Blood pressure is a concept that signals how much pressure is exerted on the walls of the arteries when blood moves through them during a pulse wave. This indicator is a marker that allows you to get a general idea of the state of the patient’s cardiovascular system.
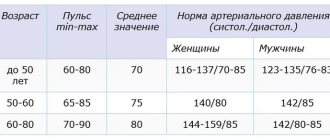
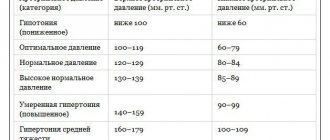
Measuring blood pressure is one of the most common and simple procedures that allows you to obtain general information about a person’s health status. Pressure is characterized by two indicators: systolic and diastolic. Systolic pressure occurs when the myocardium contracts, and diastolic pressure occurs when the heart muscle relaxes. Normally, the first indicator is 110-139 mmHg. Art., and the second – 61-89 mm Hg. Art.
Diastolic, that is, lower, pressure generally characterizes the condition of the arteries, the tone of their walls, blood viscosity and the length of the cardiac bed. Increased diastolic pressure is often observed in athletes, pregnant women and people who are often exposed to stress. At the same time, constant hypertension is a reason to contact a specialist, since such a condition indicates the development of pathologies in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels.
Normal diastolic pressure
The approximate limits of normal diastolic pressure indicators in patients of different ages are identified. It should be taken into account that fluctuations in these values are also largely due to the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. Rare small deviations from the norm may not be a cause for concern, but pronounced diastolic hypertension indicates developing pathologies.
Diastolic pressure indicators
| Patient age | Lower limit of normal | Upper limit of normal | Pathological indicators |
| 15-16 | 51 | 79 | 50 or less, 80 or more |
| 17-29 | 61 | 84 | 60 and less, 85 and more |
| 30-39 | 61 | 89 | 60 and less, 90 and more |
| 40-59 | 61 | 89 | 60 and less, 90 and more |
| 60-69 | 61 | 89 | 60 and less, 90 and more |
| Over 70 | 89 | 65 and less, 90 and more |
Attention!
If a person's blood pressure is regularly higher than normal, the specialist defines this condition as hypertension. This disease can lead to the development of various complications that significantly reduce the patient’s quality of life.
What can you do at home?
Actually, nothing. You should urgently call doctors (emergency medical care) and wait for a team led by a paramedic.
Before the doctor arrives, you should take a horizontal position and simply relax as much as your condition allows. No sudden movements or special breathing techniques are needed.
You can take medications only with the permission of the treating specialist and strictly in the prescribed dosage. No more, no less.
A sharp drop in blood pressure will also not lead to anything good (this is how classic antihypertensive medications work), and here a combination of drugs and their dosages is required.
How to reduce lower pressure if it is 100 or more, minimally affecting the upper one:
- take 1/4 Captopril tablet.
- take calcium antagonists (1 tablet of Diltiazem or Verapamil).
Exceeding dosages and taking unspecified medications is strictly prohibited. What this will lead to is unknown.
The described measure is also not a treatment and does not lead to normalization of blood pressure in the long term.
Attention:
Baths, dousing with water, folk remedies, basins with hot water - all these are sabotage techniques. This kind of advice is given by people far from medicine. Self-activity is fraught.
Upon arrival, doctors need to talk about complaints and, if possible, resolve the issue of hospitalization.
If it is impossible to go to the hospital for at least a few days, you should immediately contact a cardiologist to prescribe or adjust therapy.
Causes of diastolic hypertension
Increased pressure can be caused by both normal physiological processes in the human body and various developing pathologies. In a healthy person, diastolic hypertension may occur in the following cases:
- Consumption of alcoholic beverages, nicotine, drugs. These substances have a stimulating effect on the nervous system, sharply reducing inhibition processes in the body. As a result, a spasm of the vascular walls occurs, and the number of heartbeats per minute increases. Such changes lead to an increase in pressure, including diastolic. A cool shower, neck massage, or sleep will help relieve an attack of hypertension. If necessary, the patient is advised to use drugs to remove alcohol or drugs from the body.
