An increased heart rate of more than 100 beats per minute is called tachycardia. At the same time, the person’s pulse increases, which can be detected, for example, in the wrist or in the area of the carotid artery in the neck. A pulse of 110-114 per minute is a moderate tachycardia, which can occur both in a healthy person and in various diseases.
The main way to distinguish them yourself is the dependence of high heart rate on external conditions, for example, on physical activity. However, this is not an absolute sign, so if the pulse is 110, 111, 112, 113 and 114 beats per minute, you should consult a therapist.
What does a promotion mean?
What does it mean if your heart rate is 110 per minute? This may be a normal reaction of the body to intense physical activity or significant stress. Increased heart rate and pulse fluctuations are also observed with rapid blood loss, including internal bleeding.
The pulse becomes faster during fever, but its value of 110 per minute can only be recorded with a significant increase in body temperature (up to 39 - 40˚C).
Pathological causes of increased heart rate and pulse:
- A pulse of 110–114 beats per minute or more is observed in severe hyperthyroidism. This is a condition that accompanies some diseases of the thyroid gland, for example, autoimmune thyroiditis, in which the production of its hormones increases. These substances accelerate metabolic processes in the body.
- In some cases, a pulse of 110 per minute can be observed not only with sinus tachycardia, but also with other rhythm disturbances: atrial fibrillation or supraventricular tachycardia with simultaneous 2:1 atrioventricular block.
- A rapid pulse is observed in severe respiratory failure, which manifests itself as shortness of breath at rest. It can be caused by an attack of bronchial asthma, exacerbation of obstructive pulmonary disease, severe emphysema, pneumonia, tuberculosis, thromboembolism of the branches of the pulmonary artery and other diseases.
- Anemia (iron deficiency, B12 or folate deficiency, hemolytic, aplastic) when the hemoglobin level decreases to 100 g/l or less is accompanied by a compensatory increase in heart rate. The lower the hemoglobin concentration, the faster the resting pulse, and the faster it increases with minimal exertion. A pulse of 110 per minute or more, even in pregnant women, is usually a symptom of concomitant anemia.
- Increased heart rate with a simultaneous increase in blood pressure can be observed in young people with signs of NCD or in the early stages of hypertension. This condition is also typical for pheochromocytoma, an adrenal tumor that secretes adrenaline.
Consumption of caffeine-containing products, alcohol, smoking, and side effects of medications rarely cause heart rate to increase to 110 per minute. Typically, this condition still occurs with various diseases.
Pathological causes
The picture is completely different if the cause of a pulse of 110-115 units is pathological, that is, tachycardia exists for a long time, being a symptom of some underlying pathology, requiring clarification of the root cause of the disorder.
Most often these are cardiovascular diseases. 110-115 beats are typical for: congenital or acquired defects, rheumatism, autoimmune processes, myocardial inflammation, AMI, post-infarction cardiosclerosis, hypertension, angina pectoris, conduction disorders.
Non-cardiac pathological triggers include: VSD, neurocirculatory dystonia, endocrine pathologies, anemia of various origins, emphysema, neuroses, psychoses, dehydration due to diarrhea or uncontrollable vomiting. Excess potassium in the blood or deficiency of magnesium is also a cause of pathological tachycardia 110-115 beats/minute.
Knowing the root cause of the increase in heart rate is necessary to choose the right treatment tactics.
Main symptoms of increased frequency
What are the health risks of a pulse of 110-114 beats per minute? If it occurs in response to stress or strain, there is no danger. At rest, the heartbeat returns to normal. However, during its increase, a person may experience the following sensations:
- dizziness and fainting;
- severe weakness;
- feeling of heartbeat, pulsation in the body;
- dyspnea.
If a rapid pulse is caused by a disease, additional symptoms characteristic of this disease occur. For example, with hyperthyroidism, irritability, insomnia, sweating, and muscle tremors appear. Palpitations caused by pathology of the heart or lungs are often accompanied by chest pain, shortness of breath, and dizziness.
Thus, a pulse of 110 per minute in itself does not pose any particular danger to the heart. However, the diseases in which it occurs can lead to various complications. Therefore, with such heartbeat and pulse at rest, it is necessary to consult a general practitioner.
Symptoms requiring an ambulance call
There are quite a lot of them, you should pay attention to the following signs of problems with the heart:
- Chest pain of a pressing type, radiating to the arms or back.
- Breathing problems. Dissatisfaction after inhalation, even at rest. The frequency of movements increases, the phenomena of hypoxia also increase.
- Dizziness.
- Cephalgia (headache). Pulsating in time with the beat of the heart.
- Fatigue, drowsiness for no apparent reason. Decreased performance.
- Weakness in the legs, inability to navigate in space.
- Visual impairment.
- Decreased hearing.
In these cases, an ambulance must be called to correct the condition and possible transportation to a hospital for diagnostics.
If there is at least one of these manifestations, the issue of saving life will already be resolved:
- Acute headache in the back of the head, accompanied by neurological symptoms.
- Blindness.
- Facial distortion.
- Paralysis of half the body, paresis of the limbs.
- Inability to speak normally.
- Complete lack of orientation in space.
110 beats per minute at rest is already grounds for calling an ambulance. Adequate regulation of heart rate occurs in a matter of minutes, if not faster. Otherwise, a pathological process takes place.
Medical diagnosis of high heart rate
If you complain of a pulse of 110 per minute, the doctor uses the following diagnostic methods:
- questioning the patient, finding out potential causes of rapid pulse, including lung disease, thyroid disease, medications taken;
- examination to determine heart rate, heart size, murmurs, wheezing in the lungs, enlarged thyroid gland, etc.
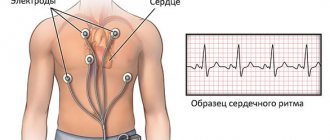
A standard ECG is prescribed. At rest, she may not show signs of heart palpitations. Therefore, if there are no deviations in the cardiogram, daily ECG monitoring is prescribed - an examination during which a continuous 24-hour recording of the cardiogram is carried out on an outpatient basis.
Depending on the results of the examination, other tests may be needed, such as blood tests to determine the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin, thyroid hormone levels, and an ultrasound of the heart to determine changes in its structure caused by the disease.
Diagnosis of the disease
A clearly manifested symptom of rapid pulse requires consultation with specialists:
- cardiologist;
- local therapist;
- endocrinologist specialist.
After consultation with the doctor, the following tests are prescribed:
- clinical blood and urine tests;
- X-ray of the heart;
- do Holter monitoring;
- echocardiogram;
- Ultrasound examination of the heart muscle and thyroid gland.
After receiving all the necessary research results, the doctor makes a final diagnosis and prescribes symptomatic treatment.
Expected duration of attack
The duration of a pulse increased to 110 beats per minute depends on its cause:
- the heartbeat as a result of the fever will return when the body temperature returns to normal;
- rapid pulse caused by blood loss is corrected after intravenous administration of solutions or blood components;
- in case of pathology of the thyroid gland, it is necessary to suppress its synthesis of excess thyroid hormones;
- a rapid pulse caused by excessive coffee consumption or the effects of medications is restored after about an hour, when the active substances begin to be eliminated from the body;
- in case of heart or lung diseases, increased heart rate persists for a long time, including at rest.
Treatment or first aid?
What to do if your heart rate is 110 beats per minute? The first thing to do is try to determine if it is related to coffee, an energy drink, or some kind of medication. In this case, it is enough to just wait quietly for about an hour. If tachycardia is caused by stress, you can take a sedative - motherwort tincture, Corvalol. If you have palpitations due to physical activity, it is enough to rest for 5 to 10 minutes for your heart rate to return to normal.
If a pulse of 110 per minute appears regularly, you should consult a doctor. Treatment depends on the cause of the rapid pulse:
- for hyperthyroidism, thyreostatics are prescribed - medications that inhibit the synthesis of thyroid hormones; if necessary, treatment with radioactive iodine or surgical removal of part of the gland is used;
- for cardiac arrhythmias, a variety of drugs are prescribed, for example, beta-blockers, calcium antagonists, sinus node I-channel antagonists, cordarone; in some cases, catheter radiofrequency ablation is indicated (a minimally invasive procedure by which the doctor destroys the area of abnormal impulses that cause the heartbeat); at the same time, anticoagulants and/or antiplatelet agents are often prescribed to prevent the formation of blood clots in the cardiac cavities;
- if increased heart rate is caused by lung diseases, proper treatment is necessary - antibiotics, bronchodilators, etc.
You need to call an ambulance in cases where the pulse is 110 beats per minute or more, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pressing, burning, squeezing pain behind the sternum;
- severe headache, loss of consciousness;
- sudden shortness of breath, cough, chest pain;
- weakness, pale skin, cold sweat, vomiting “coffee grounds” or blood, black loose stools;
- a rapid increase in blood pressure if a person does not know how to cope with it on his own.
Pathological factors
They occur much more often. Possible diseases include:
- Pulse for fat burning: how to calculate, fat burning zone for women and men
- Diabetes. Systemic endocrine condition. Requires lifelong therapy. In the early stages, it is difficult to identify; there is often a latent course: the patient can walk with the problem for years; it is discovered by chance or when it is too late for a total correction. You need to pay attention to the following manifestations: sudden attacks of hunger, tremors (shaking hands), pallor, weakness in the legs, fainting. Objectively, glucose does not always increase; you need to examine the sugar curve throughout the day. The heart and blood vessels suffer “for company”, diabetes affects all organs and systems.
- Problems with blood circulation in the brain. The result of osteochondrosis and compression of the arteries feeding the cerebral structures. The normal regulation of cardiac activity at the level of the central nervous system is disrupted. Therapy is carried out under the supervision of a neurologist.
