A cholesterol diet helps you lose weight and at the same time reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke. Learn the principles of low-fat nutrition, delicious recipes and lose extra pounds easily and safely!
Author: Kristina Lobanovskaya, doctor, practicing nutritionist Article updated: 11/10/2020
Most people associate cholesterol (cholesterol) with trans fats, junk foods, fast foods, unhealthy French fries and hamburgers. However, this is not quite true.
Cholesterol is a fatty lipophilic alcohol that takes an active part in cell division and has a positive effect on brain function, the functioning of the nervous system and the state of the immune system.
Depending on the effect it has on the human body, harmful and beneficial cholesterol are distinguished. An excess of the former negatively affects the condition of blood vessels, causing the formation of cholesterol plaques and, as a result, increases the risk of thrombosis, heart attacks and strokes. At the same time, “good” cholesterol is vital for the normal functioning of internal organs.
80% of cholesterol is synthesized by the human body independently and only 20% is absorbed from saturated fats that we eat with food (milk, butter, egg yolk, meat, cheeses). However, due to poor nutrition and dietary irregularities, doctors advise regular monitoring. For the age group of 20-40 years, it is recommended to donate blood once every five years, after 40 - annually.
The normal level of total cholesterol (Chol or TC-total cholesterol) in the blood of an adult healthy person is considered to be 5.2-6.2 mmol/l. For diabetics, the upper limit is 4.5 mmol/l.
If the TC significantly deviates from the norm, it is necessary to correct the indicators with the help of medications or special nutrition (cholesterol diet).
The goal of the anti-cholesterol diet is not weight loss or weight loss! The low-cholesterol menu is aimed at lowering cholesterol levels and improving the health of the body. However, by reducing the content of fatty foods in the diet of overweight people, they begin to lose weight and their body weight gradually normalizes.
A cholesterol-lowering diet should be prescribed by a doctor based on the results of laboratory tests. It is not recommended to “sit” on it yourself.
Doctors prescribe lipoprotein (anti-cholesterol) nutrition to patients with angina, coronary heart disease and other diseases of the cardiovascular system, as well as older people and those at risk for heart attacks and strokes. Excess weight, high blood pressure, varicose veins and diabetes can also be a reason to monitor the level of lipophilic alcohol in the blood.
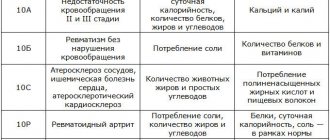
Nutritionists distinguish two types of cholesterol-lowering diets: the so-called “Two-Step Methodology,” which allows you to reduce cholesterol levels by up to 20%, and diet No. 10 (table No. 10), adherence to which reduces cholesterol levels by 10-15%.
Advantages and disadvantages of the anti-cholesterol menu
Such nutrition helps improve health, stabilize metabolism, accelerate metabolism, start losing weight and normalize weight. Due to a rich diet, you will not have to constantly feel hungry and the danger of a “breakdown” is reduced to zero. The menu can be tailored to suit your financial capabilities and individual preferences. Taking additional vitamins and minerals reduces the risk of vitamin deficiency to zero, and having a large amount of fruits and vegetables in the diet helps strengthen the immune system.
There are no disadvantages to this diet. However, it should be remembered that it should be carried out with the consent of a doctor and under his supervision, since a sharp decrease in cholesterol levels will bring more time to the body than benefit.
Advantages and disadvantages
| pros | Minuses |
|
|
Two-stage technique
With a moderate diet (second stage diet), the total amount of fat (TQF) is a maximum of 30% of the daily calorie content of the menu; the content of saturated fatty acids (SFA) is a maximum of 10%, and cholesterol is not more than 300 mg/day.
Daily ration
- Lean meat (without fat and skin) and sea fish – up to 90 grams per meal (maximum 180 g/day).
- Vegetable oil (olive, flaxseed, pumpkin, corn) in an amount not exceeding 10% of daily calories. Give preference to cold pressed oils.
- The basis of nutrition is carbohydrates and fiber - 50-65% of the diet. Therefore, it is allowed to eat whole grain bread, minimally processed cereals, fruits and vegetables.
Prohibited products:
- butter and palm oil;
- milk and fermented milk products (only zero fat content is allowed);
- egg yolk;
- meat by-products (liver, navels, heart, kidneys);
- sausages, sausage;
- shrimp, squid;
- caviar (red and black);
- sweets (cakes, pastries) and white bread baked goods.
