Composition and effect of the drug
The drug includes the main active ingredient - nifedipine and auxiliary components. Among them are polysorbate, talc, gelatin, wheat starch, lactose monohydrate and others.
Nifedipine belongs to the group of calcium antagonists. The drug has a direct effect on blood vessels, which makes it possible to expand their walls, relieve spasm of smooth muscles, and lower blood pressure. After the active component of the drug enters the blood, the direct transmembrane movement of calcium through the smooth muscles is inhibited, affecting the myometrium (the muscular layer of the uterus). The important thing is that the level of calcium in the blood remains unchanged, that is, there is no deficiency.
Nifedipine during pregnancy is used for false contractions and increased uterine tone. After entering the body, Nifedipine is absorbed by the digestive system and joins plasma proteins. The maximum therapeutic effect occurs when the active substance of the drug is absorbed by 60–98%. On average, the product begins to work in 20–30 minutes, and its duration of action is up to 8 hours. It is important to note that Nifedipine does not affect blood parameters such as lipid levels, glucose and uric acid.
Disorders of vascular-platelet hemostasis
Disturbances in this part of hemostasis most often manifest themselves as increased bleeding, a tendency to form hematomas (bruises) with the slightest contact, or even spontaneously, for no apparent reason. In some situations, on the contrary, there is a tendency to excessively easy thrombosis.
There are factors that stimulate the formation of a primary thrombus and those that disrupt it. Stimulants include the inflammatory process, because inflammation increases the content of biologically active substances in the blood. We can say that there is a readiness for the formation of a blood clot; it is only a matter of local damage to the vessel. Therefore, in severe infectious diseases, blockage of blood vessels may occur. There is an increased readiness for thrombosis during pregnancy, as well as in some hereditary diseases (thrombophilia). Among food products, table vinegar (marinades) and coffee increase platelet activity.
The process of formation of a primary thrombus is disrupted when the number of platelets decreases (thrombocytopenia) and when there is a qualitative deficiency of platelets (thrombocytopathy). Thrombocytopathy can occur when taking certain medications. First of all, these are anti-inflammatory drugs: aspirin, analgin, brufen, some antibiotics. Thrombocytopathy also develops in kidney diseases. Spices and strong alcohol can also reduce the usefulness of platelets.
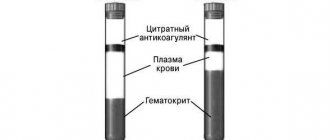
The blood coagulation system is actually several interconnected reactions occurring in the form of a cascade, or chain reaction. At each stage of this process, the proenzyme (the inactive form of the enzyme) is activated. Thirteen of these proteins (clotting factors) make up the coagulation system. They are usually designated by Roman numerals from I to XIII.
For what purpose is it used during pregnancy?
Why is the medicine prescribed to pregnant women? Nifedipine has a vasodilating effect on blood vessels. The drug is widely used in cardiological practice to normalize blood pressure and combat other symptoms of cardiovascular pathologies.
Despite the fact that the instructions for use contain contraindications such as pregnancy and lactation, doctors still prescribe the medicine in the second and third trimester among women suffering from pathologies of the heart and blood vessels. In addition, the medication is prescribed for uterine tone. Nifedipine helps reduce the threat of miscarriage, since its active components have a relaxing effect on the entire body, including the reproductive organ.
Only a doctor makes a decision on prescribing Nifedipine during pregnancy
Nifedipine is prescribed to women to lower blood pressure. During the period of bearing a baby, many patients report unstable blood pressure. To prevent complications and control the situation, doctors often use Nifedipine. During such a delicate period, even minor manifestations of cardiac dysfunction cannot be ignored. Often, heart and vascular diseases cause premature birth and even death of mother and child.
Features of treatment in different trimesters
During pregnancy, Nifedipine should only be prescribed by a qualified specialist. Self-medication with the drug can provoke the most severe complications, especially in the early stages of pregnancy. Before using the drug, a woman is prescribed all the necessary tests that will help identify contraindications and prevent the negative effect of the drug on the body of the mother and fetus.
I trimester
Most doctors are of the opinion that Nifedipine is completely contraindicated in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. It is during this period that the formation of the neural tube and the laying of the child’s organs occurs. The slightest failure can provoke severe consequences, fetal malformations. The risk of miscarriage with all the ensuing consequences for the mother is very high.
Important! In the first weeks of pregnancy, Nifedipine is used only in cases of extreme necessity, when there is a serious threat to the life and health of the mother.
II and III trimester
At this stage, the drug is used if there are certain indications for the mother. These include:
- hypertension;
- angina pectoris;
- conditions accompanied by increased uterine tone;
- risk of premature birth;
- late toxicosis.
