In modern laboratories, dozens of different tests can be performed, which help evaluate many processes in the body and play a huge role in the diagnosis of most diseases. According to statistics, 70% of decisions made by doctors are based on laboratory test data.
Over the past decades, laboratory diagnostics have become very accurate, but, unfortunately, sometimes the test results are erroneous. And it's not always the laboratory's fault. The preanalytical stage and proper preparation of the patient play a huge role. This is where about half of the mistakes occur. The result is distorted results, incorrect conclusions, incorrect treatment and unnecessary additional diagnostic methods.
One possible cause of errors in laboratory diagnostics is lipemia , a condition in which there are high levels of lipids in the blood. It occurs in 1–5 samples out of 200 received by the laboratory, and is much more common in outpatients than in inpatients. The main reason is that patients do not maintain the required interval between the last meal and blood donation. Unfortunately, not everyone knows how to properly take tests on an empty stomach, and doctors do not always explain well and cannot control the situation.
| A brief excursion into biochemistry: what are blood lipids? Fats and fat-like substances (cholesterol, triglycerides, phospholipids) are combined under the term “lipids”. By themselves, they cannot dissolve in water, so they are found in the blood plasma in the form of complexes with proteins - lipoproteins. There are several types of lipoproteins, they differ in composition, size and functions:
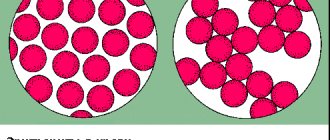
Lipemia refers to the cloudiness of a blood sample due to high levels of lipoproteins. |
Characteristics of the condition
Chilean blood - what is it and what causes it? We ask every patient who receives such a diagnosis.
Typically, blood serum is a liquid with a clear or slightly yellowish tint. But if there are certain irregularities, it acquires a more viscous consistency and a dense white color (when divided into fractions).
This condition is called plasma cholesterol.
Deviations can only be detected using biochemical analysis, since by interaction with various reagents it is possible to determine which compounds are present in the blood and in what quantities.
Practice shows that this pathology is diagnosed in both men and women, regardless of age.
The danger of this disorder is that it cannot isolate individual components of the blood, making it impossible to perform various tests. It should also be taken into account that “fat” blood is not used as donor blood.
What are triglycerides?
Triglycerides represent the body's main energy reserve. They circulate in the blood in the form of lipoproteins of atherogenic nature. The content increases after eating fatty foods, which in most cases causes blood chyle. What it is? After eating fatty foods, the fats contained in it enter the bloodstream and interfere with a full analysis.
What does a blood test show? They are the most common cause of fat deposits. They indicate the presence of atherosclerotic processes in the body.
Causes of pathology
Before determining a treatment regimen, it is necessary to understand what causes the pathology and try to eliminate the original source as quickly as possible.
In most cases, chiles are the result of poor nutrition. If the patient's diet is based on foods saturated with fat, triglycerides will enter the plasma from these compounds and their amount will continue to increase.
Fats, which form the basis of vegetable oils, form glycerol and fatty acids during processing. These compounds are absorbed by the small intestine and passed into fat tissue, but a small portion also enters the bloodstream.
Triglyceride levels change throughout the day.
The maximum value is observed 20-30 minutes after eating, and after 10-12 hours the concentration of triglycerides drops.
To obtain reliable results and accurately determine the content of fatty components in a blood test, it is recommended to carry out the test in the morning on an empty stomach.
Blood cholesterol in adults and children is more often the result of the adverse effects of factors such as:
- Diseases accompanied by metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, thyroid dysfunction, obesity).
- Kidney and liver problems. Bedsores are common in men and women who suffer from alcoholism. In addition, the disease is often diagnosed with renal failure and cirrhosis of the liver.
- Dysfunction of the lymphatic system.
- Genetic disorders of lipid metabolism. The main feature of this pathology is an increase in the level of neutral fats.
As medical practice shows, the most common reason for such a diagnosis is ignoring the doctor’s recommendations when preparing for the analysis.
If two days before taking the biomaterial a person consumes fatty and spicy foods, eggs, bananas, smoked meats and alcoholic drinks, the likelihood that the test result will be unreliable exceeds 40%. Excessive consumption of such foods always leads to excessive accumulation of lipids.
In addition, cholesis is often a consequence of the manifestation of diseases such as:
- Circulatory system disorders - cerebral ischemia, cerebral vascular thrombosis, heart attack, atherosclerosis;
- problems with the musculoskeletal system;
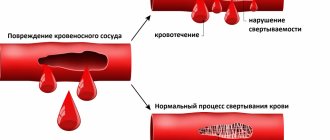
- blood clotting disorders;
- Down syndrome;
- acute and chronic pancreatitis;
- too much calcium in the body (hypercalcemia).
Symptoms
Independent suspicion of blood cholysis is almost impossible, since in 95% of cases this disorder does not affect the patient and no specific symptoms are observed. These disorders are usually detected by chance during an external examination.
In medical practice, patients extremely rarely complain of such abnormalities as plasma chylosis:
From the above it follows that the manifestation of ailments is very similar to obesity and kidney disease.
How is chylosis detected?
Detection of deviations from the norm is possible only with the help of a biochemical blood test. Other laboratory diagnostic methods are less reliable.
It is recommended to donate blood in the morning on an empty stomach. 24 hours before collection, the patient is advised to adhere to a proper diet, avoid fatty and fried foods, and alcoholic beverages.
In addition, before the analysis it is recommended to avoid taking medications, since drugs of certain pharmacological categories can also lead to unreliable results.
Blood test: interpretation, norm, table for women
To decipher laboratory analysis, you need to know the approved standards for each of the indicators. They may vary depending on gender, age and other individual characteristics.
| Index | Characteristic | Norm |
| RBC - red blood cell count | With an insufficient number of red blood cells, anemia develops and the body does not receive enough micronutrients; with an excessive number of red blood cells, cell gluing and blockage of blood vessels may occur. | 3.8-5.5x 1012/l |
| HGB, Hb - hemoglobin | It is a special protein responsible for the transfer of oxygen; a decrease in hemoglobin leads to oxygen starvation of organs; an increase in the amount of Hb indicates dehydration of the body and an increase in the content of red blood cells. | 120-140 g/l |
| HCT - hematocrit | Indicated as a percentage, it characterizes the percentage of red blood cells in the blood. | 35-45 % |
| RDWc - red blood cell distribution | Indicates the presence of red blood cells of different sizes in the blood. This condition is called anisocytosis and is a manifestation of various types of anemia (in particular, iron deficiency). | 11,5-14,5 % |
| MCV - average red blood cell size | Allows you to determine the type of anemia, each of them differs in cell size | 80-100 fl |
| MCH - hemoglobin content in erythrocytes (average) | Shows the amount of hemoglobin content in one red blood cell; deviation from the norm indicates the presence of anemia of various etiologies. | 26-34 pg |
| MCHC - hemoglobin concentration in erythrocyte | Indicates the degree of saturation of the red blood cell with hemoglobin. | 30-370 g/l |
| PLT - platelet count | They influence the formation of platelets and help prevent severe blood loss due to vascular damage. | 180-320x 109/l |
| WBC - white blood cell count | White blood cells help protect the body from infections. When the white blood cell count in the body increases, a bacterial infection or inflammatory process is often detected. | 4-9x 109/l |
| LYM - lymphocyte count | Subtype of leukocyte. Its functions include the production of immunity and antibodies to various viral infections. | 1.2-3x109 /l |
| MID - mixtures of different cells | Immature blood cells that circulate in it. | 0.2-0.8x109 /l |
| GRA - granulocyte content | Granular granulocytes indicate the presence of inflammatory processes in the body and fight infections. | 1.2-6.8x109 /l |
| MON - monocyte content | A subtype of leukocytes that, coming from the blood into surrounding tissues, are able to absorb dead cells. | 0.1-0.7x109 /l |
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate for women should be within 15 mm/h.
Treatment methods
Despite the fact that blood chylosis is not a disease and is not life-threatening, like any other ailment, it requires timely treatment.
Regardless of whether the pathology was detected in a child or an adult, therapy is prescribed only after the attending physician determines what is the primary source of the disorder. Otherwise, the positive effect will not last long, and after the end of chiles therapy it will return to action.
In the fight against this deviation, drug therapy has proven itself very well, as well as adherence to a special diet.
Drug therapy
In order to eliminate pathology as soon as possible, the approach must be comprehensive. Most therapists prescribe drugs to patients from several pharmacological categories:
- Antioxidants. Prevents the formation of fatty deposits in the vascular area.
- Fibrates. Medicines from this group normalize metabolic processes and support the elimination of cholesterol.
- Use of nicotinic acid. This substance has a pronounced anti-sclerotic effect, prevents the production of fatty acids, and also removes cholesterol.
Patients are required to take medications that normalize liver function.
Nutritional Features
If elevated serum lipid levels are detected, a special diet is an important part of treatment.
To quickly restore indicators to normal, the following foods should be excluded from the diet:
- fatty meat (regardless of how it is cooked);
- baked goods, cookies, various sweets (marshmallows, jams, gingerbreads, candies);
- High fat dairy products;
- eggs;
- alcohol.
The basis of the diet should now be vegetables and fruits, sea and river fish and grain products.
The patient is advised to pay attention to citrus fruits, ripe tomatoes and eggs. Using a diet will help to normalize your well-being as soon as possible, as well as improve the condition of the whole body.
Folk remedies
If the patient does not want to take prescribed medications, he can eliminate the problem with folk remedies, but the treatment in this case will be longer.
Fans of alternative medicine recommend eating as much garlic, cranberry compote, flaxseed oil and barley as possible.
This therapy is completely safe and can be performed even during pregnancy.
Drinking mineral water with the addition of a small amount of fresh lemon juice has proven to be an excellent way to combat pinching. The liquid can be drunk daily in unlimited quantities.
Possible complications and preventive measures
The main danger of plasma chylosis is that this disease interferes with blood tests, which are necessary for diagnosing various diseases.
It should also be remembered that “fatty” blood is often a consequence of serious diseases, so this disorder should not be ignored.
To minimize the likelihood of developing this disease, doctors advise patients to lead an active lifestyle and eat right, but there are no specific preventive measures.
If the test shows blood chylosis, do not panic. It is likely that such a diagnosis is the result of ignoring the doctor’s recommendations before taking a blood test.
To accurately determine the clinical picture, it is necessary to conduct a second analysis, only after which it will be possible to talk about the state of health and recommendations for treatment.
Prevention
Experts recommend paying close attention to your health and getting timely treatment. To prevent serious health problems, it is necessary to follow preventive measures. These include:
- rational and balanced nutrition,
- full physical activity,
- fight against bad habits,
- walks in the open air,
- strengthening the immune system.
Blood chylosis in young children is a contraindication for vaccination. Vaccination given to a child with pathology can lead to severe allergies, including anaphylactic shock. Specialists remove the medical duct only after complex treatment and a decrease in the level of triglycerides in the blood.
Chylosis is easier to prevent than to treat its consequences, which have a negative impact on the functioning of the entire body and the quality of human life. Basic preventive measures can reduce the risk of developing many pathological conditions, including lipemia.