The duration of such a nutrition system ranges from 6 to 12 weeks. After which repeated blood tests are taken. If the TC indicator has returned to normal, then it is enough to stick to proper nutrition and retake tests according to the scheme approved by the attending physician. If total cholesterol has not decreased to the desired level, then you should move to a more stringent regimen.
For the second stage diet, the diet and list of prohibited foods remain unchanged, as does the OKL (30%). In this case, EFA is reduced to 7%, and the maximum amount of cholesterol should not exceed 200 mg/day.
The transition from stage 1 to stage 2 should be carried out smoothly and under the supervision of the attending physician.
What is cholesterol
Cholesterol is a type of lipid present in the cells of animals and humans. The body synthesizes the bulk, and about 20% comes from food. Cholesterol is necessary for a person if it does not exceed the permissible norm, because it:
- strengthens cell membranes;
- participates in digestion;
- normalizes hormonal levels;
- provides protection to nerve fibers;
- reduces cellular permeability;
- Helps the body produce vitamin D.
In other words, a person needs cholesterol so that he can survive. But it is important to distinguish between “good” cholesterol and “bad” cholesterol.
Table No. 10
This diet was developed by the founder of nutrition, Professor Manuil Pevzner, with the aim of balancing metabolism, improving blood circulation, normalizing the functioning of the heart and blood vessels, as well as the hepatobiliary and digestive systems. It is advisable to cook food by steaming, without salt and spices. Meat can be boiled, fish can be baked in foil.
Basic principles of nutrition according to Pevzner:
- Meals should be frequent and small (5 times a day), total calorie intake should be 2300-2500 kcal/day.
- Dinner - three hours before bedtime.
- The basis of the diet is proteins (80-90 g/day). 40-45% of them should be plant proteins, and 55-60% animal proteins.
- The maximum amount of fat is 70 grams. Of these, 70-75% are plant-based, and 25-30% are animal.
- Carbohydrates are 300-350 g/day.
- It is recommended to consume foods that have an alkalizing effect: milk, fruits, vegetables.
- Be sure to drink a lot of water (1-1.2 liters per day).
- Consume salt as little as possible (maximum 2-3 grams per day to salt ready-made food).
- In parallel with nutrition, sodium chloride is usually prescribed in an amount determined by the attending physician.
Authorized products:
- rye bread crackers;
- first courses based on cereals or vegetable soups;
- lean meat (chicken, turkey, rabbit, nutria, beef, veal, quail);
- sea fish and mussels;
- low-fat milk and dairy products (kefir, sour cream, yogurt without sugar and additives, dietary cheese);
- egg white omelette (steamed);
- homemade jams and preserves in small quantities are allowed as desserts;
- some vegetables (broccoli, carrots, zucchini, pumpkin, sugar beets, tomatoes, lettuce);
- fruits and berries (except grapes);
- vegetable oil and butter in small quantities.
Prohibited products:
- drinks that stimulate the central nervous system (alcohol, strong tea, coffee, etc.);
- spicy and smoked dishes;
- rich broths;
- rich pastries, fresh bread, pancakes;
- fatty meat, offal;
- anything that increases flatulence (legumes, white cabbage, radishes, mushrooms, grapes);
- sweets.
Menu for one day
- First breakfast: milk oatmeal or muesli; soft-boiled egg (can be replaced with a steamed egg white omelette); tea without sugar.
- Second breakfast: oven-baked apple (you can add honey).
- Lunch: vegetarian soup with wheat cereal; steamed carrot puree (you can add a drop of olive oil); boiled meat; rosehip decoction or dried fruit compote.
- Afternoon snack: cottage cheese casserole or cheesecakes.
- Dinner: fish with vegetables (steamed); apple.
- Three hours before bedtime: a glass of low-fat kefir or unsweetened yogurt.
Authorized Products
The basis of the anti-cholesterol diet is:
- Dishes from sea/river fish (pike, tuna, mackerel, flounder, cod, hake, salmon, salmon, trout) and seafood (except squid) at least 100 g 2-3 times a week. It is useful to include seaweed in the form of salads in your diet.
- Lean red meat and poultry (turkey, chicken), boiled/baked rabbit meat.
- Vegetable soups with a small amount of cereal without frying, borscht, cabbage soup, beetroot soup.
- Rye/grain bread, with bran, flax or sesame seeds, dry biscuits, whole grain bread
- Porridges made from buckwheat and oatmeal, well boiled, brown rice, pasta made from wholemeal flour/durum wheat.
