The risk of this disease increases in people over 45 - 50 years of age. Moreover, up to 40% of hemorrhages can be fatal. How to recognize the problem and what to do? Let's find out with the expert ALENA PARETSKAYA
Pathophysiologist, immunologist, member of the St. Petersburg Society of Pathophysiologists POLINA PETROSYAN Neurologist at SM-Clinic, specialist in cerebrovascular diseases and headaches
The second name for this pathology is hemorrhagic stroke. It occurs at any age, but most often mature and elderly people suffer - approximately 15 - 20% of all serious cerebrovascular accidents are caused by cerebral hemorrhage.
What is a cerebral hemorrhage
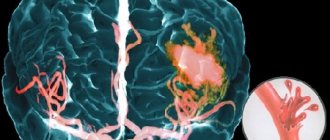
A cerebral hemorrhage is a life-threatening condition that occurs when one of the brain's arteries ruptures, causing blood to leak into the brain tissue.
The brain tissue becomes saturated with blood or a hematoma forms (an accumulation of blood that puts pressure on surrounding tissues); blood may leak into the ventricle of the brain, which disrupts the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and increases intracranial pressure. The part of the brain that has lost blood due to rupture of blood vessels and those tissues that are saturated with blood stop working, the cells die. Accordingly, the larger the vessel that ruptures, the more dangerous the consequences will be for life and health.
Causes of cerebral hemorrhage in adults
There are many reasons why blood vessels rupture and blood spills into the brain tissue. Among the most common are:
- arterial aneurysms (thinning of the wall, the formation of a sac with blood that overflows and bursts);
- vascular malformations (birth defects, thinning, tortuosity of the walls);
- ruptures of blood vessels during a hypertensive crisis due to the prohibitive load on the walls;
- head injuries with vascular ruptures;
- tumors that grow and damage arteries;
- taking blood thinning medications (if dosages are not followed);
- the development of certain systemic diseases in which the walls of the arteries are affected (for example, amyloidosis).
At a young age, the leading causes of hemorrhage are injuries and congenital vascular anomalies. In the elderly – damage to blood vessels by atherosclerosis and their rupture due to hypertension, tumor processes.
Additional Research
MRI of the brain
- Cost: 14,000 rub.
More details
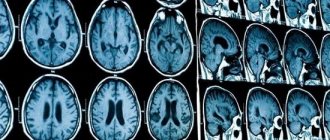
The initial diagnosis is established after examination by a neurologist, but instrumental diagnostics are always required to clarify the boundaries of the lesion. The most informative method is computed tomography, which allows a good examination of the brain matter. MRI is used for the same purpose if there is time for it.
Angiography gives excellent results, this is a study of blood vessels with contrast. It identifies malformations, dissections (dissections) and other vascular pathology. The important thing is that this study can be conducted in healthy people at risk. This is the best prevention of stroke if research is supplemented with treatment.
Lumbar puncture is used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Symptoms of cerebral hemorrhage in adults
The key symptoms that occur during a cerebral hemorrhage were given to us by neurologist Polina Petrosyan. According to her, intracerebral hemorrhage is characterized by an acute onset, with a rapid development of the clinical picture:
- sudden severe headache;
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness.
Depending on the volume and location of the hemorrhage, the following may occur:
- one-sided weakness in the limbs (hemiparesis) up to a complete lack of movement in them (hemiplegia);
- restriction of eyeball movement;
- speech impairment - both its reproduction and understanding;
- difficulty swallowing and breathing;
- disturbance of consciousness up to coma.
Much of the severity of symptoms depends on what part of the brain is damaged, how much blood leaks out, and how large the vessel is.
How does a hemorrhagic stroke occur?
Vascular rupture can occur at any time of the day. This is usually preceded by physical or emotional stress. The person suddenly falls, sometimes with a loud cry, and loses consciousness.
Approximately 30% of patients have warning signs that develop within a few minutes to several days. On the eve of a rupture of blood vessels, there may be severe headaches - ones that the person has never experienced. There is a feeling of a rush and a sharp reddening of the face. Sometimes the sensations of numbness in the limbs, muscle weakness, and facial asymmetry appear.
The main symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke are:
| Contralateral hemiplegia | The nerve pathways intersect, so the paralysis is located on the side opposite to the hemorrhage. During a stroke, the left arm and leg stop moving in the right hemisphere, and the right ones in the left hemisphere. |
| Contralateral hemianesthesia | In paralyzed limbs, sensitivity disappears on the side opposite to the rupture. |
| Aphasia | Loss of speech occurs when the dominant (dominant) hemisphere is damaged. For right-handers - right, for left-handers - left. |
| Spatial hemiagnosia with damage to the non-dominant hemisphere | If a right-hander's left hemisphere is affected, and a left-hander's right hemisphere is affected, then the person behaves as if half of the real space does not exist for him. A person does not realize that he has two halves of the body, that food can be eaten from the entire plate, and not from half. Half of everything that is located around a person is not perceived by him. |
| Facial asymmetry | One half of the face does not receive innervation and cannot contract. One nasolabial fold is smoothed out, the smile becomes one-sided, the tongue deviates to one side, water and food flow out of the mouth. |
From the moment these symptoms appear, there is only 3 hours to help the person as much as possible. After 3 (sometimes 6) hours, irreversible changes will occur, then nothing can be corrected.
Diagnostics
A doctor may suspect a brain hemorrhage based on typical symptoms, especially if they are associated with injury or other risk factors.
