Typically, dizziness, loss of balance, and loss of orientation are symptoms of a simple disease that is easily treatable. Much less often, stroke and severe genetic diseases can manifest themselves this way. But even in the first case, if the doctor does not make the correct diagnosis and starts the wrong treatment, the patient’s quality of life will greatly deteriorate. What to do if you feel dizzy?
You can suspect a diagnosis of dizziness based on the description of the symptoms. There are two types of such complaints:
- Real dizziness, when there is an illusion that everything around is starting to spin (systemic dizziness, vertigo). In this case, certain head movements provoke dizziness. Nystagmus (involuntary oscillatory eye movements) can also be noticed in a person; sometimes this requires special studies. Vertigo also makes it difficult to stay in a straight, upright position when walking or standing. There are three main diseases, the main symptom of which is systemic dizziness:
- benign paroxysmal positional vertigo;
- Meniere's disease;
- vestibular neuronitis.
In none of these situations, the cause of dizziness can be osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, although often this diagnosis can be heard at a doctor’s appointment. Throughout the civilized world they know that degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs (which, in essence, is osteochondrosis) very rarely cause any symptoms - most often you should look for some other disease. Also in Russia they like to diagnose vertebrobasilar (vascular) insufficiency and call it the cause of dizziness. However, vascular problems actually very rarely cause these symptoms.
Mechanism of development of vertigo
If we consider dizziness from an anatomical point of view, the causes of this condition are quite simple. The vestibular apparatus, responsible for human balance and coordination in space, is located in the inner ear. Vision and muscle reflexes help a person navigate the environment. All received information enters the brain. And it is he who controls the functioning of the vestibular apparatus.
Sometimes the connection between the inner ear and the brain can become disrupted. A person loses the ability to navigate in space. Dizziness appears. To restore the lost connection, the brain immediately launches several reactions at once. Some of them may affect neighboring centers (for example, emetic). This leads to the appearance of unpleasant accompanying symptoms.
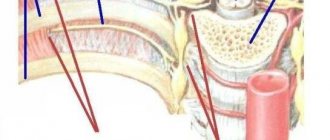
Structure and functions of the inner ear
Rice. 2. Ear structure
Anatomy of the ear
The inner ear includes a system of tubes and sacs that are filled with fluid. All this is called a labyrinth, the functions of which are hearing and balance. Sound signals from the labyrinth are transmitted to the brain through the vestibulocochlear nerve with two branches. One transmits messages from the organ of hearing, and the other from the organs of balance.
The brain processes balance signals sent through the vestibular nerve from the right and left ears. When one side is infected, it sends false signals. This is how information is presented that does not correspond to reality, which leads to dizziness.
Vestibular neuritis
(nerve inflammation) affects the branch associated with balance. This leads to dizziness, impaired sense of self in space, sudden movement of the eyeballs with a rapid phase, but no transformations with hearing occur. A person may feel like objects around them are moving, and will usually make mistakes when performing coordination exercises.
Experts also use the term “vestibular neuronitis” (damage to the sensory neurons of the vestibular ganglion). Its symptom is severe, rapidly developing, paroxysmal dizziness. It is often characterized by vomiting and imbalance. Often the development of symptoms of dizziness
precedes ARVI. Sometimes, a few weeks before the full clinical picture, patients may experience short bouts of loss of balance.
Labyrinthitis (inflammation of the labyrinth)
occurs when infection affects both branches of the cochleo-vestibular nerve. Then the hearing changes and attacks of dizziness occur. Even with slight turns of the head, the symptoms become more pronounced. Therefore, some people are forced to support their head with their hands.
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV)
BPPV is one of the most common causes of dizziness
, manifested during sudden movements and head swings. The duration of the state is limited to a few seconds or minutes. It occurs when calcium crystals (otoliths) in the inner ear begin to move. Because of this, the sensation of body rotation occurs.
The causes of BPPV include a history of traumatic brain injury, as well as otitis media. Often the cause of the disease cannot be identified. Then the diagnosis is confirmed by taking a Dix-Hallpike test. To do this, the patient quickly lies down from a sitting position and slightly lowers his head, turned 45 degrees. The test is positive if, a couple of seconds after this, an attack of dizziness and nystagmus occurs.
From 20 to 28% of patients with BPPV report spontaneous resolution of symptoms within up to a month after the onset of dizziness. The disease is benign and recurs within the first 12 months in only 15% of cases.
Rice. 3. Dix-Hallpike test: A – turn the head to the right; B - turn your head to the left.
Treatment of BPPV
Treatment techniques include the Epley maneuver. It allows, by manipulating the head, to move the otolith (crystal) to an insensitive zone - the vestibule of the inner ear.