- Eating fatty and hot foods. Normally, any meal is accompanied by a slight increase in blood pressure. High-calorie foods take a long time and are difficult to digest. At the same time, various digestive processes affect heart rate and blood density. If a patient is prone to diastolic hypertension, he is advised to avoid regularly consuming foods high in lipids.
- An increase in lower pressure is possible as a result of the use of various pharmacological agents. In women, a similar effect is often provoked by hormonal contraceptives. Corticosteroids and anti-inflammatory drugs also lead to hypertension in some cases. If there is a significant increase in diastolic pressure, it is necessary to consult a specialist and replace the medication with another one.
- Staying in areas with unfavorable environmental conditions. Living in regions with polluted air or water leads to the accumulation of toxins in the human body and disruption of the cardiovascular system.
- Playing sports. Any exercise leads to accelerated blood movement through the vessels and more frequent myocardial contractions. Hypertension can be avoided by exercising moderately, without resorting to excessive physical activity.
Diastolic hypertension can also occur due to various diseases. In this case, hypertension should be divided into primary and secondary. In the first case, the pathology develops due to hemodynamic disturbances and dysfunction of the cardiovascular system. Such disorders require long-term complex treatment. In this case, pharmacological agents must be selected taking into account the individual health characteristics of the patient.
Kidney diseases
The kidneys produce the biologically active substances renin and angiotensin. One of their functions is to regulate normal blood pressure in the human body. With the development of various diseases of the urinary system, the patient begins to produce an excess of these hormones. As a result, the lumens of blood vessels narrow, cholesterol plaques are deposited on their walls, and hypertension develops. Most often, a similar clinical picture occurs with pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, or exacerbation of urolithiasis.
Attention!
Disturbances in the urinary system lead to acute fluid retention in the body and the development of intoxication. Such pathologies pose a danger to human life and require emergency diagnosis and medical intervention.
Kidney diseases, in addition to diastolic hypertension, manifest themselves with the following symptoms:
- intense pain in the lumbar region;
- disturbance of urination, most often ischuria - urine retention in the body;
- bloating and abdominal pain;
- stool disorders, nausea, intestinal cramps;
- attacks of vomiting that does not bring relief;
- sweating, chills.
Treatment of diastolic hypertension in this case involves careful treatment of the underlying urological disease. The patient is prescribed the following medications:
- antibacterial drugs for pyelonephritis: Amoxicillin, Doxycycline, Ampicillin;
- antispasmodics: No-shpa, Drotaverine;
- analgesics: Nise, Ketorol, Ketanov;
- means for removing stones: Cyston, Urolesan, etc.
When fighting hypertension, special attention should be paid to diet. The patient is advised to minimize the consumption of salt, salty and peppery foods. Excess sodium in the body leads to an increase in the volume of intracellular fluid, thickening of the walls of blood vessels and narrowing of their lumen. This causes an increase in blood pressure.
Attention!
In some cases, to normalize the production of renin and angiotensin, a specialist prescribes drugs to the patient that reduce the activity of the renin-angiotensin system: Omapatrilat, Losartan, Valsartan.
Thyroid diseases
The thyroid gland is one of the most important organs of the endocrine system. At the same time, failures in its work immediately affect a person’s health, since the coordinated work of the whole organism is disrupted.
The follicular cells of the thyroid gland produce two main hormones:
- thyroxine or T4;
- triiodothyronine or T3.
In some cases, the patient begins to produce an excess amount of active substances, as a result of which the following changes occur in the body:
- the heart rate increases;
- vascular tone increases;
- the lumen of the arteries narrows.
As a result, a person’s diastolic pressure increases, weakness, dizziness, and intense headache occur. There may also be an increase in appetite, irritability, overexcitation, and myalgia.