Typically, the dose of the drug for a pregnant woman is up to 2 tablets throughout the day. Under no circumstances should you exceed the dose prescribed by your doctor. An overdose leads to the development of severe complications and miscarriage.
Features of application
How to take Nifedipine while pregnant? For high blood pressure and other conditions in pregnant women, Nifedipine is taken according to a regimen selected by a doctor on an individual basis. Typically, the treatment strategy is to take 1 – 2 tablets during the day. Sometimes the dose is increased depending on the clinical manifestations of the patient. The daily dose should not exceed 6 g of the product. The duration of therapy, depending on the diagnosis, ranges from a week to 1.5 months.
The drug is taken under the strict supervision of a doctor
If you take the pills for a longer period, you may become addicted to the medication. You cannot stop taking the drug on your own, even if there is no withdrawal syndrome. It is recommended to reduce the dose gradually during cessation of treatment.
Is Nifedipine dangerous during pregnancy?
The question of how negatively Nifedipine affects the fetus is quite controversial. Supporters of one point of view argue that the drug does not pose the slightest danger to the mother and fetus. Proof of this is many years of practice and some medical research. Other sources claim that no research has been conducted on this matter and the effect of the drug on the development of the fetus and the health of the woman during pregnancy can be very negative. Therefore, the use of the medicine during such a delicate period is strictly not recommended.
Information from third sources indicates that studies were nevertheless conducted and their results revealed that Nifedipine has the most negative effect on the fetus. Another point of view is that the medicine is dangerous only in the first stages of pregnancy, but in the second and third trimester the drug does not pose any threat.
It is quite difficult to understand such opposing opinions. Only a specialist can assess the benefits and risks of taking a drug in a particular case. The doctor is obliged to assess the condition of the pregnant woman and child and make a decision individually for each patient.
Nifedipine or atosiban in women at risk of preterm labor
In pregnant women at risk of preterm labor, delaying delivery by 48 hours with corticosteroids is associated with improved neonatal outcomes. This is why tocolytics are often used in clinical practice.
The APOSTEL III trial assessed the efficacy and safety of the calcium channel blocker nifedipine and the oxytocin inhibitor atosiban in women at risk of preterm labor.
Materials and methods
A multicenter randomized clinical trial included women at risk of preterm labor (25–34 weeks of gestation). They were randomized into 2 groups in a one-to-one ratio: oral nifedipine or intravenous atosiban for 48 hours.
The primary endpoint of the study was a composite of perinatal adverse outcomes (perinatal death, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, sepsis, intraventricular hemorrhage, periventricular leukomalacia, necrotizing enterocolitis).
results
From August 2011 to July 2014, the study included 254 women in the nifedipine group and 256 in the atosiban group.
The primary endpoint was met in 42 infants (14%) whose mothers received nifedipine and in 45 (15%) whose mothers received tosiban; relative risk 0.91, 95% CI 0.61–1.37.
In the nifedipine group, 16 children died (5%), in the atosiban group – 7 (2%), relative risk 2.20, 95% CI 0.91–5.33; It is believed that all deaths were not due to drug therapy.
Conclusion
In pregnant women at risk of preterm labor, the use of nifedipine and atosiban within 48 hours is associated with similar perinatal outcomes.
Larger placebo-controlled studies are needed to evaluate perinatal treatment outcomes.
Source
: Elvira OG van Vliet, Tobias AJ Nijman, Ewoud Schuit, Karst Y Heida, Brent C Opmeer, Marjolein Kok, Wilfried Gyselaers, Martina M Porath, Mallory Woiski, Caroline J Bax, Kitty WM Bloemenkamp, Hubertina CJ Scheepers, Yves Jacquemyn, Johannes J Duvekot, Maureen TM Franssen, Erik van Beek, Dimitri N Papatsonis, Joke H Kok, Joris AM van der Post, Arie Franx, Ben W Mol, Martijn A Oudijk. Nifedipine versus atosiban for threatened preterm birth (APOSTEL III): a multicentre, randomized controlled trial. The Lancet. March 2021.
Contraindications of the drug
Even in the second and third trimester of pregnancy, Nifedipine cannot always be used. The medicine has a number of contraindications, which include:
- individual intolerance to the components included in the medication;
- age under 18 years;
- acute renal failure;
- severe liver pathologies;
- recent myocardial infarction;
- arterial hypotension;
- vascular collapse;
- congenital aortic stenosis;
- development of cardiogenic shock.
During treatment, all contraindications of the drug must be taken into account.
The use of any medications during pregnancy is considered undesirable. If the need to take drugs such as Nifedipine nevertheless arises, its contraindications should be taken into account.
Side effects
Considering reviews of the drug, it should be noted that Nifedipine is well tolerated by patients. Complications and side effects more often occur when the doctor’s recommendations for taking the drug are not followed, as well as when contraindications are not followed. Negative consequences during treatment with Nifedipine are noted from various systems. These may be the following symptoms:
- in some patients, taking the medication provokes a sharp drop in blood pressure, heart rhythm disturbances, and pain in the chest area;
- from the central nervous system such manifestations as headache, apathy, irritability, and fatigue are noted;
- from the digestive system, nausea, heartburn, vomiting, bowel dysfunction, flatulence may occur;
- manifestations such as itching, hyperemia, burning, and rashes in the form of small red pimples appear on the skin.
Important! If symptoms from this list are detected, you should immediately stop treatment and make an appointment with a doctor.
Disturbances in the coagulation system
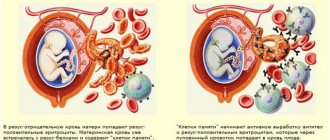
A decrease in the content or activity of coagulation factors may be accompanied by increased bleeding (for example, hemophilia A, hemophilia B, von Willebrand disease). Excessive activation of coagulation hemostasis (for example, Leiden mutation of factor V) leads to the development of thrombosis (thrombophilia).
Hemostasis and pregnancy
Among all the causes of miscarriage, problems in the hemostatic system are in second place in frequency. Second after obstetric and gynecological reasons. What's the matter?
During pregnancy, the expectant mother's body prepares for childbirth. The hemostasis system is also being prepared to minimize blood loss during childbirth. Hemostasis is activated progressively along with increasing gestational age. If a woman’s hemostasis is initially overactive, then during pregnancy microthrombi may form in the vessels of the uterus or placenta, which leads to miscarriage or frozen pregnancy.
Under what conditions can this happen?
- 1. For hereditary thrombophilia,
more often when there is a violation of the metabolism of folic acid and its compounds (folates), when the amount of homocysteine in the blood increases. The reasons for the increase in homocysteine levels may be a lack of folic acid and vitamin B12 in the diet, thyroid disease, and kidney disease. It can also increase in smokers, coffee drinkers and while taking medications such as theophylline (by the way, a relative of caffeine), nicotinic acid. Homocysteine damages the endothelium (inner layer) of blood vessels, and this damage triggers blood clots.
- 2. For antiphospholipid syndrome (APS)
– this is the name of an autoimmune disease in which antibodies are produced to one’s own clotting factors. As a result, blood clots also spontaneously form in the vessels.
Patient reviews
Anna, Moscow “I had to deal with Nifedipine at the 28th week of pregnancy, when the uterus became toned and there was a serious threat of miscarriage. I had previously heard about the drug that it should not be prescribed to pregnant women, as there is no data on this matter. Taking the medicine was quite alarming, but everything worked out and the baby was carried to term. I would like to advise expectant mothers to listen to doctors and under no circumstances self-medicate.”
Yulia, Sergiev Posad “I took Nifedipine in the late stages of pregnancy, as I developed late toxicosis, my blood pressure increased greatly, and I felt terrible. The leading doctor prescribed me Nifedipine, 1 tablet per day. Despite many negative reviews, the medicine had no effect on my child’s health. The drug relieved my blood pressure perfectly, there were no side effects.”
Svetlana, Ufa “After starting treatment with Nifedipine, the condition initially returned to normal, the pressure stabilized, but after a few days the headache began to hurt severely and rashes appeared in the face and neck. At that time I was in my seventh month. The drug had to be replaced. The doctor suggested that the medicine was not suitable for me individually, even though a sensitivity test was carried out.”
Valeria, Khimki “I was prescribed this drug several times throughout my pregnancy in short courses to relieve uterine tone. I was very afraid to take it, but the doctor assured me that the medicine was safe, saying that it was a new method of treatment. I didn’t argue with the specialist; fortunately, no side effects arose, I gave birth to a healthy baby on time.”
Hypertonicity of the uterus
Nicotine constricts the blood vessels of the expectant mother, as well as the vessels of the placenta and umbilical cord, through which the fetus is nourished. Of course, smoking by itself is unlikely to lead to hypertension, but in combination with other factors it may well
If the job involves constant stress, is hazardous, or is physically demanding, give it up at the first opportunity. If this is not possible, take advantage of your rights, which are enshrined in the labor legislation of the Russian Federation
Hypertonicity must be distinguished from Braxton-Hicks contractions: it lasts much longer than these training contractions and usually does not go away on its own (or goes away only after some long time)
what is hypertonicity
The main tissue that makes up the uterus is muscle, and according to the laws of physiology, muscle tissue contracts under the influence of any factor. The uterus contracts slightly in women every month during menstruation, and much more strongly during labor. The uterus can also contract during pregnancy; doctors call this condition hypertonicity. What it looks like: suddenly at some point the woman feels that her stomach is tense, becomes hard, as if “turning to stone.” This state lasts quite a long time - half an hour, an hour, half a day or even the whole day. Additionally, discomfort (or pain) may appear in the lower back or sacrum. It is clear that such tension in the abdomen worries the mother, because since the uterus is contracting, there may be a threat of termination of pregnancy. But here it all depends on how strongly and often the stomach tenses.
Braxton-Hicks contractions
It turns out that the stomach can tense not only when there is a threat of miscarriage. Starting from the end of the second trimester, the expectant mother can feel so-called training contractions (Braxton-Hicks contractions) - during them, the stomach also tenses for a while, as if it “turns to stone” - in general, the sensations are the same as with hypertonicity. But the main difference between such contractions and hypertonicity is that they do not last long (a few seconds to a couple of minutes) and go away on their own, even if you change your body position or take a shower. Braxton-Hicks contractions occur up to ten times a day, and towards the end of pregnancy they appear even more often. These contractions are a completely normal occurrence during pregnancy, and they do not indicate any threat of miscarriage. It’s just that with their help, the uterus seems to be preparing (training) for childbirth.
where does hypertonicity come from?
Hypertonicity can appear in any trimester of pregnancy. In the early stages, it occurs more often due to the fact that there is not enough progesterone, a hormone that is necessary for the normal course of pregnancy. Another reason for hypertonicity is some changes in the wall of the uterus, for example, fibroids (a knot of muscle tissue of the uterus), endometriosis (growth of the uterine mucosa into the thickness of the wall), inflammatory diseases. In these situations, the uterine wall is not able to stretch as it should. At later stages, hypertonicity can develop, on the contrary, when the uterus is overstretched (with polyhydramnios, a large fetus, multiple pregnancies). Very often, hypertonicity is provoked by some kind of physical activity that is too strong for a woman, for example, if, in a fit of “nesting,” the mother suddenly began to move and rearrange something in the apartment herself, or she simply moved for a very long time without resting. Some people experience hypertonicity after psychological stress.
how to recognize hypertension
Hypertonicity must be distinguished from Braxton-Hicks contractions - it, as mentioned earlier, lasts much longer than these training contractions and usually does not go away on its own (or goes away only after some long time). But if a mother cannot understand whether she has hypertension or not, she should consult a doctor. If there is still increased tone of the uterus, the doctor, simply placing his hand on the stomach, will feel compaction, tension, even the sensation of a stone under the hand. Additionally, you can always do an ultrasound, which, with hypertonicity, shows areas of local thickening of the muscular layer of the uterus, and also look at the cervix, the state of which can also be used to judge whether there is a threat of termination of pregnancy or not.
what to do for hypertension
If it appears, first of all you need to:
1. Calm down and lie down if possible. There is no need to panic; excess stress will not bring any benefit, especially since without consulting a doctor, it is still not clear whether there is hypertonicity and how severe it is. Or maybe it’s a false alarm altogether? In addition, you can use relaxation techniques (breathing, auto-training, etc.).
2. Call your doctor. Of course, the doctor will not make a diagnosis in absentia, but since he knows the history of the expectant mother, her real or possible problems, he will be able to give the right direction for further action.
3. If you cannot contact your doctor, you can go to any clinic or antenatal clinic where pregnant women are treated. If medical institutions are already closed (late evening, at night), you can call an ambulance - it will take you to the nearest hospital or maternity hospital (you can also get there by taxi).
4. Hypertonicity can be easily eliminated with special medications that relax the uterus (tocolytics), and if the doctor has prescribed them, then you should not be afraid to take them: they help quickly enough and do not harm the child.
how to prevent hypertension
There are simple rules that can prevent hypertension or reduce the risk of its occurrence:
1. Stop smoking, watch your weight, and don’t eat junk food. No matter how trivial it may sound, a healthy lifestyle is the basis of our well-being.
2. Distribute your strength correctly. Washing and cooking can wait if the expectant mother suddenly feels that she needs rest. If any activities require physical or psychological stress, cancel them for a while. Do not attend events or places where you may feel discomfort, reduce communication with people you find unpleasant.
3. Follow your doctor's recommendations: if he recommends some kind of examination or treatment, do not neglect them.
Listen to your body, follow your doctor’s advice, and stay positive—this is the key to a successful pregnancy. And then you won’t be afraid of any hypertension!