Author
Victor Gennadievich Sturov , hemostasiologist, hematologist, doctor of the highest category, Doctor of Medical Sciences
According to statistics, vascular thrombosis affects 70% of people around the world. Every year, one in 250 people living on Earth dies from this disease - despite the huge number of drugs created to combat this terrible disease.
What is thrombosis
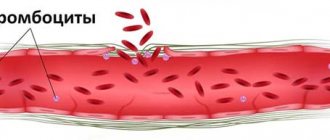
Many biological systems are responsible for the vital functions of our body. One of them is hemostasis. The task of hemostasis is to keep blood in a liquid state, stop bleeding if the walls of blood vessels have been damaged, and dissolve blood clots - blood clots that, like a patch, cover the damaged area of the vessel.
On the one hand, thrombosis protects us from blood loss. On the other hand, it can provoke serious diseases associated with impaired blood flow: stroke, myocardial infarction, ischemia of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space, gangrene of the extremities.
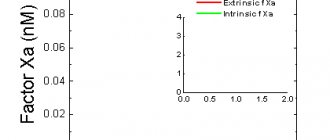
Until the mid-19th century, thrombosis remained a mystery to doctors. Rudolf Virchow, a German pathologist, managed to uncover it. He studied the mechanisms of thrombosis and identified three main causes:
- Deterioration of the condition of the walls of blood vessels (this may be the consequences of injuries and surgical interventions)
- Slow blood flow (blood clots accumulate where the speed of blood flow changes)
- Change in blood viscosity (“thick blood”)
Causes of thrombosis and its signs
- If the integrity of the vascular wall is compromised, the development of thrombosis begins. This usually happens as a result of injuries, during pregnancy, when the vessels narrow and become deformed, or if the doctor’s recommendations are not followed after operations.
- When blood stagnation occurs - due to insufficient physical activity or prolonged bed rest. Venous congestion often leads to deep vein thrombosis and varicose veins. To reduce the risk of developing blood clots, it is recommended to use venotonic agents for varicose veins: for example, Normaven® Leg Cream. This product was developed by specialists from the pharmaceutical company VERTEX, has undergone clinical studies and has all the necessary documents and quality certificates confirming its effectiveness and safety. As a result of the testing, it was found that a three-month course of using Normaven® Leg Cream helps to improve the condition of the blood vessels of the lower extremities, due to which cramps disappear, the severity of the venous pattern decreases, swelling and a feeling of heaviness in the legs disappear.
- When the number of platelets and red blood cells in the blood increases, blood clotting parameters change. The cause may be hormonal imbalances, metabolic disorders and oral contraceptives.
- Thrombosis can develop in patients with cancer, as well as with kidney dysfunction.
Factors that increase the risk of thrombosis:
- injuries;
- obesity and excess weight;
Obesity and excess weight are factors in the development of thrombosis
- pregnancy and childbirth;
- smoking;
- infections;
- long-term and frequent trips and air flights;
- age from 40 years;
- taking medications that increase blood clotting;
- surgical intervention on joints and abdominal operations under anesthesia;
- bone fracture;
- sedentary lifestyle.
Signs of vein thrombosis in the legs: what precedes it
In healthy people, blood flows freely through arteries and veins.
Signs of thrombosis:
- The speed of blood flow in certain areas decreases. This may be due to heart failure, heart defects, varicose veins or atherosclerosis.
- Blood density increases
- The blood vessels narrow. The causes of this may be the following diseases: endocarditis, arteritis.
- Blood clotting factors are deficient, and blood clots worse.
The disease occurs in the veins; inflammation of the walls usually occurs, followed by venous thrombosis. Shock and severe bleeding provoke thrombus formation.
Thrombosis is a reaction to acute diseases. It is important that the nervous and endocrine systems have sufficient response to protect against the onset of any disease. Thrombosis poses a great threat to life in diseases of the brain and changes in hormonal levels.
