Thyrotoxicosis
Hepatitis
Diabetes
53804 06 August
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. We remind you that independent interpretation of the results is unacceptable; the information below is for reference only.
Glucose (in blood) (Glucose): indications for prescription, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of results and normal indicators.
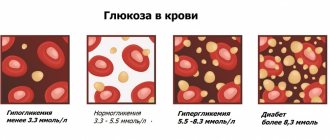
Fluctuations in glucose levels
Hyperglycemia (increase)
The patient may have either a short-term increase in blood sugar concentration or a permanent one. Increased levels on an empty stomach - more than 5.5 mmol/l, after a meal - more than 7.8 mmol/l. Hyperglycemia is divided into 4 forms:
- chronic hyperglycemia. It can be mild (6–10 mmol/l), moderate (10–16 mmol/l) and severe (more than 16 mmol/l). Occurs exclusively in patients with diabetes. Due to poor pancreatic function, the body produces insufficient amounts of insulin. And also this pathology is transmitted hereditarily.
- nutritional hyperglycemia. After eating, blood glucose levels increase, especially in the first few hours. This form of hyperglycemia does not require treatment, because glucose levels return to normal on their own after a certain period of time.
- emotional hyperglycemia. This form occurs after a stressful condition. Having excited the nervous system, the body begins to produce thyroid hormones. With a high content of them in the blood, the body stops producing glycogenesis, but the production of gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis increases. For these reasons, blood sugar increases.
- hormonal hyperglycemia. It appears due to a surge of certain hormones in the blood, such as glucocorticoids, glucagon, catecholamines and thyroid hormones.
Symptoms of hyperglycemia:
- frequent urination;
- itching of the skin;
- hunger;
- strong thirst;
- blurred vision;
- drowsiness, lethargy;
- nausea.
Treatment is prescribed only if the development of hyperglycemia is detected.
During hypoglycemia, a diabetic needs to have something sweet on hand, as sugar can drop sharply
Hypoglycemia (sharp decrease)
Indicators are less than 3.3 mmol/l.
Main causes:
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes in women
- incorrect insulin dose;
- untimely consumption of food (missing more than 6 hours);
- insufficient amount of carbohydrates in the diet;
- unplanned or intense physical activity;
- alcohol abuse;
- drug use;
- non-compliance with the diet or an incorrectly formulated diet.
Symptoms of hypoglycemia:
- shiver;
- increased sweating;
- state of pathological fear;
- dizziness, fainting;
- hunger;
- increased heart rate;
- weakened vision;
- weakness, drowsiness, apathy;
- headache;
- increased irritability.
If there is a sudden decrease in blood glucose, the patient needs to eat something sweet, such as candy, honey, or drink tea with sugar.
IMPORTANT! In both cases, it is necessary to bring blood sugar to a normal level, since jumps in both directions lead to disturbances in the body’s metabolism.
The level of glucose in the blood directly depends on the age of the woman. Statistics show that deviations from the norm in most cases are observed in women after 40 years of age.
Results
A blood sugar test is an indicator of metabolism and the endogenous work of the pancreas to produce insulin. When carbohydrate balance and hormone synthesis are disturbed, hypoglycemia (low blood sugar levels) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) develops. Basic and advanced diagnostics are performed to determine glucose levels.
The second option includes: glucose tolerance test and analysis of glycated hemoglobin levels. For the study, venous or capillary blood is taken. The main condition for obtaining objective results is to take the test on an empty stomach. The normal level of glucose in the blood is 3.3–5.5 millimoles per liter. In older people, the control indicators are not significantly higher.
A slight but stable excess of glucose levels is defined as prediabetes - a reversible change in biological processes in the body. For diabetic patients, there are separate reference sugar values that determine the stage of the disease. Unstable glucose levels are an indicator of a failure of metabolic and hormonal processes. To diagnose the exact cause of unstable glycemia, additional laboratory and hardware examination is necessary.
Table of norms for glucose levels in women
| Age | Normal (µmol/l) |
| Up to 14 years old | From 2.8 to 5.6 |
| From 14 to 60 years | From 4.1 to 5.9 |
| From 60 to 90 years | From 4.6 to 6.4 |
| 90 and older | From 4.2 to 6.7 |
Normalizing weight and properly balanced nutrition is the key to success in the fight against diabetes.
If the level of dextrose concentration in the blood approaches 6.7 mmol/l, this means that diabetes mellitus may begin to develop, and blood should be taken again to clarify the result. Having studied glucose tolerance, specialists examine the level of glycosylated hemoglobin. Based on the results, a diagnosis of diabetes is made and treatment or diet is prescribed depending on the degree of its development.
You can measure your current blood sugar level by taking tests at a clinic or using a glucometer at home (if you know your blood glucose level). Test results will vary depending on the person's age, time since last meal, and test method. The normal level of sugar in venous blood will differ slightly from blood taken from a finger prick.
Norms and deviations
In case of persistent hyperglycemia, it is necessary to find out the reason for the deviation of the results. The most common is diabetes mellitus (prediabetes). Sometimes, there are other reasons for unstable sugar levels. To carry out advanced diagnostics, the patient is prescribed additional laboratory tests: GTT (glucose tolerance test), HbA1C analysis (quantitative assessment of glycosylated hemoglobin).
Important! Official diabetes is diagnosed only on the basis of a complete inpatient or outpatient examination of the patient.
Glucose tolerance test
Testing is a two-step blood test. Initially, biofluid is collected on an empty stomach. Blood is taken again 2 hours after the “glucose load”. The loading component is glucose (75 g) dissolved in water (200 ml). The patient drinks the liquid after the first test.
The glucose tolerance test determines the ability of body cells to metabolize glucose. Testing is mandatory for women during the perinatal period and patients aged 30+ who are suspected of having non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Impaired glucose tolerance is a condition of prediabetes.
Interpretation of GTT results (sugar in capillary blood in mmol/l)
| Diagnostic data | Fine | Prediabetes | SD |
| Before meals | < 5,5 | < 6,1 | > 6,2 |
| After load | < 7,8 | > 7,8–11,0 | > 11,1 |
In difficult cases, blood is drawn every 30 minutes. Based on the data obtained, a sugar curve is compiled and analyzed.
The amount of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1C) in the blood
Glycosylated (glycated) hemoglobin is a permanent combination of glucose and hemoglobin (the protein component of red blood cells). It is formed in the blood during the addition of a monosaccharide to a protein, and occurs without the participation of enzymes (non-enzymatic glycosylation). Hemoglobin does not change its structure inside red blood cells for 4 months. HbA1C analysis determines the retrospective glucose content, that is, the quality of carbohydrate metabolism is analyzed over the past 120 days.
Blood sugar levels in children
Glycated hemoglobin is measured as a percentage. In healthy children under 14 years of age, the HbA1C norm does not exceed 6%. A deviation of more than one (7%) means a high probability of developing diabetes. Age norm for adults:
- Up to 40 years – less than 6.5%, permissible deviations 6.5-7.0, with values >7.0% diabetes is defined.
- Over 40 – less than 7.0%, borderline values are 7.0-7.5, unacceptable excess of the norm – 7.5%.
- Age category 65+ – less than 7.5%, limit values 7.5-8.0, diabetes is diagnosed with results >8.0%.
For diabetics, HbA1C analysis is a means of monitoring the disease, assessing the risk of complications, and checking the effectiveness of therapy. Normal and abnormal values for diabetic patients are presented in the table.
Differentiating the type of diabetes
Consistently elevated results of all studies are an indication for testing the blood for the amount of antibodies to glutamate decarboxylase (GAD antibodies). The analysis is carried out to differentiate the type of diabetes. A healthy person maintains a certain level of GAD antibodies. Their permissible rate is 1.0 units/ml. When the content is exceeded, the test is considered positive, that is, type 1 diabetes is determined.
Important! Blood sugar can be either high or low. Both conditions indicate disturbances in the functioning of the body. To effectively eliminate them, it is necessary to identify the cause of unstable glycemia.
Measuring sugar levels with a glucometer
This method is the fastest and most convenient. For more accurate indicators, the following tips should be followed:
- Read the instructions carefully.
- It is recommended to perform a blood test on an empty stomach (on an empty stomach).
- Wash your hands with soap and rub your finger to warm it up.
- Wipe your finger with an alcohol solution.
- Prick your finger on the side with a piercing pen.
- Take a second drop of blood onto the test strip: the first is removed with cotton wool.
- After two seconds, the test result will appear on the meter screen.
To ensure accurate results, follow the specialist’s recommendations before taking the test.
General information
Glucose metabolism in the body is regulated by two hormones: insulin and glucagon. The action of these hormones is opposite. Keeping your blood sugar at the same level is extremely important, so the concentration of blood glucose is monitored by special cells in the pancreas every few seconds. These same cells release the necessary hormone into the blood.
