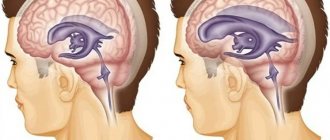
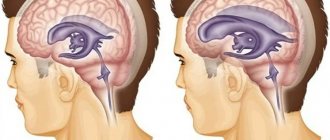
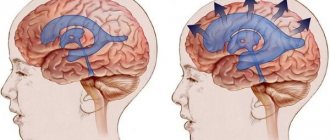
This common disorder is an extremely dangerous condition, common in both adult and pediatric patients. Interestingly, increased intracranial pressure occurs more often in women than in the stronger sex.
In the absence of timely medical care, this pathological condition can provoke the development of serious consequences in the patient - even disability. Doctors at our private clinic in Ryazan strongly recommend contacting a specialist when the first symptoms of increased intracranial pressure appear.
Reasons for the development of the disorder
The factor that provokes an increase in pressure is the impaired outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the brain. Normally, it occupies about 10% of its total volume, performing various functions, which include:
- protection of the brain from trauma - in the event of an impact or fall, the cerebrospinal fluid will “soften” the contact of the cranial bones and delicate tissues;
- it is also with the movement of cerebrospinal fluid that toxins and decay products are removed from the brain;
- Finally, it ensures that the correct electrolyte-water balance is maintained.
The most common causes of ICP include metabolic disorders that provoke insufficient flow of fluid into the blood, as well as spasm of the vessels through which the cerebrospinal fluid moves. In addition, oxygen deprivation of the brain, excess fluid in the body, obesity, severe intoxication, and inflammation of the brain can also provoke ICP. The presence of tumors in the body - benign or malignant - can also cause disruption of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid.
If the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the intracranial space is disrupted for any reason, this provokes the accumulation of its excess volume and an increase in pressure. At the same time, in both a child and an adult patient, an increase in intracranial pressure to more than 30 mm Hg can lead to the development of irreversible changes in tissues and, as a consequence, disability and even death.
Hydrocephalus
Signs, syndromes of hydrocephalus
Childbirth is a stressful time for a newborn. The baby's brain experiences the greatest stress during childbirth. Increased production of cerebrospinal fluid is provoked as a reaction to compression. An adult knows well the signs of increased intracranial pressure - headache, nausea, visual impairment, and memory impairment. The baby experiences the same pain. “Unreasonable” crying, sleep disturbances, frequent regurgitation, throwing the head back in sleep - all this may indicate increased intracranial pressure in the child.
In children under 1 year of age with hydrocele of the brain, increased excitability, increased muscle tone (hands held in fists, legs resting on toes and crossed), weak support with legs, absence of a step reflex, delayed motor and mental development may be observed.
Important!
It is important to timely stabilize the production of cerebrospinal fluid in a newborn, since in acute forms, hydrocephalus can lead to convulsions, cerebral palsy, and debility.
One of the signs of hydrocephalus in preschool children is hypermobility. Behavior can be aggressive, and hysterical manifestations are common. The child may stutter. Symptoms include enuresis, strabismus, and frequent colds. As a rule, children with hydrocephalus have delayed psycho-speech development (poor vocabulary, impaired diction, difficulty constructing complex sentences).
In school-age children with dropsy of the brain, the following may be observed: nosebleeds and headaches. Teachers may note a decrease in memory and concentration, difficulty in mastering school material: the child completes tasks slowly and makes a large number of mistakes. The child’s handwriting is not smooth, he reads slowly and does not assimilate the material he reads well. Disinhibition and neuroticism may also be observed.
Factors contributing to the exacerbation of hydrocephalus
Any stress on the body (viral infections, stress, mental and physical fatigue, concussion, vaccinations) can lead to increased intracranial pressure. Particularly insidious are combinations of stress loads that can lead to a chronic form of hydrocephalus.
The body of a child and teenager is constantly changing. Parents and teachers should take the child’s complaints seriously, especially during periods of stress, as hydrocephalus can worsen at any time. For example, with an increased study load, against the background of a cold and stress associated with the exam. The disease will lead to a decrease in academic performance and aggressive behavior of the child. The appearance of headaches and mood instability may be a sign of the disease, which is often confused with the characteristic manifestations of adolescence. Adults begin to raise a teenager, although the reason is a physiological imbalance in the body, and treatment is required.
We recommend that you seek advice from specialists to clarify the presence of the disease. If the diagnosis is made, it is necessary not only to begin treatment for internal hydrocephalus of the brain, but also to further monitor the child’s development and maintain a special regime that prevents exacerbation of hydrocephalus.
Treatment of hydrocephalus in a child
Hydrocephalus is a common condition in newborns. Unfortunately, young mothers do not pay due attention to the recommendations of doctors, having discovered the prevalence of the diagnosis and “successful” independent cases of cure and not taking into account the fact that hydrocephalus often accompanies other types of disorders of the central nervous system in newborns. Therefore, timely diagnosis is extremely important. And many mothers resort to advice from the Internet, to traditional methods of treating hydrocephalus, avoiding “chemistry”, “pills”, as well as visits to specialized qualified specialists.
Observation in the first year of life of a child at risk (for the perinatal, birth or postpartum period) is very important. The earlier the disease is detected and timely treatment is started, the fewer consequences for the child’s health will be in the future. Make an initial appointment with specialized children's specialists at the Center for Pediatrics and Neurology: neurologist, pediatrician. Get advice and professional medical assistance. The treatment regimen is prescribed strictly individually.