But the gold standard for diagnosis is brain CT. On the first day after the onset of hemorrhage, the data will be most accurate, even more significant than with MRI. On tomograms, fresh hematomas are clearly visible; the doctor can determine their exact location, size and shape. In addition, he immediately assesses how damaged the brain structures, membranes and cerebrospinal fluid circulation system are. If hemorrhage is detected after 3 days or more, an MRI will be more accurate. It will better identify a hematoma in which the blood already has oxidized, partially disintegrating hemoglobin.
If these are young people without hypertension, they may be prescribed angiography of cerebral vessels. Additionally, an ECG, chest X-ray, blood tests for electrolyte levels, PTT with APTT (coagulation indices) are performed.
Brain hematoma - symptoms and treatment
There are two types of treatment: conservative and surgical.
Conservative treatment
Methods of conservative (medicinal) treatment normalize the vital functions of the body:
- maintain blood pressure at the required level: so that the blood supply to the brain is maintained, but the volume of the hematoma does not increase;
- affect the blood coagulation system;
- prevent and eliminate swelling;
- strengthen the vascular wall.
This is an extremely important and responsible stage of treatment. All activities are carried out by a doctor, deeply analyzing the pathogenetic processes in the human body. Many methods are based on laboratory data. Conservative therapy cannot in any way be controlled or regulated by relatives or sympathizers due to their lack of this knowledge. For example, the decrease in blood pressure during antihypertensive therapy should not be sudden. It is reduced to a level that does not coincide with the norm for a healthy person. The pressure is maintained within certain limits: it should not be too high, but also too low. This reduces the risk of continued hemorrhage and maintains adequate blood supply to the brain to protect it from secondary damage due to oxygen deprivation.
Conservative methods are used for treatment in the following cases:
- hematomas are small in size and do not exert significant pressure on the brain;
- hematomas do not cause displacement of brain structures, severe depression of consciousness, and are accompanied by moderate neurological disorders.
Surgery
Surgical treatment consists of mechanical removal of the hematoma. As a result, the pressure of the hematoma on the brain stops.
Several methods of surgical removal of intracerebral hematomas are used:
- The puncture method is pumping out the liquid part of the hematoma (aspiration) through the hole. However, it is impossible to remove the entire hematoma in this way, since it usually consists of 80% blood clots, and the liquid component is 20% or less. The method is used only in severe cases of the disease to save lives. If the patient’s condition does not improve after surgery, then radical removal methods are used.
- The open method is a traditional method of removing a hematoma by creating a hole in the bone tissue of the skull (trepanation), dissecting a section of the brain (encephalotomy) and suctioning out both liquid blood and its clots. The method allows you to completely remove the hematoma. However, it is accompanied by additional surgical trauma to the brain, which leads to an increase in edema, increased displacement and deformation of brain structures and often causes repeated hemorrhage.
- The endoscopic method is a promising technology for removing intracerebral hematomas. Combines the low invasiveness of the puncture method with the possibility of complete removal of the hematoma. But the method can only be used if the environment in the operation area is transparent. For example, if there is bleeding, surgery is difficult and often impossible.
- Stereotactic method is carried out using special instruments immersed in the brain through a hole with a diameter of 5–10 mm. A special feature of the method is the transfer of hematoma coordinates using computed tomography or radiography. The technology reduced the mortality rate of deep hematomas by 22% compared to conservative treatment methods. However, in 10-16% of cases, repeated hemorrhages are possible in the first few days after surgery.
- Neuronavigation method - neuronavigation systems are used: OrthicaI Tracking System "Radionics Inc" Compass Cygnus PFS System, "Compass" Vectorvision BrainLAB. The method determines the location of the hematoma with high accuracy. The technology is especially effective for lesions in functionally significant areas of the brain. Its widespread use is not yet possible due to the high cost of equipment and limited surgical experience among doctors [13].
The tactics of surgical intervention, its volume, measures to eliminate compression of the brain, timing of the operation and much more depend on the specific situation. The decision is made by a neurosurgeon based on the patient’s condition, laboratory data and CT/MRI images.
Consequences of cerebral hemorrhage in adults
The most dangerous thing with a cerebral hemorrhage is the consequences that can develop.
Among them, Polina Petrosyan notes: “The consequences can lead to disability, but may not affect a normal lifestyle and ability to work,” says Dr. Polina Petrosyan. – After hemorrhage, one-sided weakness in the limbs, decreased sensitivity in them, and various speech disorders may persist. Full recovery is possible if rehabilitation measures are taken in a timely manner and if the patient independently puts effort into rehabilitation measures.
How to help a stroke victim?
Recovery largely depends on how the people around the patient behave. First of all, you need to call an ambulance, and until it arrives, try not to move the person. You need to place a cushion or pillow under the shoulders and head, carefully turn the person on the right side, and place a basin or bag in case of vomiting. It is advisable to measure blood pressure. Anti-pressure pills should not be given before the ambulance arrives: there is a possibility of a sharp drop in blood pressure. Only specially trained medical personnel know the rules for lowering blood pressure when it rises above 150/100 mmHg. If respiratory depression occurs, you need to start resuscitation - chest compressions, mouth-to-mouth breathing.
The best prevention is timely treatment of hypertension, atherosclerosis, identification of malformations and aneurysms before they rupture.
Our neurologists see patients every day, and every patient at the clinic can find out their risk for developing a hemorrhagic stroke. Visit your doctor while you still have time.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions