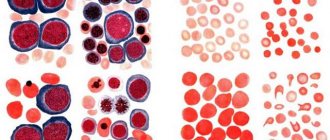
Basic functions of platelets
In appearance, platelets are round or oval red plates with a smooth surface. They are formed in the bone marrow. They mature in approximately 8 days. These components constantly circulate in the bloodstream.
The main function of platelets is to ensure blood clotting. In addition, the ability of these blood components to stop bleeding is important. This is ensured by the fact that individual platelets can stick together and stick to sites of vascular damage. The process is automatically started by the human body when there is a risk of bleeding.
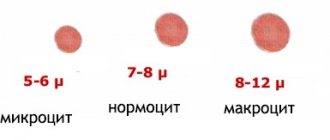
An important question is how long platelets live. Their viability time lasts approximately 10 days. Depending on the age of the red plates, their size changes: from 2 to 5 microns in diameter.
The process of platelet renewal in the blood occurs constantly. Therefore, an important factor to ensure the maintenance of blood condition is the balance between the formation of red plates and their death. Otherwise, there may be a tendency to blood clots or increased bleeding.
Cytoskeleton and shape change
The platelet cytosol is permeated by a three-dimensional network of water-insoluble protein threads (filaments), which forms the cytoskeleton. The filaments consist of polymerized actin protein and ensure that the platelet changes shape when activated. In addition, just below the plasma membrane is a membrane skeleton associated with the cytoplasmic “tails” of some receptors. It consists of short actin filaments connected to each other using special proteins. The membrane skeleton not only supports the plasma membrane, regulating the contours of the cell, and stabilizes it, preventing fragmentation, but also regulates the distribution of receptors attached to it in the plane of the membrane. It is also suggested that it plays an important role in the regulation of various intracellular events that are triggered upon activation.
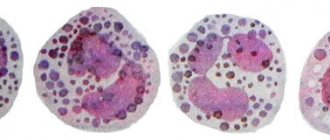
Rice. 5.
Scanning electron micrographs of the process of spreading an activated platelet (
a–d
) over the surface []
Interestingly, the cytoskeleton is a dynamic structure, thanks to which a platelet can not only change shape, but also grow “tentacles” (filopodia). With their help, it spreads over the surface of the damaged vessel (Fig. 5) and more easily adheres to other platelets (Fig. 6). Relatively recently, it was discovered that upon strong activation (by thrombin alone or together with collagen), platelets are divided into two groups (subpopulations), very different in properties and even shape, which suggests a fundamentally different organization of the cytoskeleton in them. Some of them (“regular” activated) have the appearance of amoebas - lumps with filopodia, others (procoagulant, since there is a lot of phosphatidylserine on the outer surface of their membrane) - balls without “tentacles”. The data obtained in our laboratory indicate that some membrane receptors responsible for binding cells to the surface and to each other are unequally attached to the cytoskeleton in platelets from the two subpopulations. This means that they can interact differently with the damaged vascular wall and with each other in the forming blood clot.
The sequence of processes during the restructuring of the platelet cytoskeleton has generally been studied quite little, but here is a new question: why do some cells become “amoebas” when activated, and others become “balls”?
Blood test for platelets
A complete blood test can determine the platelet count. The main indications for its implementation are the following:
- Increased bleeding of gums.
- Heavy menstruation.
- The appearance of bruises from minor impacts.
- Frequent nosebleeds.
- Difficulty stopping bleeding from minor injuries.
The number of platelets in the blood is measured in thousands per 1 microliter of blood. Counting is carried out in specialized laboratories in various ways that guarantee high accuracy.
The normal platelet count in the blood depends on gender and age and is:
- For men, 200–400 thousand.
- In women, 180–320 thousand, during menstruation the amount can decrease to 75–220 thousand, and during pregnancy to 100–310 thousand.
- In children, indicators depend on age, and the corresponding values are given in special tables.
To conduct a general blood test, blood is taken from a finger. No special preliminary preparation is required before this. To ensure accurate results, it is better to donate blood in the morning on an empty stomach. At the same time, 12 hours before the procedure it is not recommended to consume fatty spicy foods, carbonated drinks, and alcohol.
Additionally, to determine blood clotting indicators, Sukharev and Lee-White tests are performed. They are informative and allow you to obtain the necessary additional data about the pathological condition. This will allow you to carry out correct treatment measures and avoid dangerous consequences.
