Blood plasma is a liquid fraction of connective tissue; thanks to its existence, the body is able to transport and process all kinds of substances.
It is worth noting that plasma primarily consists of water, which is a natural solvent and is involved in almost all processes. At its core, it is a solution containing a lot of substances.
To understand what plasma is, it is worth turning to anatomical and physiological information.
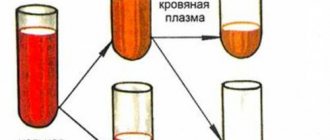
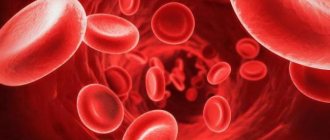
Blood itself is a heterogeneous structure. It consists of two parts. The first is shaped cells. This includes all cytological structures that circulate in the riverbed.
For example:
- Erythrocytes, red blood cells. They carry oxygen.
- Leukocytes. White cells. Ensure the functioning of the body's defenses. Without them, the functional activity of the immune system is impossible.
- Lymphocytes.
The second part is the liquid fraction of blood or plasma itself; it looks like a yellowish substance. In laboratory conditions, after processing in a centrifuge, the structure loses its shaped cells.
If there are deviations in the functional activity of plasma, its structure and quantitative composition, treatment is prescribed. Although it is not always necessary, since natural changes occur. The question is complex. Whether therapy is necessary or not is decided by the doctor.
Besides the above, what do you need to know about the liquid fraction of blood?
Plasma composition and functions of its elements
Most of the plasma is water, its amount is approximately 92% of the total volume. In addition to water, it includes the following substances:
- proteins;
- glucose;
- amino acids;
- fat and fat-like substances;
- hormones;
- enzymes;
- minerals (chlorine, sodium ions).
About 8% of the volume is proteins, which are the main part of plasma. It contains several types of proteins, the main ones being:
- albumins – 4-5%;
- globulins – about 3%;
- fibrinogen (belongs to globulins) – about 0.4%.
The essence of the method
The method is based on the ability to artificially separate blood into elements and return the necessary components back to the patient’s body. A group of techniques is used.
Centifugation. Classic, common option. It is used if it is impossible to return the plasma. Accordingly, we are mainly talking about serious illnesses and intoxications. Including alcohol.
Saline and glucose move directly from the centrifuge in the opposite direction to restore normal blood concentration. Its volume. Otherwise, hypovolemia would occur.
Filtration. Since plasma contains the most toxins, life-threatening substances, the blood is automatically passed through a special membrane, hence the name - membrane plasmapheresis. The formed cells are too large to be transported through, only plasma passes through.
Further, everything depends on the concentration of toxins and toxic substances. If they cannot be removed, then the liquid fraction is replaced by artificial solutions. This avoids hypovolemia.
- The third method is based on more thorough cleaning of the liquid connective tissue. A system (cascade) of filters for plasma filtration is used. We are talking about the so-called double plasmapheresis. After complete treatment, the blood is returned to the patient's body. This method is only suitable if it can be purified and filtered.
- Cryo-plasmapheresis. The method involves 2 key stages. The first is blood processing. Dividing it into two main components. The plasma is frozen at a low temperature. No more than -30. Then, during the second “iteration,” the liquid fraction is heated to positive values and injected back into the body.
Attention:
Cryo-technique is risky, which is why it is used relatively rarely. Although it is superior in effectiveness to all previous ones, especially in cases of severe poisoning.
Albumen
Albumin is the main plasma protein. It has a low molecular weight. Content in plasma is more than 50% of all proteins. Albumin is formed in the liver.
Protein functions:
- perform a transport function - transport fatty acids, hormones, ions, bilirubin, medications;
- take part in metabolism;
- regulate oncotic pressure;
- participate in protein synthesis;
- reserve amino acids;
- deliver medications.
A change in the level of this protein in plasma is an additional diagnostic sign. The condition of the liver is determined by the concentration of albumin, since many chronic diseases of this organ are characterized by its decrease.
Other protein structures
These may include individual substances:
- Transferrin. As the name suggests, it binds iron and transports it through the bloodstream to the tissues.
