All articles
Postpartum hemorrhoids
14.09.2017
Hemorrhoids often develop during pregnancy and even more often occur after childbirth. According to research, about 35 percent of women who have recently given birth experience its symptoms.
With hemorrhoids, the vessels that are located in the anal canal at the exit from the rectum become inflamed and swollen. Signs of the disease include rectal bleeding, pain and itching, prolapse of hemorrhoids from the anal canal and involuntary soiling of underwear.
If you notice bleeding or the pain increases significantly, be sure to consult a doctor to clarify the diagnosis and receive the correct treatment.
The most important risk factor for hemorrhoids is constipation.
Moreover, hard stools worsen the symptoms of the disease. Therefore, soft and regular stools are needed both for the prevention and treatment of hemorrhoids (as well as anal fissures). To do this, doctors advise:
There are foods that contain a lot of fiber (dietary fiber)
Vegetables and fruits, legumes and whole grain flour products are suitable. For example, prunes, apples, bran bread, boiled lentils. The recommended amount of fiber is 20-35 grams per day. Product packaging often indicates how much fiber it contains.
Drink enough water
Focus on thirst, since there are no exact recommendations, but according to rough estimates, men should drink about 3.7 liters of fluid per day, and women - about 2.7 liters. We are talking about any liquid. Juice, coffee and tea also count, as does the water contained in food.
Be active
Do suitable exercises, such as swimming or yoga.
There are several other ways to cope with the symptoms of hemorrhoids without seeing a doctor:
- Use damp toilet paper and then gently blot with a dry cloth (do not rub) to relieve pain. You can simply wet plain paper or use a hygienic shower or bidet.
- Take a warm bath without soap, foam or other additives for 10-15 minutes two to three times a day. Baths improve blood circulation and relax the muscles of the anus.
- Apply cold compresses. To do this, soak a piece of clean cloth in ice water, wring it out and apply it to the sore spot.
- Do Kegel exercises. They should help with involuntary soiling of laundry.
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, the use of any medications (including vitamins and dietary supplements) should be discussed with your doctor.
Content
- Inflammation of hemorrhoids
- External hemorrhoids in women after childbirth
- Postpartum hemorrhoids - causes and symptoms
- Effective treatment
- Is it possible to treat hemorrhoids after childbirth at home?
- What to do if you have inflammation of hemorrhoids during pregnancy and after?
I recently published on the website medklinik.by and in my telegram channel “Doctor Treats” an article “Pregnancy and hemorrhoids: new approaches to treatment.” The article provides detailed recommendations from a proctologist for women planning a pregnancy. These recommendations are based on many years of practice and have benefited many of my patients.
Surgeries to remove hemorrhoids in pregnant women in our clinic
The department has the technical equipment to perform all types of surgical intervention for hemorrhoidal disease, ranging from latex ligation to ultrasonic removal of hemorrhoids.
- Ligation of hemorrhoids. This method is used to treat internal hemorrhoids, when the manifestations of hemorrhoids include prolapse of self-reducing hemorrhoids and moderate bleeding during bowel movements. The essence of the method is that a small latex ring is placed on the hemorrhoidal node, which compresses its base with the vessels passing through it, stopping the blood flow in the node. After several days, the knot and the ring fall off, and the resulting wound heals within 1-2 weeks. This procedure is most often virtually painless.
- Sclerotherapy and infrared photocoagulation. These methods are suitable for the treatment of hemorrhoidal disease, manifested only by bleeding without prolapse of nodes.
- Hemorrhoidectomy is a surgical operation aimed at removing hemorrhoids. This is the best way to achieve complete disappearance of all symptoms. Surgical removal of internal hemorrhoids is used for prolapsed and non-reducible nodes, or when the effect of outpatient treatment is not observed, or when outpatient treatment is impossible. During surgery, excess tissue that is a source of bleeding is removed. To make the patient more comfortable, the operation is performed under spinal anesthesia with sedation.
Photo of hemorrhoids in a pregnant woman BEFORE
Photo of hemorrhoids in a pregnant woman AFTER
Taking into account the conducted research, standards for the management of patients with hemorrhoids during pregnancy and lactation have been developed, allowing for the safest possible surgical intervention and ensuring adequate postoperative pain relief. The Clinic of Coloproctology and Minimally Invasive Surgery is located in the same institution as the Clinic of Obstetrics and Gynecology. This allows us to monitor patients after surgical treatment together with gynecologists.