Expert opinion
With arterial thrombosis, a fibrin film forms at the injured site, to which platelets with a negative electrical charge begin to flock. Blood clots become fixed to the walls. Then they begin to increase in size, collecting leukocytes, red blood cells and fibrin films.
Vascular surgeon, phlebologist
Osipova Ekaterina Yakovlevna
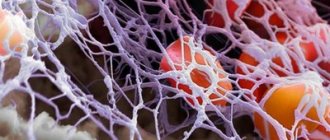
Blood clots can be:
- red (blood flows slowly, but clots well),
- white (blood flows quickly, clots slowly).
Layered blood clots that form over a long period of time are capable of splitting on their own. This phenomenon is referred to as revascularization (the throughput of the vessel is restored). It is possible to trace the signs and symptoms of thrombosis only if at least 10-50% of the vessel is affected.
Virchow's triad
Medicine identified the basic principles of thrombosis back in the nineteenth century. This was done by the famous German doctor Rudolf Virchow.
- The first principle is that for thrombosis to start, damage to the inner wall of the vessel (endothelium) is required.
- The second principle is that blood clots form in areas of blood vessels where blood flow is uneven (vortices) or where blood flow is slow.
- The last principle is that the rate of blood clot formation is influenced by blood viscosity. The higher it is, the faster the blood clots grow.
First signs of thrombosis
The formation of blood clots is painful, with a feeling of heaviness and swelling.
If the blood clot is located in the femoral or iliac vein, the entire leg swells and the skin takes on a blue tint. Due to altered blood flow, clots are redistributed into the veins under the skin. A vascular network appears, which is noticeable on the abdomen along the protruding veins. The patient indicates weakness, chills, and body temperature above normal.
When blood clots form in small veins, signs of thrombosis for various reasons may not be expressed for a long time. And only unpleasant sensations when walking will signal a problem.
Signs and features of thrombosis
Preparation for the procedure
If the doctor decides to undergo thrombectomy, the patient is prescribed a diet that excludes foods that cause gas formation in the large intestine (cabbage, legumes, fresh fruits and juices from them). The ban also includes products that cause a rush of blood to the rectum and/or have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane (smoked meats, spicy foods, alcohol).
Immediately before the procedure (in the morning and evening before the operation), you will need to cleanse the intestines using a Microlax microenema.
Preparation for thrombectomy is carried out when the patient's condition allows it. In case of severe pain and an impressive size of the node, bowel cleansing is not performed, and in the event of a threat of severe complications, surgical removal of the blood clot is carried out on an emergency basis.
Signs of thrombosis depending on the location of the thrombus
- The portal vein facilitates the flow of blood from unpaired organs in the abdominal cavity (from the stomach, intestines, spleen, pancreas). From them the blood is sent to the liver (where it is cleansed). If thrombosis occurs in the portal vein, the risk of liver disease increases.
Symptoms of portal vein thrombosis include abdominal pain and bloating, intestinal distress, vomiting, rarely black stools, and an enlarged spleen.
- The pulmonary artery becomes blocked after blood flows from the veins of the legs and pelvis. The number of clots, the reaction of the lungs to them and the action of the homeostasis system are important. The smaller the clot, the less severe the symptoms. Large blood clots interfere with gas exchange in the lungs, and hypoxia develops.
Symptoms: chest pain; the skin turns pale and blue; veins swell in the neck; a cough with bloody discharge and wheezing appears; loss of consciousness.
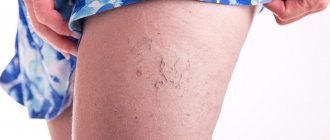
- Thrombosis of the lower extremities accounts for up to 70% of the total number of thromboses. It is especially dangerous when the deep veins in the thighs and below the knees are thrombosed (it is necessary to monitor for signs of lower leg thrombosis). The first symptoms are invisible.
Swelling, pain when walking or bending the lower leg, pain in the inner thigh and foot, reddened skin and cramps are all signs of the development of the disease. If the acute form occurs, the person begins to suffer from shortness of breath, his temperature rises, he becomes dizzy and loses consciousness. You can compare the signs of thrombosis of the lower extremities from the photo, but the diagnosis must be made by the attending physician.