- Fresh fruits/vegetables (at least 400 g/day), both in the form of side dishes and in the form of salads, seasoned with vegetable oil. Be sure to include in your diet (if tolerated) legumes, which contain a lot of vegetable protein. It is also recommended to consume fruits/berries (except bananas/grapes) raw or in the form of compotes, jellies and decoctions. They stimulate metabolic processes and normalize intestinal function.
- In addition to vegetables/fruits, it is recommended to take sesame and flax seeds, fenugreek, and bran ground in a coffee grinder. It is better to consume bran in the morning and at night before meals, 2 teaspoons, with plenty of water.
- Freshly prepared juices (apple, orange, grapefruit, berry juices). From vegetable juices - beet/carrot juices. It is recommended to include oatmeal jelly/decoction in your diet, which effectively removes cholesterol .
- Nuts, especially walnuts (at least 30 g/day), sunflower seeds, pumpkin.
- Milk/fermented milk products/low-fat cottage cheese, cheeses with a fat content of no more than 20-30%, and use sour cream and low-fat cream exclusively in ready-made dishes. It is allowed to include 1-2 whole chicken eggs per week in the diet and unlimited egg whites.
- Unrefined, cold-pressed vegetable oils (olive, sesame, corn, and flaxseed), mainly for seasoning ready-made dishes. Especially useful.
- Green/herbal tea with lemon, still mineral water, rosehip decoction up to 2.0 l/day.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| beans | 6,0 | 0,1 | 8,5 | 57 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| Brussels sprouts | 4,8 | 0,0 | 8,0 | 43 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| green onion | 1,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 19 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| squash | 0,6 | 0,1 | 4,3 | 19 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| parsley | 3,7 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 47 |
| salad | 1,2 | 0,3 | 1,3 | 12 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| soybeans | 34,9 | 17,3 | 17,3 | 381 |
| asparagus | 1,9 | 0,1 | 3,1 | 20 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| Jerusalem artichoke | 2,1 | 0,1 | 12,8 | 61 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| lentils | 24,0 | 1,5 | 42,7 | 284 |
Fruits | ||||
| avocado | 2,0 | 20,0 | 7,4 | 208 |
| oranges | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| pomegranate | 0,9 | 0,0 | 13,9 | 52 |
| grapefruit | 0,7 | 0,2 | 6,5 | 29 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| lemons | 0,9 | 0,1 | 3,0 | 16 |
| mango | 0,5 | 0,3 | 11,5 | 67 |
| tangerines | 0,8 | 0,2 | 7,5 | 33 |
| nectarine | 0,9 | 0,2 | 11,8 | 48 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| gooseberry | 0,7 | 0,2 | 12,0 | 43 |
| Red currants | 0,6 | 0,2 | 7,7 | 43 |
| black currant | 1,0 | 0,4 | 7,3 | 44 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| almond | 18,6 | 57,7 | 16,2 | 645 |
| flax seeds | 18,3 | 42,2 | 28,9 | 534 |
| fenugreek seeds | 23,0 | 6,4 | 58,3 | 323 |
| sunflower seeds | 20,7 | 52,9 | 3,4 | 578 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| wheat bran | 15,1 | 3,8 | 53,6 | 296 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| basil | 2,5 | 0,6 | 4,3 | 27 |
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
Dairy | ||||
| kefir 0% | 3,0 | 0,1 | 3,8 | 30 |
| kefir 1% | 2,8 | 1,0 | 4,0 | 40 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 0.6% (low fat) | 18,0 | 0,6 | 1,8 | 88 |
| curd tofu | 8,1 | 4,2 | 0,6 | 73 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
Bird | ||||
| chicken fillet | 23,1 | 1,2 | 0,0 | 110 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| fish | 18,5 | 4,9 | 0,0 | 136 |
| seaweed | 0,8 | 5,1 | 0,0 | 49 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| grape seed oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| linseed oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| instant chicory | 0,1 | 0,0 | 2,8 | 11 |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Menu for the week
A cholesterol-free diet is a nutritional system that features a very rich diet.
An approximate menu for 7 days might look like this:
The first day
- Breakfast: steam omelette of two proteins; green tea.
- Lunch: vegetable soup – 250 ml; steamed meatballs with vegetables.
- Afternoon snack: fruit salad of one apple, one pear, seasoned with low-fat yogurt.
- Dinner: boiled rice – 100 g; fish baked on a bed of vegetables – 200 gr.
- Three hours before bedtime, you can drink 200 ml of low-fat kefir.
Second day
- Breakfast: buckwheat – 150-200 gr.; a couple of slices of low-fat cheese; drink with chicory.
