Atherosclerosis is a dangerous chronic disease that affects both small and vital vessels. It is manifested by a narrowing of the lumen of the arteries due to the deposition of cholesterol derivatives, low and very low density lipoproteins on their inner wall. Atherosclerosis of the vessels of the neck causes a deterioration in the blood supply to brain cells, the appearance of areas of ischemia, headaches and disruption of the processes of nervous activity. This disease can become a trigger for the development of ischemic stroke. Its diagnosis is complicated by the asymptomatic course at the initial stage, so people who are at risk are recommended to undergo periodic examinations.
Causes
The main reason why atherosclerosis of the cervical vessels develops is a violation of fat and protein metabolism. However, it is impossible to determine exactly why pathological changes begin to appear in the vascular walls. There are several theories that can explain the onset of the disease development mechanism:
- lipoprotein infiltration - states that lipoproteins primarily accumulate on the inner surface of blood vessels, which then permeate it and form atherosclerotic plaques;
- dysfunction of the endothelium - initially the inner wall of the arteries undergoes pathological changes, as a result of which its protective properties are lost;
- autoimmune - a disease associated with a disruption of the immune system, as a result of which its cells (leukocytes and macrophages) settle on the inner surface of blood vessels;
- monoclonal - changes in the composition of smooth muscle cells that form the middle lining of the arteries;
- peroxide - disruption of the body's antioxidant system, intense reactions of lipid peroxidation, which leads to the processes of premature aging and apoptosis (programmed death) of cells;
- other theories, including viral, hormonal and genetic - each of them has scientific evidence.
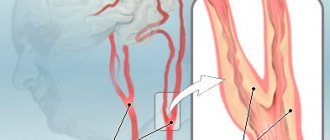
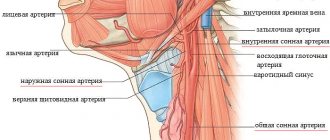
In the neck area passes the common carotid artery, which further branches and forms several branches. This is a paired main artery, which is responsible for the blood supply to the skin, muscles, organs of the neck and head, including the brain. It is just as susceptible to the development of atherosclerosis as small vessels.
IMPORTANT! Atherosclerosis in the neck area poses a danger to human life. Atherosclerotic plaques clog blood vessels and prevent normal blood flow to the brain.
Risk factors
According to statistics, atherosclerosis of the vessels of the neck and head is more common in men. Most patients with pronounced clinical signs are over 55–60 years of age. This is due to age-related changes in cells and tissues, deterioration of blood circulation, and a decrease in the strength and elasticity of vascular walls.
Pathological changes in atherosclerosis are irreversible - deposits on the internal walls do not resolve
There are risk factors that make the appearance of plaques in blood vessels more likely. These include:
- smoking - nicotine, tar and other components of cigarette smoke have a detrimental effect on blood vessels;
- chronic increase in blood pressure up to 140/90 mm Hg. Art. and more;
- violation of fat, protein, carbohydrate metabolism;
- hereditary predisposition - a history of atherosclerosis in relatives;
- unhealthy diet – high content of cholesterol source in the diet (animal fats);
- sedentary lifestyle, obesity;
- chronic diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus);
- infectious diseases;
- disorders of blood clotting and its viscosity indicators.
It is important to understand that cholesterol is normally present in the blood. It is also impossible and ineffective as a preventive measure to completely abandon products that contain it. Pathological changes begin only when this substance begins to accumulate in the vascular walls. They can be triggered by various factors, including chronic metabolic diseases, disorders of cholesterol metabolism and age-related changes.
Removal of cholesterol plaques in the carotid artery
Removal of cholesterol plaques on the carotid artery at the second stage (fibrosis) and at the third stage (calcionosis) can occur in several ways:
- increasing blood (arterial) pressure - but this path is fraught with the formation of new damage to blood vessels and, as a consequence, the formation of new atherosclerotic deposits;
- dilatation of blood vessels, however, this method is ineffective on the carotid artery and is used more often for varicose veins of the extremities;
- increased tone of blood vessels;
- cleansing the blood of cholesterol - however, this method does not so much destroy existing plaques as prevent the formation of new ones.
The cost of removing cholesterol plaques on the carotid artery using medications is entirely determined by the cost of the drugs used. The cost of surgical treatment (carotid endarterectomy, angioplasty, stenting) is even higher if it is not done according to the insurance policy. Surgical treatment is resorted to when conservative methods fail.