You should always remember that pregnancy is a special condition that requires careful monitoring and an individual approach. Therefore, even drug treatment and regime correction require consultation with a qualified specialist.
Inflammation of hemorrhoids during pregnancy and after childbirth
But what should a young mother do if hemorrhoids appeared during pregnancy and became inflamed after childbirth?
If you, my dear readers, have read the article “Pregnancy and hemorrhoids: new approaches to treatment,” then you already know why hemorrhoids occur and progress during pregnancy. For those who did not have time to read the article or forgot, I will explain. The pregnancy hormone progesterone relaxes the uterus so that pregnancy can develop. Simultaneously with the uterus, progesterone relaxes the veins, intestines, and ligaments. Under the influence of this hormone and the growing uterus, hemorrhoidal veins expand and hemorrhoids appear.
In this case, external hemorrhoids most often form and, less often, internal hemorrhoids.
How constipation manifests itself
Constipation is defined as difficult, unsystematic or incomplete bowel movements, as well as the inability to go to the toilet for more than a day and a half in a row. The following signs indicate constipation:
- hard, dry, segmented stool;
- decrease in daily stool volume;
- decreased frequency of bowel movements (less than three times a week);
- a feeling of pressure in the rectum during bowel movements.
Constipation is often accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the stomach and flatulence. A woman often experiences pain in the intestinal area.
When breastfeeding, spastic and atonic constipation may occur.
- Spastic . They occur against a background of nervous tension, stress, fear, or lack of sleep. Due to the nervous shock a woman experiences, the intestinal muscles contract and impede the passage of feces. Spastic constipation is characterized by frequent false urges to defecate. The stool is dry and scanty. Bowel movements are often painful.
- Atonic . Associated with inhibition of intestinal muscle tone. Insufficient peristalsis slows down the speed of stool movement. Stool with atonic constipation has a different consistency: hard at the very beginning of defecation and liquid at the end.
Problems with bowel movements after childbirth are considered normal. In most cases, constipation goes away on its own within a few days. If constipation becomes chronic, causes severe discomfort and is accompanied by unpleasant sensations, it is necessary to identify the cause of its occurrence.
Postpartum hemorrhoids are almost always external hemorrhoids
Many of my patients at the appointment additionally note that they themselves did not give birth, but had a Caesarean section. My dears, the process of childbirth itself does not play any role in the development of hemorrhoidal disease (recently, a woman was seen after two Caesareans - 4.5 and 1.5 years ago with quite large inflamed hemorrhoids)! Hemorrhoids grow during the 9 months of pregnancy due to high levels of progesterone and a large uterus in the second half of pregnancy, compressing the pelvic veins.
During childbirth, existing hemorrhoids “just” become inflamed and worsen due to stress.
Please remember this:
- Hemorrhoids appear and grow during pregnancy.
- During childbirth, hemorrhoids become inflamed.
This is precisely why a Caesarean section will not get rid of hemorrhoids, but it can get rid of its inflammation. Although not necessary.
Why is constipation dangerous during breastfeeding?
Deterioration of intestinal function negatively affects a woman’s physical condition. Bloating and heaviness appear in the abdomen, and appetite decreases. Constipation may cause sleep disturbances, headaches, increased nervousness and decreased performance.
In addition, with constipation during lactation, fewer digestive enzymes enter breast milk, which also affects the baby’s stool. In some cases, delayed bowel movements can cause a reduction in breast milk production.
To normalize intestinal function, it is necessary to reconsider the daily diet and physical activity regime.
Causes and symptoms
So, we agreed: hemorrhoids appear during pregnancy. Alas, it remains with you in later life if it is not removed.
Why is that? External hemorrhoids behave like varicose veins in the legs. Very often these diseases occur together during pregnancy. Or progress if they were there before. Therefore, just as varicose veins will not go away after childbirth, so hemorrhoids will also remain with you. And just as varicose veins will progress and cause problems, so hemorrhoids will increase and bother you.