- Lunch: vegetarian soup with barley 250-300 ml; steamed beef – 200 gr.; vegetable salad (one tomato, one bell pepper).
- Afternoon snack: baked apple with honey.
- Dinner: hake stewed in tomato; vegetable salad dressed with olive oil.
Day three
- Breakfast: milk porridge (buckwheat, bulgur, oatmeal, corn) – 250-300 g; rosehip decoction or green tea without sugar.
- Lunch: borscht without meat – 300 gr.; quail baked in the oven with carrots or pumpkin.
- Afternoon snack: grapefruit or orange.
- Dinner: cottage cheese casserole with fruit.
Day four
- Breakfast: carrot salad with raisins (grate one small carrot, add raisins, season with low-fat sour cream or yogurt); 200 ml kefir, 1 whole grain bread.
- Lunch: boiled turkey – 200 gr.; salad of tomatoes and cucumbers – 200 gr.; 1 whole grain bread.
- Afternoon snack: dates or dried apricots – 200 g.
- Dinner: low-fat cottage cheese with honey and fruit (apple, peach or apricot) – 200 g.
Day five
- Breakfast: granola – 250-300 g; rosehip decoction or tea.
- Lunch: vegetable soup – 250 g; stewed pike perch with broccoli – 200 gr.; a glass of orange juice.
- Afternoon snack: fruit jelly – 250 g.
- Dinner: corn porridge – 200 g; boiled chicken fillet – 200 g; one medium-sized bell pepper.
Day six
- Breakfast: soft-boiled egg or in a bag; chicory drink (possibly with added milk).
- Lunch: rice soup with vegetable broth – 250-300 g; two small veal meatballs in cream sauce; any vegetables.
- Afternoon snack: pumpkin and apple puree – 300 g.
- Dinner: boiled potatoes with herbs, seasoned with sunflower oil – 3 pcs.; boiled fish – 150 gr.; ½ orange.
Day seven
- Breakfast: vegetable salad – 250-300 gr.; a slice of low-fat cheese; one grain loaf; green tea.
- Lunch: veal stewed with vegetables in a sleeve – 300 g; vegetable juice.
- Afternoon snack: a handful of nuts or dried fruits.
- Dinner: bulgur with apple and raisins; a glass of skim milk.
Recipes
Pike perch baked with vegetables
Cut pike perch fillet (0.5 kg) into portions, brush with oil, season with fish spices and dry herbs. Place prepared and seasoned vegetables (zucchini, eggplant, garlic, onions, sweet peppers) on top of the fish fillet and cover with tomatoes, Provençal herbs, and bake for 20-30 minutes.
Hake baked with cheese and vegetables
Carrot fillet, onions, tomatoes, low-fat cheese 50 g, vegetable oil.
Cut hake fillet (500 g) into portions, marinate in allspice and fish spices. Separately, simmer grated carrots and finely chopped onions in vegetable oil. Place the marinated hake fillet in a baking dish and cover with a layer of stewed vegetables. Bake for 30 minutes, after 20 minutes sprinkle with grated cheese and place in the oven for 10 minutes.
Chicken breast baked in the oven
Chicken fillet (300 g) beat and marinate for 30-40 minutes in olive oil with the addition of milk, garlic, rosemary. Bake in the oven in a mold/foil. Lightly salt the finished dish and serve with fresh vegetables.
For a month
The duration of such a diet is agreed with the doctor and usually does not exceed 12 days. However, in exceptional (!) cases, the nutrition system can be adjusted by a specialist and extended for another 2 weeks. In this case, an approximate diet for the month will be compiled by a nutritionist taking into account the results of a blood test, body mass index, age, and other indicators.
Under no circumstances should you decide to increase its term on your own! This can lead to negative consequences and detrimental health results.
If desired, the list of dishes can be changed based on your individual preferences. Nutritionists recommend adjusting the menu taking into account the table of cholesterol content in foods.
