Every woman’s body is individual, especially when it comes to hormonal levels. Therefore, the menstrual cycle, period and amount of bleeding are different. On average, the maximum duration is 5 days. If sudden changes occur, the presence of abnormalities or diseases is assumed. Diseases of the genitourinary organs may occur, leading to bleeding similar to menstruation. Therefore, it is recommended to undergo examination by a gynecologist or urologist to determine the cause of the symptoms.
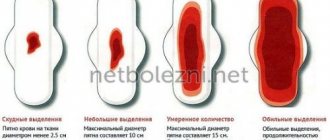
Description of normal menstrual flow
If a woman develops normal, physiological menstruation, the following properties are determined:
- During the day, on average, 40-60 ml of menstrual blood is released;
- on the first day the blood has a scarlet, bright tint;
- on the second and subsequent days, the discharge becomes darker, appears not abundantly, but in portions;
- in the last 2 days, discharge begins only with heavy load, sudden movements, or moving the body from a horizontal to a vertical position;
- presence of an odor similar to meat.
On the second and subsequent days, the shade of the discharge is different for each woman. The presence of a small amount of mucus secreted in the vagina is considered normal.
Consultation with a gynecologist is recommended for any changes. It is especially necessary to monitor changes in the shade of the discharge, its volume, and quality.
Results
Blood loss is dangerous due to the development of anemia. To understand how to determine the permissible volume of blood released, it should not exceed 80-90 ml per day. Uterine bleeding can be caused by difficult childbirth, hormonal imbalance, or menopause in women. The main and distinguishing symptom from menstruation is the continuous discharge of bright scarlet blood for more than 7 days in a row with a protracted course. What is this? How to determine menstruation or bleeding? Of course, postpartum lochia can take quite a long time to go away. But they also have a certain color, should be quite moderate and not cause any particular discomfort. Women need to pay attention to the frequency of replacing pads and the duration of bleeding. If bleeding continues continuously for more than 7 days, it becomes protracted, which is already dangerous and it is probably best to seek advice from experienced doctors.
Differences between uterine bleeding and menstruation
If any deviations occur, consult a doctor immediately. He carries out diagnostics step by step:
- initial examination;
- collecting anamnesis from the patient’s words (she should characterize her typical discharge and changes that bother her);
- carrying out laboratory and instrumental analyses.
Gynecologists identify a number of signs that should alert every woman. With such symptoms, it is recommended to quickly undergo a general examination and examination:
- a significant increase or decrease in the volume of discharge during menstruation;
- continuous bleeding;
- preservation of the liquid consistency of the discharge for the 2nd and subsequent days;
- for the last 2 days there have been no dark clots, the blood continues to be scarlet;
- absence, change in odor;
- addition of menstrual bleeding with pallor of the skin, severe weakness and fatigue;
- pain syndrome in the lower abdomen;
- During sexual intercourse or after its completion, pain, itching, pain, burning and other discomfort symptoms occur.
If such symptoms appear, it is better to make an appointment with a doctor as soon as possible to prevent complications.
Bleeding due to uterine fibroids, adenomyosis, endometrial and cervical canal polyps
Uterine fibroids, endometriosis and polyps and endometrial hyperplasia are diseases associated with benign growth of uterine tissue. They appear most often during reproductive age.
All this pathology is easily diagnosed using ultrasound. As a rule, no additional examination methods are required. You can read about possible treatment options for uterine fibroids in the corresponding section of the website www. ya-zdorova.ru. In the presence of pathology of the uterine cavity, hysteroscopy with the appropriate amount of surgical intervention is indicated to eliminate the cause of bleeding.
Etiology of bleeding
If blood loss occurs in the body, it harms internal organs and systems due to a lack of nutrients and oxygen, stress on the heart and blood vessels. Most uterine bleeding is characteristic of damage to the internal reproductive organs. They may not be life-threatening, but they do cause the following complications:
- anemia;
- malaise, weakness;
- decreased libido;
- infertility.
If a pathological process occurs, timely treatment is required. To prevent relapse, the root cause is identified, since symptomatic treatment will not help.
The main causes of bleeding are:
- natural or induced abortion;
- complications after cesarean section or natural birth;
- prolonged fasting or a strict diet leading to metabolic disorders;
- sharp changes in hormone levels, hormonal imbalance;
- lack of vitamins, microelements, minerals;
- disease of the circulatory system, hematopoietic organs, coagulation system;
- prolonged stress, neurosis, depression;
- systemic infection;
- great physical activity;
- inflammation in the urinary or reproductive system;
- disruption of the functioning of gynecological organs;
- benign or malignant tumor.
All of these conditions may have similar symptoms, so differential diagnosis is required.