Diagnostics
Thrombocytosis is detected in a clinical blood test. Although very high platelet counts are more common in hematologic diseases, platelet levels alone cannot determine the cause of thrombocytosis. Therefore, if it is detected, you should visit a therapist. The doctor carefully asks about the patient’s complaints, how long ago the symptoms occurred, and conducts a general examination of the patient. Then, based on the data obtained, an additional examination is prescribed, including:
- Blood tests
. In a general blood test, the content of other formed elements (erythrocytes, leukocytes) is determined, and the leukocyte formula is calculated. The concentration of inflammatory markers (ESR, CRP) is measured. The indicators of serum iron, TBC, ferritin are assessed. The presence of autoantibodies (RF, ACCP, antibodies to the cytoplasm of neutrophils) is checked. In case of endocarditis and sepsis, an analysis for procalcitonin and presepsin is performed. - Pathogen identification
. To identify the pathogen, microscopy, bacterial culture of urine and sputum are performed. If tuberculosis is suspected, an intradermal test with tuberculin is prescribed. Using an enzyme immunoassay, antibodies to viruses, parasites, and fungi are detected, and using the polymerase chain reaction method, their DNA and RNA are detected. To diagnose meningitis, a cerebrospinal fluid analysis is informative. - Genetic research
. In patients with myeloproliferative pathologies, mutations of Janus kinase (JAK2V617F), thrombopoietin receptors (MPL), and erythropoietin are determined using fluorescent hybridization (FISH) and PCR. Sometimes chromosomal abnormalities are detected - trisomies, deletions. In chronic myeloid leukemia, cytogenetic analysis reveals the Philadelphia chromosome (Ph). - X-ray
. On an X-ray of the lungs, in case of pneumonia, foci of darkening and infiltrates are noted, in case of tuberculosis - enlargement of the mediastinal lymph nodes, expansion of the roots of the lungs, rounded shadows (cavities) of the upper lobes of the lungs. In patients with arthritis, x-rays of the joints show a narrowing of the joint space, areas of erosion, and marginal osteoporosis. - Ultrasound
. Ultrasound of the abdominal organs in case of pyelonephritis determines compaction and expansion of the pyelocaliceal system, and in case of blood diseases - splenomegaly. In bacterial endocarditis, cardiac echocardiography reveals vegetations of the valves and sometimes effusion into the pericardial cavity. - Endoscopy
. In patients with inflammatory bowel pathologies, fibrocolonoscopy is performed, which reveals hyperemia of the mucous membrane, lack of vascular pattern, erosion, and ulcerative defects. Crohn's disease is characterized by the "cobblestone pavement" symptom - alternating deep ulcers with unchanged mucous membrane. - Histological studies
. In bone marrow aspirate for malignant hematological pathologies, hyperplasia of the megakaryocyte lineage of hematopoiesis is noted (in polycythemia vera - all three lineages), a large number of blast cells (in myeloid leukemia), proliferation of reticulin and collagen fibers (fibrosis). In case of vasculitis, a biopsy of a vessel reveals pronounced perivascular infiltration with lymphocytes and plasma cells.
Platelet count according to Fonio
Increased platelet levels
Elevated platelets are a pathological condition. It is called thrombocytosis. The main danger of the pathology is the increased risk of blood clots.
The cause of an increase in the level of platelets in the blood can be various diseases. Most often thrombocytosis occurs against the background of:
- Malignant neoplasms.
- Infectious diseases.
- Helminthic infestations.
- Surgical operations.
- Autoimmune pathologies.
- Kidney failure.
High levels of platelets in the blood are observed in older people. Temporarily, indicators may increase after heavy physical exertion, for example, after playing sports.
The symptoms of thrombocytosis are characteristic, but mild. It is imperative to conduct a general blood test if the following symptoms are noted:
- Pain in the fingers and toes.
- Itching of skin surfaces.
- Unreasonable weakness, which leads to decreased performance.
- Lack of appetite.
General information
Platelets are granulocytic blood cells without a biconvex nucleus, formed from plasma cells of the bone marrow. They are presented in different forms - young, adult and mature. The diameter is directly proportional to age: 2-4 microns. Platelets contain granules that create blood clotting proteins, lytic enzymes, phosphatase and cathepsin, create serotonin, calcium ions and ATP, and contain lysosomal enzymes.
One of the most important functions of blood platelets is participation in blood clotting (primary hemostasis).
Platelets bind clotting factors, making blood clots thicker. As a rule, in an inactive state, when the vessel wall is damaged, platelets are directed to the damaged area. Thanks to the pseudopods located on the surface of the body, they are attached to each other and the vascular wall, forming a blood clot, which is an excellent barrier to bleeding. In the active state, platelets are able to change the shape of the body, due to which they increase their area, and this allows them to completely close the damage.
In addition, platelets are able to protect the body from foreign bodies by catching them with the help of pseudopods, and then digesting them with the help of the enzyme lysocine, which is formed from platelet factors (thrombin, thromboxane), from platelet granules. Thus, platelets are important for the immune response, being “killer” cells for foreign agents entering the body.
