Arrhythmia is a pathological condition of the cardiovascular system, leading to disruption of the frequency, conductivity and contractility of the heart muscle. In cases of severe organic changes in the structure of the heart, when all its basic automatic functions are affected, installation of a pacemaker is indicated.
A cardiac pacemaker (ES) is a special medical device that works on only one principle – it affects the patient’s heart rhythm. Such an artificial heart pacemaker is installed for a patient in a hospital setting by a resuscitator.
A pacemaker is implanted if the patient's heart becomes abnormal or the heart rate slows to a critical level at which the patient may lose consciousness. An external cardiac pacemaker is often used for large myocardial infarctions. Also, its use is recommended for heart block, when the electrical impulse does not pass from the atrium to the ventricle.
At the Yusupov Hospital, cardiologist Sergei Borisovich Shornikov conducts his appointment. Under his leadership, doctors of the highest category who treat arrhythmias work in the therapeutic hospital. In their practice, they use modern examination methods and an individual approach to treating patients with cardiac arrhythmias. For each patient, doctors perform:
- An electrocardiogram that records the frequency and rhythm of the heart;
- Holter monitoring is an examination method that evaluates the work of the heart during the day;
- Treadmill test, during which the patient’s cardiogram is recorded and his response to physical activity is assessed;
- Echocardioscopy is an ultrasound examination of the heart. Using this method, cardiologists can evaluate the structure of heart muscle tissue and the pumping function of the organ.
At the Yusupov Hospital, only an integrated approach is used in the treatment of patients with various cardiac disorders.
Types of pacemakers
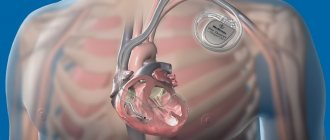
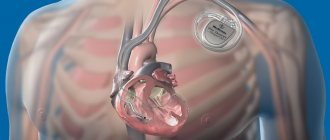
Typically, a standard implantable pacemaker is coated with a titanium shell. The device is implanted in the subclavian region under the pectoralis major muscle, and its body is fixed in the subcutaneous tissue. The operation to install the EC is performed under local anesthesia, and the electrodes of the implanted pacemaker are brought to the heart chambers through the subclavian vein.
Depending on the area of influence, the following are distinguished:
- Single-chamber pacemakers;
- Double-chamber pacemakers;
- Three-chamber pacemakers.
Single-chamber pacemakers are connected to one of the atria or one of the ventricles. Two-chamber - one atrium and one ventricle. A three-chamber pacemaker or cardiac resynchronization device is implanted in one of the atria and both ventricles.
How is a pacemaker installed?
Modern ECs are small in size, so their installation is not difficult.
The surgeon makes an incision about 3-4 cm long under the collarbone, creates a pocket under the pectoral muscle and places an artificial pacemaker in it. An electrode delivery system—intraducers—is installed into the vein, through which the electrodes are inserted and fixed into the heart cavity (under X-ray monitoring). The connector part of the electrodes is connected to the body of the device. After this, the wound is sutured. To ensure that the pacemaker and electrodes are positioned correctly, a control fluoroscopy is performed.
Pacemaker: indications for installation
The main task of a pacemaker is to generate the correct heart rhythm. Indications for installing this device are absolute relative:
Absolute indications for inserting a pacemaker include:
- Slowing of heart contractions (bradyarrhythmia) with pronounced clinical symptoms - dizziness, syncope, Morgagni-Adams-Stokes syndrome;
- episodes of cardiac arrest (asystole) lasting more than three seconds. They must be recorded on the ECG;
- Registration of heart rate below 40 per minute during physical activity;
- Combination of persistent second or third degree atrioventricular block with two-bundle or three-bundle blockades;
- Severe blockade that occurs after myocardial infarction, which has clinical manifestations.
As a rule, with absolute indications, contraindications to the installation of pacemakers are not taken into account.
Relative indications for placing a pacemaker are as follows:
- The appearance of atrioventricular block of the second type and second degree without clinical manifestations;
- Syncopal states of patients against the background of two- and three-bundle blocks.
If the patient has relative indications, the decision to implant an EC is made individually, taking into account the patient’s age, physical activity, concomitant diseases and other factors.
What is needed for preliminary diagnosis?
- ECG in 12 leads;
- Echo-CG;
- Holter ECG monitoring for 1-2 (sometimes more) days;
- Stress ECG.
- or chest x-ray.
- Ultrasound examination of the heart.
- Coronary angiography.
