Extrasystole is a type of arrhythmia in which an extraordinary contraction of the entire heart or its parts occurs. It develops as a result of disruption of the process of transmission of nerve impulses from the sinus node to the ventricles of the heart. Statistics show that episodes of extrasystole occur throughout every person’s life. The main danger of the pathology lies in its ability to develop into more serious rhythm disturbances.
Why does extrasystole occur?
Extrasystole can occur for a number of reasons, but mainly they include:
- heart diseases;
- severe anxiety, stress;
- smoking;
- damage to internal organs, especially the stomach or liver;
- disruptions in the nervous regulation of the functioning of the heart muscle;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- impaired blood circulation.
In young people, extrasystoles mainly occur due to nervousness, as well as as a result of excessive smoking. Older patients are more likely to experience arrhythmia caused by damage to the heart muscle.
Forms of the disease
In medicine, several types of gradations of ventricular extrasystole are used. The disease is classified based on the following characteristics:
- number of ectopic foci;
- time of occurrence;
- type of order;
- frequency of premature contractions.
| Form of the disease | Main features |
| According to the number of sources of excitability | |
| monotopic | presence of one ectopic focus |
| polytopic | two or more sources of excitability |
| By time of occurrence | |
| early | appear when the upper chambers of the heart contract |
| interpolated | in the intertemporal interval of atrial and ventricular contractions |
| late | occur during the diastole phase or contractions of the lower parts of the heart |
| By order | |
| disordered | There is no pattern between the appearance of normal and extraordinary contractions |
| ordered | alternation of contractions occurs in a certain sequence |
| By frequency | |
| rare | up to five additional contractions in one minute |
| mid-frequency | 6-15 extrasystoles per minute |
| frequent | over 15 extraordinary layoffs |
With frequent contractions of the heart muscles, the pulse increases significantly and general health worsens. Frequent ventricular extrasystole is fraught with the development of ventricular fibrillation; this form of cardiac pathology requires mandatory treatment.
Types and classification
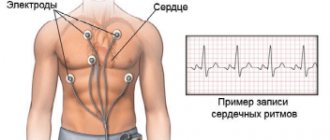
Extrasystole can be detected by analyzing round-the-clock ECG monitoring.
Classification of extrasystoles by place of origin:
| View | Subspecies | What pathology is it typical for? | When occurs with intact myocardium |
| Supraventricular (supraventricular) |
| Myocarditis, atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis, chronic pulmonary heart disease | More often they are functional in nature, due to stress, drinking alcohol, coffee and strong tea, smoking |
| Ventricular (ventricular) |
| Ischemic disease (acute - myocardial infarction, chronic - angina), acquired valvular heart disease, hypertension, non-coronary myocardial damage | For diseases of the biliary tract, diaphragmatic hernia |
Monomorphic extrasystoles appear on the ECG in the form of identical single extraordinary complexes. Their shape depends on the location. The frequency of occurrence of rare ones is up to 29 per hour, frequent ones – from 30 times and above.
Attacks of allorhythmia are characterized by a correct change between normal heart rhythm and extrasystolic episodes:
- bigeminy - a normal contraction replaces each extrasystole;
- trigeminy - an extraordinary heart beat occurs after two standard ones;
- quadrigeminy - every fourth myocardial contraction occurs earlier than expected.
Two extrasystoles in a row are called paired. Early ones are those that occur before the full cycle of cardiac activity, recorded electrographically, ends.
Polymorphic extrasystoles
An ECG is a recording of electrical potentials that arise during the work of cardiomyocytes. Their sum appears in the form of a curve obtained by electrocardiography. The line has a standard outline provided that an impulse originates in the sinus node. If the generation of potential begins in a different place, a complex of teeth and segments of a completely different nature is displayed. As a result, the right ventricular extrasystole differs from the left ventricular one.
Polymorphic (different in shape) extrasystoles are visible on the ECG, provided that each extraordinary contraction was started in a different part of the myocardium than before. This means that the cause of arrhythmia is not local dysfunction, but damage to a large area of the heart muscle.
Group extrasystoles
They appear in quantities of 3-5 pieces one after another. The impulse circulates through the myocardium, which has lost the ability to become refractory (immune to depolarization).
