Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more deep veins in your body, usually in the legs. Deep vein thrombosis can cause leg pain or swelling, but may be asymptomatic.
- Symptoms of deep vein thrombosis
- Causes of deep vein thrombosis
- Risk factors
- Complications of DVT
- Prevention of thrombosis
DVT may be associated with diseases that affect the blood clotting process. A blood clot in your legs can also form if you have not moved for a long time, such as after surgery or an accident. But walking over extremely long distances can lead to the formation of blood clots.
Deep vein thrombosis is a serious condition because blood clots in your veins can travel through your bloodstream and become lodged in your lungs, blocking blood flow (pulmonary embolism). However, pulmonary embolism can occur without evidence of DVT.
When DVT and pulmonary embolism occur at the same time, it is called venous thromboembolism (VTE).
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of DVT:
- Swelling of the affected leg. In rare cases, swelling appears in both legs.
- Leg pain. The pain often begins in the calf and may feel like cramping or soreness.
- Red or discolored skin on the leg.
- Feeling of warmth in the affected leg.
Deep vein thrombosis may occur without noticeable symptoms.
When to see a doctor
If you have signs or symptoms of DVT, contact your doctor.
If you develop signs or symptoms of pulmonary embolism (PE), a life-threatening complication of deep vein thrombosis, get emergency medical help.
Call 103
Warning signs and symptoms of pulmonary embolism include:
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Chest pain or discomfort that gets worse with deep breathing or coughing.
- Feeling dizzy or dizzy or faint
- Rapid pulse
- Rapid breathing
- Coughing up blood
Do you suspect deep vein thrombosis? Contact the professionals.
Reasons for the problem
The reasons for the appearance of veins on the hands are of different nature. They can appear from overexertion when carrying heavy objects, overheating of a person in a bathhouse or sauna, from prolonged exposure to a hot climate, smoking, from a fragile physique or age-related changes. Most often, these manifestations are temporary and do not require serious treatment. Early changes on the hands look like blue nodules and will disappear when the provoking factor is eliminated.
But not everything is so harmless when the cause of this phenomenon is varicose veins - a disease associated with a decrease in the tone of the venous walls. Quite often, the disease is accompanied by pain, which can also be signs of other diseases: arthritis, arthrosis, chondrosis and neuritis. That is why in such a situation, correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment are extremely important.
Risk factors
Many factors can increase your risk of developing DVT, which include:
- Age. At age 60, the risk of DVT increases, although it can happen at any age.
- Sitting for long periods of time, such as while driving or flying. When your legs remain motionless for several hours, your calf muscles do not contract. Muscle contractions promote blood circulation.
- Prolonged bed rest, such as during a long hospital stay or paralysis. Blood clots can form in the calves if the calf muscles are not used for a long time.
- Trauma or surgery. Injury to the veins or surgery may increase the risk of blood clots.
- Pregnancy. Pregnancy increases pressure in the veins of the pelvis and legs. Women with an inherited bleeding disorder are at particular risk. The risk of blood clots from pregnancy can last up to six weeks after the baby is born.
- Birth control pills (oral contraceptives) or hormone replacement therapy. Both factors can increase the blood's ability to clot.
- Exposure to drugs or chemicals. Certain drugs can cause blood clots. Consult your physician before use.
- Overweight or obese. Excess weight increases pressure in the veins of the pelvis and legs.
- Smoking. Smoking affects clotting and circulation, which may increase the risk of DVT.
- Cancer. Some forms of cancer increase levels of substances in the blood that cause blood clotting. Some forms of cancer treatment also increase the risk of blood clots.
- Heart failure. Increases the risk of developing deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Because people with heart failure have limited heart and lung function, symptoms caused by even a small pulmonary embolism are more noticeable.
- Inflammatory bowel diseases. Bowel diseases such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis increase the risk of DVT.
- Personal or family history of DVT or PE. If you or someone in your family has had one or both of these, you may be at greater risk of developing DVT.