Have you noticed an extra fold in your anus after giving birth? This is an external hemorrhoid with a 90% probability.
Is the fold gradually enlarging or new ones appearing? These hemorrhoids are growing.
The fold hasn't changed yet? This does not mean that hemorrhoids have disappeared or are not progressing: while the nodes are not large, their bulk is located deeper, in the anal canal. Can you check for hemorrhoids yourself? Yes, immediately after defecation, preferably without getting up from the toilet, wash your butt and touch it with your fingers. You can strain quite a bit. Soft tissue is identified under the fingers, and when you press on it, it decreases. This is the external hemorrhoid.
In such a situation, there is nothing I can do to please you. Go to a proctologist. The smaller the node, the easier it is to remove it with a laser.
Hemorrhoids - varicose veins in the anus, caused by hyperplasia of the cavernous bodies of the rectum, are the most common proctological disease. It is believed to affect more than 10% of the population aged 30 to 50 years. According to various authors [1, 2, 14], hemorrhoids occupy one of the first places in coloproctology, and its prevalence is high and amounts to 140-180 people per 1000 adults.
In women, hemorrhoids appear or worsen mainly during pregnancy and childbirth. According to statistics, hemorrhoids are 5 times less common in nulliparous women than in women who have given birth at least once. In this case, the age criterion also plays an important role: during pregnancy at 30 years of age, the disease occurs 3 times more often than during pregnancy at 20 years of age. According to N.V. Moon et al. [5], hemorrhoids occur in 7.7% of non-pregnant women, 25.7% of pregnant women and 49.8% of postpartum women. Pregnancy, although not the main pathogenetic factor of hemorrhoids, often reveals it and aggravates its clinical course. On the other hand, hemorrhoids in pregnant women often complicate the course of labor and the postpartum period [1, 10, 11].
The views of researchers on the etiology of this disease are very contradictory. If Hippocrates attributed the cause of hemorrhoids to bile and mucus, then in subsequent centuries many different theories were put forward and disputed. Congenital insufficiency of the venous system, venous congestion, and disruption of the mechanism of the rectal sphincter were mentioned as the main pathogenetic factor. At the same time, none of the hypotheses based on the pathology of the venous system could explain the origin of the main symptom characteristic of hemorrhoids - the discharge of scarlet blood. The answer to this question was given relatively recently, in 1963, when cavernous vascular plexuses were discovered located in the submucosal layer of the caudal part of the rectum. Cavernous bodies are located in the area of the base of the anal columns diffusely or, more often, grouped mainly in three zones: on the left lateral, right anterolateral and right posterolateral walls of the anal canal. It is in these areas that hemorrhoids most often subsequently form. It has been proven that, in addition to veins and arteries, these vascular formations contain elastic connective tissue and smooth muscle cells. By regulating blood flow in the anal canal area, hemorrhoidal plexuses provide the basic functions of the rectum: retaining feces and defecation, providing an effective immune barrier between the internal environment of the body and the outside world. A hemorrhoid is a hyperplastic change in the cavernous tissue of the rectum, caused by an increased influx of arterial blood into the cavernous bodies through arteries with obstructed outflow through the efferent venules. The development of dystrophic processes in the anatomical structures that form the fibromuscular framework of internal hemorrhoids contributes to their gradual displacement in the distal direction [6, 19].
A major role in the development of hemorrhoids is played by impaired blood outflow through the venules from hyperplastic cavernous bodies of the distal rectum and anus. These cavernous bodies are present normally and are formed at the 3-8th week of embryonic development and are located in the area of the base of the Morganian columns. Cavernous bodies differ from ordinary veins of the submucosal layer of the rectum in the abundance of direct arteriovenous anastomoses. This is precisely the explanation for the fact that in hemorrhoids bleeding is arterial in nature. Hemorrhoids usually occur in individuals with pronounced groups of cavernous bodies. Other factors in the occurrence of hemorrhoids are congenital functional deficiency of connective tissue, impaired nervous regulation of the tone of the venous wall, increased venous pressure due to constipation, prolonged work in a standing or sitting position, heavy physical labor, and pregnancy.