Table of cholesterol content in food (mg per 100 grams)
Oils and fats
| Product | Cholesterol content |
| melted butter | 280 |
| fresh butter | 240 |
| "peasant" butter | 180 |
| beef fat | 110 |
| pork or lamb fat | 100 |
| rendered goose fat | 100 |
| pork lard | 90 |
| vegetable oils | 0 |
| margarines based on vegetable fats | 0 |
Milk and dairy products
| Product | Cholesterol content |
| cream 30% | 110 |
| sour cream 30% fat | 90-100 |
| cream 20% | 80 |
| fat cottage cheese | 40 |
| cream 10% | 34 |
| sour cream 10% fat | 33 |
| raw goat milk | 30 |
| cow's milk 6% | 23 |
| cottage cheese 20% | 17 |
| milk 3-3.5% | 15 |
| milk 2% | 10 |
| full fat kefir | 10 |
| regular yogurt | 8 |
| milk 1% | 3.2 |
| kefir 1% | 3.2 |
| serum | 2 |
| low fat yogurt | 1 |
| low fat cottage cheese | 1 |
Meat, meat products
| Product | Cholesterol content |
| brain | 800 — 2300 |
| kidneys | 300 — 800 |
| chicken liver | 492 |
| beef liver | 270-400 |
| pork, loin | 380 |
| pork knuckle | 360 |
| chicken heart | 170 |
| veal liver sausage | 169 |
| beef tongue | 150 |
| liver pate | 150 |
| pork liver | 130 |
| raw smoked sausage | 112 |
| pork | 110 |
| roe deer meat back, leg, back | 110 |
| sausages | 100 |
| sausages in jars | 100 |
| white Munich sausage | 100 |
| lean veal | 99 |
| lean lamb | 98 |
| fatty beef | 90 |
| rabbit meat | 90 |
| duck with skin | 90 |
| skinless chicken dark meat | 89 |
| goose | 86 |
| smoked mortadella | 85 |
| salami | 85 |
| Vienna sausages | 85 |
| cervelat | 85 |
| skinless chicken white meat | 79 |
| horsemeat | 78 |
| lamb (summer) | 70 |
| lean beef | 65 |
| venison | 65 |
| skinless duck | 60 |
| boiled fatty sausage | up to 60 |
| pork tongue | 50 |
| broilers 1st category | 40 — 60 |
| chick | 40 — 60 |
| turkey | 40 — 60 |
| boiled sausage | up to 40 |
Fish, seafood
| Product | Cholesterol content |
| Pacific mackerel | 360 |
| stellate sturgeon | 300 |
| cuttlefish | 275 |
| carp | 270 |
| marble natoteniya | 210 |
| acne | 160 — 190 |
| oysters | 170 |
| shrimps | 144 |
| sardines in oil | 120 — 140 |
| pollock | 110 |
| herring | 97 |
| mackerel | 95 |
| medium fat fish (up to 12% fat) | 88 |
| crabs | 87 |
| mackerel | 85 |
| mussels | 64 |
| trout | 56 |
| fresh tuna (canned) | 55 |
| low-fat fish (2 - 12%) | 55 |
| shellfish | 53 |
| sole | 50 |
| pike | 50 |
| cancer | 45 |
| horse mackerel | 40 |
| cod | 30 |
Cheeses
| Product | Cholesterol content |
| Gouda cheese - 45% | 114 |
| cream cheese fat content 60% | 105 |
| Chester cheese - 50% | 100 |
| Camembert cheese - 60% | 95 |
| Emmental cheese – 45% | 94 |
| processed cheese – 60% | 80 |
| processed cheese "Russian" | 66 |
| Camembert cheese - 45% | 62 |
| Edam cheese - 45% | 60 |
| Tilsit cheese – 45% | 60 |
| smoked sausage cheese | 57 |
| cheese "Kostroma" | 57 |
| processed cheese - 45% | 55 |
| Camembert cheese - 30% | 38 |
| Tilsit cheese - 30% | 37 |
| Edam cheese - 30% | 35 |
| processed cheese - 20% | 23 |
| Limburg cheese - 20% | 20 |
| Romadour cheese - 20% | 20 |
| sheep cheese - 20% | 12 |
| homemade cheese - 4% | 11 |
| homemade cheese - 0.6% | 1 |
Egg
| Product | Cholesterol content |
| quail egg (100 g) | 600 |
| whole chicken egg (100 g) | 570 |
Fully or partially limited products
When following an anti-cholesterol diet, the following are excluded from the diet:
- Fatty red meats, offal, waterfowl meat (duck, goose), sausages, smoked meats, animal/cooking fats.
- Meat/fish broths, canned fish, fried foods, fish roe, crayfish, crabs, shrimp, cod liver.
- Cream pies, cakes, pastries, puff pastry products.
- Semolina, white rice, pasta.
- Full-fat cottage cheese, cheese, sour cream and cream, chicken egg yolks, products with palm/coconut oil.
- Chocolate, cocoa, ice cream, strong black tea/coffee.
