Unfortunately, a disorder such as stroke is very common. And if previously older people suffered from damage to the blood vessels of the brain, today young people also turn to specialists for help. In our information article we talk about the consequences of the disease, in particular about strabismus and how to restore vision.
In this article
- What is a stroke?
- Types of lesions
- What are the causes of stroke?
- What are the symptoms of a stroke?
- What are the consequences of a stroke related to the visual organs? How to recover? What will be the treatment?
- How to treat strabismus during a stroke?
- What does drug treatment include?
- Gymnastic exercises for the treatment of strabismus
- Surgery to treat strabismus after stroke
- Recommendations
What is a stroke?
Experts call a stroke an acute disturbance of blood circulation in the brain, which entails focal damage. Unfortunately, every year the disease becomes younger and more common: people after thirty years of age often experience a stroke. It manifests itself as sudden weakness in the limbs and disturbance of consciousness, as well as facial asymmetry, impaired speech and vision, and other signs that we will discuss below. It is important to diagnose this disease in time and begin treatment. Will the body be able to fully recover? It is difficult to answer this question unambiguously, since it will depend on physiology and age, as well as a number of other factors. In any case, treatment is necessary to correct cardiac, respiratory and metabolic disorders and combat cerebral edema. Also, a person after a stroke needs specific pathogenetic, neuroprotective and symptomatic therapy that will prevent complications.
Folk remedies
You can restore your vision after a stroke if you use the following recipes.
Mountain arnica tincture
To prepare the decoction you need:
- Take 1 teaspoon of plant flowers and pour 2 cups of boiling water.
- The product must be infused for 2 hours.
It is recommended to take 1 tbsp of the decoction. spoon before each meal. The tincture cannot be stored for more than 2 days. The benefits of using mountain arnica include the ability to relieve muscle spasms. The herb has a beneficial effect on the central nervous system.
Decoction of pine cones
The healing infusion allows you to eliminate cerebral circulation disorders. The solution contains tannins that have a hemostatic effect.
To prepare the decoction, you need to boil 5-6 fresh pine cones. The amount of water required to prepare the solution is 0.5 liters. The product should be taken 150 ml 3 times a day.
Motherwort tincture
The plant has a calming effect and helps get rid of neurological diseases.
Pour 15 g of dry herb with a glass of boiling water and leave for 30 minutes. The decoction should be taken 3 times a day, 2 tbsp. spoons. Restorative therapy with motherwort can eliminate psychological imbalance.
Eyebright compress
The plant is considered indispensable in the treatment of eye diseases.
To prepare the decoction, place 5 tbsp in a container. spoons of dry herbs and pour a liter of boiling water. It is recommended to apply a compress to the eyes daily. The optimal duration of treatment is 14 days.
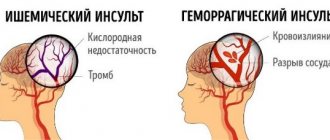
Types of lesions
Experts distinguish two types of stroke - ischemic and hemorrhagic. They are radically different from each other, as they have different mechanisms of action and principles of treatment. So, the first type can be called a cerebral infarction in another way. What happens at this moment? The work and patency of the cerebral arteries is disrupted, which leads to prolonged ischemia and changes in brain tissue in the area of the blood supply to the affected artery.
In turn, a hemorrhagic stroke is provoked by a pathological (atraumatic) rupture of a cerebral vessel with hemorrhage into the cerebral tissue. Neurologists summarize that ischemic stroke most often affects people after fifty years of age, while hemorrhagic stroke can also occur in the younger generation. For example, at the age of 40 years.
Rehabilitation exercises on simulators
The Yusupov Hospital uses two types of simulators for the rehabilitation of patients after a stroke - mechanical and robotic. Mechanical exercise machines include exercise bikes, treadmills, and exercise machines for restoring balance and gait. Robotic simulators are equipped with electronic biosensors that stimulate activity by influencing the affected limbs. Robotic simulators have wide functionality; they are programmed taking into account the patient’s needs, promote the transmission of nerve impulses from the brain to the injured limb, and stimulate motor activity.
Rehabilitation exercises after a stroke are performed using multifunctional exercise equipment and sports equipment. There are different types of simulators:
- To restore motor activity, use a flexion/extension simulator, a simulator for developing the joints of the limbs, exercise tracks, and exercise bikes.
- For bedridden patients, exercise equipment in the form of a bed or bicycle is used.
- To restore balance, gait, and motor activity, a horizontal simulator is used.