The main pathogenetic factors in the development of venous pathology during pregnancy are:
- dishormonal changes;
— functional state of the vein walls;
- increase in circulating blood volume;
- changes in the blood coagulation and anticoagulation systems;
- increased intra-abdominal pressure.
A certain role in the occurrence of hemorrhoids is attributed to the abuse of alcohol and spicy foods, as a result of which the arterial flow to the cavernous bodies of the rectum increases. With prolonged exposure to unfavorable factors, along with predisposing factors, hyperplasia of the cavernous bodies occurs and the hemorrhoidal node itself is formed [4, 10, 12].
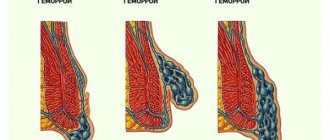
There are internal hemorrhoids, located above the pectineal line under the mucous membrane of the rectum, and external, located below the pectineal line under the skin. Approximately 40% of patients have a combination of external and internal hemorrhoids - mixed hemorrhoids. External hemorrhoids are observed infrequently - in less than 10% of patients [3, 7, 20].
With external hemorrhoids, the nodes are localized on the outside, and they should not be confused with prolapsed internal hemorrhoids. Most often, external nodes manifest as thrombosis. As a rule, bleeding from external nodes does not occur, since they are not injured during defecation. But constant stagnation of blood in them can lead to the formation of blood clots in them. Externally, the external hemorrhoidal node can be of different sizes, from 3 mm or more, which depends on its blood supply. An external hemorrhoid is usually covered by skin, while a prolapsed internal hemorrhoid is usually covered by the mucous membrane of the anal canal.
With internal hemorrhoids, there are varicose hemorrhoidal veins, which are located deep in the anal canal, so such hemorrhoids are not visible during a normal examination. In order to see them, you have to resort to special research methods: anoscopy, rectoscopy. Also, such nodes can be identified during digital rectal examination.
There are three degrees of internal hemorrhoids:
1st degree - hemorrhoidal veins are located in the anal canal, may not be palpable, cause subjective complaints by maintaining inflammation or causing bleeding.
2nd degree - nodes protrude from the anus when straining and disappear on their own.
The 3rd degree is characterized by prolapse of hemorrhoids that cannot be reduced on their own.
Hemorrhoids can occur acutely or chronically, but essentially these are phases of the same process. In acute hemorrhoids, inflammation occurs in the nodes, which, in addition to other symptoms, leads to severe pain in the anus. Spasm of the rectal sphincter increases swelling, leads to stagnation of blood in the lower rectal plexus and thrombosis of external hemorrhoids. In some cases, acute inflammation is accompanied by swelling of the perianal area and necrosis of the nodes. The often occurring tissue swelling and inflammatory infiltration create the impression of pinched hemorrhoids [2, 21].
The acute course of hemorrhoids is divided into three stages:
Stage I is characterized by thrombosis of hemorrhoids without inflammation.
Stage II is characterized by the addition of inflammation.
Stage III is characterized by widespread thrombosis of external and internal hemorrhoids with inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue, swelling of the skin of the perianal area, necrosis of the mucous membrane of the hemorrhoids.
During chronic hemorrhoids there are four stages:
In stage I, minor changes are noted in the ligamentous apparatus of the rectum, which is responsible for holding hemorrhoids in the anal canal, i.e. There was no prolapse of hemorrhoids.
In stage II, changes in the ligamentous apparatus of the rectum are expressed to such an extent that prolapse of hemorrhoids is noted during the act of defecation, but they themselves are reduced into the anal canal. In this case, bleeding may or may not be observed.
Stage III is characterized by such changes in the rectum that the prolapsed nodes no longer correct themselves, and the patient is forced to reset them himself after each act of defecation.
In stage IV, there is already a constant prolapse of hemorrhoids, and it is almost impossible to set them back. This is due to pronounced changes in the ligamentous apparatus of the rectum.
