Testicular varicose veins, or varicoceles, are a problem that many men face. Often the disease occurs in adolescence and is detected during a urological examination. According to statistics, 5-7% of young people aged 18-20 years and 15-17% of men under 40 suffer from varicocele. In 80-98% of cases, left-sided varicose veins are observed.
Varicocele is characterized by a hidden course and does not manifest itself for a long time. It is possible to detect the disease in its early stages only with the help of special tests. The Valsalva maneuver for varicocele helps to visualize pathologically dilated veins. What is this research and what are its benefits?
Anatomical reasons for varicocele.
Normal anatomy and physiology of the spermatic cord and testicular structures.
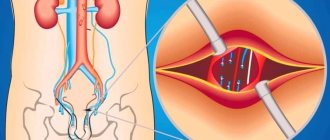
The testicles are a paired organ. They are located in the skin-muscle sac - the scrotum. The testicles are located outside the abdominal cavity due to different operating temperature conditions of the body and scrotum. The core of the body functions at a temperature of 36 - 37 ° C. The temperature regime of the scrotum differs by 1 - 2 degrees below the temperature of the core.
The testicle is in a mobile state due to the structures of the spermatic cord. This prevents the testicle from being traumatized and promotes blood circulation in the testicles. The main components of the spermatic cord: the levator testis muscle, the vas deferens, the vein and artery of the vas deferens, the vein and artery of the levator testis muscle, the own testicular artery and testicular veins in the form of a pampiniform plexus (named due to its similarity with the grapevine), as well as fascia covering muscles and lymphatic ducts. There are features of the testicular veins. The left testicular vein, passing through the inguinal canal, flows into the renal vein at a right angle, which is a predisposing factor, in contrast to the right testicular vein, which flows directly into the inferior vena cava.
Indications for use
The Valsalva method is used to diagnose the following pathological conditions:
- Varicocele;
- different types of tachycardia;
- Possibility of death after a heart attack;
- determination of the functional state of the venous valves of the lower extremities;
- determination of the condition of the ear canals.
In addition, release is used to relieve symptoms of arrhythmias, reduce heart rate and lower blood pressure.
With tachycardia, rapid heartbeat can occur both in connection with physical activity and as a symptom characteristic of myocardial dysfunction. The Valsalva maneuver not only helps classify the types of this pathology, but also helps stabilize the heart rhythm.
Causes of varicocele.
There are congenital and acquired causes that contribute to varicocele.
Congenital diseases include: duplication of the testicular vein, ring-shaped structure of the left renal vein, congenital pathologies of the valvular apparatus of the testicular vein, congenital stenosis of the renal vein, high growth.
Acquired: increased intra-abdominal pressure (jogging, weightlifting, chronic constipation), compression of the testicular vein by large vessels. These conditions lead to increased pressure in the renal vein and, secondarily, in the testicular vein, since venous pressure is hydrostatic pressure, that is, the pressure of a column of fluid.
Sample options
Depending on the purpose (diagnostic or therapeutic), the procedure is performed differently for different diseases.
Detection of varicocele
The functional Valsalva test allows you to determine not only the presence, but also the degree of development of varicocele, which is manifested by dysfunction of the venous valves located in the testicles and spermatic cord.
The diagnosis is checked while standing. Vein retention increases blood flow to the testicles, allowing palpation of their dilated veins. If we are dealing with valve disease, an enlargement of one of the testicles (often the left one) is clearly visible even to the naked eye. Very rarely there is a defect in the right testicle or both.
When a conscript is recommended to be diagnosed with varicose veins of the 2nd degree, the operation is the basis for rescheduling the service.
In the supine position, the examination is carried out if grade 3 varicose veins are suspected. To clarify the diagnosis, ultrasound is used to determine the size of the lumen of the testicular veins.
The Valsalva maneuver and ultrasound findings are important for the choice of surgical intervention.
Cardiac test
A patient's examination in cardiology is carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor. Cardiogram and blood pressure readings are recorded simultaneously.
The procedure is slightly different from the previous version (for varicocele). After taking a deep breath, you slowly (over 10-20 seconds) exhale through a special mouthpiece. This is followed by relaxation, as a result of which breathing is restored.
To determine the result, ECG readings and blood pressure are analyzed.
The test is considered positive if the pulse and blood pressure drop during inspiration but then rise.
Valsalva ratio
The ratio of long and short ventricular contractions (R - R) is used to determine the likelihood of sudden cardiac arrest.
Under normal conditions, this coefficient should not exceed 1.7. A range below 1.3 indicates possible death.
Vascular surgery
In the case of varicose veins, before using the Valsalva technique, a preliminary examination of the condition of the veins of the lower extremities is carried out - ultrasound. Then, performing the technique described above leads to an increase in pressure in the vena cava.