Blood plates serve as a storage site for serotonin, providing antitumor and radioprotective effects.
Thus, a violation of the number of platelets leads to inhibition of their functions, this certainly leads to disruption of the body’s activity and entails negative symptoms.
Decreased platelet levels
Low platelet levels, the norm of which differs between men and women, provoke the development of a condition known as thrombocytopenia. Very often it occurs against the background of uncontrolled use of medications: antidepressants and antibiotics.
The reasons for a decrease in the level of platelets in the blood can be various infectious diseases: ARVI, hepatitis, herpes, etc. Thrombocytopenia can be observed when a large number of blood thinning products are included in the diet. These are ginger, cherries, garlic, onions, etc.
Non-infectious factors that reduce the level of platelets in the blood include pregnancy, vitamin deficiency, alcohol or heavy metal poisoning.
Thrombocytopenia can be suspected based on the following signs:
- Heavy menstruation.
- Frequent nosebleeds.
- The appearance of hematomas.
With a constant pathological decrease in the level of platelets in the blood, the risks of developing severe bleeding and stroke conditions, which are life-threatening, increase.
Treatment of thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is treated by a hematologist. The treatment regimen is developed individually for each patient: the patient’s age, the presence of any diseases, the degree of deficiency, and the amount of bleeding are taken into account. It is necessary to determine the cause of thrombocytopenia so that treatment is as effective as possible. Standard drug therapy consists of:
- Corticosteroids – have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects;
- Immunoglobulins – correct the functioning of the immune system;
- Immunosuppressants – stop the destructive effect of the immune system on the body;
- Agonists to thrombopoietin receptors – promote more active production of this hormone.
In case of thrombocytopenia caused by bleeding, it is necessary to identify the source of this bleeding and stop it. Only after this the platelet correction is carried out. The patient will have to take medicinal iron and drugs that promote the production of red blood cells.
If drug treatment does not produce any results, splenectomy is indicated - surgical excision of the spleen. For hereditary diseases that prevent the body from producing enough platelets, a bone marrow transplant is necessary. If the platelet level is critically low, a blood transfusion of platelet mass from a donor is performed. If a large volume of blood is lost, a transfusion of fresh frozen plasma and red blood cells is necessary.
Restoring platelet levels in the blood
You can normalize the level of platelets in the blood with a balanced diet. It is important to saturate your diet with foods high in materials and microelements. You need to give up spicy food, alcohol, fast food and sweet carbonated drinks, lead a healthy lifestyle and maintain a drinking regime.
If it is not possible to normalize the indicators using natural methods, then you need to undergo a full examination by a hematologist. If platelet levels are elevated, special medications may be prescribed - anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents. They thin the blood and minimize the risk of blood clots. But at the same time, they should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor. It should be understood that stabilization of the condition is possible only after eliminating the underlying causes that provoke deviations from the norm.
Prevention
There is no specific prophylaxis for thrombocytopenia. It is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition, normal sleep, not to overload yourself with work, abstain from drinking alcohol and tobacco products, treat infectious diseases in a timely manner and carry out routine vaccinations. Consult a doctor promptly if there is a sudden disturbance in the body’s functioning.
Author: infectious disease doctor. Allergist-immunologist Natalia Nikolaevna Gordienko
Summarizing
Our study made it possible to describe a new mechanism of cell redistribution within the thrombus: during contraction, “slippery” procoagulant platelets are mechanically squeezed onto the surface of the thrombus, forming a heterogeneous structure of its outer part.
But the point has not yet been made in determining the role of procoagulant platelets in hemostasis. The formation of a weakly adhesive, that is, unsuitable for the adhesion of new cells, layer of dying cells and fibrin on the surface of the thrombus can help stop its growth by reducing the efficiency of fixation of non-activated platelets brought by the blood stream. However, this hypothesis requires further research.
It is pleasant to note that an important contribution to this work was made by young co-authors - students of the Department of Biophysics of the Faculty of Physics of Moscow State University - Roman Kerimov and Alexandra Yakusheva, as well as a student of the Faculty of Fundamental Medicine of Moscow State University Taisya Shepelyuk (Fig. 4). The results of the work were published in one of the leading journals of the American Cardiovascular Association and reported at several international conferences, including the Gordon Conference on Hemostasis.
Figure 4. Roman Kerimov, Alexandra Yakusheva, Taisya Shepelyuk and Dmitry Nechipurenko
This version is a modification of a note that was published in the physics department newspaper “Soviet Physicist”.
The author expresses gratitude to Anastasia Masaltseva and Yuri Nechiporenko for their assistance in editing the article, as well as to all his colleagues - co-authors of the original work.