Presence of sexual intercourse or smears taken
Pregnancy, and the formation of an unusual background of hormones, changes the structure of tissues in the female body, especially in the genitals, filling them with blood from the veins. Even a routine swab test, such as in the cervical canal, can easily cause mild bleeding. This also applies to frequent sexual intercourse, which injure the uterine cervix in the presence of erosion, ectopia or polyps, as well as other pathological phenomena. As a result, slight discharge with blood occurs. Unusual positions and gross physical intrusion can also cause them and interrupt the normal course of pregnancy.
Classification of discharge
Discharges are divided into 3 types indicated in the table.
| Types of discharge | Characteristic |
| Physiological | Bleeding associated with the formation of monthly menstruation. This is normal for the body and is required for the rejection of the uterine mucosa |
| Conditionally normal | This is a type of bleeding that can occur before or after ovulation. This includes bleeding that occurs after implantation |
| Pathological | They are formed at any age, from children to the elderly. Most often associated with hormonal changes and diseases of the endocrine glands. The cause may be a tumor, gynecological diseases, systemic abnormalities (chronic pathologies, autoimmune lesions) |
The faster the doctor classifies the lesion, the higher the chance of complete recovery, even with the most serious diagnoses.
Appropriate Actions for an Expectant Mother
First, calm down and be able to reason and act correctly. First of all, realize that the normal course of the pregnancy process is not associated with “menstruation” and other bleeding. Most likely, this is a complication of the normal course of pregnancy if you did not take a cervical smear.
It is important to concentrate and begin to remember the moments that could help provoke the unwanted condition.
Such consequences may be caused by recent sex. If the discharge is minor, spotting, and there is no pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region, there is no cause for concern. However, it is advisable to conduct an ultrasound examination in the pelvis and visit a gynecologist as soon as possible.
Important: when the discharge has a bright pink color and is abundant, then you should immediately contact an ambulance. You can drive yourself to a nearby hospital with a gynecology department.
When the pain resembles contractions and bloody discharge is present, you should immediately seek medical attention from a doctor.
It is important to know that you should be allowed through and accepted out of turn in this case. In such emergency situations, there is no need to take a ticket or wait.
Currently, medicine is able to help the expectant mother and baby in safe ways and methods. Timely and effective therapy can restore the normal course of pregnancy.
You need to know that even in the absence of conception, and the presence of severe bleeding. Contacting a gynecologist is mandatory. Only the resumption of normal menstrual cycles without severe pain is an indicator of stable health and the normal course of pregnancy.
Unfortunately, not all women experience such a stable menstrual cycle.
The presence of frequent stressful situations, the accumulation of chronic fatigue, an excessively intense work schedule and the presence of various types of diseases can adversely affect the physiology of the processes.
At the same time, you should always have knowledge about the distinguishing features of normal monthly discharge from the manifestations of excretory substances during pregnancy.
Details of each type of bleeding
Bleeding occurs at different ages, in the presence of pathological and physiological changes. It is important to determine the etiology in a timely manner in order to begin treatment as soon as possible.
Dysfunctional
Discharge is classified according to two symptoms:
- large volume of blood;
- long term.
Most often, deviations occur in patients at risk:
- teenagers with sudden changes in hormonal levels;
- women after menopause with a decrease in the production of sex hormones.
The main pathogenetic factor is a sharp change in the level of progesterone and estrogen. To carry out treatment, it is necessary to determine the state of the endocrine system. For therapy, doses of hormones are prescribed.
Dysfunctional
The condition is divided into 2 categories.
- Ovulatory
. Throughout the cycle, discharge is formed periodically. That is, not every 28 days, but much more often. They can be scanty or abundant. - Anovulatory
. Many deviations occur - changes in the period of the cycle, an increase in blood volume, poor health, constant drowsiness. The woman feels painful.
In the diagnostic process, a general examination and ultrasound of the genital organs are used. It may be necessary to undergo a culture of the contents of the mucous membrane.
Juvenile
This is bleeding that appears at a young age. The following pathogenesis is distinguished:
- failure of progesterone or estrogen production;
- disruption of corpus luteum production.
Tumors of the reproductive organs occur even in adolescence. This is one of the most common causes of juvenile discharge.
Breakthrough
More often, discharge is formed due to pathologies of the uterus. The following damaging factors are identified:
- poor-quality installation or individual intolerance to the uterine device;
- use of excessively large doses, incorrect use or individual intolerance to hormonal contraceptives.
To improve a woman’s condition, it is necessary to select an adequate method of contraception. You can continue to use the spiral, but it must be installed efficiently. The doctor is also required to adjust the concentration of contraceptive substances used.
Profuse
This type of pathological disorder is similar to the physiological loss of blood during menstruation. Pain and bleeding develop. But it is produced in excessively large volumes, this is the main symptom with which people consult a doctor.