With chronic hemorrhoids, scarlet blood is released during bowel movements, prolapse of hemorrhoids, dull, incessant pain in the anus, and itching. A typical symptom complex of the chronic course of the disease consists of repeated bleeding, usually associated with defecation and prolapse of hemorrhoids from the anus. Bleeding as the leading symptom of hemorrhoids is observed in more than half of patients. Continuous bleeding from the anal canal is a complication of the disease. Prolonged bleeding from hemorrhoids leads to anemia. The second most common symptom characteristic of hemorrhoids is prolapse of hemorrhoids. There is a direct relationship between the increase in the duration of the disease, its stage and the frequency of prolapse of hemorrhoids. Anorectal bleeding, in addition to the main symptom of hemorrhoids, is a characteristic symptom of other diseases of the colon: malignant tumors, diverticulosis, nonspecific ulcerative and granulomatous colitis. Under the guise of hemorrhoids, especially when bleeding from the rectum, diseases such as polyps and colorectal cancer often occur. Therefore, for any manifestations of intestinal discomfort and, especially, when blood is released from the rectum, it is necessary to perform a digital examination, rectoscopy, colonoscopy or irrigoscopy. One rule must always be followed: at the slightest suspicion of a tumor, always take a biopsy and completely examine the colon [6, 9, 19, 21].
In modern conditions, the problem of hemorrhoids in pregnant and lactating women occupies a special place [1, 4, 13]. The clinical symptoms of hemorrhoids during pregnancy do not differ from those during the normal course of the disease. Most often these are pain in the anus, rectal bleeding and anal itching [5, 15, 22].
Often pregnant women are diagnosed with hemorrhoids in an asymptomatic stage. These women do not present complaints characteristic of hemorrhoids, but upon examination, hemorrhoidal nodes are found in typical places on the walls of the anal canal. Timely identification of pregnant women with clinically asymptomatic hemorrhoids and implementation of preventive measures in them makes it possible in many cases to prevent its development, which complicates the course of childbirth and the postpartum period [1, 13].
The clinical picture of hemorrhoids in pregnant women develops gradually. Initially, unpleasant sensations appear in the anus, especially after defecation. As the duration of pregnancy increases, more pronounced signs of hemorrhoids appear - pain, enlargement of hemorrhoids, bleeding, anal itching, tenesmus, etc. [1, 15, 22].
About half of women who have hemorrhoids during pregnancy experience an exacerbation of the disease after childbirth. As a rule, already with the onset of labor, pain in the anal area increases sharply. During the second stage of labor, when the fetal head passes the pelvic cavity, the vessels of this area, including the rectum, are sharply compressed. Venous outflow is disrupted, blood stagnation and tissue hypoxia increase. This creates additional conditions for the opening of arteriovenous anastomoses directly into the lumen of the cavernous cavities of the rectum. The longer the second stage of labor, the more pronounced these processes are. Hemorrhoids swell, increase sharply in size, and become tense. During pushing, the anal sphincter opens, the distal end of the rectum gapes, and both external and internal hemorrhoids are clearly visible. They enlarge before our eyes, become bluish and dense. After the end of the pushing, the internal nodes decrease somewhat, and with subsequent pushing, the picture repeats. When the fetal head erupts, internal hemorrhoids, if they are sufficiently pronounced, are squeezed out and sometimes their walls rupture. After childbirth, as the anal sphincter gradually contracts, the internal nodes become smaller and reduce on their own, but often, if the sphincter contraction occurs quickly, these nodes are pinched and acute hemorrhoids occur [1, 4, 13].
Conservative treatment, the main goal of which is to eliminate pain and inflammation and normalize blood circulation in the rectal area, is carried out for acute hemorrhoids and in the early stages of chronic hemorrhoids. Conservative drug treatment can be general - drugs that increase the tone of the veins, improve blood flow through small vessels and cavernous veins, and local - wound healing, analgesic and antipruritic ointments, suppositories, microenemas and baths [8, 16, 18].
Prevention of exacerbations is also of great importance, which includes:
- combating stool disorders (getting rid of constipation and improving bowel function without prolonged straining);
- proper nutrition (a diet rich in fruits and vegetables; a strict prohibition of any alcoholic beverages, salty, hot, spicy, pickled, peppered dishes, as these products increase blood flow to the veins of the pelvic floor and primarily the hemorrhoidal venous plexuses);
- proper hygiene after defecation;
- prevention of physical inactivity (physical therapy and hygienic gymnastics help improve the function of the large intestine, increase the tone of the muscles of the anal area and abdominal wall, and reduce congestion in the pelvic veins).