At this stage, the ultrasound procedure is repeated on problem areas. This makes it possible to diagnose insufficient functioning of the venous valves, which provokes the accumulation of excess blood in the vessels.
The combined use of the test and ultrasound allows you to determine the rate of blood release from vessels damaged by varicose veins.
A positive test result is the observation of regurgitation of blood, which is an indication for surgery.
A negative test indicates leg fatigue with symptoms similar to those of varicose veins.
The test is performed for early detection of the disease when the patient complains of fatigue and swelling in the limbs, but does not yet have visible vasodilation. In the case of varicose veins, the appointment also allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment procedure.
Advanced stages of diseases of the lower extremities and thrombophlebitis are contraindications for the Valsalva maneuver, since the clot may detach. This has serious complications.
Application in neurosurgery
The test is also performed during chest surgery. It allows you to detect a pleural defect. If its shell is accidentally damaged, a sound characteristic of air entering the pleural cavity is heard.
Previously, this method was used to assess the condition of cerebral vessels. Currently, it is not used due to the advent of more advanced research methods in this direction.
However, the Valsalva technique is still effective in studying congenital brain defects. Its action is accompanied by a significant increase in headaches.
Osteochondrosis
The test is based on a load that increases in the lower back due to pressure generated in the abdomen. This leads to compression of the nerve roots of the spinal cord. The pain radiates to the limbs, which indicates an exacerbation of osteochondrosis.
A herniated disc in the lumbar region also causes pain symptoms. However, to confirm the diagnosis it is necessary to use other research methods.
Otolaryngology
The test is used as a diagnostic and therapeutic method by ENT doctors. With its help, it determines the patency of the ear canals. Additionally, purulent formations from the ear cavity are removed.
When else is it used?
Underwater divers and airline passengers use the Valsalva technique to relieve unpleasant symptoms caused by pressure fluctuations.
A positive effect during takeoff and landing of an airplane is achieved through the following actions: after inhaling, the air should not be inhaled through the mouth or nose, but exhaled through the ears.
Ultrasound for varicocele.
In the practice of a urologist-andrologist, ultrasound ranks first in the diagnosis of varicocele and has become the “gold standard”.
Modern linear high-frequency sensors are used. To assess the anatomy, a “gray scale” is used (the doctor sees all structures on the screen in black - gray - white). With this technique, tubular structures are identified in the projection of the inguinal canal and scrotum. These are the veins. The diameter of the veins is measured. Normally, the diameter of the vein should not exceed 2 millimeters and the course of the veins should be straight. With varicocele, in the projection of the inguinal canal and scrotum, a conglomerate of intertwined convoluted tubular structures is found, which seem to hang on other elements of the spermatic cord.
When studying the function of veins, additional techniques are used.
The color Doppler mapping (CDC) method helps to evaluate the functioning of the valve apparatus of the veins and speed indicators, as well as the time of blood movement in the vessel. Normally, venous outflow, that is, the work of the veins is synchronized with the act of breathing and the movements of the diaphragm. After inhalation, in the first second, the venous valves close and the movement of blood in the veins slows down and the speed of venous blood flow is zero. As you exhale, the diaphragm muscles contract and intrathoracic pressure increases. Due to these mechanisms, blood is attracted to the heart. The CDC technique clearly illustrates the reflux phase on the screen, making it possible to diagnose varicocele.
The essence of the method
The differences between such concepts as the test and the Valsalva maneuver are as follows:
- The study is a diagnostic method that allows you to identify pathological processes.
- Reception is a certain human activity that causes high pressure in the middle ear, as well as in the abdominal and thoracic areas.
Initially, this technique was successfully used in obstetrics during childbirth and to free the ear from earwax or purulent plugs.
Operating principle
The pressure created in the chest and abdominal areas as a result of deep inhalation, subsequent breath holding and pressure changes blood flow. This state is accompanied by phases of tension and relaxation.
During stress, the blood supply to the vessels of the heart decreases, which leads to a drop in blood pressure and a simultaneous increase in intracranial pressure. During relaxation, blood flow is restored and blood pressure rises accordingly.
During this stage, receptors in the cervix sense changes in blood pressure, which send a signal to the vagus nerve in the brain, helping to further reduce the heart rate. This is how a healthy body reacts to the Valsalva maneuver.
The inability of the heart muscle to change the rhythm of the heart indicates the likelihood of developing pathological conditions of the cardiovascular system.
Holding your breath and exercising also affects the pressure in the lower extremities. Abnormal changes in the venous valves of the legs and thighs reverse blood flow, indicating dysfunction.
The Valsalva technique simultaneously increases pressure in the nasopharynx and middle ear, which, when pus accumulates in it, causes perforation of the membrane and its expulsion from the auricle.
Valsalva maneuver
Sometimes, at rest, reflux with varicocele is not at all expressed; in such cases, additional tests are required, such as a test with straining and holding the breath or a Valsalva maneuver.
The Valsalva maneuver for varicocele is performed as follows: the patient takes a deep breath and begins to strain the abdomen. At this moment, in the Color Doppler mode, the doctor normally sees only the pulsation of the testicular artery and the artery of the ejaculatory duct. With a varicocele, a network of bending tubular structures in blue and red colors is visualized in the Color Doppler mode - these are varicose veins or varicoceles. Coloring of the veins for more than 1 second indicates malfunction or so-called reflux. This condition is expressed in the penetration of blood through incompetent valves and dilated varicose nodes into the testicle and contributes to the malnutrition of the testicle.
The essence of the method
During the examination, the patient is in a standing or sitting position (rarely lying down). He is asked to exhale all the air. This is followed by a long, deep breath (with your nose and mouth closed). Breathing after inhalation should be held for 15-18 seconds. Then exhale slowly, followed by sweat.
Rapid entry of air into the lungs speeds up blood flow to the heart, and stopping breathing slows down its movement. This may cause slight dizziness and weakness.
Treatment is preceded by recommendations from a specialist doctor.
Contraindications
It is strictly forbidden to use the Valsalva technique in patients prone to sudden fluctuations in pressure. In addition, the following pathologies are contraindications to the procedure:
- Stroke;
- myocardial infarction;
- thrombosis of blood vessels;
- retinal disinsertion;
- infectious diseases;
- inflammatory processes;
- chronic illnesses.
Despite its simplicity, the test cannot be used without the participation and advice of a specialist.
Its effectiveness in making a diagnosis and choosing treatment tactics can hardly be overestimated. It provides maximum information about the state of the organs and systems of the human body.
Indications and contraindications
The Valsalva maneuver is a test that is necessary in the following cases:
- Diagnosis of tachycardia,
- Determination of the risk of mortality in patients with myocardial infarction,
- Assessment of the functioning of the valves of the leg veins and diagnosis of varicose veins,
- Diagnosis of varicocele and severity of the genital baroreflex,
- Dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system,
- Determination of patency of the auditory tubes in otitis media.
The Valsalva maneuver when scuba diving at depth helps to cope with the unpleasant sensations that arise when pressure in the middle ear increases. This technique also reduces intra-ear pressure during airplane takeoff and landing.
Outside a medical institution, the Valsalva maneuver is not recommended for persons suffering from hypertension, tachycardia, cardialgia, loss of consciousness, or asthma attacks. It is strictly forbidden to conduct research if the patient has a history of the following pathologies: heart attack, stroke, heart failure stage 2 or higher, pulmonary embolism, appendicitis, peritonitis, retinopathy, febrile conditions, septic processes, thrombosis of large vessels, blockage of blood vessels in the legs, atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries , cerebrovascular accident.
The Valsalva maneuver is performed to diagnose a specific disease under the supervision of a specialist. Using this technique, along with the above, you can detect a retrosternal goiter, which is a protrusion or swelling in the neck.
Impact of pressure on the external auditory canal (diving with a helmet)
When diving without a helmet, water can flow freely into the external ear canal and reduce the volume of air remaining in the ear canal until its pressure spontaneously equalizes the water pressure. When a helmet is put on the head and the auricle is closed, the situation changes. Under the influence of pressure, the helmet is pressed against the auricle and prevents the flow of water into the external auditory canal. As a result, the pressure in it is equalized mainly due to the flexion of the helmet inside the auricle. However, the deflection of the helmet is limited by the shape of the outer ear, and the air volume can only be reduced by 2-4 times in this way. Therefore, starting from a certain depth (about 10-30 m), compensation will not be enough. When blowing, the eardrum will bend outward and may be injured. If blowing is not done, then the membrane of the round window will be under load, since the pressure of the perilymph will be equal to the pressure of water, and the pressure in the tympanic cavity will be slightly more than atmospheric. The thicker the helmet material, the greater the force required to bend it and the greater the difference between the pressures on different sides of the helmet, that is, in the external auditory canal and the water. Therefore, with a thick helmet, spontaneous pressure equalization in the outer ear is worse than with a thin one.
To facilitate equalization of pressure in the outer ear, air is released from under the helmet (especially from the space between the helmet and the auricle) at a shallow depth. In this case, to change the volume of remaining air several times, only a slight deflection of the helmet will be required, which will allow you to dive to significantly greater depths. Sometimes small holes are made in the helmet opposite the ears - this radically solves the problem of equalizing pressure in the outer ear. However, if the water is cold, this method is undesirable - there is a risk of cold ears. In this case, it is better to use a helmet without holes and pour warm water into it. However, if the holes are made small, for example with a diameter of 1 mm, then this will be enough to equalize the pressure, but the water circulation will be small.