- In the upper extremities, thrombosis is less common (subclavian vein thrombosis), and it is difficult to distinguish its initial symptoms from arm injury. They manifest themselves in swelling, pain and blueness. The patient feels a burning sensation, his hands go numb, and his skin becomes insensitive.
- The vessels of the brain connect with veins and arteries, where blood clots can also appear, and this leads to a stroke. Symptoms of cerebral thrombosis are more pronounced than with thrombosis of other vessels. The disease is accompanied by headaches, dizziness, decreased hearing and visual acuity, loss of consciousness, and periodic convulsions. The person is feeling sick.
- Blood clots also settle in the veins of hemorrhoids, this is considered a complication of hemorrhoids. Signs of thrombosis of hemorrhoids (Haemorrhoids): pain, the affected area itches, fever, swelling.
- The central retinal vein is also affected by thrombosis. Signs of the disease may not be expressed, and the person loses vision as a result.
- Thrombosis of the mesenteric veins of the intestine is manifested by prolonged abdominal pain. Other signs: bloating, high fever, vomiting and nausea. In the early stages, it is difficult to determine the disease by symptoms. Usually they talk about a complication of the pathology.
- If the femoral and iliac veins are affected, then we are talking about ileofemoral thrombosis. It is accompanied by swelling of the legs (the skin changes color from reddish to blue), when pressure is applied, brown marks appear, the legs and groin hurt, and the body temperature rises.
Treatment and diagnosis of venous thrombosis
Rules of behavior in the postoperative period
If the evacuation of hemorrhoidal blood clots was carried out against the background of the patient’s satisfactory condition, then the postoperative period does not provide for significant restrictions.
The following are prohibited: ___• physical activity, ___• thermal procedures (bath, sauna, beach holiday), ___• prolonged stay in a sitting or squatting position.
Products that cause a rush of blood to the pelvic vessels or irritation of the mucous membrane are excluded from the diet: spicy, salty, smoked foods and alcohol.
Food should be rich in fiber, which stimulates intestinal function (prunes, apples). It is not recommended to eat foods that can cause constipation (rice and semolina porridge, potatoes, pasta). If stool retention occurs, a mild laxative (for example, Forlax) is prescribed.
After each bowel movement, wash the anal area with warm water and change the sterile napkin. If suspicious symptoms appear (pain, bleeding, discharge from the wound), you should immediately consult a doctor.
Signs of thrombosis and treatment
The severity of the disease is indicated by signs of thrombosis; treatment is prescribed depending on the stage of the disease.
What to do? First of all, an accurate diagnosis is necessary. The doctor must determine where the blood clot is located, clarify its size and mobility. It is necessary to understand how firmly the blood clot is fixed and what is the likelihood that it will come off.
!
There are several main methods of therapy: surgery, thrombolysis, medication and implantation of a vena cava filter.
Heparin injections and anticoagulant drugs are also prescribed. Additionally, they can also prescribe a complex of venotonic vitamins and plant extracts, as well as prescribe a therapeutic diet.
Thrombolysis involves surgically dissolving blood clots using a catheter through which a substance is injected to dissolve the blood clot.
Surgical treatment of thrombosis
Doctors resort to surgical intervention only in case of complications, and here the location of the blood clot is important. It is possible to eliminate the entire thrombotic mass.
A vena cava filter is a metal device similar to an umbrella. It is implanted into the lumen of the inferior vena cava endovascularly.
What to consider when choosing a doctor and medical institution
If you are looking for a medical institution where to go for consultation and treatment of acute perianal thrombosis, then you need to pay attention to several factors.
- The institution has a proctological, and not just a general surgical or oncocoloproctological specialization.
- Knowledge of the Clinic staff about all possible methods of treating acute perianal thrombosis
- Possibility of performing minor coloproctological operations in a hospital setting at the Clinic
- Possibility of performing surgical treatment in the Clinic for “special” groups of patients - pregnant women, patients of the older age group
Recovery after thrombosis
Recanalization is the restoration of the capacity of an artery or vein after thrombosis. It can occur through medical intervention or naturally. Recanalization occurs no earlier than after 6 months with long-term treatment. It requires constant prevention.
After thrombosis, the clot in the vein goes away over time and normal blood flow is restored. Sometimes recanalization does not occur. Even after complete cleansing, the vein cannot function normally.
Thrombosis destroys its internal valves, and they are responsible for the outflow of blood in one direction. As a result, the outflow of blood from the limb is disrupted, the pressure in its venous system increases, and the disease develops again. Therefore, signs of recanalization of thrombosis may be short-lived.
Expert opinion
Unfortunately, thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities has a tendency to recur even after the clot has resolved. Therefore, it is extremely important to make lifestyle changes and follow the preventive measures recommended by your doctor to reduce the risk of recurrent blood clots.
Vascular surgeon, phlebologist
Osipova Ekaterina Yakovlevna
Contraindications
___• The operation is not performed if the patient’s condition is extremely serious (general exhaustion, complications of cardiovascular diseases, sepsis). ___• Surgical interventions are not prescribed for severe pregnancy (severe anemia, poorly controlled early toxicosis with dehydration, late toxicosis with generalized edema, etc.).
Since thrombectomy is a minimally invasive (low-traumatic) operation, the procedure can be prescribed after the patient’s condition has been stabilized. The decision about surgery or its inadmissibility is made individually, taking into account all risk factors.
Suspicion of thrombosis
To properly treat thrombosis, you need to make an accurate diagnosis. Different methods are used for this:
- Duplex scanning. With its help, visualization of blood vessels is created and blood flow is examined.
- X-ray contrast venography. In this case, a contrast agent is injected into the vessel.
- In case of doubt, MR-CT angiography is performed when making a diagnosis.
- If there is a risk of pulmonary thromboembolism, the patient undergoes a chest x-ray and scintigraphy.
- Impedance plethysmography is performed if there are signs of leg thrombosis. This method uses a cuff that compresses the lower leg for subsequent short-term occlusion of the veins. The new vessel volume after blood flow is then measured. This analysis provides an accurate diagnosis (up to 90%) and allows one to recognize the presence of deep venous thrombosis in the area above the knee.
At the first suspicion of thrombosis, you should immediately consult a doctor. Self-medication at home is very dangerous.
Video: how to recognize thrombosis?
is not responsible for the accuracy of the information presented in this video clip. Source - Phlebologist Ignatov V.N.
Sources:
- NEW APPROACHES TO ANTICOAGULANT THERAPY OF ACUTE DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS OF THE LOWER LIMB. Sukovatykh B.S., Belikov L.N., Savchuk O.F., Chernyatina M.A. // Kursk scientific and practical bulletin “Man and his health”. – 2008. – No. 3. – pp. 74-78.
- STRUCTURE OF RISK FACTORS FOR ACUTE DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS OF THE LOWER LIMB. Usov S.A., Rovenskikh D.N., Sartakov G.G. // Acta Biomedica Scientifica. – 2012. – No. 4 (86). – pp. 106-107.
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261258086_Scientific_Publications_on_Portal_Vein_Thrombosis…
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/7711586_Ultrasound_criteria_for_embologenicity_of_venous_th…
- https://thrombosisjournal.biomedcentral.com/
- https://www.isth.org/page/JTH
Are there ways to prevent relapses/recurrences of the disease?
Prevention of relapse of the disease is based on excluding possible causes of thrombosis. These include hard stools, constipation or diarrhea, “reading on the toilet,” insufficient or, conversely, excessive physical activity (weightlifting, fitness), and prolonged sedentary work. Unfortunately, there are no unambiguous methods for preventing the occurrence of acute thrombosis of the external hemorrhoid; we can only reduce the likelihood of its occurrence, but not completely eliminate it. However, it should be noted that with conservative treatment the likelihood of recurrence of the disease is higher than after operations.