After a meal, when blood glucose levels rise, insulin is activated. It acts as a key for glucose and thereby helps it “enter” cells that need energy. Insulin also stimulates the use of glucose in tissues and promotes the formation of glycogen. Glycogen is a substance in the form of which the human body stores excess glucose. As a result of the action of insulin, blood sugar levels decrease. If insulin malfunctions, diabetes mellitus occurs, a disease in which blood glucose levels cannot decrease.
Glucagon works when blood sugar levels are low. Glucagon stimulates the release of glucose from the body's stores so that cells can get the energy they need from it. Glucose is especially necessary for the brain, since it is the main source of energy for it. As a result of the action of glucagon, blood sugar levels rise.
How to measure blood sugar at home
A blood glucose test can also be performed at home. For this you need a special device - a glucometer. To correctly measure glucose levels, a number of conditions must be met:
- Blood sugar measurement is carried out on an empty stomach; before the procedure, you must thoroughly wash your hands with soap and dry them with a towel.
- To measure, a special test strip is used, which must be inserted into the opening of the glucometer. After this, a symbol will appear on the glucometer indicating that the device is ready for testing.
- Next, a needle or scarifier is used to puncture the skin of the nail phalanx of the ring finger. It is not necessary to treat the skin with alcohol before piercing, but if you do this, you must wait until the antiseptic has completely dried, because residual alcohol may distort the readings.
- As a result of a puncture of the skin, blood appears, but you cannot press on your finger; the blood should flow out on its own. The first drop of blood is wiped off with dry cotton wool. As the blood flows out, a second drop is formed, to which the test strip inserted into the glucometer is brought. The test strip itself absorbs the amount of blood that is needed for the test. After a few seconds, the glucometer displays the test result in mmol/l.
- After the measurement, the used needle and test strip should be thrown away.
Rules for preparing for analysis
Preparation for analysis is very important. Consumption of food or liquid entails a change in the concentration of glucose in the blood, making the analysis inaccurate. Therefore, when donating blood from a vein or finger, it is recommended to limit the consumption of foods and liquids at least 8 hours before the test. An hour after a meal, the glucose concentration reaches 10 mmol/l. After two hours, the value drops to 8 mmol/l.
If you consumed mainly high-carbohydrate foods at your last meal before the test, you should wait at least 14 hours before taking blood for a more accurate result.
In addition to food, there are other factors that influence the final result of the analysis:
- physical exercise;
- stressful state;
- infectious diseases;
- fatigue (insufficient rest).
Before taking the test, the patient needs calm and rest. Therefore, the day before the test, it is recommended to protect yourself from physical activity, emotional turmoil and other factors that can change the condition of your body. If you do not follow medical instructions, the test result will be blurred and the condition of prediabetes will not be accurately detected.
A healthy person needs to donate blood for sugar once a year; for a diabetic, measuring the level of glucose concentration in the blood reaches 5 times a day. In insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, it is necessary to measure your sugar level before each insulin injection. And it is also recommended to measure your glucose levels before bedtime and after sleep, as well as 60 minutes after meals.
Doctors recommend taking a glycemic index test for prevention purposes at least once every six months or year. This is especially true for women approaching 40 years of age and older.
In what cases should you get checked?
You need to check for sugar levels in cases where the following symptoms are observed:
- frequent thirst;
- frequent urination;
- dry skin, itching;
- dry mucous membranes;
- frequent infectious diseases;
- deterioration of vision (decreased sharpness);
- fast fatiguability;
- decreased performance.
Checks are also carried out as planned, for example, during a medical examination, passing a commission, as part of a medical examination program, etc. Patients with diabetes regularly test their blood sugar - in some cases, daily monitoring is required.
Normal blood glucose levels in pregnant women
Pregnant women should pay special attention to their blood sugar levels because they often exceed the norm. This factor is due to the fact that the hormonal background of a pregnant woman undergoes changes due to the provision of all useful substances to the unborn child. If your blood glucose levels range from 3.7 to 6.3 micromoles per liter of blood, there is nothing to worry about. When blood sugar levels are more than 6.3 µmol/L, the risk of developing gestational diabetes mellitus increases significantly. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after childbirth if you strictly follow the diet prescribed by your doctor. An increased rate of glycated sugar in the blood of a late pregnant woman indicates that the fetal weight will be more than 4500 g and the child will have a tendency to develop diabetes mellitus.
Due to hormonal changes in the body, expectant mothers are susceptible to sudden hyperglycemic surges
Hypoglycemia before and after meals
Hypoglycemia is a forced decrease in glucose levels below the critical level of 3.0 mmol/l. At values of 2.8 mmol/l, a person loses consciousness. The reasons for the body's abnormal reaction after eating are:
How to measure sugar
- Prolonged refusal to eat (fasting).
- Strong emotional shock, often of a negative nature (stress).
- The presence of a hormonally active pancreatic tumor that synthesizes insulin in excess (insulinoma).
- Physical activity that is disproportionate to the body’s capabilities.
- Decompensated stage of chronic pathologies of the liver and kidneys.
Sugar levels decrease due to excessive uncontrolled consumption of alcoholic beverages. Ethanol has the property of inhibiting (blocking) the processes of food processing, the formation of glucose and its absorption into the systemic bloodstream. However, a person under the influence of alcohol may not experience acute symptoms.
When diabetes mellitus is diagnosed, the listed reasons are supplemented by incorrect insulin therapy for the first type of disease (unauthorized increase in insulin doses or lack of food intake after the injection), exceeding the prescribed dose of glucose-lowering medications (Maninil, Glimepiride, Glirid, Diabeton) in the second type of pathology. The state of reactive hypoglycemia is life-threatening.
Signs of lack of sugar in the blood: polyphagia, unstable psycho-emotional state (unreasonable anxiety, inadequate reactions to what is happening), autonomic failures (decreased memory, concentration), impaired thermoregulation (constantly cold limbs), rapid, rhythmic contractions of muscle fibers of the legs and arms (trembling or tremors), increased heart rate.
Energy deficiency is primarily manifested by low performance and physical endurance.
How is the level of glycated hemoglobin determined?
Determining glycated hemoglobin has a number of advantages:
- Held at any time of the day.
- No preliminary preparation is required before testing.
- The analysis results will not be distorted due to physical activity, drinking alcohol, stress, colds, or changes in diet.
- The result is more accurate, it is difficult to correct it several days before the analysis.
- Women's menstrual cycle and its stage will not affect the test results.
- The result will show fairly long-term fluctuations in blood sugar, rather than short-term (recent) ones.
- The test results are not affected by the patient's age or gender.
The range of acceptable indicators is from 4.5 to 6.5. This is considered the norm for glycated hemoglobin for men and women of any age. If the result is from 5.5 to 7, the attending physician diagnoses “prediabetes”. For preventive purposes, adjustments are made to the patient’s diet, as tolerance to sugar is reduced.
Don't forget to check your glucose levels before eating
Indications for use
If a patient exhibits symptoms similar to the characteristic features of diabetes mellitus, the doctor prescribes a sugar test. These symptoms include:
- decreased visual acuity;
- decreased level of performance, feeling of frequent fatigue;
- feeling of constant thirst;
- feeling of dryness in the mouth;
- rapid weight loss;
- itching and dry skin;
- frequent urination;
It is also recommended to take the test once a year for people at risk. These include:
- patients who have relatives with diabetes in their family;
- overweight women, men and children;
- women who gave birth to a child weighing more than four kilograms;
- patients taking glucocorticosteroids;
- people with tumor diseases;
- men and women who were diagnosed with heart or vascular disease in middle age.
Pregnancy is also a reason to examine the amount of monosaccharides in the body, since during this period there may be cases of hidden diabetes.
Symptoms of diabetes in women
Oddly enough, women are more likely to suffer from this disease. The opinion that the female sex is more predisposed to eating sweets is erroneous. What is the real reason for the development of diabetes in women? The body of women is structured differently, the endocrine system is no exception; it experiences hormonal changes during a woman’s pregnancy or during menopause, hence disturbances in insulin production are observed.
The first prerequisites for diabetes mellitus in women are:
- Thirst due to dry mouth.
- Sudden weight gain.
- Sudden weight loss (for no reason).
- Frequent urination (especially at night).
- Decreased performance, rapid fatigue.
- Dryness and itching of the skin.
- The appearance of age spots on the body and face.
- Deterioration of vision.
- Memory problems.
- Changes in the menstrual cycle.
Prevention of unstable glycemia in a healthy person
Normal blood sugar levels indicate the absence of carbohydrate metabolism disorders in the body. If the glucose level changes in one direction or another, you should resort to a number of preventive measures. This will help prevent (in some cases slow down) the development of pathological processes.
