Aching, headache... How often do we have to talk about this. And sometimes a person does not attach importance to the onset of a migraine, attributing his poor health to a sharp change in temperature, pressure changes, age, or simply to his own fatigue or lack of sleep. Most people take headaches for granted and do not consider it a problem. But, in fact, such a harmless symptom may hide processes that are dangerous to the body. For example, discirculatory encephalopathy. Simply put, it is a narrowing of blood vessels in the brain. Due to the narrowing, blood does not flow to the brain in sufficient quantities. And if a large area of the brain is damaged by this process, a “harmless” headache or dizziness can lead to ischemia.
Conditions for the occurrence of narrowing of veins and arteries
The causes of vasoconstriction are very diverse. They depend on the type of vessel, external and internal factors, and the duration of their exposure.
External reasons
Arteries have a pronounced muscular layer, so they more often react with spasm to unfavorable factors. During spasm, small arteries narrow temporarily, but frequent repetition can lead to loss of the ability to relax and become stable.
Contributing factors are:
- smoking,
- stressful situations,
- alcohol consumption,
- hypothermia.
A similar external effect on the arteries is observed:
- with the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- in the initial stages of hypertension and ischemic disease;
- with frostbite of the extremities;
- with Raynaud's syndrome.
Longer-term narrowing of arterial vessels from external factors is observed with mechanical compression:
- during severe injuries (long-term compartment syndrome);
- tumor growth near blood vessels;
- the pressing action of the bone tissue of the spinous processes of the spine;
- prolonged incorrect use of a tourniquet to stop bleeding (this is why first aid requires placing a note indicating the time of application).
Internal reasons
Internal causes of vasoconstriction include:
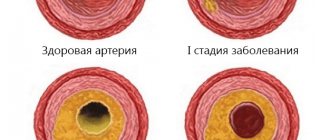
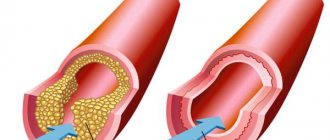
- atherosclerotic damage to the wall - between the middle and inner membranes of arteries of the muscular-elastic type, a low-density fraction of lipoproteins is deposited with the formation of plaques, over time they are supplemented with calcium salts, the lumen of the vessel loses its diameter;
- inflammatory changes (vasculitis, arteritis) - swelling of the walls reduces blood permeability;
- endarteritis - an unclear allergic reaction from the intima of the arteries of the legs and arms, leading to complete obliteration of the vessel;
- congenital pathology (aortic stenosis);
- thrombosis and embolism - play an important role in the development of pathology of the brain and heart;
- metabolic disorders in diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis, obesity.
Causes of deterioration of blood circulation in the brain
In some pathologies, stenosis (narrowing) of the lumen of the vessel or its obstruction (blockage) occurs. As a result, the speed of blood flow slows down, ischemia (oxygen starvation of the tissue) occurs in certain areas of the brain, leading to necrosis (death) of the tissue.
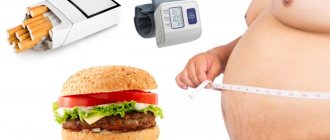
Risk factors are:
- hypertension;
- cardiac ischemia;
- diabetes;
- hormonal imbalance, including the use of contraceptives;
- atherosclerosis;
- overweight;
- physical inactivity;
- stress;
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- lipid metabolism disorder.
When do veins narrow?
The venous system is more prone to lose tone, but there is a pathology that leads to a persistent gradual loss of the diameter of the venous capillaries, and then the cessation of blood supply. We are talking about cirrhosis of the liver. All blood flowing from the tissues necessarily passes through this organ. With chronic inflammation of the lobules of liver cells (hepatocytes) and replacement of the interlobular space with scar tissue, the venules narrow. Then the blood flow through them completely stops. Problems arise in the area of the portal vein. Due to its sharp narrowing, hypertension and stagnation occur in the underlying sections, and overload of “excess” into the veins of the esophagus.
On the right is the liver of a patient with cirrhosis, there are no vessels between the compacted lobules
Thrombophlebitis (inflammation + thrombosis) cannot be excluded as a cause. In diseases that cause a decrease in blood flow velocity (stagnation), the process of parietal thrombus formation is activated. The spread of infection from chronic foci increases the narrowing of the affected area of the vein.
Symptoms of circulatory disorders due to altered vascular lumen depend on the specific location of the affected area. Let's look at the manifestations of the most significant diseases.
Vascular atherosclerosis: treatment and diagnosis at CBCP
At an early stage of the disease, it is extremely important to undergo a high-quality diagnosis and begin treatment, during which negative consequences can be minimized. If you notice alarming symptoms, contact the Center for Circulatory Pathology, where you will be offered modern diagnostics and effective treatment methods.
CBCP provides a wide range of methods that provide objective and detailed information about the patient’s condition: location of pathology, complexity, possible complications.
Clinical manifestations of impaired blood supply to the brain
Signs of cerebral insufficiency are caused by narrowing of the carotid and vertebral arteries, which carry blood to the brain.
For adults, the main importance is given to:
- atherosclerosis;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- congenital pathology of vertebral vessels;
- hypertension;
- thromboembolic complications.
The disease can take a long-term chronic course or occur suddenly in the form of a stroke.
For the child, the most important are:
- mother's condition during pregnancy;
- birth injuries;
- previous vasculitis due to childhood infections;
- congenital pathology of the heart and blood vessels.
If you faint, a stroke cannot be ruled out.
In acute cases, concern:
- severe headaches;
- dizziness to the point of loss of consciousness;
- noise in ears;
- impaired vision;
- decrease or disappearance of sensitivity and movements in the limbs;
- impaired speech.
Chronic deficiency occurs gradually, all symptoms begin with irritability, insomnia, and impaired attention. Then memory loss, fatigue, headaches, and insomnia increase. Further narrowing of blood vessels leads to a change in personality, the inability to contact others, and movement disorders.
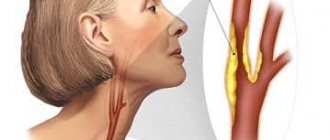
Clinical features for narrowing of arteries in the neck
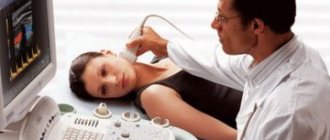
Atherosclerosis of the carotid artery is considered the first manifestation of the disease. It is detected during Doppler sonography in individuals who do not yet have symptoms. Osteochondrosis affects the processes of the vertebrae in the cervicothoracic region, which compress the vertebral artery. The patient is concerned about:
- headaches in the temples, back of the head, forehead;
- feeling of "pressure";
- connection of well-being with turning and tilting the head to the side;
- dizziness, darkening of the eyes;
- possible loss of consciousness;
- nausea, vomiting.
Less often they complain of numbness of the tongue and hands.
Symptoms of carotid artery stenosis
The disease is dangerous because the symptoms are practically invisible, and only when stenosis becomes the cause of other pathological conditions does a person consult a doctor. Among such conditions, ischemic attacks (mini-stroke, small stroke) are primarily distinguished, when the blood supply to the brain is disrupted for a short period of time. This condition manifests itself as follows:
- numbness of hands/arms,
- speech distortion,
- temporary loss of vision, visual acuity,
- temporary disorientation,
- numbness of the face.
And more general symptoms
- headache,
- nausea,
- weakness.
Carotid artery stenosis develops slowly, often asymptomatically, and people attribute general fatigue and increased fatigue to excessive stress or the weather. Therefore, doctors recommend carefully monitoring your condition, and, if you experience prolonged general weakness without obvious reasons, contact a specialist. Some diseases are so dangerous if not diagnosed promptly that the risk of their presence justifies an unplanned trip to the doctor, who will reassure you if there is no cause for concern, or carry out the necessary diagnostics if suspicions arise.
What manifestations suggest a narrowing of the blood vessels of the heart?
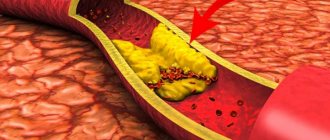
The vessels of the heart or coronary arteries are very sensitive to factors contributing to spasm. And the local location of atherosclerotic plaques in them seriously changes the blood supply to the myocardium. “Oxygen starvation” manifests itself:
- attacks of angina pectoris;
- arrhythmia.
The pain is pressing or squeezing in nature, located behind the sternum or on the left, radiating to the left jaw, shoulder blade, arm, lasting up to 30 minutes.
With more intense and prolonged pain, severe weakness of the patient, and a feeling of arrhythmia, one should think about acute myocardial infarction. In this case, the narrowing of the vessel leads to an area of tissue necrosis.
Slow blood flow through the narrowed area promotes the formation of a blood clot
Coronary artery stenosis - symptoms and treatment
There are two groups of treatment methods:
- conservative and medicinal;
- surgical.
In the early stages of the disease, conservative treatment . It involves changing your lifestyle towards a healthy one, giving up bad habits, optimizing your level of physical activity and following a low-cholesterol diet. Meals should be fractional. The consumption of salt, sweets, alcohol, fatty meats and baked goods is limited. The diet includes vegetable oils, fish oil and complex carbohydrates found in cereals. It is also important to drink up to 2 liters of liquid and change the principle of cooking: foods should be boiled, stewed or baked.
For coronary heart disease, medications are prescribed , for example:
- hypocholesterol drugs - reduce blood cholesterol levels (statins, fibrates, PCSK9 inhibitors, ezetimibe);
- disaggregants and anticoagulants - “thin” the blood, reduce its coagulability and viscosity, prevent the formation of blood clots (acetylsalicylic acid, clopidogrel, warfarin, apixaban, rivaroxaban, dabigatran, prasugrel);
- antianginal - dilate blood vessels, prevent attacks of angina (nitroglycerin, amlodipine, sidnopharm, bisoprolol, ranolazine);
- angioprotectors - protect blood vessels from damage and stretching (ACE inhibitors);
- medications to stabilize blood pressure, reduce heart rate and prevent arrhythmias - diuretics (indapamide, hypothiazide, torsemide), ACE inhibitors (ramipril, perindopril), beta-blockers (metoprolol, bisoprolol) and ivabradine;
- metabolic - normalize metabolism (trimetazidine, neoton).
The duration of use for each drug is different. Dose adjustments and replacement of medications are carried out strictly under the supervision of a physician.
Surgical treatment includes two main types of treatment for coronary artery stenosis:
- stenting;
- shunting.
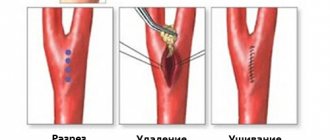
Stenting involves installing a stent into a narrowed vessel. The stent is a metal frame. Using a guide through the femoral or radial artery, this frame is advanced to the affected coronary artery, fixed there and straightened. It prevents the artery from narrowing and normalizes blood flow.
Stenting is performed both planned for the prevention of myocardial infarction and urgently. The operation is minimally invasive: it does not require extensive incisions or general anesthesia.
Bypass surgery aims to create a new blood flow path around the blocked vessel. The material for the shunt is the patient's own veins and arteries. The surgeon stitches them above and below the narrowing of the coronary artery.
Such manipulation involves opening the chest, often leading to long rehabilitation and serious complications, such as ischemic stroke, anemia, arrhythmia, blockage of shunts with a blood clot, prolonged healing of the sternum with the formation of a false joint and the formation of fluid in the lungs, swelling and long healing of the leg [1] [2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10][13][14][15][16][17][18][19][20 ][21].
There is also a third surgical method for treating stenosis - endarterectomy . It involves removing a blood clot and cholesterol plaque from the lumen of the heart artery. However, now endarterectomy is practically not used, since it is accompanied by high risks and does not exclude the re-formation of blood clots.
Symptoms of insufficient blood supply to the legs
Signs of narrowing of the arteries of the lower extremities are detected in obliterating endarteritis, vascular atherosclerosis, and Leriche syndrome.
Concerned:
- pain in the legs, first only when walking, then at rest;
- symptom of “intermittent claudication”, after stopping the pain disappears;
- numbness and chilliness of the feet;
- increased sweating;
- cramps in the calf muscles;
- in severe stages, trophic disorders - ulcers, non-healing cracks in the feet, gangrene.
What does narrowing of the fundus arteries indicate?
The fundus arteries undergo the same changes as others. They are considered a “mirror” of the state of cerebral circulation. The degree of narrowing is influenced by the following external and internal reasons:
- bad light;
- eye strain when working at a computer;
- watching TV for a long time;
- increased blood pressure.
The patient complains of:
- blurred vision;
- headache;
- throbbing pain in the eyeballs.
The ophthalmoscopy procedure allows the ophthalmologist to examine the arteries and veins of the fundus of the eye.
Prevention of cerebral atherosclerosis
- Daily physical exercise will help keep your blood vessels toned: physical activity that is appropriate for your age should be at least 40 minutes a day.
- To normalize cholesterol levels, watch your diet, weight, follow a special diet, and give up bad habits.
- Walk more in the fresh air to saturate your blood with oxygen.
- Limit emotional stress - protect yourself from stress.
- Monitor your blood pressure and glucose levels.
How to treat narrowed blood vessels
Treatment for vasoconstriction depends on the underlying causes. If there is a connection with external factors, their complete exclusion is necessary. Any temporary spasm carries the possibility of turning into permanent obstruction. Therefore, you should take the recommendations for regimen and diet seriously:
- stop sitting at night in front of the computer and TV;
- normalize sleep;
- pay more attention to active recreation, walks;
- learn to relieve stress;
- establish nutrition according to the requirements of an anti-atherosclerotic diet (do not indulge in coffee, spicy foods, fatty meat dishes, add enough fruits, vegetables, and dairy products to the diet);
- choose feasible exercises and do morning physical exercises.
You should treat your illness with medications only as prescribed by your doctor.
If necessary, the following are prescribed:
- cholesterol-lowering agents;
- antispasmodics;
- medications that stimulate collateral (auxiliary) blood circulation;
- drugs that strengthen the vascular wall;
- means to reduce tissue oxygen demand;
- vitamin complexes;
- physiotherapeutic supportive treatment.
The diagram shows connecting “tubes” - these are the auxiliary vessels at work
Disturbed metabolic processes in tissues are treated with antioxidants and nootropics.
Depending on the severity of the patient’s condition and after determining the degree of narrowing of the afferent vessels, angiosurgeons choose surgical treatment. Methods include:
- replacement of a damaged vessel with an artificial analogue;
- bypass installation operation;
- removal of a blood clot from a large artery;
- installation of stents to expand the spasmodic area.
Get ahead of the disease and help yourself
The prognosis for a disease such as cerebral vasoconstriction depends mainly on how quickly it was diagnosed and how quickly treatment was started. The technique should only be determined by the attending physician. Because in each specific case, tactics must be individual. However, the following can serve as general recommendations:
- It is necessary to change the food system, where the daily diet must certainly consist of fresh vegetables and fruits containing useful substances and always greens! Be sure to include fish in your daily menu, but it is better to limit sweets, smoked foods, sausage, carbonated water, and salt or eliminate them altogether.
- You should reconsider your lifestyle and engage in more sports, go for walks in nature more often, get fresh air, start an active, eventful life, prevent excess weight, and move a lot.
Is it possible to be treated with traditional methods?
You cannot straighten a narrowed vessel with folk remedies. You should not collect and test on yourself numerous “tips” for cleaning and getting rid of atherosclerosis.
Using a combination of garlic, lemon and honey is more of a dietary recommendation. It has a good effect on the immune system, so it is always useful. The product will help in the recovery period after stress, injury or infection. But it is impossible to “dissolve plaques” at the current level.
Medicines will help delay further narrowing. People's advice can be tried against the background of their application.