Increased intracranial pressure: symptoms
Unlike patients suffering from hypertension and hypotension, people with increased intracranial pressure cannot measure it themselves. This disorder can only be diagnosed by consulting a doctor. You can suspect increased pressure inside the skull based on the following symptoms:
- headache, which paradoxically intensifies during the night's rest. Gets worse when trying to turn your head, as well as sneezing and coughing;
- swelling of the face and eyelids;
- tinnitus and hearing loss;
- visual disturbances - swelling of the optic nerve, first double vision and disturbances in reaction and peripheral vision, and then a pronounced deterioration in central vision;
- nausea and vomiting;
- decreased blood pressure, lightheadedness, fainting;
- paroxysmal increased sweating;
- weakness, fatigue, decreased performance;
- unhealthy appearance – in particular, pronounced “bruises” under the eyes;
- painful sensations in the neck.
It is worth mentioning the symptoms of increased intracranial pressure in a child, in particular an infant. These are sleep disturbances, lethargy, moodiness, vomiting, convulsions, hydrocephalus, as well as blood vessels clearly visible under the skin of the face and head.
If the patient has one or more symptoms from this list, you should consult a doctor. Only in a specialized medical institution can a full diagnosis be carried out.
Symptoms of sinusitis
There are acute and chronic forms of sinusitis, which differ in their symptoms.
Acute sinusitis. Symptoms:
- Runny nose lasting more than 7-10 days, without signs of improvement;
- nasal congestion, mucous or purulent discharge from the nose;
- mucus running down the back of the throat, copious discharge of purulent sputum in the morning;
- headache, heaviness and pain in the inflamed sinus area. Sometimes pain in the teeth, eyes, cheekbones, cheeks;
- increased sensitivity of the facial skin in the projection of the affected sinus;
- increase in body temperature (up to 38°C and above). As a rule, this symptom is observed in an acute case. In a chronic process, body temperature rarely rises or remains at subfebrile levels (37-37.50°C);
- weakness, fatigue, irritability. Photophobia, lacrimation, loss of appetite, sleep disturbance;
- weakened or absent sense of smell;
- swelling of the cheeks and eyelids.
Chronic sinusitis. Symptoms:
Symptoms of chronic sinusitis depend on the form of the disease. Outside of an exacerbation, symptoms may be very mild or absent. The most common symptoms of concern are:
- nasal congestion, difficulty in nasal breathing;
- scant mucous or purulent discharge from the nose, may be in the form of drying crusts;
- constant leakage from the nose, causing cracks and abrasions at the entrance to the nose;
- mucus running down the back of the throat;
- dry throat;
- headache;
- bad breath.
As the disease worsens, symptoms characteristic of acute sinusitis may appear.
Treatment of increased intracranial pressure at ON CLINIC Ryazan
If ICP is a secondary disorder and represents one of the complications of any disease, it is necessary first of all to treat the primary pathology. In other cases, symptomatic treatment of ICP is performed.
There are conservative and surgical treatments for this pathology. Conservative - taking medications prescribed by the attending physician that enhance the outflow of fluid according to the regimen prescribed by the attending physician. These can be either regular diuretics or anti-inflammatory steroids. Physiotherapy and massage have also been proven to treat increased intracranial pressure.
Surgical intervention is performed in the most severe cases of ICP. Usually this is bypass surgery - the installation of a special shunt through which excess fluid moves away from the brain, rushing into the abdominal cavity.
Untreated ICP in a timely manner can lead to such serious complications as stroke, partial and complete paralysis, impaired coordination, reflexes, speech, as well as loss of vision and mental problems. If you experience symptoms that may be signs of a deterioration in the flow of cerebrospinal fluid from the brain, consult a doctor as soon as possible! “ON CLINIC Ryazan” - Your health is our concern!
Treatment of sinusitis at MedicCity
Conservative methods of treating sinusitis
If you are concerned about how to treat sinusitis in Moscow, be sure to contact the MedicCity specialists! Our clinic provides treatment for sinusitis without puncture and without pain. However, non-surgical treatment of sinusitis is possible only at the initial stage. Don't waste time!
In the vast majority of cases, treatment of sinusitis in our clinic is carried out without a puncture.
- Using YAMIK (sinus catheter). The YAMIK method is the use of a device called the “YAMIK sinus catheter.” Using the YAMIK sinus catheter, controlled pressure is created in the nasal cavity and the purulent contents of the sinus are pumped out through the natural anastomosis (openings), and then a medicinal substance (antibiotics, mucolytics) is administered.
- Rinsing the nose and paranasal sinuses using the moving method (“cuckoo”). It is carried out using a special suction - an aspirator; in the process, pathological contents are removed from the nasal cavity and sinuses and the drug is injected into the sinuses.
- Inhalation therapy using a special inhaler PARI SINUS. This method is based on the introduction of microparticles of the drug into the affected paranasal sinuses through a pulsating supply of an aerosol. In this case, the aerosol of the medicinal substance is deposited in the sinuses and has an effect directly at the site of inflammation.
All proposed methods for treating sinusitis are painless and effective.
When using combined treatment, complete recovery in case of acute sinusitis is achieved within 7-10 days.
If puncture treatment is necessary, it is possible to install special catheters in the sinus, which eliminate the need for repeated punctures.