The development of hemorrhoids during pregnancy, as well as its complications, especially in the postpartum period, significantly affects not only the patient’s condition, but also her quality of life. When choosing a drug for treating a pregnant or lactating woman, one should take into account its safety both for the patient herself and for the fetus and newborn, which significantly limits the doctor’s choice [1, 10, 17].
For asymptomatic hemorrhoids, women are prescribed only preventive measures.
In stages I-II of the disease, treatment is carried out with suppositories and ointments, infusions of medicinal herbs, and the prescription of drugs taken orally. After defecation, it is possible to use rectal suppositories containing analgesic components. For spasm of the anal sphincter, it is possible to add suppositories with oil.
When hemorrhoids are combined with anal fissures, or acute hemorrhoids, conservative treatment is carried out in a hospital. It includes rest, diet, cleansing enemas, laxatives, novocaine blockades in the anus, local treatment with suppositories and ointments.
In case of prolapse of internal nodes, without symptoms of acute inflammation, they limit themselves to careful repositioning of the nodes after defecation (it is better to do this in a warm sitz bath). When there is a urge to defecate, small-volume cleansing enemas are recommended. Women are strictly prohibited from heavy physical labor and certain types of domestic work.
Pregnant women suffering from hemorrhoids with prolapse of internal nodes and frequent exacerbations of the disease are subject to hospitalization and surgical treatment. The timing of the operation is determined individually. Patients with such complications are treated with surgical (hemorrhoidectomy - excision of nodes) or minimally invasive treatment methods (minor or bloodless operations). These methods include sclerotherapy, ligation, infrared photocoagulation and laser coagulation. If the pregnant woman’s condition allows, all interventions are postponed to the postpartum period. Exacerbation of hemorrhoids, especially in combination with postpartum perineal trauma, is the most common disease that affects the quality of the postpartum period.
Currently, in obstetric practice for hemorrhoids, Procto-Glivenol is widely used, which is available in the form of rectal cream (1 g contains tribenozide 50 mg and lidocaine hydrochloride 20 mg) and rectal suppositories (1 suppository contains tribenozide 400 mg and lidocaine hydrochloride 40 mg).
The therapeutic effectiveness of Procto-Glivenol for hemorrhoids is due to the combination of two components: tribenoside and lidocaine. Tribenoside has a venotonic and anti-inflammatory effect. The venotonic effect is manifested by improving vascular tone, reducing venous stagnation, reducing the permeability of capillaries and venules and improving microcirculation. The anti-inflammatory effect is manifested by an inhibitory effect on some endogenous substances (bradykinin, serotonin, histamine), which act as mediators in the development of inflammation and pain. Lidocaine has a local anesthetic effect.
The above properties of Procto-Glivenol allowed it to take one of the leading places among antihemorrhoidal drugs, which is explained by the optimal composition, high efficiency and safety of use, especially during pregnancy (starting from the second trimester) and during breastfeeding, since it is during these periods that safety drugs is especially relevant.
Material and methods
We assessed the effectiveness and tolerability of Procto-Glivenol (cream and rectal suppositories) in the treatment of hemorrhoids in pregnant women. 85 pregnant women with clinical signs of hemorrhoids were examined.
All patients were divided into three groups depending on the stage of the disease. The 1st group consisted of pregnant women with asymptomatic hemorrhoids, who underwent preventive measures, including a diet with limited spicy foods and a sufficient amount of plant fiber, physical therapy, walks, and using the anal toilet after defecation. Group 2 consisted of patients with complaints of bleeding, anal itching, and pain during defecation. These women, in addition to the above measures, were treated with suppositories and cream with procto-glivenol from the second trimester of gestation. Group 3 (4 pregnant women) included patients suffering from hemorrhoids subject to surgical treatment. These were women with prolapse of internal nodes and with a history of frequent exacerbations, with heavy hemorrhoidal bleeding, as well as with acute hemorrhoids in the stage of necrosis of the prolapsed strangulated nodes. Pregnant women of group 3 were consulted by a proctologist, together with whom general tactics for further management were developed. These patients were also prescribed Procto-Glivenol according to individual regimens for preoperative preparation.