To relieve hypertension, it is necessary to carry out comprehensive treatment of hyperthyroidism, that is, pathological excessive production of hormones. Depending on the degree of development of the disorders, the patient is indicated for conservative or surgical treatment.
Drug treatment in this case is aimed at reducing the secretion of the thyroid gland. Patients are prescribed thyreostatics: Propylthiouracil, Thiamazole. It is also mandatory to follow a diet rich in proteins, carbohydrates and amino acids. In this case, you should limit the intake of foods that excite the nervous system.
If the patient’s condition does not improve, persistent hypertension, disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, and severe headaches are noted, then surgery to excise the thyroid gland is prescribed. After the intervention, the patient must take medications throughout his life to maintain normal hormonal levels.
Symptoms of pathology
When diastolic readings increase, a person feels all the signs of hypertension, so it is difficult to independently diagnose the disease.
Signs of high heart rates:
- severe headache localized in the occipital and temporal parts;
- weakness, limbs become weak;
- dizziness, nausea;
- redness of the skin.
Elevated diastolic pressure is often referred to by doctors as the “silent killer.” What does it mean? Symptoms of the disease often do not cause concern for people; many attribute them simply to overwork and stress. But if the lower pressure readings often increase, the likelihood of a stroke or heart attack increases several times.
Symptoms of diastolic hypertension
Hypertension, both systolic and diastolic, is usually manifested by the following symptoms:
- dizziness, cephalalgia, feeling of heaviness in the head;
- throbbing pain in the occipital or temporal region, often radiating to the eyeballs;
- pulsation in the head;
- “floaters” before the eyes and noise in the ears;
- facial skin hyperemia;
- tremor and numbness of fingers;
- irritability, anger, increased excitability;
- decreased performance;
- chills;
- sweating;
- tachycardia.
Attention!
Each patient may exhibit signs of high blood pressure individually. If you have frequent attacks of hypertension, you must have a blood pressure monitor and regularly monitor your condition.
Ways to lower diastolic pressure
Diastolic hypertension is a condition that can lead to a sharp deterioration in a person’s well-being. Therefore, at the first signs of the development of pathology, it is necessary to take a number of measures aimed at normalizing the functioning of the patient’s body:
- The patient should be placed face down on the couch, and a cold compress or ice pack should be applied to his neck and collar area for 5-10 minutes. This will reduce blood flow tension in the vessels supplying the brain.
- Resort to acupuncture, that is, a procedure for stimulating active points of the body. You need to lightly press on the hollow under your earlobe and move your fingertip to the middle of the collarbone. Repeat the manipulation on the other side of the head.
- Take a cool shower, take a nap. Relieving stress and resting will help lower your blood pressure.
Attention!
All these measures can be used only if the patient feels satisfactorily and does not complain of impaired speech, consciousness, drowsiness or severe dizziness. Otherwise, you should immediately seek emergency medical help.
Drug therapy for diastolic hypertension
Drug treatment for diastolic hypertension should be taken only as prescribed by a specialist. The doctor must take into account the individual health characteristics of the patient, his general well-being, and the presence of chronic or acute diseases. In most cases, the following pharmacological agents are prescribed for the treatment of this pathology:
- Beta blockers: Anaprilin, Atenolol, Metoprolol
and so on. These drugs dilate blood vessels, help to quickly lower blood pressure, and reduce the level of glucose in the blood plasma. These medications are widely used for the treatment of hypertension, but are sold only by prescription. - Angiotensin converting enzymes: Captopril, Enalapril, Quinapril
etc. They are used to treat both systolic and diastolic hypertension. They block the action of an enzyme that causes an increase in blood pressure. - Calcium antagonists: Nifedipine, Verapamil
. These are drugs that are prescribed only for severe hypertension and are used for urgent relief of a hypertensive crisis, that is, to reduce very high blood pressure.
