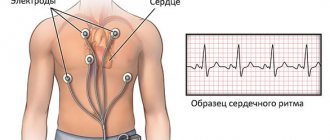
Low pulse is one of the complaints of patients in cardiology departments. This phenomenon can cause many unpleasant moments, since it is accompanied by fainting states, weakness, cold sweat, dizziness, often being a sign of serious illness. Its systematic occurrence is a reason to seek professional medical help.
In order to find out the cause of a rare pulse, the doctor prescribes comprehensive diagnostic tests to identify existing problems. The pulse is represented by jerky oscillations of the arterial walls, by which the heart rate can be tracked and, having identified their violations, appropriate measures can be taken.
If you look at the accepted indicators of normal heart rate for different ages, you can conclude that it decreases as you get older. This is due to the growth of the muscular middle layer, known as the myocardium. The larger the volume of the heart, the fewer beats it needs to make in order to pump blood.
Causes of low heart rate
Despite the fact that the maximum frequency indicators can be called conditional and individual, depending on a number of factors (undoubtedly, within certain limits), the pulse is below 50 beats/min. - a sign of the presence of a disease. Its reduction to forty beats poses a threat to health and life, since the brain suffers from oxygen starvation. If it does not exceed forty beats within seven days, this is a sign of bradycardia, and with a progressive decrease, you should urgently seek professional medical help.
Almost all initiating factors of a pulse below normal are related to pathological conditions. For convenience, experts divide them into different categories, which can be found in our table.
| Category of reasons | How is it manifested? |
| Physiological | There are a number of natural factors and external influences that initiate a low pulse at normal pressure. Such conditions are not dangerous. This:
|
| Cardiological | The reasons for low blood pressure and low pulse may lie in the weakness of such a vital organ as the heart. They occur in the following diseases:
|
| Toxicological | Low blood pressure and low pulse can develop due to interaction with toxic substances when:
|
| Associated pathological conditions |
|
Low heart rate in the elderly is associated with age-related changes in the body. It often develops due to concomitant diseases or a natural slowdown in the body’s metabolic processes.
Recommendations from experts
- A drop in heart rate during the day or at night can be either a physiological (meaning normal and not dangerous) or a pathological condition.
It is better to consult a doctor in advance, without waiting for disturbances in the body and cardiovascular system.
- You can increase your pulse rate with medications and folk remedies; it is only important to understand that neglect of such a symptom is fraught with serious consequences.
- A healthy lifestyle will help normalize your heart rate
- In order to combat and prevent heart rate abnormalities, it is necessary to optimize your lifestyle.
- Lack of physical activity and sedentary work can cause a decrease in heart rate.
- Daily walks in the open air, simple morning exercises and a cool shower work no worse than medications.
- There is no need to exhaust yourself with training. It is enough to walk 2 kilometers in the morning and evening, and the result will certainly appear.
- A prerequisite for recovery is adherence to sleep and rest patterns.
- Nutrition should be radically revised:
- less fatty foods, which cause the progression of atherosclerosis;
- more plant fiber, dairy products, fish and greens.
- The drinking regime should include the consumption of a sufficient amount of liquid. This will ensure that the vessels are filled with a good volume of circulating blood, increase blood pressure and normalize the pulse rate.
Clinical manifestations of low heart rate
A moderate decrease in pressure most often does not lead to the development of clinical manifestations and is not accompanied by circulatory disorders. However, with a heart rate of no more than forty beats per minute, the following are observed:
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- semi-fainting and fainting;
- feeling of constant fatigue;
- labored breathing;
- pain symptoms in the chest area;
- blood pressure surges;
- inability to concentrate;
- forgetfulness;
- visual impairment.
Symptoms with a low pulse correspond to circulatory disorders that appear against its background. So, if it is slowed down, the brain suffers from a lack of oxygen and hypoxia develops (that is, oxygen starvation). As a result, the patient is susceptible to convulsions and loss of consciousness, lasting from several seconds to one minute. Such conditions are life-threatening and can cause respiratory arrest and therefore require immediate medical attention.
general characteristics
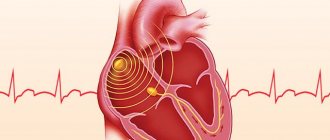
Arterial pulse is a rhythmic contraction of the arterial wall caused by the release of blood during contraction of the heart muscle. Pulse waves are formed at the mouth of the aortic valve during the period of blood ejection from the left ventricle. The stroke volume of blood occurs at the moment of increase in systolic pressure, when the diameter of the vessels expands, and during diastole, the dimensions of the vascular walls are restored to their original parameters. Consequently, during the period of cyclic contractions of the myocardium, a rhythmic oscillation of the aortic walls occurs, which causes a mechanical pulse wave that spreads to large and then to smaller arteries, reaching the capillaries.