- For patients who cannot yet stand, a seated exercise machine has been created to develop and strengthen the back muscles.
What are the causes of stroke?
What is the cause of stroke? Given the statistics, there may be various reasons. For example, arterial hypertension or atherosclerosis. Plus, unhealthy diet, dyslipidemia, alcoholism, severe stress, etc. Heredity also plays an important role.
An ischemic stroke develops as a result of a disruption in the passage of blood through one of the blood vessels supplying the brain. For example, due to occlusion of the carotid arteries. The cause of a sharp deterioration in cerebral blood supply may be a minor vascular spasm or thromboembolism. In turn, the cause of the latter is often cardiac pathology. The occurrence of the second type of stroke, that is, hemorrhagic, may be associated with the presence of various vascular pathologies. For example, cerebral atherosclerosis, systemic vasculitis and collagenosis. Rarely, but there are still cases when this type of stroke directly depends on blood clotting or incorrect therapy with anticoagulants and fibrinolytics.
What are the symptoms of a stroke?
Of course, the symptoms of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke are different, but they also have common signs. First of all, it is worth noting that the first type of disease develops more slowly than the second. At first, focal and general cerebral symptoms signal a stroke. In turn, the hemorrhagic type develops more rapidly, begins with general cerebral manifestations, against the background of which focal symptoms appear and progressively increase. In the case of subarachnoid hemorrhage, meningeal syndrome is typical.
Now about all the symptoms in more detail. By general cerebral pain we mean severe headaches, nausea, and often loss of consciousness. Focal signs depend on where in the brain the stroke occurs. If in the carotid artery, then there is a decrease or complete loss of muscle strength in the limbs of one side of the body. Homonymous hemianopsia is also possible, that is, loss of the same halves of the visual fields of both eyes. In some cases, photopsia (false appearance of light flashes, sparks, luminous lines) and visual hallucinations are noted. With a stroke in the vertebrobasilar area (it forms the right and left vertebral arteries that supply the cerebellum, trunk and occipital lobe of the brain), dizziness, diplopia, visual field defects, hearing impairment, oculomotor disorders, dysphagia (inflammation of the oral cavity, pharynx of the esophagus) are noted. Since without medical help it is impossible to understand where exactly the stroke occurred, one should rely on general cerebral signs. Once the diagnosis is made, surgical treatment is necessary.
Central retinal vein occlusion
Venous outflow from the vessels of the retina is carried out by one single vessel - the central retinal vein . If this vein becomes obstructed, various problems may occur, proportional to the degree of obstruction. In the case of such a pathology, the patient notices:
* vision impairment,
* blurred image,
* appearance of floaters
* loss of visual fields.
These changes occur unexpectedly and progress over a period of time (from several hours to several days). As a rule, these changes occur in one eye, rarely in both eyes.
The basis of this pathology is, as a rule, vascular changes, blood clots (as well as with blockage of the arteries).
The most effective treatment for this disease is treatment of concomitant diseases (diabetes, hypertension, atherosclerosis) in the hope that blood flow will be restored.
In about a third of all cases, vision is almost completely restored, in a third it remains at the same level, and in a third there is further deterioration and significant loss of vision.
In the most severe situations, it is necessary to resort to laser treatment to prevent dangerous forms of glaucoma . however, laser treatment will not restore vision.
How to treat strabismus during a stroke?
Since strabismus after a stroke is one of the most common problems, the question of how to cure strabismus after a stroke becomes the most pressing. To restore visual function after a stroke, there are several time-tested techniques. These include:
- drug therapy;
- therapeutic and preventive gymnastics for the eyes;
- operation.
What the treatment will be is decided by the ophthalmologist together with the neurologist, taking into account the type of disease, how the stroke progresses, the individual physiological characteristics of the patient and many other factors. In some cases, a comprehensive approach is used to achieve maximum recovery. Below we will talk about each method of treating strabismus after a stroke.
What does drug treatment include?
Despite the great development of medicine, there are still no special drugs aimed specifically at restoring vision after a stroke, but there are drugs that can solve local problems. The effect of medications after a stroke is usually aimed at the following results:
- normalization of blood flow in the brain;
- regeneration of rheological properties of blood;
- elimination of metabolic disorders;
- reducing the volume of necrotic tissue;
- normalizing oxygen delivery to the brain and reducing the sensitivity of cells to its lack.
Using such an integrated approach, it is possible not only to minimize the number of necrotic neurons, but also to restore some sections that were slightly damaged. The ophthalmologist also recommends taking medications aimed at relieving tension and blockage of blood vessels, which will help regulate blood supply. But usually such drugs are used in the first few hours after a stroke in order to eliminate focal signs as soon as possible.
Vasoactive drugs are used to reduce the volume of necrotic tissue. If the patient has increased sensitivity of cells to hypoxia, then vitamin E is prescribed. It is a powerful antioxidant.
Hand exercises
Before developing hands after a stroke, the patient needs to warm them up using a heated towel or a regular burner. The main set of exercises for paralyzed limbs:
- Close your fingers, then raise them above your head for as long as possible and move them to the sides. It is important that the elbows of the raised arms are straight. This exercise for the arms after a stroke should be performed until slight fatigue occurs.
- From a lying position, place the limbs along the body. Then you need to bend your right arm at the elbow joint and slowly lower it. Repeat the action with your left limb. This exercise after a stroke should be performed with each hand 10 times. If the patient is able to do more, there is no need to stop him.
- Pour pencils, pens, buttons and other small objects of different shapes into a deep bowl. The main task is to alternately transfer objects from a bowl to another container. This exercise helps improve motor skills.
Before you restore your arms after a stroke, you need to remember about muscle hypertonicity, which is the main problem when developing limbs. Due to prolonged lack of motor function, muscle tissue loses elasticity and shortens, causing movement to become constrained.
The process of hand recovery after a stroke can slow down when the patient does not perform any actions using the paralyzed limb, loading only the healthy one. It is especially important to ensure that, in addition to complex exercises, the patient strains his non-functioning arm at home.
Before you work out your left arm after a stroke, you need to consult with your doctor, who can choose the most effective set of exercises.
Gymnastic exercises for the treatment of strabismus
This method is certainly one of the simplest, but quite effective. Especially when it comes to strabismus. However, you need to be patient, since eye gymnastics is not the fastest method of restoring vision. The ophthalmologist will tell you more about the exercises that are necessary after assessing the situation. It is worth noting that in most cases, gymnastics only relieves tension from the eyes, eliminates redness and burning, but cannot completely restore vision. It is recommended to train not only the visual organs, but also all parts of the body that have atrophied as a result of the stroke.
Basic methods of vision restoration
Today, there are several methods for restoring vision. Let's look at the basic ones and study the exercises that are included in the complexes of popular authors.
Norbekov's technique
The author of this technique is Mirzakarim Sanakulovich Norbekov, who does not have a medical education! This should be taken into account when performing exercises. We strongly recommend that you first consult with an ophthalmologist when performing gymnastics.
Recovery “According to Norbekov” is based on physical and psychological aspects. It implies:
- gymnastics,
- auto-training aimed at improving the emotional state of the patient.
Norbekov’s position is that only a person who perceives himself as healthy and happy can achieve healing.
The set of exercises developed by the author provides a fairly gentle effect on the visual organs. When performing gymnastics, you should not experience any discomfort.
To achieve maximum effect from exercises, Norbekov recommends:
- follow the sequence of actions;
- perform the complex not only with eyes open and closed, but also mentally;
- tune in to achieve the desired result;
- carry out all actions only in high spirits.
Norbekov’s gymnastics are quite simple. It includes 7 exercises:
- Track with your eyes the movements of an imaginary object, first from bottom to top, and then from top to bottom.
- Move your eyes from left to right and right to left. Imagine that your gaze passes first through your left and then through your right ear.
- Mentally draw various shapes with your gaze. Don't forget to blink regularly. Perform vigorous actions for centuries.
- Draw an imaginary vertical figure eight with your eyes. Make sure that the virtual number does not extend beyond the contours of your face. Alternate directions regularly. Remember to blink after each repetition.
- Concentrate on the tip of your nose. Look ahead of you. Don't move your eyes, but try to look at objects on the sides. Fix your gaze alternately in front of you, on your nose, in the corners of the room, or on specific objects located on either side of your face.
- Bring your index fingers to your nose. Concentrate your gaze on them. Now spread your fingers. Don't lose sight of them.
- Imagine a large clock in front of you. Take a look at the contours of the dial. Try to focus on each number. Perform eye movements first in one direction and then in the other direction.
Zhdanov's technique
The author of the method is Vladimir Georgievich Zhdanov. He also does not have a medical education, but often calls himself a professor. In his opinion, numerous vision problems are caused by malfunctions of the muscular system of the eye.