If only extrasystoles are recorded on the ECG for half a minute, they are called “unsustained tachycardia.”
How to recognize the disease?
Extrasystole does not always have an obvious clinical picture. Its symptoms depend on the characteristics of the body and its general condition. In most people, this type of arrhythmia does not manifest itself in any way, it does not cause pain or discomfort and, as a rule, is an incidental finding during preventive electrocardiography. However, there are patients who tolerate arrhythmia very poorly.
Typically, extrasystole manifests itself in one of the following ways:
- strong heartbeat;
- feeling as if the heart stops for a while;
- a feeling of short-term cardiac arrest, accompanied by a strong blow in the chest;
- pulse disturbance.
Extrasystole may be accompanied by:
- chest pain;
- pale skin;
- anxiety;
- shortness of breath;
- excessive sweating;
- a sharp feeling of heat;
- fatigue.
In fact, all of the above symptoms are nonspecific and can be observed in a number of other diseases, sometimes not even related to the pathology of the cardiovascular system. A reliable way to register extrasystole is an ECG, but even this method does not allow one to fully assess the extent of the disease, since it covers only a short period of time.
- Treating lower back pain at home
In such cases, the doctor refers the patient to 24-hour Holter monitoring, with the help of which it is possible to record and analyze the electromechanical processes occurring in the myocardium during the day.
Lead tactics
Functional extrasystole does not interfere with the normal course of pregnancy and gestation. We usually do not identify any contraindications to natural delivery. A woman can give birth to a healthy baby at term and avoid complications.
Extrasystole associated with organic damage to the heart or other organs, endocrine disorders and other conditions requires mandatory observation by a specialist. The management tactics for a woman will depend on the severity of the underlying disease.
All pregnant patients, regardless of the severity and form of extrasystole, are under the supervision of a therapist and cardiologist until delivery. If the condition of the woman and fetus is stable, a control examination (ECG) is carried out before birth. If the patient's condition worsens or complications of gestation develop, additional examination is indicated.
Indications for caesarean section for extrasystole are rare. They are usually associated with concomitant pathology or complications of pregnancy. In a planned procedure, the operation is performed at 37-39 weeks, in an emergency - at any time.
Have you encountered such a phenomenon as extrasystole during pregnancy? What did the doctor recommend to you in this situation?
How is extrasystole diagnosed?
Having analyzed the patient’s complaints, the doctor proceeds to an objective examination, through which pulsation of the jugular vein (presystolic) and arrhythmic cardiac activity are detected. Auscultation reveals a change in the sound of the 1st tone and a bifurcation of the 2nd.
Next, it is necessary to conduct instrumental studies. Initially, an ECG and Holter monitoring are advisable. They record unscheduled ventricular contraction, atypical QRS, absence of P before the extrasystole.
The bicycle ergometry used helps to determine the cause through physical activity. With the idiopathic type, extrasystoles decrease after exercise. If cardiac changes are present, the load only provokes the formation of extrasystole.
If necessary, TEE, rhythmocardiography, and echocardiography are recommended. When there is ventricular extrasystole, its treatment is determined after examination, otherwise fibrillation is likely.
Is it possible to get rid of ventricular extrasystoles?
When there are no symptoms, medications are not used. In this case, it is recommended to follow a dietary regimen, quit smoking, alcohol, and heavy physical activity. Therapeutic tactics are based on taking beta blockers (obzidan, anaprilin), sedative medications of natural origin or tranquilizers. This combination provides a reduction in extrasystoles.
For bradycardia, it is advisable to use anticholinergics. In case of severe heart rhythm disturbances or deterioration of health, the use of antiarrhythmic drugs (cordarone) is recommended. Medication prescriptions and their doses are established exclusively by the cardiologist based on the examination results.
When drugs do not normalize heart rhythm, radiofrequency catheter ablation must be performed. When there is ventricular extrasystole, treatment with folk remedies is not allowed without a preliminary examination and consultation with a cardiologist, because in the case of cardiac changes, ventricular fibrillation is possible, which threatens a person’s life.