In this case, drug treatment should be comprehensive and long-term. The medications should be taken regularly. Refusal of therapy prescribed by a doctor can lead to a worsening of the condition and the development of persistent hypertension.
Diagnostics
During the initial examination, the cardiologist performs a physical examination and measures the pressure in the arms and legs. To obtain the most reliable results, 24-hour blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) is prescribed. The diagnostic search is aimed at finding the etiological factors that caused high blood pressure. The examination plan usually includes:
- ECG.
According to the electrocardiogram, signs of myocardial hypertrophy and disturbances in repolarization processes are revealed. When blood pressure changes towards higher levels, single extrasystoles and other rhythm disturbances may occur, and manifestations of congenital or acquired cardiac malformations may be detected. - Ultrasound.
Echocardiography evaluates heart function. Left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy is often visualized. To exclude renal hypertension, an ultrasound of the kidneys and Doppler sonography of the renal arteries are required. According to indications, sonography of the main endocrine glands is performed. - Standard tests
. A general blood test and fasting glucose level are measured. In a biochemical study, the levels of urea and creatinine are studied, the lipid spectrum is the levels of cholesterol, different fractions of lipoproteins. In a general urine test, the amount of protein and cellular elements is determined. - Advanced laboratory tests
. If there are typical symptoms of endocrine pathology, the level of a number of hormones is examined: corticosteroids, aldosterone, catecholamines. To assess renal function, creatinine clearance is calculated. To exclude metabolic syndrome, a glucose tolerance test is recommended. - Additional instrumental studies
. To determine the cardiothoracic index, the shape and size of the heart, a survey radiography of the OGK is performed. To confirm atherosclerotic vascular damage, angiography is performed. For a more detailed study of the structure of the kidneys and adrenal glands, CT and MRI are prescribed.
Prevention of hypertension
To prevent the development of diastolic hypertension, some preventive measures should be taken:
- Follow a diet
. A patient with diastolic hypertension should avoid eating high-calorie foods high in cholesterol and lipids. These substances can be deposited on the walls of blood vessels, leading to the formation of cholesterol plaques. - Limit the amount of salt and liquid in the diet
. It is especially dangerous to drink a lot of carbonated sweet drinks, as they only increase thirst. - Do not drink alcohol or smoke
. Alcoholic drinks and nicotine have a pronounced detrimental effect on vascular tone and blood viscosity, which leads to increased blood pressure and the development of various pathologies of the cardiovascular system. - Body weight control
. Excess weight puts extra strain on the heart, and the walls of blood vessels experience increased pressure. As a result, they quickly lose the tone necessary for normal blood pumping. - Try to avoid severe stress and negative emotions
. Psychological trauma causes increased heart rate and increased blood pressure. - Treat inflammatory processes in the body in a timely manner
. Various diseases of the kidneys and myocardium are especially dangerous. In this case, therapy not prescribed on time can lead to complete disruption of the urinary system.
Video - Blood pressure. What does low blood pressure mean?
Diastolic hypertension is a pathological condition that indicates excessive resistance of the artery walls as blood moves through them. An increase in lower pressure can occur due to the body’s normal reaction to various stimuli: physical activity, stress, overeating. At the same time, diastolic hypertension also develops due to various pathologies of the urinary, cardiovascular or endocrine systems. If your blood pressure regularly increases, you should consult a specialist and identify the cause of the problem. For the most effective remedies for sinusitis, read our article.
Dangerous!
If blood pressure is persistently above 140/90 millimeters of mercury and left untreated, the risk for heart attack, peripheral artery disease, stroke and myocardial infarction increases. Congestive heart failure, cardiac arrhythmias, and renal failure may occur.
You cannot ignore systematic headaches and constantly resort to citramon for salvation. And if, when measuring pressure, DD is above 80 mm. Hg, it is vitally important for you to contact a doctor at the Pulmonology Center.