amplitude (up to 30-60 beats per minute).
- dip 3 – long lasting, more than 1 minute, with high amplitude. They are considered the most dangerous and indicate severe fetal hypoxia.
What type of CTG during pregnancy is considered normal?
An ideal cardiotocogram is characterized by the following features:
- Basal rhythm from 120 to 160 beats/min.
- There are 5 or more accelerations within 40-60 minutes of CTG recording.
- Rhythm variability ranges from 5 to 25 beats. per minute
- There is no deceleration.
However, such an ideal version of CTG is rare, and therefore the following indicators are allowed as variants of the norm:
- The lower limit of the basal rhythm is 110 per minute.
- There are short-term single decelerations, lasting no more than 10 seconds and small in amplitude (up to 20 beats), after which the rhythm is completely restored.
When is CTG considered pathological during pregnancy?
There are several pathological options for CTG:
- Silent fetal CTG
is characterized by the absence of accelerations or decelerations of the rhythm, while the basal rhythm may be in the normal range. Sometimes such a cardiotocogram is called monotonic; the graphic image of the heartbeat looks like a straight line. - Sinusoidal CTG
has the characteristic appearance of a sinusoid. At the same time, the amplitude is small, equal to 6-10 beats. per minute This type of CTG is very unfavorable and indicates severe fetal hypoxia. In rare cases, this type of CTG may appear when a pregnant woman takes narcotic or psychotropic drugs. - Lambda rhythm
is an alternation of accelerations and decelerations immediately after them. In 95% of cases, this type of CTG is the result of compression of the umbilical cord.
In addition, there are many types of CTG that are considered conditionally pathological
. They are characterized by the following signs:
- The presence of decelerations after accelerations;
- Reduced fetal motor activity;
- Insufficient amplitude and rhythm variability.
Such signs may appear when:
- Umbilical cord entanglement;
- The presence of an umbilical cord knot;
- Impaired placental blood flow;
- Fetal hypoxia;
- Baby's heart defects;
- The presence of diseases in the mother. For example, with hyperthyroidism in a pregnant woman, thyroid hormones can penetrate the placental barrier and cause rhythm disturbances in the fetus;
- Anemia of the baby (for example, with hemolytic disease associated with immunological incompatibility of the blood of the mother and fetus);
- Inflammation of the membranes (amnionitis);
- Taking certain medications. For example, Ginipral, widely used in obstetrics, can cause an increase in the baby’s rhythm.
Diagnostic procedure technique
To perform CTG, a device with a specialized ultrasound sensor based on the Doppler effect is used. The device is fixed on the belly of a pregnant woman in the area where the baby’s heartbeat can be clearly heard.
To determine the attachment site for the cardiotocograph sensor, the obstetrician-gynecologist listens to the expectant mother’s abdomen with a special stethoscope.
A signal wave arrives from the ultrasound sensor to the fetal heart, which is transformed from the organ and returns to the sensor again. The information obtained during this process reflects the contractions of the child’s heart muscle in 60 seconds. CTG results can be recorded on tape using various methods - light, graphic and sound.
It is recommended to perform the diagnostic examination on an empty stomach. After eating food, the concentration of glucose in the blood of the expectant mother increases - this provokes an increase in the baby’s activity and its sensitivity to influences from the external environment.
On the eve of diagnosis, a pregnant woman should rest well and eat food 2–3 hours before the test. The child’s activity mode is also important - conducting CTG is pointless during the child’s sleep. It is necessary to find a comfortable position for the woman - she should not feel any discomfort. To improve the conductivity of electrical impulses, a special gel is applied to the sensor.
During pregnancy with complications, CTG is performed once a week. There are many variants of deviations from the norm; it is difficult to organize them into one system. There are cases in which diagnostic parameters are within the acceptable range, but their combination with other factors indicates a violation of the fetal condition.
Sometimes, during a normal pregnancy, a false CTG recording is possible, which indicates the presence of pathologies. This is observed when conducting diagnostics without using a gel for the sensor, as well as during the baby’s sleep, multiple pregnancy, or the expectant mother being obese.
