In modern medicine, the procedure of blood transfusion is still quite often used. Blood transfusion by blood group is the process of transferring it from a healthy donor to a patient with health problems (recipient). It requires compliance with certain rules, and is not without complications. Therefore, this operation is carried out with the utmost concentration of attention from medical personnel.
Transfusion rules
Blood transfusions based on blood groups are carried out taking into account certain basics. Indications for the manipulation and the required dose of fluid transfused are prescribed by a medical specialist based on clinical data and tests performed. The rules for blood transfusion by group are created for the safety of both the donor and the recipient. The specialist must, regardless of previously received examinations, personally do the following:
- Find out the group according to the ABO system and compare the data with the available indications.
- Find out the characteristics of red blood cells, both donor and recipient.
- Test for general compatibility.
- Conduct a bioassay.
What are the consequences of blood flow group mismatch?
An immunological conflict occurs when the mother’s blood does not match the child’s blood substance. A conflict in the blood substance group during pregnancy can lead to hemolytic pathology of the baby. Hemolytic disease of the newborn, abbreviated as HDN, threatens the development of hemolysis of red blood cells, resulting in a huge risk of fetal death. In any case, erythroblastosis disrupts the full functioning mechanism of the baby’s circulatory system. With such a pathology, there can be no question of any proper development of the embryo.
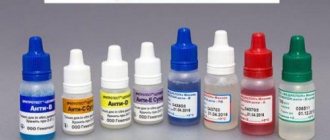
The process of determining blood identity
An important point in transfusion is to determine the identity of the biological fluid and the presence of infections in it. To do this, a blood sample is taken for a general analysis, the resulting amount is divided into two parts and sent for research. In the laboratory, the first one will be checked for the presence of infections, the amount of hemoglobin, etc. The second one is used to determine the blood type and its Rh factor.
Blood compatibility during pregnancy
If a married couple decides to become pregnant, they must follow this process from the planning stage until the birth of the child. With regard to the potential possibility of Rh conflict during pregnancy, you should be wary of:
- Married couples in which the woman is Rh negative and the man is Rh positive. The maximum probability of a conflict pregnancy is 50% if the partner is homozygous (each of the chromosomes of one pair encodes the Rh antigen) and 25% if he is heterozygous (Rh is encoded by only one chromosome of the pair);
- Spouses whose blood mixing could potentially result in an Rh-conflict pregnancy, with previous pregnancies and births. Their favorable outcome does not mean anything. On the contrary, the likelihood of developing maternal-fetal blood incompatibility increases with each subsequent pregnancy.
Blood group compatibility and the table are compatible with the Rh factor with possible options for its inheritance by the child.
| Mother's Rh factor | Father's Rh factor | Probability of Rh-ness of the child | Probability of Rh-conflict pregnancy |
| Positive | Positive | If the parents are homozygous – 100% positive; If the parents are heterozygotes – 50% positive; If one of the spouses is homozygous and the other is heterozygous, 75% positive. | There is no conflict pregnancy |
| Positive | Negative | If the partner is Rh positive or the partner is homozygous for Rh – 50% positive; If heterozygous - 25% positive. | The probability of a conflict developing does not exceed 50% |
| Negative | Positive | ||
| Negative | Negative | The child's blood will be Rh negative in 100% of cases. | There is no conflict pregnancy |
Note: A homozygote is a person who contains identical genes on similar chromosomes. When they become part of the fetal chromosome set, they will unambiguously encode the synthesis of the Rh factor. A heterozygote contains such a gene in only one of the chromosomes, which significantly reduces the risk of inheriting it.
Important to remember!!!
- The blood of an Rh-positive mother is compatible with any blood of the fetus;
- The likelihood of a conflict regarding the Rh system is possible only in mothers with Rh-negative blood and does not exceed 50%;
- The inheritance of the Rh factor by a child depends not only on the actual Rh factor of the parents, but also on the set of genes that did not manifest themselves but were inherited by the child.