The gymnastics he proposed are similar to the exercises developed by Bates at the beginning of the last century. According to Zhdanov, simple techniques will help cope not only with myopia, but also with other common pathologies.
All exercises should be performed with 6-10 repetitions. The whole complex will take you 10-15 minutes. Gymnastics includes:
- Eye movements up and down.
- Moving your gaze from right to left.
- "Drawing" diagonal lines.
- Frequent blinking.
- Focusing the gaze on the bridge of the nose, on a close object, on an object located in the distance.
- “Drawing” with the eyes of eights and dials.
Particular attention in Zhdanov’s technique is paid to palming. This exercise allows you to effectively relax. You need:
- Sit at the table in a comfortable position.
- Place your elbows on the surface.
- Place your palms tightly together and close your eyes with them.
- Open your eyelids in absolute darkness.
- Sit for 2-3 minutes.
While palming according to Zhdanov, you should detach yourself from everything that is happening around you.
Tibetan technique
In the East, human eyes are associated with wood and the color of grass.
Adherents of the technique recommend it to office workers, schoolchildren and students and advise:
- Place a green object on your desktop and carefully examine it regularly.
- Surround yourself with plants.
- Several times a day, perform an eye massage, which consists of stroking the eyelids.
- Take 5-minute breaks from work every hour and devote them to gymnastics.
The advantages of the proposed eye exercises include:
- ease of implementation (you can practice not only at home),
- minimum time costs.
The complex includes the following manipulations:
- First, place your index fingers at arm's length from your face. Gradually spread them apart and follow your fingertips with your eyes.
- Now focus your gaze on your fingertips, and then move it as far as possible. Focus on an object in the distance. Fix your gaze on your fingers again.
- Slowly close your eyes, but don't squint. After this, gently press on the eyelids with your fingertips.
- Close your eyes and open your eyelids. Look ahead for a while. At the same time, try not to blink for at least a few seconds.
- Look ahead of you. Now look to the right, then to the left, down and up. Repeat the exercise several times.
- Blink for a couple of minutes.
In the Tibetan method, special attention is paid to washing the eyes. It should be carried out in cold water. If necessary, you can even add ice to it. Pour water into a large, shallow bowl (a large cup will do). Lower your face. Open your eyes underwater and look in different directions. Repeat the exercise at least 10 times. After such washing, the face should be rubbed with a terry towel to stimulate blood circulation.
Surgery to treat strabismus after stroke
Often, for strabismus after a stroke, doctors resort to surgical intervention. It is important to understand that the operation will not eliminate the causes of strabismus and the consequences of a stroke, but will return the eyes to their natural position and reduce the risk of diplopia, that is, double objects, so that a person can normally perceive the world around him. At the moment, there are several types of elimination of strabismus after a stroke. But what type of operation the specialist chooses will depend on the type of strabismus and the general condition after the stroke.
Recommendations
Stroke is an extremely serious disease that leads to damage not only to the visual organs, but also to other organs. Therefore, immediate contact with specialists at the first signs of a stroke is of paramount importance. It is also important to note that an independent disease such as an eye stroke often occurs. In this case, a separate course of treatment is prescribed. The recovery period will directly depend on how quickly medical care was provided and, of course, on the degree of damage and the age of the patient. Today, strabismus after a stroke can be cured in various ways or using an integrated approach. What kind of therapy will be determined solely by the ophthalmologist.
Most common causes of vision loss
Each of us should imagine the degree of danger to the eyes, which sometimes lies in even the most harmless disease or injury. Therefore, the following is a list of the most common reasons that contribute to the loss of visual acuity:
- Conjunctivitis. This is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the organ of vision. The disease can occur due to infection or exposure to allergens. In the first case, to eliminate it, therapy with antibacterial or antiviral agents is necessary (depending on the type of pathogen); in the second, the use of antihistamines that can relieve allergy symptoms. The disease is very often accompanied by lacrimation and mucus secretion. Loss of visual acuity is caused precisely by excess secretions.
- Injuries. Any injury to the eye can cause a sudden deterioration in vision. Therefore, even if there are minor manifestations, you should consult a specialist after it.
- Postoperative complications.
- Common infectious diseases.
- Excessive mental stress, overwork, stress.
Any of the above reasons may lead to a decrease in visual acuity. However, with adequate timely treatment, vision is restored quite quickly and completely. But there are also more serious diseases, which can result in sudden loss of vision, sometimes in one eye, sometimes in both at once. At the same time, recovery, as a rule, continues for a long time and is not always complete.