Today, the prenatal medical industry has modern devices that, using computer programs, automate the interpretation of cardiotocography results as much as possible.
What to do if CTG indicators are borderline between normal and pathological?
When registering a CTG and receiving a questionable result, you must:
- Conduct additional research methods (ultrasound, study of blood flow velocity in the uteroplacental system, determination of the biophysical profile).
- After 12 hours, repeat the CTG study.
- Avoid taking medications that may affect the baby's heart rate.
- Carry out CTG with functional tests:
- Non-stress test - consists of studying the heart rate in response to fetal movements. Normally, after the baby moves, the rhythm should speed up. The lack of acceleration after movements is an unfavorable factor.
- Stress test - characterized by a change in heart rate after administration of 0.01 units of oxytocin. Normally, after this drug enters the body of a pregnant woman, the fetal rhythm accelerates, there is no deceleration, while the basal rhythm is within acceptable limits. This indicates the high compensatory capabilities of the fetus. However, if after the administration of oxytocin the fetus does not experience accelerations, but, on the contrary, heart contractions slow down, then this indicates intrauterine hypoxia of the baby.
- A mammary test is an analogue of a stress test, but instead of administering oxytocin, the pregnant woman is asked to massage her nipples for 2 minutes. As a result, the body releases its own oxytocin. The results are evaluated in the same way as in a stress test.
- Physical stress test - a pregnant woman is asked to climb the stairs of the 2nd floor, immediately after this a CTG recording is performed. Normally, the fetal heart rate should increase.
- Breath-hold test - while recording a cardiotocogram, the pregnant woman is asked to hold her breath while inhaling, while the baby’s heart rate should decrease. Then you need to hold your breath as you exhale, after which the fetal rhythm should speed up.
Classification of accelerations
Spontaneous increase in fetal heart rate is a positive sign that characterizes the absence of anomalies in the development of cardiac muscle control mechanisms and good adaptation of the unborn child to the external environment. Normally, an increase in heart rate parameters lasts for 15–20 seconds with an amplitude of more than 15 beats/min. When interpreting CTG results, all other increases in fetal heart rate with parameters below those indicated are included in the column of oscillations - instantaneous fluctuations in the basal rhythm.
The following types of accelerations are distinguished:
- Sporadic - occur during the baby’s physical activity; on the graphic CTG image they look like small narrow teeth.
- Periodic - a response to a fight.
- Variables are the most reliable sign of the prosperous condition of the fetus.
- Uniform - frequently repeated periodic accelerations, observed with a lack of oxygen.
How is CTG scored?
To ensure that the interpretation of CTG results is not subjective, a convenient system for assessing this type of study has been developed. It is based on studying each CTG indicator and assigning certain points to it.
For ease of understanding of this system, all characteristics of CTG are summarized in the table:
| 2 points | 1 point | 0 points | |
| Basal (basic) rhythm | From 120 to 160 | From 100 to 180 | Less than 100, more than 180 |
| Amplitude | From 6 to 25 | 3-5 | < 3 |
| Variability | > 6 | 3-6 | < 3 |
| Number of acceleration episodes in 40 minutes | >5 | 1-4 | none |
| Decelerations | Not registered | Short-term | Long, heavy |
| Fetal movements | >3 | 1-2 | No |
The interpretation of the results is assessed as follows:
- CTG is considered good if it scores 9-12 points;
- A score of 6-8 points indicates signs of hypoxia; in such situations, daily monitoring and treatment are required.
- Less than 5 points is extremely unfavorable.
Important!
Pronounced pathological changes on CTG may indicate a terminal condition of the fetus. Of course, in such situations, it is absolutely impossible to carry out any functional tests. In these cases, emergency delivery may be required, since delay is very dangerous.
Preparation for the procedure
The study does not require special preparation. However, it is worth considering the duration of the procedure. It will be important for mom to relax and be calm. On the eve of the procedure, the pregnant woman is recommended to get a good night's sleep and rest. On the day of the study, you should take care of a light meal 1-2 hours before. And immediately before the procedure, go to the toilet. During CTG, the expectant mother should not be distracted or disturbed by anything. You can take a book or magazine with you, but electronic devices, including your phone, will have to be turned off, as the equipment creates interference with the recording.