Procto-Glivenol cream was used for external hemorrhoids, applied to the affected areas in a thin layer 2-4 times a day, and after the pain disappeared - once for 7 days. Procto-Glivenol suppositories were used for internal hemorrhoids 2 times a day for 5-7 days, after the disappearance of painful sensations, once a day for another 7 days.
Results and discussion
It has been established that identifying pregnant women with clinically asymptomatic hemorrhoids and carrying out the special preventive measures described above make it possible to prevent the development of the disease, which complicates the course of childbirth and the postpartum period.
Clinically, the symptoms of hemorrhoids during pregnancy were almost no different from those among other categories of patients with this diagnosis. Of 85 pregnant women with clinical signs of hemorrhoids, pain in the anus was observed in 40 (47.1%), bleeding of nodes - in 28 (32.9%), anal itching - in 26 (30.6%). 55 (64.7%) of the observed women had external hemorrhoids, which was characterized by the appearance of hemorrhoids in the form of warty formations or folds, dense to the touch and not decreasing in volume upon palpation. In internal hemorrhoids (30-35.3%), the nodes were located between the folds of the mucous membrane, could be either single or multiple, collapsed when pressed and filled when coughing. In addition, in 13 (15.2%) pregnant women, hemorrhoids were combined with an anal fissure. It should be noted that if in pregnant women aged 20 to 30 years, hemorrhoids are detected in approximately every fifth, then after 30 years - in every second.
When assessing the results of therapy, the severity of remaining clinical symptoms was assessed by patients as average by the 7th day of treatment and as weak by the 15th day. At the same time, such a clinical symptom as pain during defecation was observed in 9 (10.5%) patients by the 7th day of treatment, and was not observed in any pregnant woman by the 15th day, bleeding - in 5 (5.9%) and 2 (2.4%), anal itching - in 6 (7.1%) and 2 (2.4%) women on the 7th and 15th days of treatment, respectively.
Clinical tolerability was assessed by patients and doctors on a scale: excellent, good, average, poor. Tolerability of treatment with Procto-Glivenol was excellent and good in 96% of cases.
conclusions
1. Procto-Glyvenol is the drug of choice for the conservative treatment of hemorrhoids and the prevention of its complications during pregnancy. The use of Procto-Glivenol, both in the form of cream and rectal suppositories, is an effective way to treat pregnant women with hemorrhoids.
2. The speed of action and good tolerability make it possible to recommend Procto-Glivenol for widespread use in obstetric practice.
Treatment of postpartum hemorrhoids
Laser coagulation of hemorrhoids is well tolerated, is performed on an outpatient basis and does not require giving up breastfeeding .
Let's look at a few more situations that are very common after childbirth.
During childbirth, hemorrhoids became inflamed, and then the inflammation went away and nothing bothers me. There was only a small fold of skin left in the butt. A common situation. There are hemorrhoids, but they are small and there are no clinical manifestations of the disease now.
There are two options for the development of the situation that most often occur.
- As the child grows up, the load increases and the hemorrhoids begin to become inflamed or bleed. If there is dense feces, a tendency to constipation, then problems appear earlier and bother you more often. Medicines don't help much. This option occurs in about a third of patients. They are contacted earlier, most often before a year and a half from childbirth, hemorrhoids are usually small or medium-sized, and respond well to treatment. Treatment results are most often good or excellent.
- There are external hemorrhoids, they progress slowly, gradually, and do not bother me much. Medicines initially relieve exacerbations well. But gradually exacerbations occur more often, more severely, medications stop helping, and the situation forces you to see a doctor.
In both situations, the later you contact a proctologist, the more difficult it is to improve the health of your butt. This is understandable: the larger the hemorrhoids, the more problems, the larger the operation needed to correct the problem. And the more extensive the operation, the more traumatic it is and the less likely it is that the butt will fully recover to its pre-illness state.
What you won’t see in the prime! Years, 3-5-10 years of meaningless treatment often lead to monstrous hemorrhoids. Sometimes inpatient surgery does not help to cope with such hemorrhoids.