The mechanism of pulse wave formation in blood vessels
The further the vessels and arteries are located from the heart, the lower the blood and pulse pressure becomes. In the capillaries, pulse fluctuations are reduced to zero, which makes it impossible to feel the pulse at the level of the arterioles. In vessels of this diameter, blood flows smoothly and evenly.
Diagnosis of low heart rate
Determining the causes of a pathologically low pulse requires a comprehensive diagnosis. First of all, the doctor listens to the patient’s complaints, collects anamnesis and conducts an examination. If bradycardia (i.e., decreased heart rate) is detected, the patient is prescribed a consultation with a cardiologist. As for diagnostic studies, they are as follows:
- Electrocardiography;
- Daily Holter monitoring;
- Ultrasound scan of the heart;
- EchoCG;
- Bicycle ergometry.
In addition, if necessary, TEE can be performed, which allows one to study the conduction pathways of the heart and determine the organic or functional nature of the disease.
What factors are taken into account when measuring?
- Times of Day. The heart rate, even in a completely healthy person, can change throughout the day, which is confirmed by daily ECG monitoring. The lowest readings occur at night or in the morning; in the evening, on the contrary, the heart rate increases, and the difference can be up to 10 beats. Such fluctuations in the absence of other signs are considered a physiological norm.
- Body position. When sitting, the frequency is always higher than when a person is lying down, but as soon as he gets up, the indicator goes off scale. This is due to the increased workload on the heart associated with physical activity.
Treatment for low heart rate
A moderate decrease in heart rate that occurs without symptoms does not require therapy. However, if it exists, the underlying pathology must be treated. The strategy depends on the underlying disease, but in any case is aimed at:
- Elimination of symptoms of low heart rate;
- Eliminating the risk of heart rhythm disturbances;
- Prevention of thrombosis development.
If the problem arose as a result of uncontrolled use of pharmacological drugs, their dose is adjusted - or, if they are not needed, completely canceled.
Symptoms
If the pulse decreases significantly, the person experiences:
- weakness of the body as a whole;
- headache of varying strength;
- numbness in the limbs and a decrease in their temperature;
- problems with vision, attention, concentration.
Once again, it is worth emphasizing that symptoms are not always immediately visible, so it is worth, especially in old age, to measure your pulse immediately after waking up.
How to quickly increase your heart rate?
If a rare pulse is not a symptom of heart disease and appears for physiological reasons, you can speed it up and eliminate unpleasant symptoms by using simple remedies available in almost every home. Before starting activities, it is important to take into account the circumstances under which the heart rate decreased.
| Initiating factor | How and with what is it manifested? |
| Stress, shock, nervous disorders | If the heart rate decreases to forty beats per minute or below, you can take sedatives:
|
| Decreased blood pressure and pulse | The best option is to take decoctions for:
|
| Increased blood pressure and decreased heart rate | The best solution would be:
|
| Pregnancy |
|
If a person is sufficiently resilient and healthy, physical activity (from running, jumping and squats to cardio exercises) would be a good option.
Determination methods
The study of the arterial pulse is carried out on the main (carotid) and peripheral (wrist) arteries. The main point for determining heart contractions is the wrist, where the radial artery is located. For an accurate examination, it is necessary to palpate both hands, since situations are possible when the lumen of one of the vessels may be compressed by a thrombus. After a comparative analysis of both hands, the one on which the pulse is better palpated is selected. When examining pulse impulses, it is important to place your fingers so that 4 fingers are on the artery at the same time, with the exception of the thumb.
Determination of pulse fluctuations on the radial artery
Other ways to determine your pulse:
- Thigh area. The study of pulse impulses on the femoral artery is carried out in a horizontal position. To do this, you need to place your index and middle fingers in the pubic area, where the inguinal folds are located.
- Cervical region. The carotid artery is examined using two or three fingers. They should be placed on the left or right side of the neck, 2-3 cm away from the lower jaw. It is recommended to carry out palpation from the inside of the neck in the area of the thyroid cartilage.
Determining the pulse on the radial artery can be difficult in case of weak cardiac activity, therefore it is recommended to measure the heart rate on the main artery.
Prevention of rare pulse
Preventive measures boil down to timely treatment of organic heart lesions, elimination of the effects of toxic substances on the myocardium, competent selection of doses of pharmacological drugs and their administration under medical supervision. Don't forget to make regular preventive visits to your therapist and cardiologist.
Make an appointment with CELT specialists and find out the reasons for your rare pulse without delay.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions