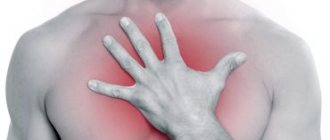
Skin hyperemia (redness in certain areas) is always caused by excessive plethora of small vessels - capillaries. They come close to the surface and are visible through the outer layer. Since the capillary bed has two bends (arterial and venous), redness can be caused by one of the types of vessels or be of a mixed nature.
Hyperemia cannot be considered a disease. We know many physiological conditions under which a healthy person develops a bright blush, a flush of embarrassment or shame on his face, or a pinkish body after a bath.
However, it is impossible to ignore such a symptom, which manifests itself paroxysmally or too often in unusual conditions. Therefore, when diagnosing various diseases, skin hyperemia is always taken into account as an essential sign.
What is facial hyperemia
Increased blood flow to internal organs or increased blood pressure due to diseases is called hyperemia (plethora). The condition is characterized by bright skin redness. In clinical practice, there are three types of hyperemia:
- Venous. It is characterized by a violation of the venous outflow of blood from internal organs and tissues.
- Arterial. Occurs with persistent high blood pressure (hypertension).
- Focal. In this case, blood circulation in a localized area is disrupted.
Causes
Hyperemia of the facial skin occurs when blood vessels, internal organs and tissues are overfilled with blood, hormonal imbalances, and exposure to adverse environmental factors. The pathogenesis of the disease consists of excessive blood supply or impaired venous outflow. Tonic hyperemia of the face and neck appears with a sharp increase in body temperature during colds, during physical exertion or emotional overstimulation.
As a rule, a hyperemic face is a temporary phenomenon; the symptom goes away after the main cause of the pathology is eliminated. Among the causes of redness on the skin are:
- exposure of the skin to wind, frost, sunlight or chemicals;
- overheating of the body due to visits to the sauna, hot climate;
- excessive physical activity;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system (hypertension, heart defects, rheumatism);
- hormonal changes due to menopause, pregnancy, taking medications;
- autoimmune pathologies (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatism, sarcoidosis);
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- dysbacteriosis;
- renal failure;
- hypersensitivity reactions (allergy);
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- alcohol abuse, smoking.
Symptoms
Sometimes hyperemia may appear as red spots or a rash. Hidden signs of the disease include acceleration of blood flow through the vessels, weakening of the walls and expansion of veins (varicose veins). Often, redness of the facial skin, similar to hyperemia, is observed in children of the first year of life, which appears as a result of an allergic reaction to complementary foods or breast milk. Typical clinical manifestations of hyperemia in adults include:
- local increase in temperature;
- severe swelling of the face;
- bags, bruises under the eyes;
- itching;
- rosacea (red spider veins on the cheeks, nose);
- tides;
- hyperemic skin has a bright color;
- peeling of the skin.
Infectious pathologies
Various pathogens can provoke the development of infectious inflammation of the skin - bacteria, fungi, viruses or parasites. This form is characterized by an acute course, which can turn into a chronic form. The patient needs immediate medical attention.
In its acute form, the most common erythema infectiosum in children is caused by parvovirus B19. It is characterized by the sudden onset of the disease, the characteristic signs of which are:
- rapidly rising body temperature;
- muscle pain, headache;
- the appearance of a red rash covering the face and body on the third or fourth day after the onset of the disease;
- gradual increase and closure of spots.
After some time, clinical manifestations gradually fade away until they disappear completely. If left untreated, the process can become chronic. The patient remains able to transmit the infection to healthy people for several days after recovery.
Treatment of facial hyperemia
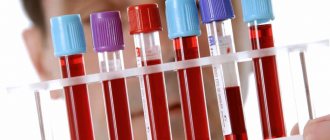
To prescribe effective treatment, it is necessary to accurately diagnose the disease and establish its cause. During the examination, the doctor interviews the patient and examines him. In addition, it is necessary to measure blood pressure and pulse. To exclude dermatovenerological diseases, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist and get tested. The following diagnostic methods help determine the etiology of hyperemia:
- clinical minimum (general, biochemical blood and urine tests);
- ultrasound examination of internal organs (ultrasound): thyroid gland, liver, ovaries;
- colonoscopy (visual examination of the intestines using a rectal probe);
- chest x-ray;
- gastroscopy (visual examination of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum using a gastroscope).
Article on the topic: Which drugs for hypertension are better and more effective?
Complex treatment of hyperemia includes the use of pharmacological drugs for local (ointments, gels) and systemic (capsules, tablets) use. Additionally, the patient must adhere to a diet and a healthy lifestyle. In the absence of contraindications, various folk remedies, soothing cosmetics (ointments, masks), and physiotherapy can be used at home.
Drug treatment
To reduce redness and relieve swelling, corticosteroid ointments are used topically. The main pharmacological therapy is aimed at eliminating the root cause of the disease:
- For vegetative-vascular dystonia and erythrophobia, the use of sedatives is effective: Valocordin, Corvalol, tinctures of valerian root, decoctions of St. John's wort.