Does it happen that after childbirth there are no hemorrhoids? It happens, of course. I am currently treating a young mother who gave birth 4 months ago. She doesn't have hemorrhoids. I also saw one patient after three births without hemorrhoids. And about 15 - 20 patients after two births without hemorrhoids. But this comes from many years of practice. Of course, with healthy veins after the first birth, not everyone has hemorrhoids, but more than half definitely have it.
Laxatives
A laxative during breastfeeding is necessary to provide immediate assistance to yourself. However, some remedies help normalize intestinal function in general. To understand the mechanism of their work, consider all groups of laxatives:
- stimulating;
- volumetric;
- osmotic;
- softening.
The first act on intestinal receptors. They are addictive and can cause complications such as lazy bowel syndrome. In addition, taking stimulant laxatives is not allowed during lactation, so the doctor will not recommend using drugs from this group.
Osmotic drugs do not pass into breast milk and are not addictive. They are often prescribed to nursing mothers. However, a significant part of such drugs are used in coloproctology and gastroenterology as a measure of preparation for endoscopic diagnostic methods, surgical interventions, etc. They reliably cleanse the intestines, but have a pronounced effect - they can cause frequent loose stools.
Softening agents are oils, glycerin, etc. They help soften stool and simplify their movement through the intestines. However, such drugs are not approved for continuous use, since they impair the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. This can be fraught with the development of hypovitaminosis for a young mother.
Bulk laxatives are represented by herbal or synthetic-based drugs. They act similarly to natural fiber - they are not digested in the intestines, absorb water and swell, increasing the volume of intestinal contents and softening the stool. In addition, such drugs gently stimulate intestinal motility, causing defecation. The components of such products do not pass into breast milk. They are allowed for nursing mothers and can be taken for a long time.
One such remedy is the British drug Fitomucil Norm. It contains psyllium seed hull and plum fruit extract - natural soluble and insoluble fiber. The drug gently stimulates bowel movements and promotes regular bowel function.
Is treating hemorrhoids after childbirth effective at home?
Unfortunately, women suffer from hemorrhoids. They are treated periodically using venotonics, various suppositories and ointments, and sometimes laxatives are added. And when conservative treatment completely stops helping, exacerbations become too strong and frequent, they come to the appointment and ask for a miracle to be performed.
A miracle means complete relief from hemorrhoidal problems. It is desirable, as an additional bonus, to receive an aesthetically attractive anus; and so that later you don’t have to use medications, at least periodically.
My dears, miracles in treatment happen only in the initial stages of the development of any disease, before changes have yet occurred in the organ itself and surrounding tissues. In relation to the anus - as long as the disease has not changed or significantly changed the anatomical structure of the anus.
Physical exercise
One of the effective and affordable methods for preventing constipation in a nursing mother is light physical activity. Regular exercise will help strengthen the abdominal and perineal muscles. As a result, muscle tone increases, which helps to activate intestinal motility. Yoga, walking, swimming, and Pilates are suitable exercises for nursing mothers.
Also, don't ignore your daily warm-up. It is best to do exercises on an empty stomach. You should start with simple exercises, gradually increasing complexity. There are also specific exercises that increase intestinal contractility and help cope with constipation, for example:
- Stand straight with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Take a deep breath, then strongly draw in and then sharply push out your stomach.
- Repeat the action 10 times and take a break.
Exercises must be performed at a slow pace, without sudden jerks. The main thing is regularity. As you get stronger, you can increase the number of repetitions. Gymnastics will help normalize bowel movements and improve your well-being.
Exercises while lying on your back
- Take a breath, stick out your stomach. As you exhale, draw in your stomach and lightly press your hands on the abdominal wall.
- Place your hands behind your head and stretch. At the same time, pull in your stomach. As you exhale, lower your arms and place them along your body.
- Lying on your back, bend your knees without lifting your heels off the floor.
- Pull your right knee towards your stomach as you exhale. Lower your leg while inhaling. Repeat the same with your left leg.
The “bicycle” and “scissors” exercises are good for constipation.
Exercises while lying on your stomach
- Place your hands under your shoulders. Get on all fours, without taking your hands off the floor, and then roll onto your feet. Take the starting position.
- Perform alternating leg swings with simultaneous retraction of the abdomen as you exhale and retraction as you inhale.