- Treatment of baldness in women at home
Extrasystoles in osteochondrosis
Content:
Today, extrasystoles with osteochondrosis can very often be observed in this or that patient, since a sudden disruption of the functioning of one or another part of the muscles or spine always sends unwanted urges to the heart. If you begin to notice that sometimes the heart may stop working in a normal rhythm and mode, if you experience pre-fainting states that are accompanied by micro-losses of consciousness, you must immediately consult a doctor, since extrasystole itself is far from a simple thing, like may seem at first glance.
As has been established by many workers in medical institutions, along with the presence of extrasystole in a person inside the body, the risk of developing cardiovascular disease, as well as atrial fibrillation, increases. But the latter term can extremely easily lead to sudden cardiac arrest and, as a consequence, death. For this reason, we invite you, dear readers of the portal, to carefully study all the information that we give you, and then draw several conclusions based on what you read. Today, along with osteochondrosis, heart rhythm disturbances can often be observed, since the presence of inhibition of work (during an exacerbation of the disease) is just the very beginning, when there is a nervous urge to the cardiac region. A person may accidentally wake up at night or in the morning, feel that pain will begin in the back or collarbone, after which the nerve endings will begin to act on the heart. And it is after this that we can say that it is necessary to see a doctor as quickly as possible.
In general, extrasystole in osteochondrosis can be treated if you know how to influence the very manifestation of the disease. As you know, osteochondrosis is a disease of the spine due to incorrect walking or incorrect posture. Many people also say that playing sports on a hard surface (we are talking about running) can affect the development of the disease in geometric progression in relation to the time of the presence of the disease. (See also: Extrasystole with osteochondrosis)
IMPORTANT: Today, dear readers of the portal, we will tell you what extrasystoles are and how they can manifest themselves in the human body. If you have some idea (or none at all), you can always learn the most from our articles, which are created specifically for those interested in curing the disease as quickly as possible.
The main provisions of extrasystoles and the interaction of osteochondrosis with them
Today, it is possible to understand what extrasystole is only with a full-fledged approach to analyzing the problem using an experimental format of examples. So, for example, we will present several possible methods that allow you to get rid of such a concept as “extrasystole”, since the presence of this term in the human body does not bring health to him, but, on the contrary, only aggravates it. If you are interested in obtaining as much knowledge as possible, you need to read some information below, since this is what we offer you as the basis for further actions to combat this unpleasant disease.
- So, today, the concept of “Extrasystole” must be understood as a variant of the process of heart rhythm disturbance, which is characterized by extraordinary contractions of individual areas of the organ. As a rule, a person can feel an extremely strong shock or, conversely, the absence of shocks when working for some time. In this sense, it is necessary to talk about a lack of air volume or anxiety, cardiac arrest. In some cases, it is customary to talk about fainting. As a rule, extrasystole differs in that the patient feels a disturbance in cerebral blood flow, and therefore has a greater chance of acquiring angina or atrial fibrillation in the future.
- How is extrasystole connected with osteochondrosis? If you feel that in the morning you feel strong tension between your shoulder blades or in your spine, after which small shocks are heard in your heart, not quite suitable for the normal functioning of the organ, know that this is extrasystole, which is a consequence of the body’s reaction to improper functioning inside.
IMPORTANT: The spine seems to give off alarm signals, so the heart begins to work in a way that is not necessary.
- As a rule, similar things can be felt when standing, lying or sitting positions are taken. If a person moves, such symptoms are not felt so strongly, as a result of which at first no attention is paid to this. Remember that at the first urge of abnormal heart function against the background of pain in the spine, you must immediately consult a doctor and wait for his advice.
IMPORTANT: In general, do not forget that our materials are just introductory articles, therefore, following the basis of treatment or the fight against this or that ailment against the background of osteochondrosis is necessary only with the vigilant supervision of a doctor. Don't forget about this, please.
- Many people experience interruptions within their movements. If, for example, you go to work in the morning, you feel the unpleasant sensations of extrasystole, but in the process of performing the actions you forget and, as they say, “get used to the sensations,” and in the evening everything resumes (for example, while going to the kindergarten to pick up your child), you need to you can quickly contact medical institutions, since the named illness can end badly: above we described the approximate consequences of extrasystole on the body.
How to react to the manifestation of extrasystole?