Conservative methods of removing cholesterol plaques include taking specialized medications, increasing the proportion of foods in the diet that cleanse blood vessels of cholesterol, performing (daily) therapeutic exercises for atherosclerosis, and taking statins or other medications for high cholesterol.
How to remove cholesterol plaques from the carotid artery safely? Surgery has some risks, and drug treatment has contraindications and side effects. Drug treatment can be aimed at reducing the level of cholesterol synthesis by the liver, increasing energy metabolism in cells - this is how it is possible to remove excess cholesterol from the blood and carotid arteries. An alternative is infusions and herbs for cholesterol plaques, but their effectiveness remains unproven.
Symptoms of the disease
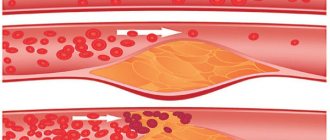
Atherosclerosis of the neck arteries in the early stages is asymptomatic. First, a fatty spot forms on their inner wall, to dissolve which special enzymes are synthesized. However, they fail to cope with this function, and lipid deposits begin to grow and increase in size. At this stage, stenosis occurs - narrowing of the lumen of the vessel. This phenomenon is dangerous for the patient’s life, since plaques can impede the flow of blood to the brain, and in later stages, completely block the arteries.
Doctors recommend contacting for a full diagnosis when the first symptoms of the disease appear:
- weakness that comes on suddenly and goes away after circulation is restored;
- frequent headaches, dizziness;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- confusion of thoughts, memory loss, deterioration of attention and concentration;
- numbness, decreased sensitivity of facial skin;
- difficulty speaking.
Signs of atherosclerosis often first appear during a microstroke, or transistor ischemic attack. It is triggered by a short-term cessation of oxygen supply to the brain, caused by blocking the lumen of the vessels of the cervical spine. This condition is dangerous, because with prolonged oxygen starvation, nerve cells die and are not restored, and rehabilitation is long and consists of the formation of new neural connections. If there are predisposing factors, it is recommended to undergo periodic scheduled examinations for early detection of the disease and its timely treatment.
Atherosclerosis can manifest itself not only in the vessels of the neck, but also in other parts of the circulatory system. Thus, when the intestinal arteries are damaged, the functioning of the digestive tract is disrupted, and the formation of plaques in the vessels of the upper and lower extremities is also characteristic. With disease of the coronary arteries, which carry blood to the myocardium, there is a risk of developing coronary heart disease and heart attack.
Frequent headaches and surges in blood pressure are the first symptoms of cerebrovascular accident
Symptoms
Because carotid atherosclerosis develops slowly and is often asymptomatic, the first manifestation of this disease may be a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA), sometimes called a mini-stroke. TIA causes stenosis of the carotid arteries: they are accompanied by headaches, short-term loss of vision and speech impairment, numbness of half the body and limbs.
A stroke or TIA is a medical emergency. If you or a loved one shows signs or symptoms of a stroke, call emergency medical services immediately. Do not try to get to the hospital on your own. Warning signs and symptoms include:
- Sudden numbness or weakness in the face and limbs, often on only one side of the body
- Loss of ability to move limbs
- Impaired speech and understanding of the meaning of someone else's speech
- Sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes
- Dizziness or loss of balance
- Sudden severe headache without a specific cause
Types and stages of atherosclerosis of the cervical arteries
Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease that progresses over time. There are several stages in the development of the disease, which replace each other as it develops. Each of them is characterized by certain biochemical changes in the internal walls of the arteries.
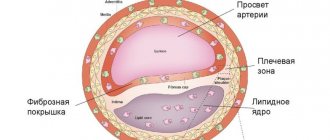
- The first is the fat stain stage. At this stage, the movement of blood through the vessels is not difficult, but lipids and cholesterol accumulate on the endothelium. The enzymes that are activated to break them down do not cope with their functions, so fat deposits increase. The vascular wall becomes loose, less strong and elastic.
- Liposclerosis is the second stage, at which the accumulation of not only fat, but also connective tissue occurs. This leads to the formation of an atherosclerotic plaque. At first it is liquid and can dissolve, but then it becomes dense.
- Atherocalcinosis is the accumulation of calcium salts in the chemical composition of the plaque. Due to this element, it becomes strong and clogs the lumen of the artery, causing disruption of blood flow.
Depending on the stage of atherosclerosis, the nature of its course and other factors, several types of this disease are distinguished. They differ in symptoms and degree of danger for the patient:
- non-stenotic - atherosclerosis, in which there is no narrowing of the lumen of the arteries, can be diagnosed in the early stages;
- stenosing - deposits and plaques cause narrowing of the vessel and a decrease in blood flow to the brain;
- obliterating - manifests itself when plaques form, which partially or completely block the vessels of the neck.
