Emerging pain in the heart with osteochondrosis can be reflected or true. In the first case, a person experiences unpleasant sensations spreading along the pinched nerve fiber of the roots responsible for the innervation of the intercostal muscles on the left side. In the second case, the situation is much more serious and develops against the background of damage to the radicular or cranial nerves responsible for the innervation of the heart muscle, pacemaker, coronary blood vessels or the formation of the vagus nerve.
More often, pain in the heart is recorded with thoracic osteochondrosis, since the radicular nerves responsible for the innervation of the intercostal muscles and sternum are subject to compression in this type of disease. Also, if the intervertebral disc is damaged in the thoracic region, an inflammatory process may occur that affects the intercostal muscles. The second factor of negative influence is the static tension of the muscular frame of the back, which tries to compensate for the shock-absorbing load that the damaged intervertebral disc cannot cope with.
The pain in the heart that occurs with cervical osteochondrosis is dangerous because it is often associated with damage to the paired cranial nerves. One of these pairs is responsible for the parasympathetic nervous system, which ensures the performance of the myocardial muscle and regulates the work of the pacemaker. The second pair is responsible for the formation of the vagus nerve, which also regulates cardiac activity and controls the volume of arterial blood released into the systemic circulation. If this work is disrupted, a primary form of vascular heart failure may develop.
Damage to the radicular nerves in the lower structures of the cervical spine leads to disruption of the innervation of the coronary vascular bed. This can contribute to the development of coronary heart disease, acute myocardial infarction, etc.
Pain in the heart area that occurs with osteochondrosis is a reason to urgently seek medical help. It is necessary to get an appointment with a vertebrologist or neurologist as soon as possible. Only an experienced doctor will be able to exclude the development of cardiac pathology and prevent negative consequences, such as aortic thrombosis, acute myocardial infarction, coronary artery stenosis, etc.
In Moscow, you can make an initial free appointment with a neurologist at our manual therapy clinic. To do this, just call the administrator and agree on a time convenient for your visit. During the free consultation, the doctor will conduct a full examination, make a preliminary diagnosis, and give individual recommendations for subsequent examination and treatment.
How does osteochondrosis affect the heart?
If there are several factors of how osteochondrosis affects the heart, they are divided into external and internal. An external factor of negative influence is the constant use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which are necessary for pain relief and relief of acute symptoms of this disease. These pharmacological agents act negatively both on the hematopoietic system, triggering the production of defective red blood cells by bone marrow structures, and on the epithelial layer inside the vascular bed. Long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs increases the aggregation (tendency to stick together) of platelets, which contributes to the formation of blood clots in the coronary blood supply (this is the main cause of the development of acute myocardial infarction). The ability of red blood cells to transport oxygen changes, so the tissues of the heart muscle suffer from constant oxygen starvation.
Internal factors of the negative impact of osteochondrosis on the heart are:
- disruption of the process of innervation of the vascular bed, resulting in its spasm, alternating with prolapse, which entails instability of the blood supply to the myocardium;
- compression of the radicular nerves responsible for the performance of the intercostal muscles - as a result, the breathing process is disrupted and a secondary form of oxygen deficiency may develop, the biochemical parameters of gas exchange change;
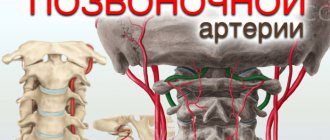
- development of posterior vertebral artery syndrome, which leads to a significant deterioration in the blood supply to the medulla oblongata, where the respiratory center is located;
- compression of the cranial nerves responsible for the formation of the vagus nerve and solar plexus - this entails disturbances in heart rhythm, dislocation of the ventricles and atria, disruption of hemodynamics within the heart muscle and in the pulmonary circulation.
Other negative factors include a forced sedentary lifestyle, as the patient tries to avoid increased physical activity in case of severe pain. A secondary change in posture due to static tension in the muscular frame of the back can lead to curvature of the spine and compression of the heart muscle due to deformation of the chest.
“Payback for upright walking”: causes of the disease
Osteochondrosis can develop for a number of reasons, ranging from a sedentary lifestyle to injuries and overload.
“There is an opinion that spinal osteochondrosis is a person’s retribution for walking upright,” notes neurosurgeon of the highest category at SM-Clinic, Ph.D. Sergey Alexandrovich Kuznetsov
. – Currently, the cause of osteochondrosis is considered to be a combination of factors affecting the spine during a person’s life. An additional risk of developing the disease comes from spinal injuries and poor posture. A sedentary lifestyle and lack of proper physical activity also play an important role. This leads to insufficient functioning of the natural muscle “corset” that holds the spine in an anatomically correct position. As a result of this, and also in the presence of excess body weight, the intervertebral discs are overloaded with the development of a degenerative process in them.”