- C-reactive protein. Works as part of the body's defense system. Acts as a kind of marker of an autoimmune inflammatory process. Therefore, it is actively used in medical practice.
- Immune substances. In addition to the globulins mentioned above.
- Prothrombin. Participates in normal blood clotting. It is often removed from the liquid fraction when planning a transfusion.
There are several other substances. However, these are the ones that are studied most often.
Globulins
The remaining plasma proteins are classified as globulins, which are large in molecular weight. They are produced in the liver and in the organs of the immune system. Main types:
- alpha globulins,
- beta globulins,
- gamma globulins.
Alpha globulins bind bilirubin and thyroxine, activate the production of proteins, transport hormones, lipids, vitamins, and microelements.
Beta globulins bind cholesterol, iron, vitamins, transport steroid hormones, phospholipids, sterols, zinc and iron cations.
Gamma globulins bind histamine and participate in immunological reactions, which is why they are called antibodies, or immunoglobulins. There are five classes of immunoglobulins: IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, IgE. Produced in the spleen, liver, lymph nodes, and bone marrow. They differ from each other in biological properties and structure. They have different abilities to bind antigens, activate immune proteins, have different avidity (rate of binding to antigen and strength) and ability to pass through the placenta. Approximately 80% of all immunoglobulins are IgG, which have high avidity and are the only ones that can cross the placenta. IgM is synthesized first in the fetus. They are also the first to appear in the blood serum after most vaccinations. They have high avidity.
Blood composition
Fibrinogen is a soluble protein that is produced in the liver. Under the influence of thrombin, it is converted into insoluble fibrin, due to which a blood clot is formed at the site of vessel damage.
Fibrinogen
Acts as a special protein. It is produced in the liver. The main task is to ensure normal blood clotting. The process takes place in several stages.
- As soon as the body needs to close a wound, a gap in the tissues, the synthesis of special substances-factors begins. These include fibrinogen.
- Once the amount of a substance reaches a certain value, it is subject to breakdown. A special compound called thrombin is involved.
- Fibrinogen is destroyed and breaks down into sticky components. The so-called threads.
- After the factor has precipitated, it adheres to the site of the lesion, platelets, ensuring normal coagulation. A blood clot forms and covers the wound surface. It then forms a hard scab.
The process occurs whenever a lesion is formed. If there is not enough fibrinogen, coagulopathies begin. Normal clotting is disrupted. The blood becomes too thin.
Amino acids
They act as a kind of building material for the cells of the body. They are also part of their walls, ensuring normal conductivity of the cytoplasmic membrane. And at the same time its strength and elasticity.
- Fats. Lipids, like amino acids, are the main building materials. The key one is cholesterol, which is well known to everyone.
- Glucose. Acts as a nutrient. Works as a special stock. Because during splitting a large amount of energy is released. As a rule, during the production of donor material, glucose is not removed; it remains in place.
- Hormones. Those that are produced in the patient's body. They act as a kind of mediators, substances that transmit signals to tissues and entire systems. This is their main task.
- Minerals. Iodine, iron, chlorine, dozens of other substances. Both in the form of a complete compound that does not enter into simple reactions, and in the form of charged ions. It is the latter that maintain normal blood acidity and participate in the functioning of cells and cytoplasmic membranes.
All substances perform two main functions. If we talk about the issue in general.
Which ones exactly:
- Ensuring proper metabolism.
- Maintaining a state of homeostasis. When the body is in balance, works correctly and is stable in relation to itself.
A deficiency or excess of any compound immediately results in disorders. In this case, treatment is required.
Non-protein components
In addition, blood plasma includes non-protein substances:
- organic nitrogen-containing: amino acid nitrogen, urea nitrogen, low molecular weight peptides, creatine, creatinine, indican. Bilirubin;
- organic nitrogen-free: carbohydrates, lipids, glucose, lactate, cholesterol, ketones, pyruvic acid, minerals;
- inorganic: sodium, calcium, magnesium, potassium cations, chlorine anions, iodine.
The ions in the plasma regulate the pH balance and maintain the normal state of cells.
Quality control
Before inviting Russian citizens to donate plasma, specialists carefully find out their medical history.