- Products containing easily digestible carbohydrates - honey, jam, jam, sugar, confiture.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
Bakery products | ||||
| bagels | 16,0 | 1,0 | 70,0 | 336 |
| bagels | 16,0 | 1,0 | 70,0 | 336 |
| crackers | 11,2 | 1,4 | 72,2 | 331 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jam | 0,3 | 0,1 | 56,0 | 238 |
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| ketchup | 1,8 | 1,0 | 22,2 | 93 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
| sour cream 30% | 2,4 | 30,0 | 3,1 | 294 |
| sour cream 40% (fat) | 2,4 | 40,0 | 2,6 | 381 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cheese | 24,1 | 29,5 | 0,3 | 363 |
| cottage cheese 18% (fat) | 14,0 | 18,0 | 2,8 | 232 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| pork liver | 18,8 | 3,6 | 0,0 | 108 |
| pork kidneys | 13,0 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 80 |
| pork fat | 1,4 | 92,8 | 0,0 | 841 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| beef liver | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
| beef kidneys | 12,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 66 |
| beef brains | 9,5 | 9,5 | 0,0 | 124 |
| mutton | 15,6 | 16,3 | 0,0 | 209 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 16,2 | 44,6 | 0,0 | 466 |
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
| sausages | 10,1 | 31,6 | 1,9 | 332 |
| sausages | 12,3 | 25,3 | 0,0 | 277 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| salted fish | 19,2 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 190 |
| Red caviar | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| squid | 21,2 | 2,8 | 2,0 | 122 |
| shrimps | 22,0 | 1,0 | 0,0 | 97 |
| salmon | 19,8 | 6,3 | 0,0 | 142 |
| sturgeon | 16,4 | 10,9 | 0,0 | 163 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| semi-finished fish products | 12,5 | 6,7 | 14,7 | 209 |
| sardine | 20,6 | 9,6 | — | 169 |
| mackerel | 18,0 | 13,2 | 0,0 | 191 |
| cod (liver in oil) | 4,2 | 65,7 | 1,2 | 613 |
| boiled oysters | 14,0 | 3,0 | — | 95 |
| fresh oysters | 14,0 | 6,0 | 0,3 | 95 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| creamy margarine | 0,5 | 82,0 | 0,0 | 745 |
| coconut oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| palm oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| rendered beef fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| rendered pork fat | 0,0 | 99,6 | 0,0 | 896 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| cola | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 42 |
| lemonade | 0,0 | 0,0 | 6,4 | 26 |
| Pepsi | 0,0 | 0,0 | 8,7 | 38 |
| sprite | 0,1 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 29 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Juice therapy
In addition to special nutrition, nutritionists have also developed a method for reducing the overall level of fats in the blood by drinking juices according to a special scheme.
The duration of the course is 5 days. During this time, in the morning, on an empty stomach, you need to drink fresh juice (freshly squeezed juice).
First day: 70 ml celery juice and 130 ml carrot juice.
Second day: mix 70 ml of beet juice with 100 ml of carrot juice and 70 ml of cucumber juice.
Beetroot juice must be squeezed out 1.5-2 hours before consumption.
Third day: mix 70 ml apple juice and 70 ml celery juice with 130 ml fresh carrot juice.
Fourth day: add 70 ml of apple juice to 130 ml of carrot juice.
Fifth day: 130 ml orange juice.
Juice therapy can reduce TC by 10% and lose a little weight.
What does “bad” cholesterol mean?
A “good” lipoprotein has a high density, and a “bad” one has a low density. Lipoprotein is cholesterol in an apolipoprotein shell.
What does high density mean? The fact is that the cholesterol itself in the compound is only a small part and the main composition is protein. This ratio is most optimal for the body, since the lipid easily enters the liver and exits along with bile, without settling along the way. Therefore he is "good".
Low-density lipoprotein, on the contrary, contains a lot of cholesterol and is excreted poorly, clogging blood vessels and causing atherosclerosis.
With age, cholesterol accumulates in the body: in a child it is much less than in an adult. This accumulation process does not stop throughout life: the older a person is, the higher his cholesterol level.
| Age | Cholesterol level |
| 25+ | Men: 6.33 Women: 5.74 |
| 35+ | Men: 6.57 Women: 5.94 |
| 45+ | Men: 6.93 Women: 6.54 |
| 55+ | Men: 7.39 Women: 7.14 |
| 65+ | Men: 7, 68 Women: 7, 50 |
| 70+ | Men: 7, 88 Women: 7, 72 |
If cholesterol levels are higher than the given norm, you should consult a doctor. It is also extremely important to maintain proper nutrition. It is advisable to worry about an anti-cholesterol diet at a young age, but in adulthood this must be done.