- Hyperthyroidism. Excessive production of thyroid hormones as a result of poor nutrition, natural factors, and the development of tumors. Accompanied by increased body temperature, headaches, shortness of breath, weakness, fatigue, inability to sleep, bulging eyeballs, changes in the relief of the neck (goiter), and mental disorders of a depressive-affective nature. Treatment under the supervision of an endocrinologist.
- Hypercorticism. Another pathology of the same profile. The concentration of adrenal hormones, primarily cortisol, only increases. Secondary Itsenko-Kushang disease occurs with sudden weight gain, uneven fat deposition, destruction of the spine and entire skeleton, and mental problems. Often results from a tumor of the adrenal gland or pituitary gland. Treatment under the supervision of an endocrinologist and neurosurgeon.
- Violations from the heart itself. As a result of irritation of the third reflex zone of the organ, the heart rate accelerates. The assessment is carried out by a cardiologist. Despite the variety of diseases, their symptoms are almost the same: chest pain of a pressing nature, radiating to the arms and back, shortness of breath even at rest, especially after physical activity, sweating, blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle, pallor of the dermal integument, fatigue, arrhythmias ( not only by type of tachycardia). Mandatory electrocardiography is carried out, and, if possible, stress tests.
- Vascular diseases. First of all, atherosclerosis, with narrowing or blockage of the lumen by cholesterol plaque. Lipid deposits grow radially, along the entire diameter of the blood supply structure, making it more difficult for blood to overcome resistance. That's why the heart speeds up. This is the only visible symptom. Another, less obvious one is increased blood pressure.
- Panic attack, affective disorders. Psychotherapeutic problems.
A pulse of 107-112 beats per minute is the result of hemodynamic and endocrine pathologies. Often in the system. Therefore, treatment is carried out under the supervision of a group of doctors of different profiles.
Lifestyle change
Regardless of the underlying disease, with a frequent pulse of up to 110 per minute or more, it is recommended to observe certain restrictions:
- refusal of intense physical activity, staying in hot rooms, in direct sunlight, drinking caffeine, smoking;
- eating healthy foods low in salt and animal fats;
- reducing stress levels by avoiding traumatic situations or learning breathing exercises and meditation techniques;
- regular leisurely walks, which train the heart and help cope with nervous overload;
- Drinking enough fluids to avoid dehydration.
Preventive actions
The main prevention of cardiovascular diseases with symptoms of tachycardia (rapid pulse and heartbeat) is to follow certain rules:
- mandatory walks (on foot) in the fresh air, several hours a day;
- constant physical activity (in the gym, yoga, Pilates, gymnastic exercises);
- average consumption of clean, unflavored drinking water daily – at least several liters;
- positive moods - when listening to music, doing creative work, hobbies;
- try to avoid obviously stressful situations;
- practice using relaxation and meditation techniques.
Timely seeking medical help and monitoring your own health is the best solution to problems with sudden palpitations (fast pulse).
Heart-healthy herbal remedies
Simultaneously with the treatment of the underlying disease that has caused the heart rate to increase to 110 beats per minute or more, you can take home remedies that may improve metabolic processes in the heart muscle.
Of course, the effectiveness of such drugs has not been proven, so whether to use them or not is a personal matter for each patient. With a frequent pulse of more than 110 per minute, you can use oats, passionflower, capitol, black cohosh (cohosh), and skullcap. However, valerian helps best with this condition.
A decoction of the roots or an infusion of the leaves of this plant helps normalize heart function, slows down the pulse, reduces stress and anxiety, eliminates irritability and excitability. It is a relaxant and increases blood flow to the brain.
Regardless of whether medicinal herbs help reduce a rapid heart rate or not, you should consult a doctor.
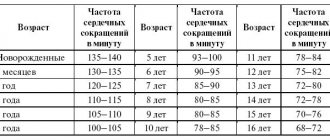
Heart rate is normal
They are used by specialists to determine the level’s compliance and its relationship to standard indicators.
| Person's age (in years) | Rest value (lowest) | The highest allowed value at rest | Conditional norm at rest |
| Up to 12 months | 105 | 165 | 133 |
| Up to 2 years | 95 | 155 | 125 |
| From 2 to 5 | 85 | 125 | 105 |
| From 6 to 8 | 80 | 120 | 100 |
| From 8 to 10 | 70 | 110 | 90 |
| From 11 to 12 | 65 | 105 | 85 |
| From 13 to 15 | 60 | 90 | 80 |
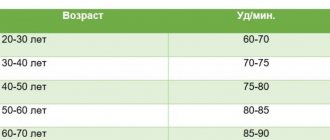
| From 16 to 50 | 62 | 85 | 72 |
| From 51 to 59 | 65 | 86 | 75 |
| From 60 to 80 | 70 | 90 | 80 |
PCSS
are directly combined with the general condition of the body and the slightest deviations should attract the attention of both the patient and specialists.
The first signs of a high frequency pulse are an alarming symptom, indicating the onset of a disease or a complicated course of an existing disease.
Unequal time intervals or different pulse depths indicate disruption of the heart muscle (arrhythmia).