- Dopplerography.
- Endocardial electrophysiological study.
- Consultation with a cardiologist;
- Consultation with an arrhythmologist to determine indications for surgery and select the type of pacemaker;
- Standard list of preoperative tests.
Pacemaker: installation
Staging an EC is a rather complex procedure that requires professional precision from a cardiologist.
The procedure for installing a temporary pacemaker is as follows:
- First, a probe electrode is inserted through the crankcase in the central vein;
- Then, the tip of the electrode is placed in the right atrial appendage under fluoroscopic control (for atrial pacing). With ventricular pacemaker, the lead tip is placed at the apex of the right ventricle;
- The electrode is passed through the tricuspid valve;
- The next step will be to rotate the tip of the electrode towards the apex of the right ventricle;
- Then it is fixed in the wall of the right ventricle;
- For atrial stimulation, the electrode is placed in the right atrium;
After completing the procedure described above, checking the stimulation threshold begins. As a rule, they start with a frequency 10–20 beats higher than the heart rate and an amplitude of 5 mA. If the rhythm is not imposed, the electrode is rearranged; if it is, the stimulation amplitude decreases until the rhythm ceases to be imposed.
Every day after EC implantation, the patient is monitored for signs of infection, pneumothorax, and malfunction of the device.
Pacemaker: complications
According to statistics, complications after the installation of a pacemaker occur in no more than 3-5% of cases. Critical situations during this procedure may arise both during and several days, even weeks after the operation.
The following complications may occur directly during the operation:
- allergic reaction to anesthetic;
- development of pneumothorax (formation of an air pocket in the lungs);
- damage to blood vessels and nerve endings.
The occurrence of complications during the installation of a pacemaker leads to the patient being transferred to the intensive care unit for approximately 2-3 days.
Early postoperative complications:
- Development of thromboembolism - closure of the lumen of the pulmonary artery with a thrombus;
- Development of bleeding;
- Insulation failure, displacement, fracture of the electrode;
- Development of infection of the surgical wound area.
Long-term complications:
- The appearance of shortness of breath, dizziness, decreased blood pressure, occasional loss of consciousness;
- Development of tachycardia caused by pacemaker;
- Premature failures in the ECS.
The operation to implant a pacemaker should be performed by an experienced surgeon under X-ray guidance. After discharge from the hospital, the patient is required to undergo regular examinations and be registered with a dispensary.
What complications occur after implantation of pacemakers? And how can you prevent them?
Like any surgery, pacemaker implantation carries certain risks.
1. By making a skin incision, an infection . In order to prevent possible infection, before the operation the doctor administers an antibacterial drug to the patient, and the surgical field is treated with modern antiseptics. 2. In very rare cases, if the pleura, the film that ensures the tightness of the chest cavity, is damaged, air can penetrate into the latter due to the negative pressure inside. This condition is called pneumothorax . The air compresses the lungs, prevents them from expanding and makes breathing difficult. This can be eliminated by installing pleural drainage and pumping out air. In order to make sure that there is no such complication, or to detect and eliminate it in time, the doctor prescribes a chest x-ray after the operation. pain may occur when moving your arm , but usually it is not severe and passes quickly. If necessary, painkillers are prescribed for several days. 4. Next to the subclavian vein is the subclavian artery. Due to the individual anatomy of each patient, the surgeon can inject it with a puncture needle. Then there will be a hematoma (bruise) in the subclavian region, along the biceps and under the chest, which, as a rule, resolves after 7-10 days. 5. Some patients develop allergic reactions to medications or materials used during implantation. If a severe allergy (anaphylactic shock) occurs, doctors will interrupt the operation and provide assistance . Surgical treatment is carried out accompanied by an experienced anesthesiologist and resuscitator. 6. Hemorrhage under the skin . It will go away in a few days, there's nothing to worry about.
Modern technologies and small sizes of pacemakers make it possible to minimize risks, make implantation quick and painless, less traumatic, and reduce postoperative rehabilitation time. Still, this is a serious procedure. The quality of life of the patient in the future depends on how successfully it is performed.
Pacemaker: life after surgery
Installation of a pacemaker, although not long, is still a difficult operation. Therefore, in the postoperative period, a patient with an pacemaker has a number of restrictions regarding physical activity and electromagnetic factors, which have a negative effect on the operation of the device. Before any examination or course of treatment, it is necessary to warn doctors about the presence of an pacemaker.