The fact is that lipoprotein excess leads to the formation of cholesterol plaques on the walls of the arteries. These plaques, overgrown with calcium ions, completely close the lumen in the vessels. As a result, blood flow slows down.
High cholesterol increases the risk of the following conditions:
- oncology;
- stroke;
- cardiac ischemia;
- peripheral vascular pathologies;
- heart attack;
- hypertension;
- diabetes.
Quitting the diet
To maintain positive dynamics after completing the low-cholesterol course, you should lead a healthy lifestyle, give up smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and junk food. Make sport a part of your life. Swimming, Pilates, yoga, walking and any aerobic exercise will have a beneficial effect on the condition of the heart and blood vessels. However, pay special attention to nutrition. Subsequently, the diet should consist of foods that regulate blood cholesterol levels, namely:
Fish containing large amounts of Omega-3 PUFAs
Herring, salmon, salmon, trout, and tuna prevent the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, strengthen blood vessels and contain many B vitamins.
Cabbage
White cabbage, cauliflower, kohlrabi, and broccoli prevent the absorption of cholesterol.
Buckwheat
Due to the high content of lecithin, porridge breaks down cholesterol and removes it from the body, reducing the risk of plaques and blood clots. It is advisable to buy “green” buckwheat that has not been roasted.
Apples
Apple pectin and tannin regulate lipid and sugar levels, so eating raw and baked apples is a great way to strengthen the walls of blood vessels, improve metabolism and lose several kilograms. Fresh raspberries have the same effect.
Berries and fruits of blue, purple, and red colors
Due to the polyphenol content in them, the synthesis of “good” cholesterol increases by 3%.
Garlic
It is recommended to eat one or two cloves of garlic per day. You can replace it with pharmaceutical supplements in capsule form.
Oyster mushrooms
Just 10 grams of oyster mushrooms per day slows down the absorption of harmful substances. This is due to the content of a special natural component in mushrooms - lovastine.
Barley
Beta-glucans contained in cereals slow down the absorption of harmful fat by the intestines, thereby reducing cholesterol levels in the body.
Legumes
Beans, chickpeas, peas, lentils, and other legumes are rich not only in fiber, but also in healthy vegetable protein.
Lean meat
It is not advisable to limit meat consumption, because it contains iron that is beneficial for the body. However, it is necessary to choose low-fat varieties, cut off the skin from the bird, and also drain the “first” broth when preparing first courses.
Avocado
The high content of monounsaturated fats makes avocados an indispensable product of proper nutrition.
Spinach, lettuce
Nuts
Nutritionists say that regular consumption of walnuts, almonds and cashews effectively reduces the level of harmful substances and the risk of heart and vascular diseases.
It is also advisable to take multivitamins, especially calcium and magnesium supplements.
Reviews and results
The anti-cholesterol diet, according to patients, is a fairly effective remedy, and in combination with increased physical activity, smoking cessation and medications, it can normalize blood cholesterol levels.
- “... I have been struggling with high cholesterol for almost 2 years. For the last 2 months I’ve been on a strict diet, because my cholesterol levels, although they are decreasing, are not as fast as I would like. I excluded almost all animal fats, potatoes, rice, pasta, sugar, most sweets and everything fried. I limited chicken eggs, now I eat only whites, removed cream and cheese. I hope this will help, but if not, I’ll have to take medications”;
- “... I decided to adjust my cholesterol levels because I am afraid of coronary artery disease (my parents and relatives have cardiovascular diseases). I started with losing weight, since my weight exceeds the norm by almost 13 kg. After 4 months, I lost 10 kg and switched to an anti-cholesterol diet. I strictly limit myself; I also quit smoking and started going to the gym with my son to play volleyball. Now the numbers are approaching normal, but the doctor warned me that I still need to monitor my weight and continue to eat right, although maybe not with such strict restrictions.”
Folk remedies in the fight against cholesterol
You can combat high levels of unhealthy fats not only with diets and healthy foods, but also with the use of folk remedies. Be sure to remember that the use of any prescriptions should occur after consultation with your doctor. Allergic reactions may occur due to individual intolerance to the components. We offer several proven ways to reduce cholesterol:
Dill seed tincture
Ingredients:
- half a glass of dill seeds;
- a tablespoon of crushed valerian root;
- a glass of honey.