CTG during childbirth
Heart rate examination is necessary both in the first (cervical opening) and in the second (pushing) stages of labor. This is necessary in order to prevent acute intrauterine hypoxia, which threatens the life of the fetus and is an indication for emergency caesarean section.
It is for this reason that CTG recording must begin at the first signs of labor. During normal labor, it is enough to register a CTG every hour.
This study also shows:
- After the rupture of amniotic fluid;
- When performing epidural anesthesia during childbirth (after administration of the anesthetic).
Permanent CTG recording is necessary for conditions such as:
- Loss of umbilical cord loops;
example of indication for multiple pregnancy
Bloody discharge from the genital tract;
- Pelvic position of the fetus;
- Multiple pregnancy;
- Two- and three-fold entanglement of the umbilical cord around the fetal neck;
- Signs of gestosis;
- Diabetes;
- Yellow or green amniotic fluid;
- Hemolytic disease of the fetus;
- Intrauterine growth retardation;
- Premature birth;
- Scar on the uterus after previous operations;
- With weak or excessively strong labor.
- When inducing labor with drugs, such as Oxytocin or prostaglandins.
However, it should be remembered that CTG during pregnancy and childbirth is not the same thing.
Therefore, the interpretation of the results must be approached differently. The natural question is: why does this happen?
The fact is that during contractions the muscle fibers of the uterus contract, which means that spasm of the vessels located in the thickness of the myometrium occurs. As a result, uteroplacental blood flow deteriorates and moderate fetal hypoxia develops. During this period, the child's heartbeat may slow down or, conversely, be excessively fast. For this reason, the common phrase that “childbirth is stressful for a child” has a constructive explanation. However, after the contraction, placental blood flow is restored and the heartbeat returns to normal. In this regard, clear criteria for assessing CTG during childbirth have been developed.
Normal indicators of the birth cardiotocogram are characterized by:
- The heart rate ranges from 110 to 160 beats per minute.
- The presence of at least two episodes of rhythm acceleration (accelerations) lasting more than 15 seconds during the period of CTG registration.
- The presence of rhythm variability from 5 to 25 beats min.
- After the cervix is opened by more than 4-5 cm, early decelerations lasting no more than 30 seconds are allowed.
CTG is considered doubtful if the following signs are present:
- The rhythm is in the range from 100 to 110, or from 160 to 170 beats per minute.
- Within an hour there is not a single episode of increased heart rate.
- Low variability (less than 5 beats per minute).
- There are slowdowns in the rhythm that last from 30 to 60 seconds.
Pathological CTG is characterized by:
- The rhythm is too slow (less than 100 beats per minute) or too fast (more than 170 beats per minute).
- Prolonged episodes of deceleration, lasting more than 1 minute.
- Lack of variability, in other words, monotonous rhythm.
- The so-called sinusoidal nature of CTG, when the heartbeat graph resembles a sinusoid.
Fetal health indicator (FSI)
This value is calculated automatically. The following PSP options are distinguished:
- Less than 1 is normal. However, if the CTG value is from 0.8 to 1.0 during pregnancy, it is recommended to repeat it.
- From 1 to 2 – initial changes in the general condition of the fetus. Outpatient treatment and control cardiotocography after one week are recommended.
- From 2 to 3 – the child’s condition is serious. Urgent hospitalization and immediate initiation of treatment are required.
- More than 3 – the condition is extremely serious. The question of emergency management of childbirth is raised.
How does CTG influence medical tactics?
{banner_banstat9}
The results of the study must be taken seriously. The doctor who evaluates the CTG bears great responsibility. It is for this reason that each film recording cardiac activity must be evaluated by the responsible physician, certified by his signature indicating the time of the study and pasted into the birth history.
A normal cardiotocogram is a sign of correct and careful management of labor.
When receiving a questionable CTG, the doctor has no more than 40 minutes to correct labor activity. At this stage, it is necessary to eliminate all risk factors leading to hypoxia:
- Stop administering “oxytocin” and prostaglandin-based drugs;
- Explain to the woman how to breathe correctly during contractions;
- Determine the position of the fetus and exclude compression of the umbilical cord;
- Perform an ultrasound to exclude incipient placental abruption;
- Administer drugs that improve the rheological properties of blood.
Poor CTG is a good reason to change delivery tactics in favor of emergency cesarean section,
or eliminate the causes of acute hypoxia. Ignoring pathological CTG is absolutely unacceptable, because this can cause fetal death.
In other words, CTG is a serious tool in the hands of an obstetrician.
Can there be errors when determining accelerations?
Of course yes! The indicators of the CTG curve are considered taking into account data from the anamnesis, clinical picture and other studies. A change in the functional activity of the fetal heart muscle is a response of the autonomic system, which only indirectly reflects the processes occurring in the body of a developing baby.
If, with insufficient oxygen supply, the fetal tissues have managed to adapt to this condition, hypoxia will not affect the study graph in any way. That is why practicing specialists consider CTG, although a very important technique for diagnosing pathologies of fetal development, but only an additional one. Its indicators reflect only part of the “mother-placenta-fetus” system and the results of cardiotocography alone do not make a diagnosis.
conclusions
{banner_banstat10}
Cardiotocography is rightfully one of the most widely used studies in obstetrics. However, like any other technique, it is effective only if it is applied correctly (in accordance with all standards), as well as with proper interpretation of the results obtained.
Unfortunately, there are still disputes and different interpretations of some complex and dubious cases. For this reason, we should not forget that there are also additional research methods that can either confirm or refute possible concerns.
In addition, CTG results remain relevant and informative for no more than 1 week, which means that the key to a favorable pregnancy is regular monitoring of the condition of the fetus.
Indications for the study
The purpose of cardiotocography is timely diagnosis and detection of fetal disorders. Based on data from a number of functional diagnostic studies, such as ultrasound, CTG, Doppler measurements, anamnesis, the obstetrician-gynecologist chooses pregnancy management tactics, treatment, the optimal date and method of delivery.
Indications for additional cardiotocography may include:
- Rhesus conflict
- Preeclampsia in the second half of pregnancy
- Maternal diseases
- Post-term pregnancy
- History of premature birth
- Fetal growth restriction
- Pregnancy pathologies and fetal development abnormalities identified by ultrasound
- Oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios
- Multiple pregnancy
- Complicated obstetric and gynecological history (previous abortions, miscarriages, premature births)
- Changes in the nature of fetal movements (complaints about a decrease or increase in the number of fetal movements per day)
Treatment of placental insufficiency
There are currently no specific treatments for placental insufficiency, since there are no drugs that selectively improve uteroplacental blood flow. That is why all measures to combat placental insufficiency are aimed at prevention. If the patient is at high risk for the development of placental insufficiency, from early pregnancy she is prescribed medications whose effectiveness is well proven and which prevent the early development of severe placental dysfunction.
If, during additional methods of assessing the condition of the fetus, initial disturbances in the supply of oxygen to the baby are detected, drug treatment is carried out aimed at increasing the flow of blood and oxygen through the placenta and mandatory control examinations during the therapy. If the changes are serious and the baby experiences a severe deficiency of oxygen and nutrients, his condition suffers, then in such cases an emergency delivery is performed.
Our doctors
General Director Anshina Margarita Beniaminovna Make an appointment
Director of the Rizhinashvili clinic Semyon Iosifovich Make an appointment
Obstetrician-gynecologist-reproductologist Zhordanidze Diana Omarovna Make an appointment
Obstetrician-gynecologist-reproductologist Torchinov Aslanbek Ruslanovich Make an appointment
Obstetrician-gynecologist, reproductive specialist. Efimova Maria Sergeevna Make an appointment
Obstetrician-gynecologist, reproductive specialist Khubonshoeva Leila Yuryevna Make an appointment
Obstetrician-gynecologist-reproductologist Anna Sergeevna Fedorova Make an appointment
Obstetrician-gynecologist, reproductive specialist Shagunova Marina Olegovna Make an appointment
Obstetrician-gynecologist Samoilova Tatyana Evgenievna Make an appointment
Urologist-andrologist of the highest qualification category Gablia Mikhail Yurievich Make an appointment
Obstetrician-gynecologist-endocrinologist Sharyafetdinova Failya Abdulkhaevna Make an appointment
Obstetrician-gynecologist Pushkina Valeria Vadimovna Make an appointment
Obstetrician-gynecologist Margarita Yuryevna Skvortsova Make an appointment
Obstetrician-gynecologist Slobodchikova Valeria Yuryevna Make an appointment
Obstetrician-gynecologist Peskova Irina Evgenievna Make an appointment
Perinatologist Nelly Idrisovna Kokhno Make an appointment
Obstetrician-gynecologist Olga Borisovna Kuharkina Make an appointment
Obstetrician-gynecologist Pitskhelauri Elena Germanovna Make an appointment
Obstetrician-gynecologist Abdullaeva Adilya Akhmadovna Make an appointment
Hemostasiologist Lopukhin Vadim Olegovich Make an appointment
Oncologist-mammologist Victoria Borisovna Akimova Make an appointment
Ultrasound diagnostics doctor Olga Ivanovna Babaeva Make an appointment
Ultrasound diagnostics doctor Brilliantova Nadezhda Nikolaevna Make an appointment
Ultrasound diagnostics doctor Natalya Sergeevna Gorovaya Make an appointment
Vascular ultrasound diagnostics doctor, vascular surgeon Anna Mikhailovna Nikitina Make an appointment
Cardiologist Maria Viktorovna Cherkasova Make an appointment
Endocrinologist Anzhelika Vladimirovna Manovitskaya Make an appointment
Gastroenterologist Golysheva Svetlana Valerievna Make an appointment
Obstetrician-gynecologist-reproductologist Olga Aleksandrovna Iskorostinskaya Make an appointment
Urologist-andrologist Iskorostinsky Evgeniy Vladimirovich Make an appointment
Psychologist Barskaya Ekaterina Sergeevna Make an appointment
Therapist Alexandra Vladimirovna Kabakova Make an appointment
Anesthesiologist-reanimatologist Isaev Oleg Vladimirovich Make an appointment
Psychiatrist, sexologist Teona Otarievna Kacharava Make an appointment
Head of the Embryology Laboratory. Ph.D. Sergeev Sergey Alexandrovich Make an appointment
Embryologist Kalinina Irina Ivanovna Make an appointment
Embryologist Kalyuzhny Sergey Andreevich Make an appointment
Embryologist Matveeva Elona Olegovna Make an appointment
Embryologist Vladimir Viktorovich Ovsyankin Make an appointment
CTG assessment occurs both during the process and after the end of the recording. If the medical staff sees obvious abnormalities in the baby’s condition on CTG, there is nothing to wait for – they begin treatment measures. If, according to the first impression, everything is fine, they wait until the end of the procedure to evaluate the result in detail. For example, if the curve is monotonous, with a tendency for the basal rhythm to decrease to critical numbers, there is no point in waiting; the condition of the fetus is cause for concern. It happens that the fetus is “caught” in the “sleep phase”, then they wait for it to “wake up”.
What does CTG show during pregnancy?
Using the KTG method, specialists are able to identify possible pathological abnormalities or refute their presence.
The study can determine the development of such dangerous conditions during pregnancy as:
- lack of oxygen in the fetus (hypoxia);
- development of infectious processes of an intrauterine nature;
- lack or excess of amniotic fluid;
- abnormal processes in the baby’s cardiac activity;
- functional disorders in the placenta (placental insufficiency);
- accelerated maturation of the placenta, which threatens premature birth.
Early detection of abnormalities using cardiotocography allows a specialist to adjust pregnancy management or prescribe special treatment to prevent serious complications.