Rice. 4. Epley maneuver
If the effectiveness of such treatment is low, the patient is additionally prescribed a set of exercises to perform at home. This is Brandt-Deroff gymnastics, according to whose method it is necessary to practice 2-3 times a day for 1 to 3 weeks. Taking medications in this case usually does not give positive dynamics.
Rice. 5. Brandt-Daroff gymnastics
Operations are performed when repositioning techniques do not lead to anything. Surgical interventions carry the risk of complications such as facial nerve injuries and hearing loss.
Possible operations include:
- obstruction of the posterior semicircular canal;
- removal of the vestibular nerve;
- labyrinthectomy;
- selective neurectomy.
Meniere's disease
A disease characterized by repeated attacks of rotational vertigo. They last for several hours and are not without noise in the ears, tinnitus, fullness or distension, as well as hearing impairment. It occurs in approximately 0.2% of the population, usually in people between 40 and 60 years of age. The disease is based on expansion of the endolymphatic system in the inner ear, which leads to degeneration of the labyrinthine receptors.
The disease has the following manifestations:
- dizziness;
- unsteady gait;
- hearing impairment;
- problems with the perception of sounds;
- nausea and vomiting;
- tinnitus.
Treatment of Meniere's disease
Treatment of an attack occurs by taking vestibulosuppressors. Prevention of the disease necessarily includes following a low-salt diet, avoiding alcohol and caffeine, and using betahistine and diuretics.
If the chosen therapy does not lead to positive dynamics, more serious treatment is required. This may involve injecting medications directly into the ear or undergoing surgery.
Diagnosis for dizziness
For dizziness, patients undergo Halmagi tests to identify the level of the vestibulo-ocular reflex. Its violation indicates central and peripheral lesions.
The Halmagi test does not require the use of additional equipment or lengthy preparation. The patient needs to look at the bridge of the nose of the specialist who is sitting opposite. In this case, the doctor holds the patient’s head with both hands and turns it from side to side by 15 degrees. With a normal vestibulo-ocular reflex, the eyes remain looking at a given point. If there is a violation, then the gaze turns along with the turn of the head.
Rice. 6. Halmagi sample
Severe dizziness with repeated bouts of vomiting continues for up to 3-4 days, after which the patient recovers. Recovery can take up to several months. In older people, it usually drags on and is often incomplete. If positive dynamics are not observed within a month, then an MRI of the brain and audiometry should be performed to exclude Meniere’s disease.
Sudden dizziness: 5 simple reasons
Typically, loss of communication between the brain and the vestibular system is rare and does not last long.
Dizziness that occurs is not considered a pathology in the following cases:
- Ride the carousel. Such entertainment creates a serious load on the vestibular apparatus. And if it is naturally weak and untrained, then it may well fail. Such dizziness usually occurs in women, since they also have psycho-emotional experiences added to the load.
- Stress, anxiety. If dizziness occurs during a speech in front of a large audience or after a reprimand from a boss, then the cause of vertigo is the production of a large amount of adrenaline. This hormone causes vasospasm. And this leads to a temporary deterioration in blood flow in the brain.
- Climbing to heights. In this case, the unpleasant phenomenon is also considered a physiological norm. When rising to a height, a person’s eyes cannot quickly focus on distant and close objects. Abrupt switching between objects causes dizziness.
- Hunger. Similar problems are common to all fans of strict diets. If a person does not receive enough nutrition, then a glucose deficiency occurs in his body. The absence of the main “fuel” leads to deterioration of brain function and the appearance of dizziness.
- Active exercises. Exercise enthusiasts should remember moderation. Excessive exercise can cause low blood pressure. This leads to dizziness and sometimes fainting. The unpleasant condition may be caused by unsuccessful sudden movements of the head, as a result of which the blood supply to the brain is disrupted.
An attack of dizziness may occur in response to taking certain medications. The most common sources of unpleasant symptoms are NSAIDs, antidepressants, antibiotics, and cancer medications. If your head is “turned” by medications, be sure to consult a doctor to change the drug.
Not frequent dizziness
Let's consider situations and diseases in which such symptoms may occur. Dizziness may not be systematic. but only a rare effect. However, this may be a signal of serious illnesses or developing pathologies.
Presyncope
In this state, which lasts no more than a few seconds or minutes, it seems to a person that surrounding objects are moving, he feels hot, sweats profusely, feels nauseous, his eyes become cloudy, vision may even disappear, and the person becomes pale. Presyncope usually occurs when the patient is sitting or standing, but not lying down. The cause may be orthostatic hypotension (a decrease in pressure after moving from a horizontal to a vertical position), arrhythmia and vasovagal crisis (excessive activity of the vagus nerve, leading to a decrease in heart rate).
Mental disorders
Depression, anxiety or panic disorder, alcohol addiction or personality disorder can lead to non-systemic dizziness. For example, if a person, in addition to this symptom, also has shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat and sweating, then most likely we are talking about a panic attack. A psychiatrist works with all these conditions.