As noted by the senior medical consultant of the Teledoctor24 service, Neya Georgieva
, to one degree or another, osteochondrosis develops in all people with age. “Roughly speaking, this is one of the processes of aging of the body,” she says. “However, injuries and overloads of the spine contribute to the earlier onset of this disease. The main point in the occurrence of osteochondrosis is the constant overload of the spinal motion segment: poor posture, individual sitting style (wrong posture), walking with an uneven spinal column cause additional stress on the discs, ligaments and muscles of the spine. The occurrence of osteochondrosis of the lumbar region is often associated with its overload when bending and lifting heavy objects.”
It is necessary to monitor your posture from early childhood. But, unfortunately, our lifestyle does little to contribute to this: first we slouch at our desks at school, then in an office chair - and so on until old age. Many of us no longer even remember what a straight back should look like.
“When sitting, the head, shoulders and pelvis should remain at the same level. The back must be kept straight even when walking, when additional dangers may await, for example, due to shoes with heels, since when wearing such shoes the center of gravity shifts. But that's not all. Shoes with flat soles also harm the health of the musculoskeletal system, because they lack shock absorption - the spine suffers from impacts on the surface during normal walking or running. Few people know, but the center of gravity can be shifted due to flat feet, because unnatural foot placement leads to a change in gait and a twisted body position,” says Sergei Aleksutov.
Can osteochondrosis radiate to the heart?
Many patients are concerned about the question of whether osteochondrosis can radiate to the heart and for what reasons this happens. Yes, degenerative dystrophic disease of the intervertebral discs can cause vague pain in the heart area, both due to direct influence and irradiation of the pain syndrome.
Osteochondrosis is a disease in which the destruction of intervertebral discs occurs. They are a kind of protective structural parts that ensure uniform distribution of the shock-absorbing load on the spine during movement and static position of the human body. The intervertebral disc consists of a dense fibrous membrane (annulus) and an internal pulposus (nucleus pulposus). These structures do not have their own circulatory network. They receive large amounts of fluid and nutrients dissolved in it during diffuse exchange with surrounding muscle tissue.
If the muscular frame of the back, collar area and neck is not subjected to regular physical activity, then the diffuse nutrition of the intervertebral disc is disrupted. The fibrous ring becomes dehydrated and loses its elasticity. Numerous cracks appear on its surface, which are filled with deposits of calcium salts. This is the initial stage of the development of osteochondrosis.
At the next stage, the intervertebral disc loses its physiological height and does not provide protection for the radicular nerves from compression of the adjacent vertebral body and osteophytes developing on their surface. It is at this stage that pain irradiates (spreads) to the heart area.
Disruption of the innervation of the coronary bloodstream, posterior vertebral artery syndrome, infringement of the vagus nerve at its base - these complications, provoking serious pathologies of the cardiovascular system, are formed already at the third and fourth stages of osteochondrosis of the cervical and thoracic spine.
Possible consequences
In the absence of proper treatment for a long time, osteochondrosis continues to progress, leading to serious complications. Thus, damage to the lumbar region can cause the formation of intervertebral hernias, the development of sciatica and lumbar syndrome. With sciatica, the sciatic nerve is pinched or inflamed, and the person experiences a burning, stabbing or shooting pain, usually radiating to the buttocks, thigh or lower leg. Lumbago syndrome is characterized by “lumbago” - powerful spasms in the lumbar area, during which a person is often not even able to move.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is dangerous due to the risk of developing intercostal neuralgia (tokaralgia). Chest pain can be constant or intermittent, occurring only during physical activity or at rest. Sometimes the pain radiates to the arm and neighboring areas of the body. In addition, the patient may be bothered by muscle tension, which causes difficulty breathing and discomfort when coughing. With cervical osteochondrosis, neurological complications such as cervicago (“lumbago in the neck”) and cervicalgia (rather intense chronic pain, accompanied by muscle tightness) develop.
One of the most dangerous consequences of osteochondrosis is spinal stroke. Even with timely medical intervention, acute circulatory disorders in the spinal cord can lead to dangerous complications in the future. With extensive damage, there may be a complete loss of pain and temperature sensitivity in the areas innervated by the damaged area, lameness, partial or complete paralysis of the body. In some cases, pelvic function disorders develop (urinary and fecal incontinence, impotence). Due to the massive death of neurons, even after rehabilitation, lost functions may not be fully restored. Often, a spinal stroke causes disability: for example, musicians or massage therapists who have lost tactile sensitivity can no longer work normally. Movement disorders are characterized by paresis (significant decrease in muscle strength, lethargy) and over time lead to muscle atrophy.
How to distinguish heart pain from osteochondrosis?
There is only one way to distinguish pain in the heart from osteochondrosis - an ECG examination, which records changes in the functioning of the heart muscle at the level of electrical impulses. An ECG is the initial stage of examination, which shows the presence of a focus of pathological changes in the structure of the heart muscle.