- Genetics. Some people inherit genetic risk factors or disorders, such as factor V Leiden, that make their blood clot more easily. The hereditary disease itself may not cause blood clots unless it is combined with one or more other risk factors.
- Risk factor unknown. Sometimes a blood clot in a vein can occur without an obvious underlying risk factor. This is called unprovoked VTE.
Examination of patients with pain in the veins of the leg
When examining patients who have leg pain in the vein area, phlebologists pay attention to the location of the pain and the color of the skin over the vein. If a vein appears on the leg and it hurts, an ultrasound scan is performed. Doctors use 1, 2 or 3 research modes. The main one is B-mode. Additionally, color coding of blood flow or pulsed wave Doppler, as well as a combination of both, is used. The method allows you to simultaneously examine the vein in the leg that hurts, determine the direction of blood flow and its parameters. Patients who have pain and stretching of the veins in their legs must undergo an examination of the superficial and deep veins of both lower extremities.
At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors for ultrasound scanning use devices that are equipped with linear sensors with a frequency of 5 MHz and more from the world's leading manufacturers. To scan deep veins, especially in obese patients, convex sensors with a lower radiation frequency (from 3.5 to 5.0 MHz) are used.
Doppler ultrasound allows you to obtain sound information, which doctors use to judge the presence or absence of blood flow through the main veins. By changing the sound signals during functional tests, blood reflux (reverse discharge) is detected. During X-ray contrast venography, the phlebologist examines the deep and superficial veins. He receives comprehensive information about the morphological changes of the venous system. This research method is used when planning surgery in patients with blocked or underdeveloped veins. Phlebologists at the Yusupov Hospital use the technique of transfemoral ascending phlebography.
Radionuclide phlebography allows you to obtain data on the nature and direction of blood flow through deep, superficial and perforating veins under conditions that are as close as possible to physiological ones. The study is carried out with the patient standing while simulating walking. Radiophlebography allows for an integrative assessment of blood flow throughout the entire system simultaneously.
Intravascular ultrasound examination is carried out to determine the shape and extent of the narrowed segment of the vein when its patency is impaired after thrombosis or compression of the venous vessel from the outside. Infrared thermography, computer thermal imaging, radiothermometry are used as an additional method of studying patients whose cause of pain in the veins of the legs is chronic venous insufficiency. Using this method, the dynamics of the inflammatory process in tissues is monitored, as well as the effectiveness of therapeutic measures is assessed.
Complications
Complications of DVT may include:
- Pulmonary embolism (PE). PE is a potentially life-threatening complication associated with DVT. This occurs when a blood vessel in your lung is blocked by a blood clot that travels to the lung from another part of your body, usually your leg. If you have signs and symptoms of PE, it is important to seek medical help immediately. Sudden shortness of breath, chest pain when inhaling or coughing, rapid breathing, rapid pulse, feeling weak or faint, and coughing up blood may occur with PE.
- Postphlebitic syndrome. Damage to the veins by a blood clot reduces blood flow to the affected areas, causing leg pain and swelling, skin discoloration, and skin ulcers.
- Complications of treatment. Complications may arise from blood thinners used to treat DVT. Bleeding is a side effect of anticoagulants. It is important to have regular blood tests when taking these medications.
Treatment
To treat identified diseases, minimally invasive methods are used: sclerotherapy, phlebectomy and laser therapy. Physiotherapeutic procedures are also included in the treatment: electrophoresis with venotonics and angioprotectors, darsonvalization, magnetotherapy, ultrasound treatment (destroys blood clots), balneotherapy (whirlpool and contrast hand baths with bischofite, radon, hydrogen sulfide), massage compression. Another popular method is hirudotherapy (treatment with leeches). They produce a special enzyme that has a positive effect on the circulatory system and increases the elasticity of tissue in the affected area. Despite the somewhat unconventional nature of the method, it is considered quite effective.
To choose a specific method (including surgery), it is first necessary to find out the original causes of the pathology and eliminate provoking factors. In this case, the treatment will be effective.
Question answer
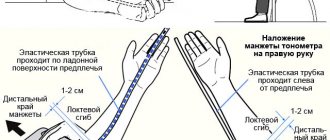
Why might my arm hurt after taking blood from a vein?
Prevention
Measures to prevent deep vein thrombosis include the following:
- Don't sit still. If you have had surgery or were on bed rest for other reasons, try to get back to work as soon as possible. If you sit for any period of time, do not cross your legs as this can block blood flow. If you are traveling long distances by car, stop every hour or so and take a walk. If you're on an airplane, stand or walk occasionally. If you can't do this, stretch your shins. Do some exercises. Try raising and lowering your heels while keeping your toes on the floor, then lifting your toes while pressing your heels into the floor.
- Do not smoke. Smoking increases the risk of developing DVT.
- Do exercises and control your weight. Obesity is a risk factor for DVT. Regular exercise reduces the risk of blood clots, which is especially important for people who sit a lot or travel frequently.
Filler Ellanse
The world's smartest product for contouring will help give the skin of your hands a velvety feel - an innovative filler produced by the Netherlands, Ellanse.
A distinctive feature of Ellans is that it not only restores tissue volumes lost over the years, but also stimulates the formation of type 1 youth collagen at the injection site. Namely, collagen of the first type creates the effect of velvet skin and excellent lifting.
Ellanse still has many advantages. For example, the fact that it gives immediate results, and is also not visible even under the lightest and thinnest skin and cannot be felt. In other words, no one will ever guess that you visited a cosmetologist, but they will definitely notice the beauty of your hands! Ellans is a one hundred percent biodegradable drug. After the filler has fulfilled its purpose, the stage of biodegradation begins - the complete removal of the drug from the body. But unlike other biodegradable fillers, the cosmetic effect of which steadily decreases day by day, starting from the moment of their introduction, Ellans demonstrates the stability and consistency of the effect throughout the entire period of action. And this validity period can be “programmed” depending on the individual characteristics and wishes of the patient. Ellans can be valid from 1 to 4 years. A single use of the drug is enough to get all the men in your hands!
Sclerotherapy (scleroobliteration) of unaesthetic veins on the arms - cost of the procedure
| Service | Treatment category | Price |
| Sclerotherapy (microsclerotherapy) on one lower limb (one session) | Reticular varicose veins and spider veins | 8000₽ |
| Postoperative sclerotherapy (microsclerotherapy) on one lower limb (one session) | Reticular varicose veins and spider veins | 4000₽ 8000₽ |
| Sclerotherapy (microsclerotherapy) on one lower limb (course of treatment) | Does not depend on the number of sessions | 35000₽ |
| Removal of unaesthetic veins on one arm (one session) | 10000₽ | |
| Laser removal of spider veins on one lower limb (one session) | 10000₽ |
Payment by Visa and Mastercard is possible. At the end of the course of treatment, the patient is given a package of documents to submit to the tax office for tax deduction.
How to prevent the development of varicose veins?
Primary prevention of varicose veins is the maximum possible correction of existing risk factors, eliminating the causes of the disease that can be influenced (8, English).
Prevention of varicose veins
Main methods of prevention:
- increasing general physical activity, including “physical exercise minutes” in the daily routine, and walking daily;
- normalization of body weight;
- timely treatment of developing dishormonal conditions, careful selection of oral contraceptive and replacement therapy regimens;
- treatment of diseases accompanied by increased intra-abdominal pressure, prevention of constipation;
- detection and treatment of tumor diseases of the pelvis and abdominal cavity.
Body weight control, proper nutrition, and regular physical activity as indicated are the basis for the prevention of varicose veins.
If there is a family predisposition to varicose veins, during pregnancy, while taking oral contraceptives, it is advisable to undergo regular preventive examinations to monitor the condition of the veins of the lower extremities.
Author of the article: Letunovsky Evgeniy Anatolyevich Last update: 09/28/2020.