“We check everyone who left requests in the call center using the EMIAS system, we find out that the person really got sick, that enough time has passed since recovery, that he has negative tests for COVID,” says Alexander Kostin.
Additional tests are taken from the donor on site, and testing of the biomaterial begins during the blood donation process.
“Immediately after the procurement procedure, the plasma undergoes a special treatment - photochemical inactivation of pathogens. We add certain substances to the plasma and expose it to ultraviolet light or visible light. This is a standardized technique that is designed to remove those potential pathogenic microorganisms for which we do not test the donor. In addition, testing for blood-borne infections (hepatitis B, C, HIV, syphilis) is mandatory. The results are usually ready the next day, and until this process is completed, the plasma is not used for patients,” explains the doctor.
Plasma functions
Blood plasma performs many functions, including:
- transportation of blood cells, nutrients, metabolic products;
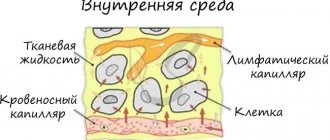
- binding of liquid media located outside the circulatory system;
- making contact with body tissues through extravascular fluids, thereby achieving hemostasis.
Donor plasma saves many lives
General information
It is worth noting that plasma primarily consists of water, which is a natural solvent and is involved in almost all processes. At its core, it is a solution containing a lot of substances.
To understand what plasma is, it is worth turning to anatomical and physiological information.
Blood itself is a heterogeneous structure. It consists of two parts. The first is shaped cells. This includes all cytological structures that circulate in the riverbed.
For example:
- Erythrocytes, red blood cells. They carry oxygen.
- Leukocytes. White cells. Ensure the functioning of the body's defenses. Without them, the functional activity of the immune system is impossible.
- Lymphocytes.
The second part is the liquid fraction of blood or plasma itself; it looks like a yellowish substance. In laboratory conditions, after processing in a centrifuge, the structure loses its shaped cells.
If there are deviations in the functional activity of plasma, its structure and quantitative composition, treatment is prescribed. Although it is not always necessary, since natural changes occur. The question is complex. Whether therapy is necessary or not is decided by the doctor.
Use of donor plasma
In our time, transfusions often require not whole blood, but its components and plasma. Therefore, blood transfusion centers often donate blood for plasma. It is obtained from whole blood by centrifugation, that is, the liquid part is separated from the formed elements using a machine, after which the blood cells are returned to the donor. The procedure lasts about 40 minutes. The difference from donating whole blood is that blood loss is much less, and you can donate plasma again after two weeks, but no more than 12 times during the year.
Blood serum is obtained from plasma, which is used for medicinal purposes. It differs from plasma in that it does not contain fibrinogen, but contains all the antibodies that can resist pathogens. To obtain it, place sterile blood in a thermostat for an hour. Then the resulting clot is peeled off from the wall of the test tube and kept in the refrigerator for a day. After this, using a Pasteur pipette, the settled whey is poured into a sterile container.
Harmful or useful
There are different, often directly opposite, opinions about whether donating blood plasma is harmful. Some are convinced that such an activity definitely harms our body and strongly advise against resorting to it. Others, on the contrary, believe that donating it brings benefits to the donor. Modern medical scientists have convincingly proven that such a procedure poses absolutely no threat to the health of the person donating plasma, being completely harmless. Moreover, after donating plasma, the work of protective functions and immunity is activated, so experienced doctors often prescribe plasma donation to patients as a medicinal and health-improving procedure.
Requirements for donors
- Age from 18 to 60.
- Body weight must be at least 50kg
- Have identification documents
- Have no health problems
- Women do not have blood drawn during their periods.
- Blood is not collected from people with low hemoglobin levels
- Before donation, a doctor’s examination and a blood test to determine the Rh factor and possible infectious diseases are required.
- You must not consume alcoholic beverages 48 hours before the test
- 72 hours before – do not take analgesics
- Do not smoke an hour before the test
- Fried, fatty, spicy and smoked foods are not recommended on the eve
The procedure is as follows:
Blood is taken from one arm, which goes into a centrifuge. There, the process of separating red blood cells and platelets from the plasma occurs. On the second arm, a platelet-erythrocyte mass, which was obtained during the centrifugation process, is injected into a vein. And the resulting plasma is frozen.