Every day, patients who are bothered by pressing pain in the heart area come to see a cardiologist. There may be several reasons for this condition, and these are not always cardiovascular pathologies. In any case, this symptom cannot be ignored, since life-threatening diseases cannot be excluded. For example, myocardial infarction or the most severe manifestation of allergies – anaphylactic shock. Although it is believed that pressing pain in the heart is not typical for a heart attack, this option is quite possible.
How to distinguish heart pain?
As a rule, cardiac problems are not particularly pronounced, and patients usually describe their sensations quite briefly. At the same time, patients suffering from neuroses usually talk in great detail about the numerous and very diverse manifestations of the disease. The following signs indicate the cardiac origin of pain:
- increase in heart rate – tachycardia;
- dizziness, which may appear for a short time or be constant;
- heart rhythm disturbance - arrhythmia;
- dyspnea;
- pale or bluish skin tone;
- pain radiates to the back, left arm, jaw;
- nausea and vomiting;
- fainting.
Causes of true heart pain
True heart pain occurs due to malnutrition of a certain area of the heart muscle. This is possible with:
- spasm of the coronary vessels, their impaired tone, incorrect reaction (hypertension, vegetative-vascular dystonia);
- inflammation of the myocardium (myocarditis);
- the occurrence of ischemia from a pronounced atherosclerotic process or thrombosis;
- myocardial dystrophy and cardiosclerosis;
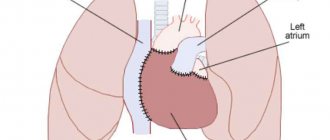
- heart defects;
- chronic heart failure.
Ischemic pain is most pronounced in acute myocardial infarction. They are intense, retrosternal, last up to a day or more, and are accompanied by pallor and a drop in blood pressure.
Angina pectoris often depends on physical or emotional stress. Substernal pressing pain radiates to the left, to the shoulder, shoulder blade, jaw.
Other heart diseases cause long-term, intermittent, dull or stabbing pain with varying degrees of radiation. Accompanied by arrhythmia, increased blood pressure, body temperature, dizziness, and general weakness.
Women often complain with complaints during menopausal changes in the body. Here the pain is caused by a lack of sex hormones. They are provoked by anxiety and poor nutrition. Accompanied by many vivid emotions: fear of death, suffocation (without increased breathing), darkening of the eyes, interruptions in rhythm, sweating. In men, menopause also matters, but it usually occurs later and coincides with the development of atherosclerosis and true ischemia.
Angina pectoris
Compressive pain in the heart may indicate angina pectoris. It is caused by insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle. Pain during angina pectoris is paroxysmal in nature and is not constant. It occurs suddenly, usually during physical activity (fast walking, running, lifting weights) or emotional shock. The patient complains of squeezing pain in the heart, radiating to the arm, shoulder blade, neck, and lower jaw. Sometimes there is a burning sensation in the chest, like heartburn. As a rule, during an attack of angina, blood pressure rises. The pain goes away if the person rests, calms down, or takes a nitroglycerin tablet.
Diagnostics
After an in-person examination, collection of anamnesis and communication with the patient, the doctor creates an examination plan. It includes:
- pulse measurements;
- blood pressure monitoring for 7–14 days;
- auscultation of the heart;
- neurological tests;
- general blood analysis;
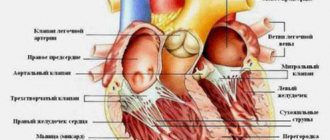
- electrokariogram (ECG);
- Ultrasound of the heart (EchoCG);
- X-ray of the chest organs (survey and targeted when suspicious areas are detected);
- FGDS;
- MRI or CT scan with or without contrast agent;
- endoscopy;
- X-ray of the stomach with contrast;
- X-ray diagnostics or MRI of the spine.
Such an examination will create a complete picture of the disease. Based on the data obtained, treatment is prescribed.
Myocarditis
Another cause of pressing pain in the heart is myocarditis. This is an inflammation of the heart muscle, most often of infectious and also toxic origin.
Heart pain is the most common complaint with myocarditis of any nature. They can manifest themselves in different ways: cutting, stabbing, aching or pressing. Attacks can be repeated several times during the day, but they are not relieved by nitroglycerin.
In addition to the pressure in the chest, other signs are observed with myocarditis:
- elevated temperature;
- general weakness;
- prostration;
- fast fatiguability;
- feeling of a sinking heart;
- dyspnea;
- interruptions in heart function;
- cardiopalmus.
Pressing chest pain can be a sign of various diseases, both cardiac and non-cardiac
"Bad" cholesterol will never become good cholesterol
— You often hear from doctors about risk factors that every person should know about. But what is it and what should you pay attention to first?
- The most important risk factors for cardiovascular mortality, which had already become known by the end of the 50s, are the following conditions and diseases: age and family history - factors that cannot be influenced. But there are other factors: smoking, arterial hypertension, cholesterol levels, diabetes, obesity, which can be influenced. By the forties of the twentieth century, it became clear that people most often die not from infections, as was the case before, but from cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, the American Heart Institute was organized, and since 1948, in Framingham, a small town near Boston, all residents of the city were included in a study that continues to this day. They measured blood pressure, sugar, fibrinogen and many other indicators. These data were subsequently confirmed in large randomized controlled trials. Special tables have been created that allow one to estimate the risk of death within 10 years depending on the presence of selected factors. By the way, controlling these risk factors lengthens life and improves its quality.
— And what level of cholesterol in the blood can be considered normal?
— Not so long ago, a cholesterol level of 6.5 mmol/liter was considered the norm in Russia, and 3.5 mmol/liter in Japan. Now in Europe, the USA and Russia, the normal level of total cholesterol is considered to be below 5.2 mmol/l. However, the main indicator is low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, popularly called “bad cholesterol”. In people with a low risk of developing coronary heart disease, it should be less than 3.0 mmol/l, in patients with a high risk - less than 2.6 mmol/l, and in those who have atherosclerosis and its complications - coronary heart disease, brain disease and other vascular zones, its target level is less than 1.8.
— I was prescribed statins, but I’m afraid to take them, supposedly they cause cataracts, strokes, diabetes, impotence, etc. Is this true?
— Cholesterol in elevated quantities actually causes a number of diseases, primarily vascular damage. Statins are drugs that lower cholesterol levels, thereby preventing these diseases. But in addition to this, statins also have a unique anti-inflammatory effect inside blood vessels. To date, there are no drugs in this area that are more effective than them, and with few side effects. As for cataracts, stroke, impotence, research results do not confirm these complications. An increased incidence of diabetes mellitus was shown in one recent analysis, but mainly in patients with a hereditary predisposition to the disease. In diabetes mellitus, the benefits of such drugs are especially high, since it is with this disease that atherosclerosis develops more often and earlier.
photo: Alexandra Zinovieva
But: statins are not prescribed in the presence of severe liver failure and liver diseases; for this purpose, biochemical markers are initially monitored.
— Are statins prescribed in old age? I am 64 years old. When walking, pain began to arise in the legs, which went away very quickly after stopping. I can walk about 300–400 meters at a slow pace. Is this related to smoking? And where should I go?
— Statins are especially effective in old age, when the processes of growth of atherosclerotic plaques are most active. For patients over 80 years of age, I try to prescribe not the highest doses, taking into account the condition of other organs. As for pain in the legs, then, most likely, you have developed obliterating atherosclerosis of the arteries of the legs, which is characteristic of smokers. That is, the arteries that bring oxygenated blood to the legs are partially blocked by atherosclerotic plaques. Smoking often leads to damage to the arteries in the legs. What should we do now? First of all, do not wait for complete closure of the vessels and gangrene, but quit smoking to stop the progression of the process. Then do an ultrasound duplex scan of the arteries of the legs, preferably the vessels of the neck - smoking is the enemy of all blood vessels. Your cardiologist will then prescribe therapy to stabilize the plaque and improve blood flow. It will also become clear whether and what kind of vascular surgery is necessary. In any case, the success of therapy and surgery depends on you - you must quit smoking.
“My dad suffered a stroke, and now doctors say that more than half of his carotid arteries are closed. We are afraid of surgery. How can we solve this problem?
— If during the last six months your father suffered a stroke and a vascular examination revealed stenosis in the carotid arteries of more than 70%, then he is indicated for revascularization surgery, that is, an operation to restore normal blood flow in the arteries of the brain. In addition, all patients with atherosclerotic changes in the carotid arteries should receive optimal drug therapy to reduce cholesterol, blood pressure, blood sugar, etc.
Cardioneurosis
This disease is associated with a disruption in the functioning of the central nervous system, but, as a rule, no changes in the heart muscle occur. However, patients experience severe squeezing pain in the chest, reminiscent of angina pectoris. The pain can radiate to the shoulder blade, forearm, and lower jaw, so patients are often convinced that they are suffering from a serious cardiac disease. In this case, the pain can be permanent and does not go away with nitroglycerin, but the condition improves after taking sedatives, eliminating stress, normalizing the daily routine and giving up bad habits. In addition to pressure in the heart, the following manifestations are characteristic of cardioneurosis:
- anxiety;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- fainting conditions;
- increased sweating;
- sleep disorders;
- rapid fatigue even with low physical activity;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- difficulty trying to take a deep breath;
- spasm of the esophageal muscles during swallowing.
Symptoms may intensify with emotional stress, lack of sleep, drinking alcohol, strong coffee and tea, medications, and smoking.
Discomfort not related to the heart
The main physiological problems with similar symptoms are the following pathologies:
- Disorders in the musculoskeletal system - osteochondrosis of the cervical and thoracic spine, intercostal neuralgia associated with pinched nerve roots.
- Gastrointestinal diseases - ulcerative lesions, tumor formations of the stomach and esophagus, hernia, gallstones.
- Problems with the functionality of the respiratory system - inflammation of the lining of the lungs (pleura).
- Neurosis and panic attacks are emotional imbalances in the body associated with an acute experience of a stressful situation.
Determining whether the listed anomalies relate to cardiac disorders is helped by the addition of accompanying symptoms, which include deterioration of well-being without signs of shortness of breath, rapid pulse, and the spread of pain to the upper extremities, neck or face. It is important to remember what preceded the onset of discomfort, whether there was severe hypothermia or high physical activity before this.
What to do with pressing pain in the heart?
If you detect pressing pain in the heart area, you must go to the hospital for examination. Such a symptom may indicate different diseases that require different treatments.
If it is angina, you need to stop or sit down, provide air access, take nitroglycerin, and the pain will go away in five minutes.
Treatment for myocarditis depends on the cause of its occurrence, but in any case bed rest is required. Anti-inflammatory and desensitizing drugs are usually prescribed; in case of a bacterial infection, antibiotics are prescribed.
For neuroses, a healthy lifestyle is recommended. You need to avoid stress, spend more time outside, follow a daily routine, get enough sleep (at least eight hours a day), engage in physical labor, and get rid of bad habits. As a rule, herbal sedatives (motherwort, valerian) are prescribed. In more severe cases, tranquilizers may be prescribed.
How and where is a heart test performed?
The best way to determine the source of pain is a tomographic examination using an MRI machine. It can be carried out in any clinic that has the necessary equipment. You can find the nearest organization on the website of the unified registration service or get a free consultation by calling the phone number listed at the top of the page. Choose a diagnostic center, sign up for a scan and receive a special discount from the service in the amount of 1000 rubles.