REFERENCE! A dangerous complication of atherosclerosis is the formation of a plaque, which then breaks off from the inner surface of the vessel and migrates with the bloodstream. It can cause acute cerebrovascular accident - ischemic stroke.
What it is
First, it is necessary to explain what atherosclerotic plaques are. The development of atherosclerosis begins with cholesterol deposits on the walls of the arteries, aorta, large and small capillaries, which can be located in any part of the body.
To ensure that all internal organs and the brain are fully supplied with blood, the inside of the vessels is lined with a special layer - the endothelium. With excessive accumulation of lipid substances inside the capillary, its lumen becomes narrower, the endothelium suffers from the introduction of “bad” cholesterol. The walls of the arteries become rougher and tougher.
As the disease progresses, the calcified growths increase in volume and harden, taking on the shape of tubercles, which is why the lumen of the artery may be completely blocked. Plaque formation typically occurs in all areas of the body, and the resulting bumps contain calcium and foreign substances.
Diagnostic methods
Early diagnosis of atherosclerosis is the key to its successful treatment and prevention of dangerous complications. If you experience frequent headaches, dizziness and other signs of illness, you should consult a doctor to determine their cause. The examination scheme is selected individually and may include the following methods:
- physical examination and medical history, including changes in blood pressure;
- blood tests - the concentration of various fractions of cholesterol and lipoproteins is determined in the laboratory;
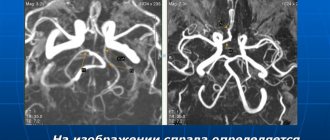
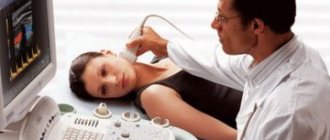
- Dopplerography - ultrasound examination of blood flow velocity in a certain area, carried out using a contrast agent;
- Computed angiography is a modern technique that allows you to track not only the characteristics of blood flow, but also the exact location and structure of blood vessels in the area under study.
Preventive examinations are recommended annually after the age of 50 years. They are necessary to detect the disease in its early stages, at which its development can be stopped.
It is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis at home; this will require complex instrumental techniques
Treatment of atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis must be treated immediately after its first symptoms appear. In this case, conservative methods will be quite effective and will help achieve stabilization of the condition. In each case, the regimen is selected individually - it depends on the stage of the disease, clinical signs, age of the patient and concomitant pathologies.
Conservative treatment necessarily includes diet. For atherosclerosis, it is recommended to avoid fatty and fried foods and reduce the consumption of meat and offal. The basis of the diet should be cereals, fruits and vegetables, lean meats and fish. Vasodilators and specific agents to normalize lipid metabolism may also be prescribed.
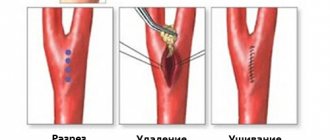
In later stages of atherosclerosis, surgical treatment may be required. The operation is carried out in several ways:
- installation of a catheter to expand the lumen of the damaged vessel;
- carotid stenting is a minimally invasive technique in which a stent is installed in the affected arteries under endoscopic control;
- open surgery, the most invasive method;
- carotid endarterectomy is a method of intervention in which the lumen of the vessel is cleared of harmful deposits under endoscopic control.
Atherosclerosis is a dangerous vascular disease that leads to disruption of the blood supply to certain organs and tissues. The neck area contains vital arteries that carry blood to the brain, so damage to them is especially dangerous. To prevent dangerous complications, including stroke, it is necessary to undergo routine examinations, monitor your well-being and not miss the first signs of the disease.
Cholesterol-lowering drugs
Statins are a group of drugs designed to reduce cholesterol levels in the blood. The action of statins is based on blocking the formation of cholesterol in the liver, which reduces its level in the blood, since all the cholesterol in the body is produced there, and does not come from food. The cholesterol that we eat is only material for the synthesis of our own.
- Rosuvastatin – Crestor (Rosucard, Rozulip, Tevastor)
Prescribed to patients at high risk of stroke and heart attack. Taking Rosuvastatin depends on the level of lipids in the blood and is in a standard dosage of 5 to 10 mg per day.
- Atorvastatin – Liprimar (Tulip, Torvacard, Atoris)
Atorvastatin is a very effective drug with minimal side effects. Suitable for long-term use.