The initial stage of profuse bleeding is extremely difficult to determine.
But when a woman realizes that there is too much blood discharge and it does not stop, she needs to urgently consult a doctor. In severe cases, even death can occur. It is important to quickly eliminate bleeding through surgery.
Menopausal deviations
When a woman reaches menopause, the level of sex hormones changes dramatically. Because of this, neoplasms of a benign or malignant type can develop. Growths on the uterus are formed due to a strong decrease in estrogen, which was responsible for the frequency of the menstrual cycle. This can lead to bleeding, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- severe pain during intercourse;
- periodic appearance of bloody discharge even after the onset of menopause.
Urgent diagnostic tests are required to prevent complications, including death.
Hemorrhage during pregnancy
During pregnancy, menstruation stops completely, since the embryo is in the uterus, its mucous membrane is not rejected. If any bloody discharge from the vagina appears, you should immediately consult a gynecologist. It is better to call an ambulance so that the patient can be examined on the spot and taken to a medical facility. The following negative symptoms may occur:
- pain syndrome spreading to the lower abdomen;
- cramping attacks;
- severe nausea, which may lead to vomiting;
- sweating;
- dizziness, fainting.
Vaginal discharge during pregnancy is dangerous not only for the fetus, but also for the woman herself. They can lead to miscarriage, premature birth, and heavy blood loss in the patient’s body.
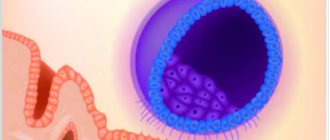
Presence of an ectopic pregnancy
When the egg rises through the tube after fertilization, it may become embedded in the wrong place. More rarely, attachment occurs near the ovary, in the uterine cervix, in the abdominal cavity, which leads to the subsequent development of bleeding of varying strength. At the same time, it is not easy to determine whether these are signs of pregnancy or menstruation. This process is accompanied by nagging painful sensations and a bloody brown smear - signs of the onset of rejection and miscarriage.
Ectopic pregnancy
At the same time, the lower abdomen aches and hurts, contractions and the release of bloody formations, both spotting, brownish, and copious with ichor, are possible. Signs of a threatened miscarriage may depend on injuries in the abdominal and lumbar regions. When breastfeeding a baby, fertilization can occur without menstruation. The first egg released will be fertilized immediately. In this case, a discharge containing blood appears, similar to menstruation.
First aid methods
As soon as spotting occurs, the following rules must be used:
- ban on any physical activity;
- exclusion from the diet of meat-type foods and iron-rich foods (beets, pomegranate, beef liver);
- lying down with the pelvis slightly elevated to eliminate the abundant blood flow to the reproductive organs (to do this, you can place a pillow under the pelvis, put your feet on a wall or sofa);
- applying a towel or heating pad to the stomach that has been supplied with cold water (this will help narrow the blood vessels and reduce blood flow).
The symptoms that appear cannot be ignored. It may be the first sign of a serious illness that needs to be treated promptly. If bleeding occurs in a pregnant woman, urgently contact a clinical facility so that she does not die or lose the child. It is important to know the difference between menstrual blood and bleeding, this will help identify abnormalities at an early stage.
What can you do at home to ease heavy periods?
- If you are in pain, take a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. You can also apply a heating pad to your stomach—the heat eases cramps.
- Iron-rich foods and iron-containing supplements can help ease heavy menstruation and cope with iron deficiency in mild forms of anemia.
- Foods rich in iron include beef, liver and other offal, turkey, spinach, fish, pumpkin seeds, dried apricots, white beans, cocoa beans, and champignons. It also makes sense to increase your vitamin C intake because it helps with iron absorption. A lot of vitamin C is found in kiwi, bell peppers, strawberries, citrus fruits, broccoli, tomatoes, kohlrabi, pineapple.
- Drink enough water.
If you have heavy bleeding for several days, your blood volume may decrease significantly. Drink 4-6 extra glasses of water to maintain your blood volume.
Diagnosis of the problem
At the appointment, the doctor should ask you about your cycle, at what age it began, whether there have been pregnancies or abortions, how long the cycle lasts, how heavy your periods are and whether there are any clots. How much discomfort do you experience? Before your visit, it makes sense to count the number of hygiene products you use per day and over the entire period. After consultation, a number of tests are prescribed:
- blood test for hormones, iron and coagulation;
- Pap test - a painless smear from the cervix to check for cell changes. In serious cases, an intrauterine biopsy is prescribed (the procedure takes about 15 minutes and is well tolerated);
- Ultrasound.
Based on these initial examinations, additional examinations may be prescribed, for example hysteroscopy (a minimally invasive method using an optical tube).