- For high blood pressure, complex therapy is prescribed with drugs from the groups of beta blockers, ACE inhibitors (angiotensin-converting enzyme), and vasodilators. The drugs relieve attacks of tachycardia, eliminate attacks of hypertension, and improve blood circulation in tissues. Captopril, Losartan, Propranolol, Nadolol, etc. are effective.
- Therapy for autoimmune diseases is carried out using anti-inflammatory pharmacological agents, corticosteroids and immunosuppressants: Prednisolone, Cyclophosphamide, Methotrexate.
To eliminate local manifestations of the disease (redness, swelling, itching), vasotonic and anticoagulant agents are used in the form of gels or ointments. The following pharmacological drugs are popular:
- preparations with horse chestnut extract;
- heparin ointment;
- Troxerutin;
- gel with tea tree extract;
- Troxevasin;
Diet
One of the important components of the treatment and prevention of any disease is diet. The following products are allowed for hyperemia:
- vegetables boiled, stewed or baked;
- fresh fruits;
- porridge;
- dairy products;
- nuts;
- dried fruits;
- Fish and seafood;
- lean boiled meat (poultry, beef, veal, rabbit).
Excessively salty foods, fatty foods, and fried foods should be excluded from the diet. The following products should also be limited in consumption:
- fast food;
- flour;
- sweet;
- alcoholic drinks.
When hyperemia occurs, you should consume large amounts of vitamins (K, C, E, P). They help strengthen the vascular wall and maintain optimal blood viscosity. Check out the list of foods that contain large amounts of vitamins:
| Vitamin | Where is it contained? |
| R | Rosehips, buckwheat, blackcurrant, pomegranate, apple, grapes, cabbage, apricot. |
| Ascorbic acid (C) | Sweet peppers, rose hips, black currants, citrus fruits, white cabbage. |
| TO | Seaweed, banana, tomato, pear, carrots, pear, lentils, red meat, low-fat fish (pollock, hake). |
| Tocopherol (E) | Vegetable oils, nuts, sunflower and pumpkin seeds, olives, papaya. |
Folk remedies
The use of folk recipes in addition to the main treatment will help eliminate hyperemia. Home remedies may have side effects and contraindications for use, so you should first consult with a specialist. Among the popular folk remedies for hyperemic facial skin, the following recipes are suitable:
- Aloe and cucumber mask. Take 1 small aloe leaf, rinse, peel, then mash. Mix with the juice of one cucumber. Apply the composition 1-2 times a day to the affected areas for 15-20 minutes. The product eliminates peeling and swelling well.
- Beet juice lotion. Mix half a glass of freshly squeezed beet juice with boiled water. Wipe your skin with the mixture 3-4 times a day. This folk remedy moisturizes the skin and enriches it with vitamins. In addition, you can wipe your face with a small cold piece of root vegetable - this helps remove swelling and redness.
- Plantain leaf mask. Take 10–15 plantain leaves, rinse well under running water, cut into small pieces, then mash until the juice releases. Apply to face, leave for 20 minutes. Use the product daily before bed. The mask improves vascular tone and relieves redness.
- Fresh potato mask. To prepare the product, take 1-2 medium potatoes, peel and grate. Apply to face for 30 minutes 2-3 times a week. Potatoes have a decongestant, anti-inflammatory, tonic and softening effect, and prevent the appearance of rosacea. If you have dry skin, then use a moisturizer after the mask, because... potatoes can cause peeling.
Diet food
Many foods can affect the condition of facial skin. Some, on the contrary, can strengthen the vascular network and improve health. It is recommended to eat foods high in vitamins E, P, C. In case of hyperemia, the following is allowed:
- root vegetables - beets, turnips, carrots;
- fresh vegetables, fruits or berries, including sweet ones - black currants, cherries, citrus fruits, apricots, grapes, cabbage, bell peppers, tomatoes, cucumbers;
- sprouted grains and cereals;
- dairy products - cottage cheese, yogurt, cream, low-fat milk.
Fatty meats should be limited for a while; preference is given to chicken fillet, white fish, and seafood. Too fatty milk, cheese, and sour cream should also be excluded, as should chicken eggs. High protein content in foods interferes with normal blood flow. It is absolutely necessary to avoid spicy, salty and sweet foods. Alcohol or tobacco products negatively affect the functioning of the liver and heart, so it is undesirable to use them.
It is possible to cure hyperemia by following proper nutrition and following the recommendations of your doctor. Further prognosis depends on the form of the disease and the patient’s condition. As a rule, the disease does not return again. Proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle will help prolong the results of treatment.
You can ask your question to our author:
Migratory type pathology
Infectious dermatosis in the form of migratory erythema after a tick bite initially looks like a slight redness, which quickly increases in size and becomes ring-shaped with a clear hyperpigmented border. Unpleasant sensations, itching or burning may occur in the affected area. The stain persists for several days, in some patients up to a month. If left untreated, the disease becomes chronic, which is difficult to treat.
The disease is caused by the bacterium Borrelia, which is carried by ticks. The pathogen spreads in the body through the lymphatic and circulatory systems, penetrates various organs and other areas of the skin. The joints, muscles, and nerve tissues are most often affected, and less commonly, the tissues of the heart muscle and the lining of the brain.
Are you experiencing symptoms of erythema?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call