Veins are blood vessels that carry blood to the heart. In turn, blood is collected in the veins from capillaries. With healthy arteries, the circulatory system works stably. But what happens if problems arise with the veins? Swelling, pain in the legs, slight numbness, goosebumps, heaviness, impaired sensitivity in the form of paresthesia, convulsions, trophic disorders. These signs, repeated day after day, are most likely recognized by the doctor as venous insufficiency.
Excess body weight can lead to varicose veins
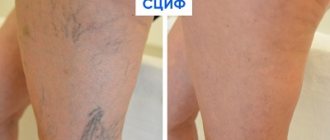
Chronic venous insufficiency
Chronic venous insufficiency is a common peripheral vascular disease that occurs as a result of impaired blood flow through the veins of the lower extremities and changes in the permeability of the vascular wall. Most often, venous insufficiency develops in women. The disease occurs when the valves that close the veins are unable to prevent blood from flowing back due to increased pressure on them. As a result, this leads to stretching of the walls of the venous vessels. The permeability of the vascular wall for blood and plasma proteins increases, swelling and compaction of adjacent tissues appear. Where small vessels are compressed, areas of ischemia (insufficient blood supply with oxygen) occur, which contributes to the formation of trophic ulcers.
The main risk factors for the development of chronic venous insufficiency include:
- weakness of the muscular wall of the veins (hereditary);
- overweight and obesity;
- pregnancy and childbirth;
- long-term constant work in a standing or sitting position, with limited movement (cooks, office workers, surgeons, etc.);
- chronic constipation;
- fluctuations in hormonal levels in women (contraception with hormonal drugs, hormonal treatment during menopause, etc.);
- wearing tight underwear and clothing, corsets.
The following stages of development of varicose veins are distinguished:
- Stage 0 – no major symptoms upon examination.
- Stage I - “morning fatigue” of the legs, complaints of intermittent swelling in the evenings (disappears in the morning).
- Stage II – persistent swelling, skin pigmentation disorders; some areas of the skin become thicker, the skin above them cannot be folded (lipodermatosclerosis), redness appears on the skin, accompanied by itching and weeping (eczema).
- Stage III – the formation of trophic ulcers (active or healed), difficult to treat with medication.
The disease is accompanied by pain of varying intensity and the presence of evening cramps. In the treatment of varicose veins in the early stages, compression with elastic bandages and compression hosiery, physiotherapy and therapy in a sanatorium are used.
Composition and therapeutic effect of the drug Detralex
A therapeutic course of venotonic drugs is also prescribed. Detralex is used most often.
It is based on flavonoids - substances of plant origin. The active ingredients are hesperidin and diosmin, which eliminate venostasis (blood stagnation).
Detralex restores and increases the tone of venous walls and blood microcirculation in small vessels. Capillaries become elastic and plastic, their permeability decreases. The medicine reduces the distensibility of the veins, which reduces the release of plasma and proteins from the bloodstream into the surrounding tissues.
Detralex has an angioprotective and venotonic effect.
In addition, the drug Detralex increases the outflow of lymph, thereby providing lymphatic drainage.
Indications
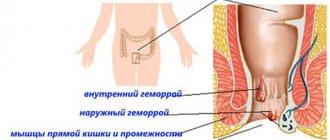
Indications for the use of the drug Detralex are organic and functional venous-lymphatic insufficiency of the lower extremities. Detralex is also used for the symptomatic treatment of acute hemorrhoidal attacks.
The medicine Detralex can be used for tired legs
Detralex is indicated for:
- pain;
- cramps of the lower extremities;
- feeling of heaviness and fullness in the legs;
- "fatigue" in the legs.
- swelling of the lower extremities;
- trophic changes in the skin and subcutaneous tissue;
- venous trophic ulcers.
Side effects
When taking the drug Detralex, in rare cases, the following adverse reactions may develop:
- from the gastrointestinal tract: dyspepsia, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, colitis;
- from the central nervous system: headache, dizziness, general malaise;
- from the skin: urticaria, itching, rash, isolated swelling of the face, eyelids, lips, angioedema.
If any side effects occur, you should consult your doctor and adjust your treatment.
Contraindications and side effects
Contraindications to the use of the drug are:
- Increased individual sensitivity to active or auxiliary substances that are part of the dosage form.
- The instructions for use do not contain data on taking the drug in children.
The drug is usually well tolerated.
Side effects from the gastrointestinal tract are possible, but mild (nausea, upset, pain and discomfort in the stomach).
Sometimes reactions from the autonomic nervous system occur - slight dizziness, weakness and headache or itching and skin rash.
Both cases do not require discontinuation of use.
It is not allowed to take the drug while breastfeeding, as there is no data on the interaction of the active substances with mother's milk.
Detralex does not lower or increase blood pressure.
How to take Detralex?
Detralex is used as a symptomatic remedy for varicose veins and hemorrhoids. Often, the attending physician prescribes therapy that includes venotonic ointments or gels. When treating hemorrhoids, rectal suppositories and ointments can be used to relieve pain and inflammation, improve vascular tone, reduce blood clots and stop bleeding.
Before taking the medicine, you must carefully read the instructions
Detralex tablets are intended for oral use. Depending on the indications and general condition of the patient, the daily dose of the drug and the duration of the course of therapy are determined by the doctor.
- Venous-lymphatic insufficiency: 2 tablets/day (1 tablet in the middle of the day and 1 tablet in the evening with meals).
- Chronic hemorrhoids: 2 tablets/day (1 tablet in the middle of the day and 1 tablet in the evening with meals). After 7 days, you can change the dosage regimen of Detralex and use the drug 2 tablets once, with meals.
- Acute hemorrhoids: 6 tablets/day (2-3 tablets at equal intervals) for 4 days, then 4 tablets/day (2 tablets in the morning and 2 tablets in the evening) for the next 3 days.
The duration of treatment with Detralex depends on the severity of the disease, the patient’s medical history and, on average, is about 2-3 months. As prescribed by a doctor, the therapeutic course can be repeated.
Please note that taking Detralex for acute hemorrhoids does not replace specific therapy. That is why it is necessary to contact a specialist who will prescribe a therapeutic course, including drug treatment.
Tips for taking the drug
For people with impaired venous circulation, to increase the effectiveness of the drug, it is recommended:
- avoid standing for long periods of time and prolonged exposure to the sun;
- adjust body weight and diet;
- wear compression stockings to improve blood circulation;
- hike.
As for drinking alcohol during treatment with Detralex, there is no direct prohibition. You just need to consider the effects of alcoholic beverages on the cardiovascular system. Thus, alcohol increases blood pressure and dilates blood vessels, in turn, a sharp blood flow provokes stagnation. That is, alcohol reduces the effectiveness of treatment.
Features of the drug use
Tablets for veins "Detralex" are prescribed to adults only orally, depending on the severity and nature of the disease:
- When treating venous insufficiency and varicose veins, patients are recommended to take it twice a day: 1 tablet in the morning and 1 tablet in the evening. The drug is taken during meals with water. After a week, they switch to a single dose: 2 tablets in the morning.
- In the treatment of acute hemorrhoids, take up to 6 tablets per day for 4 days, not on an empty stomach. Then they switch to the regimen: 2 tablets in the morning and 2 in the evening.
Duration of treatment is 3 days. Maintenance dose – 2 tablets per day. The course of treatment is 2-3 months under the supervision of a doctor.
Detralex during pregnancy and lactation
Detralex is not recommended for pregnant women
The use of Detralex by pregnant women and children during breastfeeding is not recommended due to insufficient research and clinical data. There is no information on the occurrence of side effects in pregnant women, nor has there been any information recorded on the ability of the active ingredients - diosmin and hesperidin - to pass into breast milk during breastfeeding, as well as in children during breastfeeding.
Special Recommendations
Use during pregnancy
Studies conducted on animals have not revealed any negative effects of the drug on the body during pregnancy. During the period of bearing a child, the risks of varicose veins, with swelling and heaviness in the legs, increase significantly! For this reason, maintenance therapy should be approached comprehensively, using compression hosiery, topical medications in the form of ointments and gels.
There are no strict restrictions on taking Detralex orally during pregnancy, but before use it is important to consult with a specialist and assess the potential benefits for the expectant mother and the risks to the fetus.
Taking Detralex while breastfeeding
Oral use of the drug is not recommended during lactation. Despite its relative “harmlessness,” Detralex has insufficient clinical studies and reliable data on its use during breastfeeding and its ability to pass into breast milk.
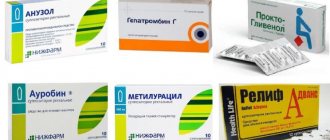
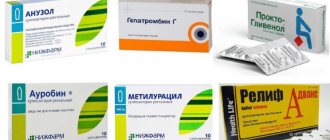
Analogues of the drug Detralex
For problems with veins and varicose veins, it is possible to use Detralex analogues. They can have a similar therapeutic effect, but have their own contraindications, dosages and possible side effects. Be sure to consult a specialist!
So the pharmaceutical market offers us the following analogues of Detralex:
Venozol
The main active ingredients, like Detralex, are diosmin and hesperidin. Pharmacological action is similar to Detralex. Release form: tablets, gel and cream.
Vasocket
The active substance (diosmin) reduces the distensibility and increases the tone of the veins, thereby preventing the appearance of edema. Available in tablet form.
Antistax
Bioflavonoid drug belongs to the group of venotonic drugs. Available in tablet form.
Troxevasin
Produced under the trade names Venoruton, Troxerutin. Improves the condition of the walls of blood vessels and has an anti-edematous effect. Main forms of release: capsules, gel for topical use, solution for injection in ampoules.
Analogues of the drug Detralex
Anavenol
Combined venoprotective drug. Available in tablet form. Side effects: bleeding, dizziness, nausea. Contraindicated for children under 15 years of age.
Venoruton
Angioprotective drug. The active ingredient is hydroxyethylrutoside. Release form: tablets and gel for external use. Possible use in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy.
Ginkor fort
Venotonic and venoprotective drug It contains a standardized extract of ginkgo biloba, heptaminol hydrochloride and troxerutin. Available in the form of capsules and gel for external use. In case of overdose, blood pressure may increase. According to indications, the drug can be prescribed in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. Contraindicated in hyperthyroidism and concomitant use of MAO inhibitors.
Detralex or Venarus?
Venarus is a generic drug. That is, it is based on the same active ingredients (diosmin and hesperidin), but the original drug (Detralex) always contains components of a higher degree of purification. Therefore, its effectiveness is higher and its tolerability is better. In addition, Venarus is characterized by lower bioavailability and more often provokes adverse reactions in the body. The drug is also contraindicated during lactation. The pharmacological action is similar to the drug Detralex. There is no fundamental difference between them. Recommendations for taking medications for varicose veins and hemorrhoids are identical.
Detralex or Phlebodia?
The active ingredient of the drug Phlebodia 600 is diosmin. But its concentration in Detralex is 450 mg/tablet (plus its enhancing hesperidin 50 mg/tablet), and Phlebodia 600 is available in the form of tablets with a diosmin concentration of 600 mg/tablet.
The medicine has a therapeutic effect similar to Detralex. It also increases the tone of the venous wall, improves blood flow, and normalizes the permeability of vascular walls.
Nevertheless, Detralex is absorbed into the body faster than its analogue, and its concentration in the blood plasma reaches its maximum after three to four hours.
Popular questions about Detralex
Detralex: how to take the drug?
Detralex in the treatment of leg swelling is taken 2 times a day. Take the medicine according to the following regimen: 1 tablet in the morning and 1 tablet in the evening after meals. The drug is washed down with water at room temperature.
How to take Detralex for hemorrhoids?
To reduce acute effects and alleviate the symptoms of hemorrhoids, the drug is used 2 tablets in the morning, afternoon and evening, not on an empty stomach. Daily dose - 6 tablets. Course – 4 days.
How to use Detralex 1000 for varicose veins?
Detralex is available in tablets that contain 500 and 1000 mg of active ingredient.
The difference is in the amount of diosmin and hesperidin in one tablet (450 and 50 mg in the first case and 900 and 100 mg in the second) and the number of tablets in the package - 60 and 30 pieces. In pharmacies, the drug is presented in two dosage forms, the price of which differs slightly. The frequency of taking Detralex 1000 is halved. To treat varicose veins, take 1 tablet once after a meal.
Detralex. How long to take the drug?
The duration of treatment depends on the course of the disease and is usually 2-3 months under the supervision of a doctor.