Cooking method:
- Mix the ingredients, pour 1 liter of boiling water, leave for 24 hours. Keep refrigerated.
Mode of application:
- A tablespoon three times a day 30-40 minutes before meals.
Garlic oil
Ingredients:
- 2 cups olive oil;
- 10 cloves of garlic.
Cooking method:
- Add garlic, previously passed through a press, to the oil. Leave for 7 days.
Mode of application:
- Use as a flavorful seasoning for salads and other favorite dishes.
Garlic tincture
Ingredients:
- garlic – 400 g;
- vodka – 250 g.
Cooking method:
- Pass the garlic through a press or chop it in a garlic press. Pour vodka (or alcohol) and keep in a dark place for 10 days.
Mode of application:
Take on an empty stomach (it is better to add it to milk), half an hour before meals according to the following scheme:
First week
You need to start with two drops and increase the amount of tincture every day so that on the seventh day you take 17-20 drops.
Second week
20 drops three times a day 30 minutes before meals.
Third week
Gradually reduce the amount of tincture you use from 20 drops so that you end the seventh day with 2 drops.
This treatment regimen can be repeated once every three years.
Dry linden blossom (linden flour)
Cooking method:
- Grind linden flowers in a coffee grinder until it becomes flour.
Mode of application:
- Three times a day, a teaspoon. Drink with a glass of water.
Duration of treatment is 1 month. After a 14-day break, the course is repeated.
Healthy dessert
Ingredients (all in equal proportions):
- lemons;
- honey;
- dried apricots;
- raisin;
- walnuts.
Cooking method:
- Pass dried fruits through a meat grinder, pour in natural honey, leave for a day.
Mode of application:
- Eat a tablespoon of the sweet mixture half an hour before breakfast.
The healthy dessert must be stored in the refrigerator.
4% propolis tincture
Directions for use: dissolve 7 drops in 40 ml of water, take 3 times a day 40 minutes before meals. Course duration: 4 months.
Celery
An excellent option for breakfast or afternoon snack during a cholesterol diet.
Cooking method:
- Place celery stalks in boiling water for 2-3 minutes. Cool, sprinkle with vegetable oil, sprinkle with sesame seeds and add a little honey.
Horseradish with sour cream
Ingredients:
- horseradish root;
- a glass of low-fat sour cream.
Cooking method:
- Grind the horseradish root, add sour cream.
Mode of application:
- 3-4 times a day along with meals.
Flax-seed
Flax and flaxseed have proven themselves to be an excellent anti-sclerotic agent. You can take flaxseed oil, decoctions and tinctures, and also eat flaxseed.
Herbal decoctions
Decoctions of various herbs are also part of lipid-lowering therapy. Dandelion roots, alfalfa, licorice, corn silk, buckthorn, motherwort, mint, golden mustache, hawthorn and many others are suitable for this purpose.
Low cholesterol: dangers and complications
When working to lower your bad cholesterol levels, you should remember that common sense and the right approach to diet are the key to success. When removing “bad” fats, you can overdo it and deprive the body of such useful and necessary “good” nutrients.
You should be concerned if during treatment you notice the appearance or worsening of the following conditions:
- decreased or lack of appetite;
- intestinal disorder;
- muscular dystonia;
- drowsiness, lethargy, slow reaction;
- sudden mood swings, aggression, depressive syndromes;
- decline in sexual activity.
All this may indicate low total cholesterol.
Why is it dangerous?
- Vessels become vulnerable and fragile, cerebral circulation worsens.
- A decrease in serotonin synthesis due to the lack of healthy fats leads to depression, suicidal conditions, increased anxiety, and sleep disorders. In older people it provokes dementia (senile insanity), Alzheimer's disease.
- The level of production and absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, including vitamin D and calcium, sharply decreases. The result is osteoporosis.
- People with low TC are at risk for infertility, because sex hormones require cholesterol.
- Insulin resistance is impaired, which leads to type 2 diabetes.
Therefore, if you feel worse, you should see a doctor and take another blood test. The doctor will be able to take timely measures and adjust your diet.
The need to follow a diet
By following the diet recommended by a specialist, you can regulate the content of high and low density lipoproteins. Thanks to this, the level of bad cholesterol is significantly reduced. Proper nutrition when cholesterol increases can normalize its content in the body without drug treatment.
This cleanses the blood vessels, normalizes blood circulation, and has a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system. The recommended products contain a large percentage of antioxidants, which helps slow down the aging of the skin, prevent the development of pathologies of internal organs and increase vitality.