Preventive measures include:
- Changes in eating behavior. It is necessary to reconsider your diet and diet. Eliminate simple carbohydrates, fatty foods, fast food, and sweet carbonated drinks from the menu. Eat at least 5 times a day at equal intervals.
- Correction of physical activity. The load must correspond to physical capabilities. In addition, it is necessary to agree with your doctor which sports training is most suitable in each individual case (aerobic, interval, cardio, etc.).
- Refusal of drinking alcoholic beverages. The pancreas needs to be freed from alcohol load.
- Constant control over body weight (obesity leads to diabetes, anorexia can cause hypoglycemia).
- Regularly checking your sugar level (on an empty stomach and after meals).
- Strengthening the immune system. Hardening, systematic walks in the fresh air, course intake of vitamin and mineral complexes (before use, you must obtain consultation and approval from a doctor).
- Normalization of sleep. Night rest should be at least 7 hours (for an adult). You can eliminate dysania with the help of soothing decoctions and tinctures. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe medications.
Important! If you feel unwell, you should seek medical help. Simple fatigue can be a symptom of unstable glucose levels.
How to use a glucometer
The glucometer is easy to use. Some devices measure indicators in the blood, some in the blood plasma. This must be taken into account when calculating indicators.
The operating principle of the devices is the same:
- Wash your hands well before measuring your blood sugar. It is better to use warm water, which will help speed up blood circulation.
- The needle is released and the puncture depth is set on the lancet.
- The device is used to pierce the fingertip. Important! The puncture site should not be wiped with disinfectants; this may change the study data.
- A drop of capillary blood is applied to a special test strip. It is important that the area is completely filled with blood, otherwise the test will not be performed.
- After about 10 seconds, the sugar content appears on the display.
Devices may have an error of 10-15%. The most accurate indicators can be obtained from laboratory tests when collecting venous blood and plasma.
What is total sugar control?
To know how the body reacts to the prescribed diet and medications, you need to conduct careful self-monitoring of sugar concentration. Therefore, the device often takes measurements, namely:
- immediately after sleep;
- before breakfast;
- 5 hours after insulin injection;
- always before meals;
- after any meal after 2 hours;
- before sleep;
- before and after physical labor;
- after stress;
- if you suspect that your sugar has changed;
- in the middle of the night.
All numbers are entered into a notebook. This helps figure out what is causing the sugar spikes.
Clear interface
Who needs a glucose tolerance test?
If hyperglycemia is suspected, the doctor prescribes repeat tests. These are tests with a sugar load, allowing you to understand how ready the body is to cope with a one-time supply of glucose in large quantities. This is how the pancreas functions and its ability to produce insulin in large volumes is tested. Tests are carried out after consuming 75 g of glucose dissolved in water. Then the indicators are measured four more times with an interval of half an hour.
During pregnancy, this test is used to diagnose gestational diabetes. A glucose tolerance test is mandatory for all pregnant women at 24-28 weeks. For pregnant women in the risk category (history of gestational diabetes, body mass index more than 30), the test is performed earlier than these dates. It includes two stages of research, which are carried out on an empty stomach and after consuming glucose.
How to determine glycemia
Sugar levels should be monitored at least once a year, even for healthy people. You can measure your level at home using a glucometer. The study should be carried out at different times of the day:
- On an empty stomach in the morning. Before the study, it is forbidden to take food and drinks except water for 8 hours.
- After meal. Control is carried out two hours after eating food.
Also, patients with diabetes are recommended to check their sugar levels several times during the course, especially in the first period after diagnosis.
Low glucose (hypoglycemia)
- Pancreatic dysfunction;
- Hypothyroidism (insufficient production of thyroid hormones);
- Insulinoma (usually a benign neoplasm that is capable of secreting insulin);
- Diseases of the liver, kidneys, adrenal glands, incl. malignant;
- adrenal insufficiency (Addison's disease);
- Hypopituitarism (impaired secretion of hormones by the pituitary gland);
- Glycogenosis (a group of hereditary diseases caused by disruption of the process of synthesis and breakdown of glycogen due to existing defects in various enzymes).
Provoking factors:
- prolonged fasting, following a strict diet or fasting;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, autonomic disorders, postoperative conditions;
- overdose of insulin or other glucose-lowering drugs;
- intoxication (poisoning) with arsenic;
- alcohol abuse;
- heavy physical activity;
- feverish conditions;
- taking medications: steroids, amphetamine, etc.