Blood groups
Blood transfusion according to blood groups is necessary to prevent red blood cells from sticking together in the patient’s body due to an agglutination reaction upon receipt of the test sample. The blood groups of the human body according to the ABO classification system are divided into 4 main types. According to the ABO classification, separation occurs due to the presence of specific antigens - A and B. Each of them is attached to a specific agglutinin: A is attached to α and B to β, respectively. Depending on the combination of these components, the well-known blood groups are formed. Combining components of the same name is impossible, otherwise red blood cells will stick together in the body, and it simply will not be able to continue to exist. Due to this, only four known combinations are possible:
- Group 1: no antigens, there are two agglutinins α and β.
- Group 2: antigen A and agglutinin β.
- Group 3: antigen B and agglutinin α.
- Group 4: agglutinins are absent, antigens A and B are present.
Diet
If people with the second blood group adhere to a proper diet, the risk of developing many pathologies that arise in them due to predisposition will decrease. The diet must include the maximum amount of healthy foods containing vitamins, trace elements, and minerals.
They also provide a list of products that are contraindicated for patients. They can harm internal organs and cause allergic reactions. The restrictions especially apply to people with chronic inflammatory diseases of the digestive tract and obesity.
Healthy foods
If the patient has a second positive blood group, it is recommended to eat less meat. His digestive tract is more predisposed to vegetables and fruits. When eating vegetables, the following positive qualities arise:
- stimulation of the digestive tract due to the intake of large amounts of fiber and organic acids;
- supply of large amounts of microelements, minerals and vitamins that stimulate metabolism.
It is recommended to eat vegetables after heat treatment. But some of them can be used raw. For example, tomatoes and cucumbers.
For representatives of the second blood group, the following types of vegetables bring greater effect:
- cucumbers, carrots, bell peppers;
- broccoli, potatoes, tomatoes;
- eggplants, white cabbage.
People with blood type 2 are recommended to eat large amounts of fruits and berries. But overly acidic foods are not recommended, otherwise they will increase the acidity of the stomach, which will provoke an increase in digestive pathologies.
If a person wants to eat meat, it is recommended to choose a lean type. For example, veal, turkey, chicken, rabbit. It is advisable to boil, steam, stew. You can't fry, it increases cholesterol.
Fish is very useful. It saturates the human body with Omega fatty acids and vitamin D. But excessively fatty varieties, which cause heaviness in the stomach and difficult digestion, are not recommended.
To improve the function of the gastrointestinal tract, it is recommended to consume cereals 3-4 times a week:
- millet, pearl barley, rice;
- barley, buckwheat porridge.
You can enhance digestion with different types of vegetable oils. Among them, sesame or linseed oil is of particular importance. Legumes, such as beans, are useful. But they can be used only in the absence of increased gas formation. Recommended drinks include freshly squeezed juice, tea, and fruit compote.
Harmful products
Fatty meats are not recommended, as they aggravate the digestion process and make it difficult:
- pork;
- mutton;
- duck;
- fatty and tough beef.
Fatty fish are not recommended. For example, halibut, mackerel. Due to the excessive acidity of the stomach contents, fruits with sour properties are excluded. Citrus fruits are excluded from them. For example, grapefruit, lemon.
Dairy products, especially fatty ones, complicate the digestion process and increase stomach acidity. They can cause increased gas formation and heaviness in the stomach. However, in high concentrations it is allowed to use only hard cheese and natural yogurt.
Various types of seasonings are excluded:
- ketchup, tomato paste, red sauce;
- mustard, horseradish, mayonnaise.
Marinades and canned foods are not recommended. Significantly reduce the amount of consumption of baked goods, chocolate, sweets, and cakes.
It is necessary to reduce the amount of alcohol consumption to a minimum. It is advisable to eliminate it completely. Also reduce the amount of coffee.