There are no ways to determine whether heart disease or osteochondrosis is present at home; all the tests described using nitroglycerin have one feature. It is important to understand that if acute myocardial infarction develops, taking this vasodilator drug does not reduce pain. To provide medical care to patients with advanced myocardial infarction, narcotic painkillers are given.
Of course, osteochondrosis in the heart area does not cause such intense pain. But it is quite difficult for the patient to determine this parameter subjectively. You can try to diagnose pain in the heart area with osteochondrosis using palpation. If, when pressing on the intercostal spaces or spinous processes of the spine, increased pain occurs, then there is a high probability that this is osteochondrosis. If the pain does not increase, then most likely it is caused by coronary vascular pathology.
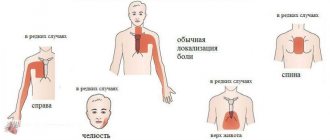
Very often, osteochondrosis radiates to the heart, upper limb (with numbness of the little finger) and under the shoulder blade. When you try to raise your arm up, the pain increases. Confirmation of the diagnosis is carried out using x-rays of the cervical and thoracic spine.
How does the heart hurt with osteochondrosis - symptoms
You need to know how the heart hurts with osteochondrosis, what distinctive signs can be used to identify this condition. First of all, you should pay attention to the primary and secondary symptoms - how the heart hurts with osteochondrosis, at what time the attack begins, what can provoke it, what remedies help stop it, etc.
Distinctive symptoms of heart pain with osteochondrosis include:
- development after prolonged static stress (sedentary work in one position);
- prolonged attacks lasting more than 3 hours (sometimes up to several days);
- feeling of stiffness in movements after sleep and prolonged stay in a static position;
- pain on palpation of the thoracic spine, intercostal spaces and sternum;
- difficulty when trying to raise a straight arm up;
- absence of rhythm disturbances (atrial fibrillation, extrasystole, etc.).
If the pain in the heart area is radiating, then there are no secondary signs of myocardial damage. These are swelling of the legs, pastyness of the face, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, shortness of breath, cough when trying to lie in bed in a horizontal position without raising the head end.
What to do with osteochondrosis and heart pain?
The first thing to do if pain occurs in the heart area due to osteochondrosis of the thoracic or cervical spine is to consult a neurologist. Only an experienced doctor can eliminate the risk of developing cardiovascular pathology. In most cases, cervical osteochondrosis and the heart are connected due to impaired innervation. Therefore, if you have a serious heart disease (coronary disease, atherosclerosis, vascular stenosis, angina pectoris, impaired intracardiac electrical conductivity, arrhythmia, etc.), then you should definitely examine the cervical spine for pinched cranial and radicular nerves . It is this circumstance that provokes most of the pathologies of cardiovascular diseases.
Also, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine can affect the heart with the development of posterior vertebral artery syndrome. This condition is also accompanied by arterial hypertension, dizziness, and frequent headaches.
It is necessary to treat cervical, thoracic osteochondrosis and the heart simultaneously - for this an individual course of manual therapy is being developed. If compression of the radicular nerves is detected, an experienced doctor will conduct several sessions of traction traction of the spinal column. This will stop all the negative consequences of osteochondrosis. Then a planned course of restoration of intervertebral discs will be carried out by enhancing the diffuse nutrition of their cartilage tissue. For these purposes the following can be used:
- reflexology (acupuncture) to activate biologically active points responsible for the regeneration of damaged cartilage tissue, increasing the vitality of the human body;
- osteopathy and massage, improving microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid, increasing the elasticity of all soft tissues, promoting the removal of calcium salts;
- therapeutic exercises and kinesiotherapy to restore the process of diffuse nutrition and increase the tone of the muscular frame of the back and collar area;
- physiotherapy, laser treatment, etc.
If you need treatment for osteochondrosis and pain in the heart area, then make an initial free appointment at our manual therapy clinic. An experienced doctor will make an accurate diagnosis and give individual recommendations for the treatment of the identified disease.
Nutrition rules
Proper nutrition during treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis is the lion's share of success. It is necessary to eat foods that contain substances necessary for the body at this time. For example, jellied meat, jelly and other dishes with gelatin help cartilage tissue to recover, as they contain chondoprotectors.
The abundance of protein is also important. Dairy products, meat and fish are animal sources of protein. Legumes (especially beans), nuts, seeds, eggplants and other vegetables are vegetable. Also, fresh fruits and vegetables are very useful for the proper functioning of the immune system and strengthening the body as a whole. Eating greens, broccoli, and celery will have a positive effect on treatment.
Dishes must be steamed or boiled.
Instead of bread made from white flour, you should choose whole grain, rye, or replace them with bread.
One of the main microelements necessary for the treatment of osteochondrosis is calcium, found in dairy products, almonds, greens and rose hips. Sunflower seeds, nuts, avocados and other magnesium-rich foods are essential in your daily diet. You should avoid concentrated broths, salted and smoked foods. An abundance of flour, sugar and seasonings is harmful, and preservation is also unacceptable.