If you need to figure out what actions are supposed to be taken in the process of influencing the solution of a problem, if you need advice and recommendations, read again what we suggested just above, since all the information received will help you take the necessary actions based on the facts. Remember the main thing: extrasystole is an extremely, extremely serious illness that is a consequence of osteochondrosis, therefore, for a long-term effect, it is necessary to understand now what exactly is required to prevent and relieve the current condition. So, for example, you need:
- Start working on exercise therapy. Consult a doctor who will suggest an appropriate set of developmental exercises. It is he who will give advice on how best to proceed and what training to start going to. In general, physical education will help not only develop the strengthening of the body, but also influence the current state of affairs (help cure osteochondrosis and eradicate the manifestation of extrasystole).
- The next step is the prescription of certain drugs that will affect the relief of the disease. It is necessary to discuss this with your doctor, since only he knows for sure what medications should be prescribed.
- Finally, it is worth reading articles or watching videos on the Internet, since today numerous forums and sites offer real communication between patients with osteochondrosis along with the manifestation of symptoms of extrasystole. They, like no one else, know better what options there are in order to eradicate unpleasant sensations and prevent it for the future.
Treatment of reflex extrasystole
With reflex extrasystole, when the cause is not in the heart, but outside it, treatment comes down to the general improvement of the body, namely:
- Losing extra pounds with the help of fasting and cleansing diets, since the diaphragmatic reflex caused by large body weight often contributes to rhythm disturbances.
- Rationalization of nutrition, since gastrointestinal disorders (bloating, constipation) often cause attacks of extrasystole
- Cleansing the liver and gallbladder from bile (by blind probing, tubing) since the distension of these organs contributes to the excitation of the vagus nerve, which provokes the occurrence of extrasystoles.
- Elimination of inflammatory diseases of the genital area in women, as they can cause arrhythmia.
What are the symptoms of the pathology
Symptoms of extrasystole are:
- periodic sensation of heartbeat;
- freezing in the chest;
- feeling that the heartbeat is arrhythmic;
- lack of air due to chest discomfort;
- failure of breathing rhythm;
- syncope (temporary loss of consciousness).
The occurrence of extrasystoles in the supine position
If the sensation of a change in the functioning of the myocardium manifests itself in the supine position, this indicates the functional nature of the extrasystoles that occur. Symptoms disappear when moving to a sitting position, the pulse becomes rhythmic. This arrhythmia does not pose a danger to the body. In this case, standard drug therapy will be ineffective; taking sedatives will be an effective solution.
Drug treatment
The treatment tactics of practicing cardiologists in the fight against heart diseases involves a gradual transition from weak drugs, in case of their ineffectiveness, to stronger ones. (from sedatives to antiarrhythmics)
The main stages of therapy include:
- Sedatives that prevent excessive excitation of extrasystole foci by influencing brain signals.
- Potassium- and magnesium-containing drugs that strengthen the heart muscle (Asparkam, Panangin). If the patient uses diuretics that wash out the necessary electrolytes, intravenous infusions of these drugs (Adenosine) are prescribed.
- In cases of extrasystole occurring against the background of bradycardia, they are treated with drugs containing belladonna (Atropine).
- In cases of extrasystole against the background of tachycardia, glycosides (medicines from digitalis), administered in small doses, have proven themselves.
- Antiarrhythmic drugs (Propafenone, Amiodarone, Moracizine, Bretilium) were created specifically to help patients with rhythm disturbances that occur in the atria and ventricles of the heart. They have serious contraindications and side effects and cannot be treated independently.
Table of drugs for extrasystole
| Type of drug | Name | Treatment dose |
| Beta blockers | Cardanol, Metoprolol | 50 mg/day |
| Atenolol, Betacardin | ||
| ACE inhibitors | Pyramil, Sinopril | 1.25-2.5 mg/day |
| Amprilan, Enalapril | ||
| Calcium channel blockers | Verapamil, Cinnarizine, Nifedipine | 40-80 mg 3 times a day |
| Antiarrhythmic drugs | Moracizin, Bretylium | 450-600 mg/day |
| Amiodarone, Propafenone |
Pharmacological drugs are prescribed if there are serious disturbances in the functioning of the heart, when pathological changes are observed in the internal organs and brain. In these cases, hospital treatment with intravenous administration of antiarrhythmic drugs under the supervision of a physician is indicated.
In the absence of a positive effect of treatment, they resort to surgery, which consists of introducing a coagulator through the coronary vessels and thus eliminating the source of excitation. If the arrhythmia is complicated by ischemia or hypertension, the doctor may prescribe additional medications:
- Beta blockers.
- Agents that slow down the delivery of calcium ions to the myocardium.
- Medicines that inhibit the synthesis of enzymes in the heart muscles.
Clinical case
Last week I observed a 47-year-old man who came to me with complaints of dizziness, periodic sensations of “fading” of the heart, and a feeling of lightheadedness.
Among the bad habits the patient noted was smoking tobacco with an experience of 26 years. Upon examination, I found an irregular pulse, dry rales in the lungs and slight blueness of the lips. Upon detailed questioning, the patient said that in recent months he began to notice sputum discharge in the morning and shortness of breath during physical activity. I ordered Holter ECG monitoring, chest x-ray and spirometry (respiratory function test). The ECG shows frequent atrial extrasystole (polytopic) with a total number of ES per day of 843. The X-ray shows signs of chronic bronchitis. Spirography showed impaired patency of the small bronchi. Based on these data, a diagnosis of “Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease of moderate severity” was made. Seretide (a combination drug in the form of a powder inhaler) and Verapamil were prescribed for treatment. Recommendations for lifestyle changes are given.
When can you stop taking medications?
There are clinical options when extrasystole does not require drug treatment and can go away on its own after a certain period of time. Such cases include extraordinary cardiac contractions of neurogenic origin, as well as so-called drug extrasystoles caused by taking medications.
Neurogenic extrasystole, which develops against the background of nervous overstrain, anxiety, and severe stress, usually goes away after normalizing sleep patterns and taking sedatives, which are easy to prepare at home.
To relieve patients from this type of extrasystole, doctors recommend swimming in the pool, relaxing massage, yoga and other relaxation techniques.
- Treatment of thyroid gland at home
If extrasystoles are a side effect of a drug, then to eliminate the pathological manifestations it is enough to cancel the harmful drug and henceforth avoid direct contact with it.
Doctors always warn their patients about the possible negative effects of taking a particular medication. But we all know cases when patients prefer to prescribe pills on their own or on the advice of friends. This should not be done under any circumstances, as such behavior can have very disastrous consequences.
What needs to be done to provide assistance?
It is quite possible to relieve an attack of extrasystole at home. However, it should be remembered that if this arrhythmia is accompanied by other symptoms of damage to the cardiovascular system (pain in the heart area, significant shortness of breath, swelling), then it is better not to delay contacting a cardiologist. Such a combination may indicate the organic nature of the pathology.
First of all, the effect of the etiological factor should be removed. It is necessary to stop physical activity, stop drinking alcohol or coffee. In most cases, these measures will be quite enough to eliminate an attack of extrasystoles at home. If the abnormal heartbeat does not stop, it is better to consult a doctor immediately.
Expert advice
For the most effective drug therapy, I recommend that my patients adjust their lifestyle, i.e. avoid factors that provoke the appearance of extrasystoles. To do this, it is necessary to reduce the amount of coffee, “energy” and alcoholic drinks consumed, and completely stop smoking. It is also worth remembering that the presence of PE itself may indicate the presence of another disease. Therefore, you need to try to find out the cause of PE and be examined to look for a possible disease (primarily cardiac).
When you can't do without treatment
Some types of extrasystoles are dangerous evidence of serious cardiac dysfunction. If the course of the disease is unfavorable, rhythm disturbances can result in atrial fibrillation, chronic coronary and renal circulatory failure.
A complication of ventricular extrasystole is often paroxysmal tachycardia. Therefore, if fibrillation and other pathologies are suspected, urgent measures should be taken.
The following types of extrasystoles require a qualified approach:
- Allorhythmia, which refers to a pathological type of contraction in which an irregular extrasystole occurs after three or four normal ones.