Group Compatibility
Compatibility of blood groups for transfusion plays an important role during the operation. In medical practice, transfusions are performed only of identical types that are compatible with each other. Many people wonder what blood type universal donors are, but don't understand the process itself. And yet there are such suitable components. Which blood type is universal is a question that has a clear answer. People with the first blood group, due to the lack of antigens, are universal donors, and those with the fourth are considered universal recipients. The blood group compatibility table is used to understand the blood transfusion process.
| Blood type | Who can transfuse (Donor) | Who can the transfusion be given to (recipient) |
| 1 group | 1 group | All groups |
| 2nd group | 1st and 2nd groups | 2 and 4 groups |
| 3 group | 1st and 3rd groups | 3 and 4 groups |
| 4 group | All groups | 4 group |
Despite the fact that in the modern world there are many ways to treat various diseases, it is still not possible to avoid the process of transfusion. The blood group compatibility table helps medical specialists perform the operation correctly, which helps preserve the life and health of the patient. The ideal transfusion option will always be to use blood that is identical in both type and Rh. But there are cases when a transfusion is vitally necessary to carry out as soon as possible, then universal donors and recipients come to the rescue.
Why is Rh conflict dangerous?
Antibodies that are produced to foreign proteins upon contact between the blood of a woman and the fetus destroy the red blood cells of the unborn child. He develops anemia and also increases bilirubin levels, which usually occurs when red blood cells break down. Bilirubin is toxic and has a negative effect on the brain. The bone marrow of the unborn baby cannot cope with the production of new red blood cells; the spleen and liver are involved in the process. As a result, they increase in size, and this leads to an increase in pressure in the veins, swelling of the subcutaneous fat and other tissues. Such disturbances in fetal development are called hemolytic disease, which can lead to brain pathologies and even intrauterine death. Thus, Rh conflict has the following consequences for the child:
- swelling (dropsy);
- jaundice;
- hypoxia;
- anemia;
- mental retardation;
- intrauterine death.
For the health of the mother, Rh conflict does not pose a danger and manifests itself as an allergic reaction.
Rh factor
During scientific research in 1940, an antigen was found in the blood of macaques, which later received the name Rh factor. It is hereditary and depends on race. Those people who have this antigen in their blood are Rh positive, and if it is absent, they are Rh negative.
Transfusion compatibility:
- Rh negative is suitable for transfusion to people with Rh negative;
- Rh positive is compatible with any Rh blood.
If you use Rh-positive blood for a patient with a Rh-negative category, then special anti-Rhesus agglutinins will be produced in his blood, and with another manipulation, red blood cells will stick together. Accordingly, such a transfusion cannot be carried out.
Any transfusion is stressful for the human body. Whole blood is transfused only if the loss of this biological fluid reaches 25% or higher. If less volume is lost, blood substitutes are used. In other cases, transfusion of certain components, for example, only red blood cells, is indicated, depending on the type of lesion.
Treatment
Thanks to medical advances, even Rhesus-incompatible spouses can produce healthy children.
At the first visit to the antenatal clinic, the pregnant woman is immediately sent for a blood test for the Rh factor. If the expectant mother is Rh negative, the future father must also donate blood. If he is Rh negative, then the conflict will not occur, but if he is positive, special monitoring of the woman and the developing fetus is required, since it can inherit the father’s blood. The expectant mother will have to periodically donate blood for Rh antibodies. If their production has begun, special treatment is required. If sensitization is detected in time and timely therapy is started, the child will be born healthy.
First, the doctor constantly checks the condition of the unborn child in order to detect symptoms of Rh conflict. If signs appear, treatment will depend on their severity. The main thing is to support the vital activity of the fetus, which is to combat oxygen starvation and developmental delays. It is important to increase the level of red blood cells in the blood, which may require intrauterine blood transfusion through the umbilical cord vein under ultrasound guidance. But more often a blood transfusion is given to a child after birth. Sometimes this even requires early birth.
If no antibodies are detected in a pregnant woman when donating blood, it means that sensitization has not occurred, but prevention is still required. To prevent the production of antibodies when fetal red blood cells come into contact with maternal blood, anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin is prescribed in a special course, which prevents fetal red blood cells from being recognized as foreign, thus preventing sensitization.
Immunoglobulin is usually prescribed in the following cases:
- if antibodies are not detected at the 28th week of pregnancy;
- such therapy is required after the birth of an Rh-positive child to prevent postpartum sensitization (during the first 72 hours);
- after cases such as abortion, ectopic pregnancy, miscarriage, taking chorionic villi and amniotic fluid for analysis and other risk factors.
The effect of immunoglobulin does not last long - about 12 weeks, so each subsequent pregnancy of an Rh-negative woman requires repeating the course.
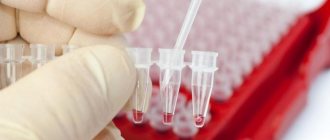
Sample methods
To conduct a compatibility test, the selected recipient serum is mixed with a sample from the donor on a sheet of white paper, tilting it in different directions. After five minutes, the results are compared, if the red blood cells do not stick together, the donor and recipient are compatible.
Next, the compatibility of the sample during Rh blood transfusion is checked in one of two ways.
- The donor's red blood cells, purified with saline, are loaded into a clean test tube, the mass is diluted with a warm gelatin solution and two drops of the recipient's serum. Place the mixture in a water bath for 10 minutes. After this time, it is diluted with saline in an amount of 7 milliliters and mixed thoroughly. If red blood cell adhesion is not detected, the donor and recipient are compatible.
- 2 drops of recipient serum, 1 drop of polyglucin and 1 drop of donor blood are dripped into a centrifuge tube. The test tube is placed in a centrifuge for 5 minutes. Then, dilute the mixture with 5 ml of saline, place the test tube at an angle of 90° and check compatibility. If there is no adhesion or color change, the donor and recipient are compatible.
Methodology
After all the necessary manipulations have been carried out to determine the blood group and compatibility, the transfusion itself begins. The injected blood should not be cold; only room temperature is allowed. If the operation is urgent, then the blood is heated in a water bath. The transfusion process is carried out drip-wise using a system, or directly using a syringe. The rate of administration is 50 drops in 60 seconds. During the transfusion, medical specialists measure the patient’s pulse and blood pressure every 15 minutes. After the manipulation, the patient is advised to rest and undergo medical observation.
Prevention and treatment of hemolytic disease of the fetus
All pregnant women with Rh-negative blood, even in the absence of antibodies in their blood, as well as in the presence of AB0 sensitization, should undergo 3 courses of nonspecific desensitizing therapy on an outpatient basis lasting 10-12 days, at 10-22, 22-24, 32-34 weeks.
As part of nonspecific desensitizing therapy, the following is prescribed: intravenous administration of 20 ml of 40% glucose solution with 2 ml of 5% ascorbic acid solution, 100 mg of cocarboxylase; orally rutin 0.02 g 3 times a day, theonicol 0.15 g 3 times a day or methionine 0.25 g and calcium gluconate 0.5 - 3 times, iron supplements, vitamin E 1 capsule. Antihistamines are used at night: diphenhydramine 0.05 or suprastin 0.025.
In case of complicated pregnancy: threat of miscarriage, early toxicosis of pregnant women, gestosis, etc., patients should be hospitalized in the department of pathology of pregnant women, where, along with treatment of the underlying disease, a course of desensitizing therapy is carried out.
Pregnant women who have a high titer of Rh antibodies and a history of spontaneous miscarriages or delivery of a fetus with an edematous or severe form of hemolytic disease are recommended to use plasmapheresis. This procedure removes antibodies from the blood plasma. Plasmapheresis is carried out once a week under the control of antibody titer, starting from 23-24 weeks. pregnancy, before delivery.
To treat hemolytic disease of the fetus, hemosorption using activated carbon is also used to remove antibodies from the blood and reduce the degree of Rh sensitization. Hemosorption is used in pregnant women with an extremely complicated obstetric history (repeated miscarriages, stillbirth). Hemosorption begins at 20-24 weeks in the hospital, with an interval of 2 weeks.