Damage due to medication
Some aminoglycosides (for example, gentamicin) can be toxic to the vestibular system: they damage the hair cells of the inner ear, provoke imbalance and cause oscillopsia (the illusion of vibration of surrounding objects) when moving the head. This condition can become chronic.
Antiepileptic drugs, sedatives, and tranquilizers can also cause non-systemic dizziness. Sometimes blood pressure-lowering medications are too effective and blood pressure drops to abnormal levels, causing symptoms similar to dizziness.
Acoustic neuroma
When walking, a person begins to sway, surrounding objects move, his hearing may also deteriorate, and tinnitus may occur - these are the main symptoms of an acoustic neuroma (benign neoplasm). In most cases, such patients are prescribed surgery or radiation therapy.
Stranding syndrome (sea sickness on land)
After traveling on water, in very rare cases, a person may develop this syndrome: the patient feels that he is losing his balance, he is swaying, it seems to him that he is walking on uneven ground. This condition usually goes away within a couple of days. However, in more severe cases, your doctor may prescribe benzodiazepines or the antiepileptic drug clonazepam.
Non-systemic dizziness can also be caused by anemia (accompanied by fatigue, weakness and pallor), hypoglycemia (low blood sugar, which may be manifested by sweating and confusion), inflammation of the ear, heat stroke or dehydration.
Severe dizziness: 6 pathological causes
The causes of dizziness are not always harmless. Sometimes illnesses become sources of unpleasant conditions. In this case, dizziness occurs quite often and can last longer than a few seconds. To cope with this phenomenon, you need to consult a doctor. The severity of a symptom can be reduced (and sometimes completely eliminated) only through proper treatment of the underlying disease.
So, the causes of dizziness may include the following pathologies:
- Vegetovascular dystonia (VSD). A complex disorder in which a person experiences multiple impairments. All these symptoms are associated with malfunctions of the autonomic system. One of the common signs of VSD is dizziness. Such attacks are usually caused by sudden movements and rapid changes in posture. Dizziness does not last long. They go away on their own, without any intervention.
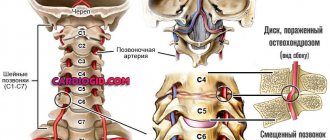
- Disorders in the cervical spine. Various injuries, osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernias can periodically remind you of themselves with sudden attacks of dizziness. They usually appear after active neck movements. The attack is accompanied by pain in the affected area, sometimes a crunching or crackling sound is heard.
- Anemia. Dizziness may occur due to iron deficiency. Most often this pathology is observed in children and women. With anemia, attacks are accompanied by high fatigue, weakness, pale skin, and pre-fainting conditions.
- Psychogenic dizziness. The reason for this pathology lies in the patient’s increased anxiety (people with an unstable psyche) or in the stress they have endured. Such people usually complain of poor sleep, fear of losing consciousness, a periodic feeling of shortness of breath, and increased heart rate.
- Vertebrobasilar insufficiency. This is a pathology in which blood flow in the vertebral or basilar arteries is weakened. Such problems lead to disruption of brain function. The pathology is characterized by regular attacks of dizziness, which can last up to an hour. In addition, patients complain of nausea, vomiting, and visual disturbances may occur. I often have a headache.
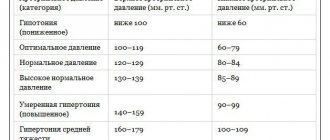
- Hypotension. A decrease in blood pressure is often accompanied by attacks of dizziness. Sometimes lightheadedness may occur.
Dizziness during pregnancy
False dizziness (a feeling of weakness, instability, near fainting) is very often observed during pregnancy. Attacks of dizziness in such cases are usually associated with hypotension, as well as a decrease in blood glucose concentration. We bring to your attention the following recipe, which is an effective method of treating dizziness during pregnancy:
In a mug of warm, boiled water, you need to dissolve 1-2 tbsp. l. sugar and drink immediately after waking up or before leaving the house.
Pregnant women (especially during the first half of pregnancy) should always carry water with them, and at the first sign of dizziness, try to drink as much as possible.
Severe dizziness: 6 dangerous reasons
In some cases, vertigo signals the development of severe conditions that require immediate medical attention. Causes of severe dizziness may include:
- Labyrinthitis (internal otitis). A viral infection in the inner ear may be asymptomatic at first. The only sign of otitis media is dizziness, which lasts for several minutes. Such attacks are repeated quite often. In the future, the viral process can affect the nervous system or brain.
- Concussion. Sometimes after a head injury, only dizziness appears. This symptom should not be ignored. It serves as direct evidence of a concussion. To eliminate the risk of swelling or serious brain damage, you should immediately seek medical help.
- Stroke. If dizziness is accompanied by sudden weakness, complaints of numbness of a body part, visual impairment, speech disturbances, then the risk of stroke is high. This is a severe pathology in which blood circulation in the brain is disrupted.