- Occurring in different parts of the heart, without a permanent focus (polytopic arrhythmia). With such an unstable rhythm, there is a high probability of developing complex arrhythmia or heart failure.
- Multiple systoles in the heart, that is, more than 5 in 60 seconds.
- Persistent extrasystoles after cessation of atrial fibrillation. There is a high probability of their strengthening with any provocation.
Signs of atrial extrasystole on an ECG and examples of films
There are several distinctive ECG signs of atrial extrasystole:
- premature appearance of a morphologically altered or negative P wave followed by a normal (sinus) QRST complex;
- a small compensatory pause after PE in the form of a straight line without teeth or complexes.
It may also be that the electrocardiogram displays the P wave, but the QRST complex that follows it does not. This is called blocked PE. Often repeated blocked PEs are confused with sinus bradycardia.
In my practice, I often see cardiograms in which atrial extrasystoles appear with a certain regularity (allorhythmia). There are the following types of allorhythmia:
- bigeminy – PE occurs after each normal QRST complex;
- trigeminy - PE after every second complex;
- quadrigeminy - PE after every third complex.
Very rarely, with PE, the QRS complex becomes wide and deformed, which makes it look like a ventricular extrasystole.
Sometimes the shape of the P is not the same in different leads. Then PE is called “polytopic atrial extrasystole”. I constantly observe this ECG picture in patients with a long history of smoking and suffering from COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease).
To count the total number of extrasystoles and to diagnose other possible heart rhythm disturbances, I prescribe daily (Holter) monitoring.
How to treat extrasystoles with folk remedies
Extrasystole is a state of heart rhythm in which there is a premature contraction of the heart, felt by a person in the form of interruptions in cardiac activity, cardiac arrest, “turning over” and freezing inside the chest.
Conventionally, ecstasystoles are divided into benign and pathological (associated with heart disease). Benign extrasystole does not require drug treatment; it is necessary to follow a basic healthy lifestyle and take sedatives of herbal origin:
- hawthorn flowers;
- motherwort grass;
- Baikal skullcap herb;
- lavender flowers;
- rosemary leaves;
- Baikal skullcap herb;
- pine needles and bark;
- Golden mustache;
- lemon;
- honey;
- valerian roots;
- yarrow;
- swamp grass;
- chamomile inflorescences.
To treat extrasystole, mix crushed motherwort grass and hawthorn flowers - 3 parts each, lavender flowers, rosemary leaves and Baikal skullcap - 2 parts each. Pour 3 tablespoons of one and a half liters of boiling water into a thermos and, after leaving for an hour, strain through double-layer gauze. Take half a glass three times a day half an hour before meals.
Take three large leaves of golden mustache, chop them into small pieces with a knife, pour in the juice of one medium lemon and, adding 300 grams of honey, mix thoroughly. Take one tablespoon three times a day 40 minutes before meals. The course of treatment is 10 days, then a break for 7 days. After this, repeat the treatment.
Grind 100 grams of pine needles and bark, mix. Pour 5 tablespoons of the mixture with a liter of boiling water and, putting it on low heat, cook for 10-15 minutes. Pour into a thermos along with the plant material and leave overnight. After straining in the morning, take 2/3 cup warm 3-4 times a day, regardless of meals.
To restore normal heart rhythm, prepare the following mixture. Take 2 parts each of valerian roots and cudweed herb, 1 part each of yarrow herb and chamomile inflorescences, chop and mix. Brew 2 tablespoons of herbal tea with 500 ml of boiling water and leave for 20 minutes, strain. Take 50 ml 3 times a day before meals. The course is 21 days, then a week break and repetition of treatment.
Pathological extrasystole is observed in cardiosclerosis, myocardial infarction, inflammatory diseases of the heart gland, etc. In all these cases, treatment is necessary not for extrasystole, but for the underlying disease. In case of extrasystole, individual selection of methods for restoring heart rhythm is recommended. For some, taking a deep breath helps, for others, holding your breath, or changing your body position, etc.
You should know that pathological extrasystole is not noticed by the patient and is often detected when examining the heart muscle and taking a cardiogram. Pathological extrasystole hides both diseases of the heart itself and diseases of other organs - thyroid dysfunction, spinal osteochondrosis, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. In these cases, it is not the extrasystole that is treated, but the underlying disease.
Single extrasystoles occur even in healthy people who practically do not notice them, and group extrasystoles are observed more often in young and middle-aged people. Often they are caused by improperly organized work schedule and diet.
Calendula infusion
A special feature of calendula medicines is that they affect not only the heart muscle, but also the arterial vessels. The positive effect of taking it is associated with the high content of microelements (Ca, Mg, Na) involved in the processes of repolarization and depolarization during the excitation of cardiomyocytes.
To prepare this medicine yourself, you need to take about 30 g of dried calendula flowers, put them in a saucepan and pour 2 cups of boiling water over them. Close the pans and let the infusion cool to room temperature. After about an hour, the product must be filtered through several layers of gauze.
Calendula infusion will not be able to remove the permanent form of arrhythmia, but it will be very effective in exacerbating extrasystole. If you feel the appearance of extrasystoles, it is recommended to take 100 ml every couple of hours.
Infusion of zyuznik herb
Zyuznik, or water horehound, is a herbaceous plant that grows in marshy areas. When properly prepared, it has a positive effect on the functioning of the cardiovascular system and eliminates palpitations caused by disorders of the thyroid gland.
The recipe for making the infusion is very simple. You need to take 2 cups of boiled water and pour dried zuznik into the pan. Cool the infusion in a dark place, protected from contact with children. It is recommended to take the product 30 ml 3 times a day. The treatment course is 30 days. If desired, the course can be repeated after a couple of months.
Horsetail infusion
Infusions and decoctions of this remedy have long been familiar to lovers of traditional medicine as a powerful remedy that can strengthen and strengthen the heart muscle. An important point is the correct collection of horsetail. The maximum concentration of beneficial components is observed in the summer, so if you cut the plant at another time of the year, the horsetail will lose a significant part of its healing properties.
To prepare a water infusion, you need to take 4 cups of boiling water and add a tablespoon of dried horsetail to it. Then let stand in a cool, dark place for about 4 hours. In order for the product to work, it must be taken a tablespoon 5 times a day.
Reasons for appearance
PE can appear both in a completely healthy person for no apparent reason, or in someone who suffers from serious heart disease.
Even during inspiration, atrial extrasystole can occur in any of us. Numerous factors that can cause PE are as follows:
- sneezing, sudden movement, fear;
- fairly rapid temperature change: going outside in cold weather, contrast shower;
- stress, neuroses;
- autonomic dysregulation syndrome (neurocirculatory dystonia);
- any physical activity;
- cardiac diseases: ischemic heart disease, myocarditis, pericarditis, cardiomyopathies, heart failure, etc.;
- frequent consumption of coffee and energy drinks;
- diseases of the digestive system: stomach and duodenal ulcers, gallstones (due to reflex irritation of the nerves of the heart);
- bad habits: smoking, drinking alcohol;
- any infections;
- chest injuries;
- use of medications: many medications can cause rhythm disturbances, incl. adrenomimetics, antidepressants, cardiac glycosides;
- hormonal changes - this mainly concerns thyroid diseases;
- diseases of the respiratory system – bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease;
I would like to note that the prognosis for life and the occurrence of adverse consequences are mainly determined by the nature of the disease (especially cardiac), against which the PE occurred.
Prevention of extrasystole
Untreated extrasystole continues to develop further, developing, for example, into tachycardia or flickering arrhythmia. Sometimes extrasystoles cause renal failure or circulatory problems. Therefore, it is advisable to devote enough time to getting rid of extrasystole, and even better to prevent its occurrence.
Prevention measures include:
- Regular visits to a cardiologist if heart problems have already become permanent.
- Taking medications only in consultation with a cardiologist.
- Treatment of diseases associated with extrasystole.
- Daily complete rest.
- Minimizing stress by drinking herbal teas that calm the nervous system or taking anti-anxiety medications.
- Strong physical activity.
Although extrasystoles are most often completely harmless to humans, sometimes they “get out of control.” In this case, you need to literally listen to the call of your heart and go to a cardiologist.
Sources used: medbur.ru, narodnie-med.ru, nc59.ru, mkn.su, mirkardio.ru