Treatment of hemolytic disease of the fetus during pregnancy is also possible by transfusion of blood to the fetus under ultrasound guidance.
Pregnant women with Rh sensitization are hospitalized in the maternity hospital at 34-36 weeks. pregnancy. With AB0 - sensitization, hospitalization is carried out at 36-37 weeks. If there are appropriate indications indicating a pronounced nature of the complication, hospitalization is possible at an earlier date.
In the presence of hemolytic disease of the fetus, early delivery is advisable due to the fact that towards the end of pregnancy the flow of antibodies to the fetus increases. In case of severe hemolytic disease of the fetus, pregnancy is terminated at any time during pregnancy. However, in most cases, pregnancy can be prolonged until an acceptable delivery date. As a rule, delivery is carried out through the natural birth canal. Caesarean section is performed in the presence of additional obstetric complications.
During childbirth, careful monitoring of the condition of the fetus is carried out, and hypoxia is prevented. Immediately after birth, the baby is quickly separated from the mother. Blood is taken from the umbilical cord to determine the content of bilirubin, hemoglobin, the child’s blood type, and his Rh status. A special test is performed to identify the newborn's red blood cells associated with antibodies.
Advertising
Necessity and contraindications
Many people associate blood transfusion with a simple drip of medication. But this is a complex process in which foreign living cells enter the patient’s body. And even with perfectly selected compatibility, there is a risk that the blood may not take root. That is why it is extremely important for doctors to determine that such a procedure cannot be avoided. The specialist prescribing the operation must be firmly convinced that other treatment methods will not be effective. If there is doubt that a transfusion will be beneficial, it is better not to do it.
How to resist Rhesus conflict
Knowing that the next pregnancy may turn out to be Rh-conflicting, the first-time mother is given drugs with anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin in the first 72 hours after the baby is born. This eliminates the red blood cells of the fetus that have entered the maternal bloodstream, and thus eliminates the need to build an immune defense from antibodies.
For prevention, immunoglobulin is also indicated at 28 and 34 weeks; an anti-Rhesus drug is also administered for bleeding or after invasive medical interventions. During the next pregnancy, in the absence of antibodies, the procedure with immunoglobulin is repeated.
Consequences of incompatibility
If compatibility during blood transfusion and blood substitutes is not complete, the recipient may develop negative consequences from such a procedure.
Disturbances from such an operation can be different; they can be associated with problems in internal organs or systems.
Frequent malfunctions of the liver and kidneys appear, metabolism, activity and functioning of the hematopoietic organs are disrupted. Changes may also occur in the respiratory system and nervous system. Treatment, for any type of complications, should be carried out as early as possible, under the supervision of a doctor.
If incompatibility occurs during a bioassay, the person will also feel negative manifestations, but to a much lesser extent. The recipient may experience chills, pain in the chest and lumbar spine. The pulse will increase, and a feeling of anxiety will appear. If these signs are detected, a transfusion should not be given. Currently, incompatibility during blood transfusion by blood group practically does not occur.
Character traits
The sedentism of ancient people required the acquisition of communication skills. Those who survived were those who knew how to negotiate with the neighboring tribe, with whom it was pleasant to work together. Probably, in those days they also thought about justice.
Among all group characteristics, the following traits are typical for the second group: decency towards relatives and neighbors, a tendency to do work together, care for loved ones, and empathy.
They often cede leadership to others, but this does not mean that they themselves consider themselves unworthy. On the contrary, they dream of a high destiny, carefully hiding it. Such restlessness leads to internal stress and is harmful to health.
When choosing a profession, you should take into account your inclinations and not try to break the properties given by nature. Holders of the second group will be excellent teachers, doctors, and social workers. They have irreplaceable abilities in working with personnel and can successfully help in an election campaign.
Any commander needs experienced commissars