Living with a heart pacemaker imposes the following restrictions on a person:
- You cannot undergo an MRI;
- You cannot engage in sports that are fraught with the development of injury;
- You must not approach transformer booths;
- You cannot put a mobile phone in your breast pocket;
- You should not stay near metal detectors for a long time;
- You cannot undergo shock wave lithotripsy without first setting up an pacemaker or perform electrocoagulation of tissues during surgery.
In addition to the recommendations described above, the patient should always carry a pacemaker passport with him. In case of emergency situations and emergency care for the patient, the doctor must be aware of the type of pacemaker and the reason why it was installed.
The patient is recommended to remain at a distance of at least 15-30 cm from sources of electromagnetic radiation - TV, cell phone, hair dryer, electric razor and other electrical appliances.
The presence of an installed pacemaker is not a contraindication for pregnancy. Despite this, the patient needs to be monitored by a cardiac surgeon throughout her pregnancy. In such cases, delivery must be carried out by caesarean section as planned.
Also, a patient with a pacemaker may be assigned a disability group. It is approved only if the patient’s working conditions are determined by the clinical expert commission to be severe or potentially dangerous (that is, they may harm the stimulant). For example, work using electric welding or electric steel-smelting machines, or other sources of electromagnetic radiation.
Pacemaker: expiration date
The lifespan of a pacemaker is determined by the battery capacity. It is designed for 7-10 years of operation. In most cases, when the battery life is approaching, the device will sound an alarm during the next scheduled examination. After this, the patient should replace the battery with a new one.
Most often, medical practice shows that people with a pacemaker installed, subject to all doctor’s recommendations, live no less than other people. But still, a patient with a pacemaker should adhere to certain rules. Therefore, the question of how long people live with a pacemaker depends on the regularity of visiting the doctor and following the recommendations given to the patient.
You need to visit a cardiologist after surgery:
- Three months after installation of a pacemaker;
- Six months after the first post-operative visit;
- Once every six to twelve months for a routine inspection;
- Unscheduled - in cases of sensation of electrical discharges, return of symptoms of the original illness, appearance of signs of inflammation at the site of installation of the device;
- After the pacemaker's stated service life has expired. Usually it is 6-15 years.
What is a pacemaker
With age, the heart, like any muscle, wears out . Decreased quality of life can be corrected by installing a pacemaker. It is a small microprocessor in a sealed titanium case.
The pacemaker is inert in relation to the biological environment of the body, which means the risk of rejection is minimal.
The pacemaker has several parts:
- The power supply can be compared to a battery. The service life is about 7 years.
- Microprocessor – converts electricity into impulses to stimulate the heart.
- A block with conductors and electrodes are impulse conductors. They come into direct contact with the surface of the heart.
- Programmer – controls the operation of the stimulator. It is used to adjust the device settings for various changes in heart rhythm - tachycardia, bradycardia, fibrillation.
The implant is placed under the skin or muscle. It helps maintain a normal heartbeat. Modern models are autonomous - they detect the electrochemical activity of the heart and, in case of deviations, create an additional electrical charge. Doctors call this method “resynchronization therapy.” The entire operation lasts 1.5–2 hours .
Pacemaker: cost of installation
In the Yusupov Hospital, the cost of installing a pacemaker depends on many factors: the severity of the patient’s pathological condition, the presence of concomitant diseases, the type of stimulator, the brand and its manufacturer.
Cardiologists at the Yusupov Hospital Therapy Clinic select individual drug therapy and develop a physical and rehabilitation program for patients with various diseases of the cardiovascular system.
The clinic’s specialists work in the field of evidence-based medicine and practice an integrated approach. They constantly support and improve their skills, introduce innovative approaches to diagnosis and therapy into their practice. The hospital has a powerful clinical, laboratory and diagnostic base, which makes it possible for the timely onset of the most severe pathologies. Cardiologists of the highest category help patients relieve pain, return to work and active life, improve well-being by normalizing the functioning of internal organs and muscle mobility. The patient can make an appointment with the doctor around the clock, any day of the week, by calling the phone number listed on the website. Also, anyone who wants to receive a specialized consultation from a cardiologist at the Yusupov Hospital can sign up online on the website page.
What does the price depend on?
The cost of the operation depends on the chosen clinic and package of services . In a regular hospital, a surgeon will install a pacemaker for free, but it is the patient’s job to buy it.
In private clinics, in addition to the pacemaker, you will also need to pay for the services of a surgeon. Since there are pacemakers of various equipment, the price of modern models with greater functionality will be higher.