- Migraine. Dizziness accompanied by a severe headache may indicate a migraine. Many people believe that this condition is harmless. But doctors say that migraine, especially in an advanced state, can lead to severe damage (sometimes even to a heart attack or stroke).
- Cardiovascular diseases. Such pathologies are characterized by the appearance of dizziness every time a person gets up. It is caused by a sharp decrease in pressure. Symptoms like these may indicate dehydration, which is causing your blood to thicken. But if the problem is not fluid deficiency, then it may be the development of arrhythmia or heart failure.
- Tumors. Regular attacks of vertigo combined with headaches, usually in one side of the head, can signal the development of a tumor in the brain.
How does the human balance system work?
In most cases, true (central, systemic) dizziness is a manifestation of various diseases of the system that provides balance and control of body position in space. This system consists of the following 3 components:
- The vestibular apparatus, which is located deep in the skull, where sensitive receptors are located that respond to the angular or linear acceleration of the body in space.
- Eyes that provide visual information about the location of the body and its parts in space, as well as in relation to other objects.
- Sensitive receptors (proprioceptors) that are found in human bones, joints, muscles and ligaments. They provide reliable information about the position of body parts in space, as well as relative to each other.
All these 3 components of the balance system simultaneously send information to the brain, where it can be analyzed and processed into a person’s idea of his position in space and relative to other objects.
If for any reason the data that comes from one of the sources is distorted (for example, irritation of the receptors of the vestibular apparatus by an inflammatory reaction when there is no movement and acceleration), then an incorrect idea is created in the brain about the position and movement of the human body in space . Then an illusory sensation of movement or rotation arises, when in reality the body is motionless.
The causes of a disorder in a person’s balance system can be very different. Nowadays, more than 80 diseases are known that can cause dizziness. Below we describe the most common causes of dizziness.
What to do?
It is almost impossible to independently determine the causes of frequent attacks of dizziness. Therefore, those who regularly experience vertigo are advised to go to an appointment with a therapist, or a neurologist. The specialist will carefully examine the patient’s complaints and prescribe diagnostic tests. If necessary, the doctor will refer the patient for consultations with an ENT specialist, an ophthalmologist, a cardiologist, or an endocrinologist.
To identify the causes of vertigo, the patient may be prescribed the following tests:
- Neurological tests. They allow you to assess the functionality of the vestibular apparatus.
- MRI or CT. Such brain studies reveal various disorders (hemorrhages, tumors, vascular pathologies).
- Ultrasound Doppler. Using Doppler ultrasound, the condition of the vessels of the head and neck is studied.
- Audiometry. Diagnostics allows us to assess hearing function.
- EEG. To study the activity of the cerebral cortex, the doctor will prescribe electroencephalography.
To quickly cope with dizziness (of course, if it is not caused by dangerous reasons), you can sit on any surface, relax a little and take 5-6 deep breaths. Be sure to open the window (if you are indoors) to provide fresh air. If the causes of vertigo are harmless, then such actions are quite enough for the dizziness to disappear without a trace.
Treatment methods
The patient must understand that dizziness is not an independent disease, but only a symptom of a particular pathology.
In order to get rid of it, it is necessary to influence the root cause of the violation:
- BPPV may require surgery to remove the otoliths from the inner ear. However, if they do not block his passages, then you can take a wait-and-see approach. Sometimes the disorder goes away on its own.
- For infections of the inner ear, the patient may be prescribed antibiotics to fight bacteria, corticosteroids to eliminate inflammation, and Diazepam to reduce the pathological activity of the central nervous system.
- For Meniere's disease, treatment should be aimed at eliminating pathological symptoms; the person is prescribed antiemetics or benzodiazepines. Patients receive diuretics on an ongoing basis.
- For migraines, the patient is prescribed antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and beta blockers. Analgesics and antihistamines can be used to relieve an attack.
- If a patient has anemia, then he needs to start eating right, enrich his menu with meat dishes, eggs, cottage cheese, fresh vegetables and fruits. It is possible to take iron supplements and B vitamins. In severe cases, the patient is advised to receive a transfusion of red blood cells.
- If low blood sugar leads to dizziness, then the patient needs to eat something sweet as quickly as possible. In severe cases, hospitalization is indicated. In the future, the patient will need to carefully monitor blood glucose levels.
Pathological conditions do not always lead to dizziness. To help yourself cope with an attack that was associated with emotional or physical fatigue, you first need to lie down. Before doing this, open the windows to allow fresh air into the room. You can apply a towel soaked in cool water to your forehead.
Be sure to measure your body temperature. If an attack of dizziness does not go away after 20-30 minutes, and a person’s condition worsens, then he needs to call an ambulance.
Video: Dr. Evdokimenko on methods of treating dizziness: